Abstract
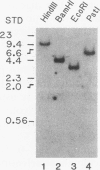
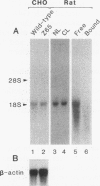
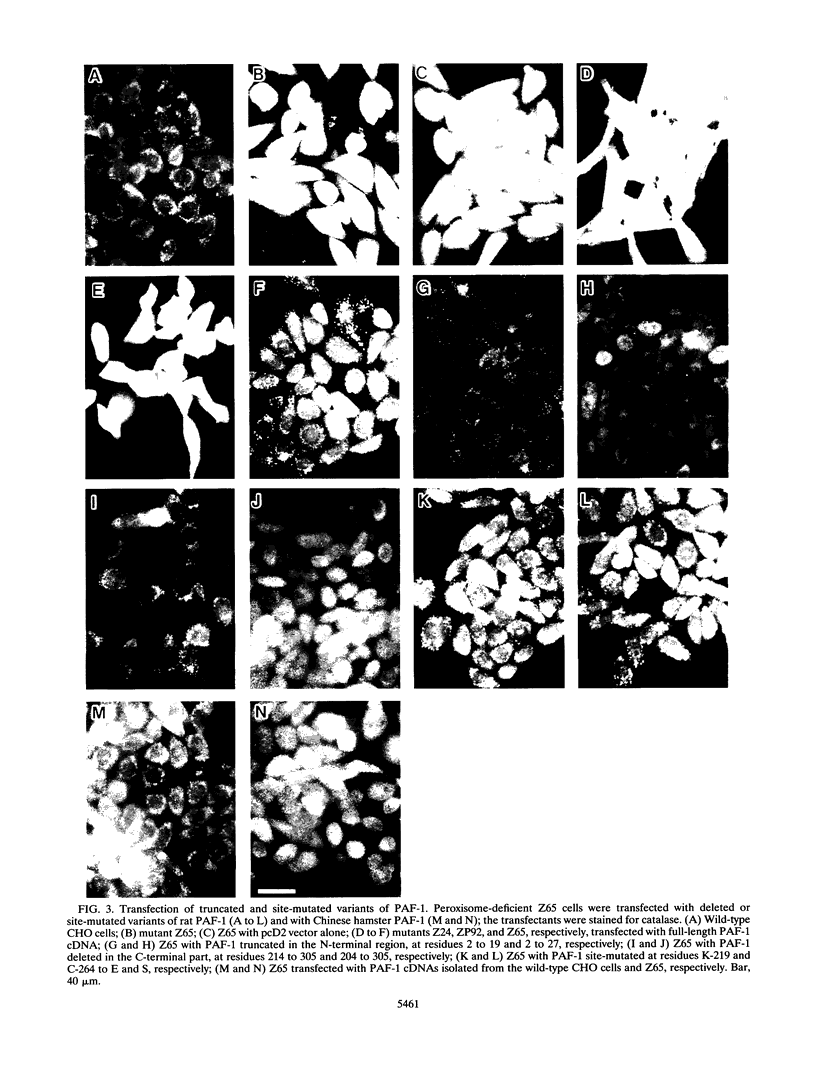
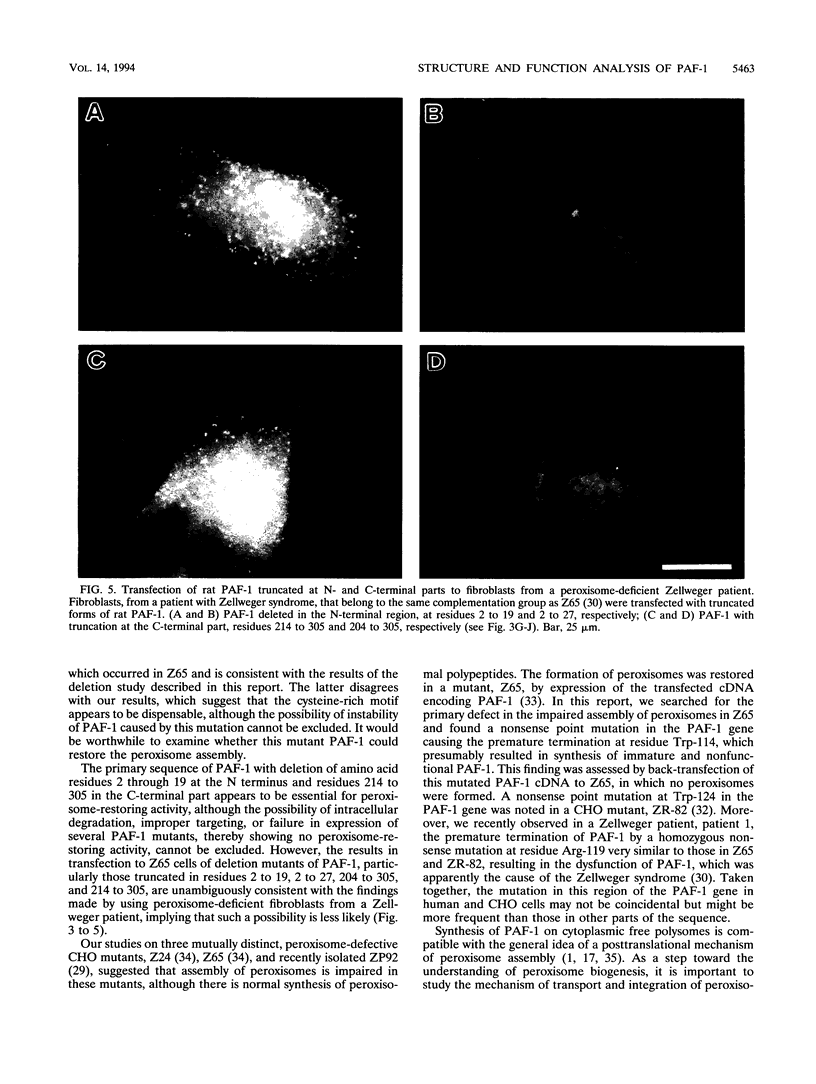
A cDNA encoding 35-kDa peroxisome assembly factor 1 (PAF-1), a peroxisomal integral membrane protein, was cloned from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and sequenced. The CHO PAF-1 comprised 304 amino acids, one residue shorter than rat or human PAF-1, and showed high homology to rat and human PAF-1: 90 and 86% at the nucleotide sequence level and 92 and 90% in amino acid sequence, respectively. PAF-1 from these three species contains a conserved cysteine-rich sequence at the C-terminal region which is exactly the same as that of a novel cysteine-rich RING finger motif family. PAF-1 cDNA from a peroxisome-deficient CHO cell mutant, Z65 (T. Tsukamoto, S. Yokota, and Y. Fujiki, J. Cell Biol. 110:651-660, 1990), contained a nonsense mutation at the codon for Trp-114, resulting in premature termination. Truncation in PAF-1 of either 19 amino acids from the N terminus or 92 residues from the C terminus maintained the peroxisome assembly-restoring activity when tested in both the Z65 mutant and the fibroblasts from a Zellweger patient. In contrast, deletion of 27 or 102 residues from the N or C terminus eliminated the activity. PAF-1 is encoded by free polysomal RNA, consistent with a general rule for biogenesis of peroxisomal proteins, including membrane polypeptides, implying the posttranslational transport and integration of PAF-1 into peroxisomal membrane.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borst P. How proteins get into microbodies (peroxisomes, glyoxysomes, glycosomes). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 5;866(4):179–203. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brul S., Westerveld A., Strijland A., Wanders R. J., Schram A. W., Heymans H. S., Schutgens R. B., van den Bosch H., Tager J. M. Genetic heterogeneity in the cerebrohepatorenal (Zellweger) syndrome and other inherited disorders with a generalized impairment of peroxisomal functions. A study using complementation analysis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1710–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI113510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann R., Veenhuis M., Mertens D., Kunau W. H. Isolation of peroxisome-deficient mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Hanson I. M., Trowsdale J. A novel cysteine-rich sequence motif. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Rachubinski R. A., Lazarow P. B. Synthesis of a major integral membrane polypeptide of rat liver peroxisomes on free polysomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7127–7131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Rachubinski R. A., Mortensen R. M., Lazarow P. B. Synthesis of 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase of rat liver peroxisomes on free polyribosomes as a larger precursor. Induction of thiolase mRNA activity by clofibrate. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 15;226(3):697–704. doi: 10.1042/bj2260697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould S. J., Keller G. A., Hosken N., Wilkinson J., Subramani S. A conserved tripeptide sorts proteins to peroxisomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1657–1664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould S. J., Keller G. A., Subramani S. Identification of peroxisomal targeting signals located at the carboxy terminus of four peroxisomal proteins. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):897–905. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould S. J., McCollum D., Spong A. P., Heyman J. A., Subramani S. Development of the yeast Pichia pastoris as a model organism for a genetic and molecular analysis of peroxisome assembly. Yeast. 1992 Aug;8(8):613–628. doi: 10.1002/yea.320080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner J., Moser H., Valle D. Mutations in the 70K peroxisomal membrane protein gene in Zellweger syndrome. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):16–23. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höhfeld J., Veenhuis M., Kunau W. H. PAS3, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene encoding a peroxisomal integral membrane protein essential for peroxisome biogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1167–1178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamijo K., Taketani S., Yokota S., Osumi T., Hashimoto T. The 70-kDa peroxisomal membrane protein is a member of the Mdr (P-glycoprotein)-related ATP-binding protein superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4534–4540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiryo T., Abe M., Okazaki K., Kato S., Shimamoto N. Absence of DNA in peroxisomes of Candida tropicalis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):269–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.269-274.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarow P. B., Fujiki Y. Biogenesis of peroxisomes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:489–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H., Tan X., Veenhuis M., McCollum D., Cregg J. M. An efficient screen for peroxisome-deficient mutants of Pichia pastoris. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):4943–4951. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.4943-4951.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovering R., Hanson I. M., Borden K. L., Martin S., O'Reilly N. J., Evan G. I., Rahman D., Pappin D. J., Trowsdale J., Freemont P. S. Identification and preliminary characterization of a protein motif related to the zinc finger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura S., Kasuya-Arai I., Mori H., Miyazawa S., Osumi T., Hashimoto T., Fujiki Y. Carboxyl-terminal consensus Ser-Lys-Leu-related tripeptide of peroxisomal proteins functions in vitro as a minimal peroxisome-targeting signal. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14405–14411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa S., Osumi T., Hashimoto T., Ohno K., Miura S., Fujiki Y. Peroxisome targeting signal of rat liver acyl-coenzyme A oxidase resides at the carboxy terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):83–91. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi T., Fujiki Y. Topogenesis of peroxisomal proteins. Bioessays. 1990 May;12(5):217–222. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi T., Tsukamoto T., Hata S., Yokota S., Miura S., Fujiki Y., Hijikata M., Miyazawa S., Hashimoto T. Amino-terminal presequence of the precursor of peroxisomal 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase is a cleavable signal peptide for peroxisomal targeting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):947–954. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92028-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachubinski R. A., Fujiki Y., Mortensen R. M., Lazarow P. B. Acyl-Coa oxidase and hydratase-dehydrogenase, two enzymes of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation system, are synthesized on free polysomes of clofibrate-treated rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2241–2246. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscher A. A., Hoefler S., Hoefler G., Paschke E., Paltauf F., Moser A., Moser H. Genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity in disorders of peroxisome biogenesis--a complementation study involving cell lines from 19 patients. Pediatr Res. 1989 Jul;26(1):67–72. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198907000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimozawa N., Tsukamoto T., Suzuki Y., Orii T., Fujiki Y. Animal cell mutants represent two complementation groups of peroxisome-defective Zellweger syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1864–1870. doi: 10.1172/JCI116063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimozawa N., Tsukamoto T., Suzuki Y., Orii T., Shirayoshi Y., Mori T., Fujiki Y. A human gene responsible for Zellweger syndrome that affects peroxisome assembly. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1132–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.1546315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinkels B. W., Gould S. J., Bodnar A. G., Rachubinski R. A., Subramani S. A novel, cleavable peroxisomal targeting signal at the amino-terminus of the rat 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3255–3262. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04889.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieringer R., Raetz C. R. Peroxisome-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells with point mutations in peroxisome assembly factor-1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12631–12636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto T., Miura S., Fujiki Y. Restoration by a 35K membrane protein of peroxisome assembly in a peroxisome-deficient mammalian cell mutant. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):77–81. doi: 10.1038/350077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto T., Yokota S., Fujiki Y. Isolation and characterization of Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants defective in assembly of peroxisomes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):651–660. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Leij I., Van den Berg M., Boot R., Franse M., Distel B., Tabak H. F. Isolation of peroxisome assembly mutants from Saccharomyces cerevisiae with different morphologies using a novel positive selection procedure. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):153–162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemer E. A., Brul S., Just W. W., Van Driel R., Brouwer-Kelder E., Van Den Berg M., Weijers P. J., Schutgens R. B., Van Den Bosch H., Schram A. Presence of peroxisomal membrane proteins in liver and fibroblasts from patients with the Zellweger syndrome and related disorders: evidence for the existence of peroxisomal ghosts. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;50(2):407–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima S., Suzuki Y., Shimozawa N., Yamaguchi S., Orii T., Fujiki Y., Osumi T., Hashimoto T., Moser H. W. Complementation study of peroxisome-deficient disorders by immunofluorescence staining and characterization of fused cells. Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;88(5):491–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00219334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoeller R. A., Allen L. A., Santos M. J., Lazarow P. B., Hashimoto T., Tartakoff A. M., Raetz C. R. Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants defective in peroxisome biogenesis. Comparison to Zellweger syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21872–21878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoeller R. A., Raetz C. R. Isolation of animal cell mutants deficient in plasmalogen biosynthesis and peroxisome assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5170–5174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoeller R. A., Rangaswamy S., Herscovitz H., Rizzo W. B., Hajra A. K., Das A. K., Moser H. W., Moser A., Lazarow P. B., Santos M. J. Mutants in a macrophage-like cell line are defective in plasmalogen biosynthesis, but contain functional peroxisomes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8299–8306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H., Schutgens R. B., Wanders R. J., Tager J. M. Biochemistry of peroxisomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:157–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]