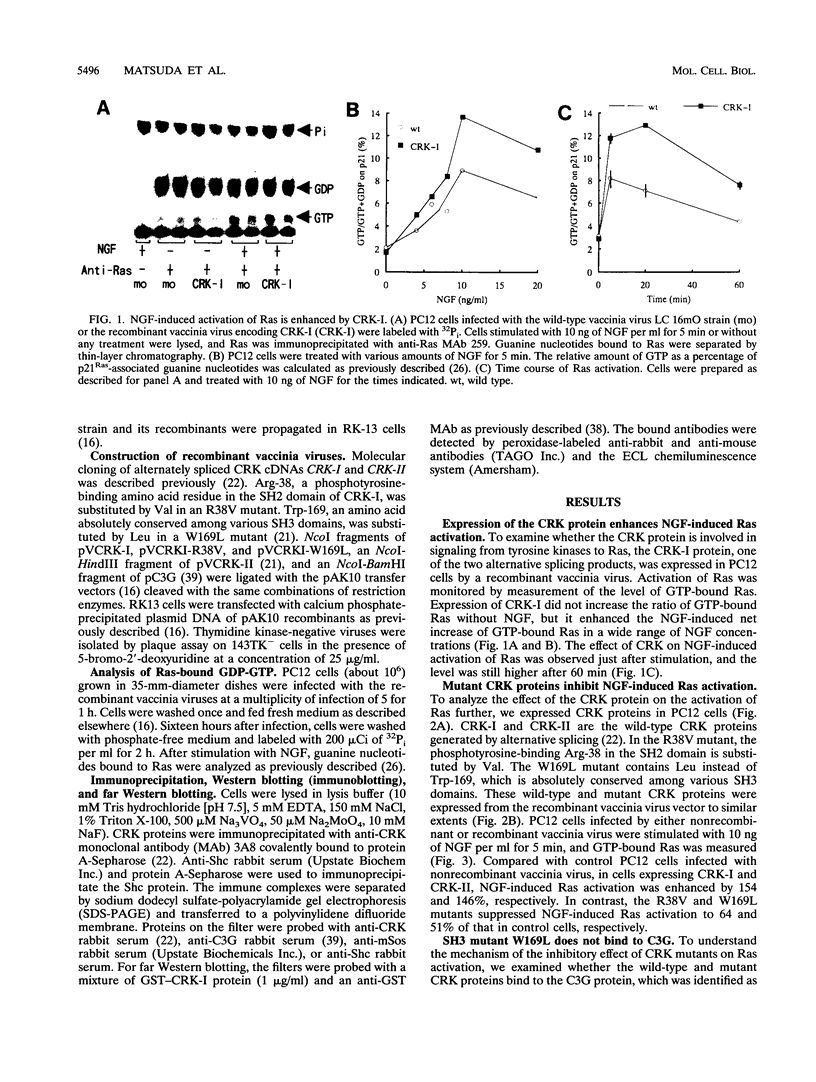
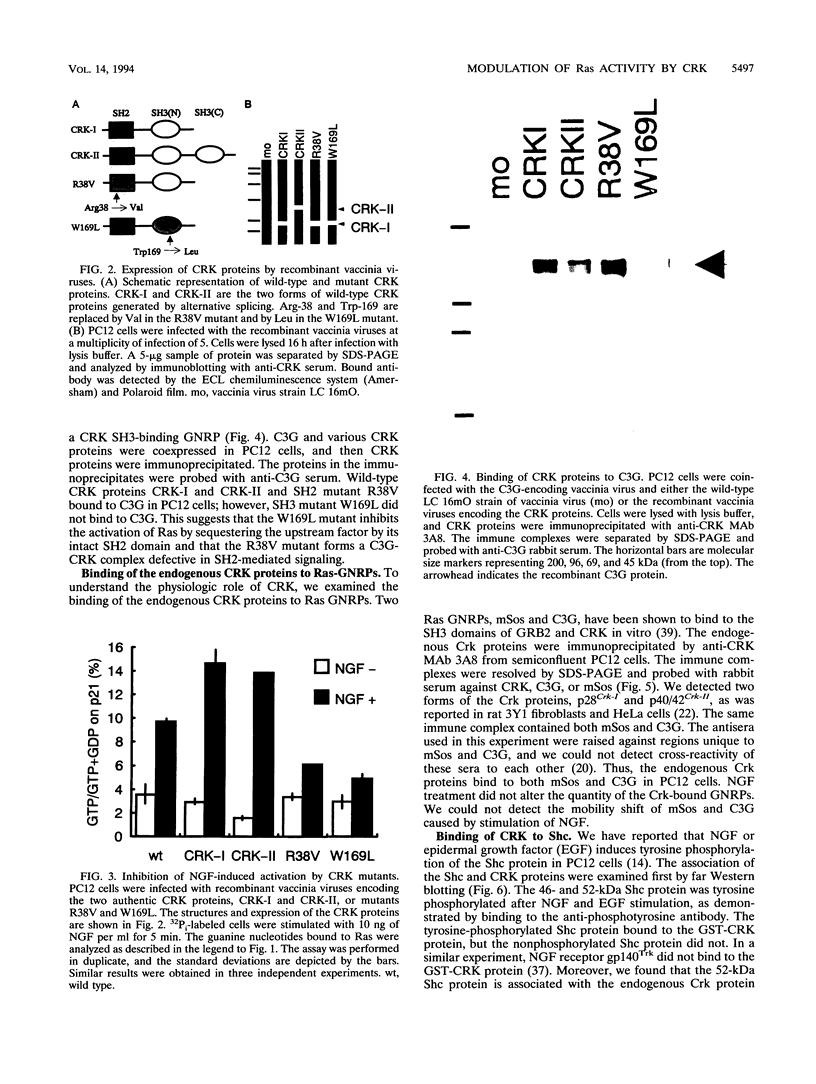
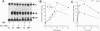Abstract
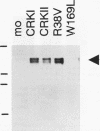
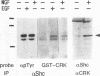
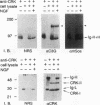
It has been reported that growth factors activate Ras through a complex of an adaptor type SH2-containing molecule, Grb2, and a Ras guanine nucleotide-releasing protein (GNRP), mSos. We report on the involvement of another adaptor molecule, CRK, in the activation of Ras. Overexpression of wild-type CRK proteins CRK-I and CRK-II enhanced the nerve growth factor (NGF)-induced activation of Ras in PC12 cells, although the basal level of GTP-bound active Ras was not altered. In contrast, mutants with a single amino acid substitution in either the SH2 or SH3 domain of the CRK-I protein inhibited the NGF-induced activation of Ras. Two GNRPs for the Ras family, mSos and C3G, were coimmunoprecipitated with the endogenous Crk proteins in PC12 cells. The association between C3G and the CRK mutants was dependent upon the presence of intact SH3. The SH2 domain of CRK bound to the SHC protein phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by NGF stimulation. The results demonstrate that, in addition to Grb2, CRK participates in signaling from the NGF receptor and that two GNRPs appear to transmit signals from these adaptor molecules to Ras.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A. Growth factors and cancer. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1146–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.1659742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltensperger K., Kozma L. M., Cherniack A. D., Klarlund J. K., Chawla A., Banerjee U., Czech M. P. Binding of the Ras activator son of sevenless to insulin receptor substrate-1 signaling complexes. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1950–1952. doi: 10.1126/science.8391166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. B., Fajardo J. E., Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Tyrosine-phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor and cellular p130 provide high affinity binding substrates to analyze Crk-phosphotyrosine-dependent interactions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10588–10595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90146-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cen H., Papageorge A. G., Vass W. C., Zhang K. E., Lowy D. R. Regulated and constitutive activity by CDC25Mm (GRF), a Ras-specific exchange factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7718–7724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V. Growth factor signaling: where is the specificity? Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):995–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90068-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Camonis J. H., Gale N. W., van Aelst L., Schlessinger J., Wigler M. H., Bar-Sagi D. Human Sos1: a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ras that binds to GRB2. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1338–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.8493579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio V., Welham M. J., Abraham S., Dryden P., Schrader J. W. p21ras activation via hemopoietin receptors and c-kit requires tyrosine kinase activity but not tyrosine phosphorylation of p21ras GTPase-activating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1587–1591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Giddings B. W., Brooks M. W., Buday L., Sizeland A. M., Weinberg R. A. Association of Sos Ras exchange protein with Grb2 is implicated in tyrosine kinase signal transduction and transformation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):45–51. doi: 10.1038/363045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo J. E., Birge R. B., Hanafusa H. A 31-amino-acid N-terminal extension regulates c-Crk binding to tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7295–7302. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale N. W., Kaplan S., Lowenstein E. J., Schlessinger J., Bar-Sagi D. Grb2 mediates the EGF-dependent activation of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ras. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):88–92. doi: 10.1038/363088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Matuoka K., Takenawa T., Muroya K., Hattori S., Nakamura S. Different interactions of Grb2/Ash molecule with the NGF and EGF receptors in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):869–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Birge R. B., Fajardo J. E., Glassman R., Mahadeo D., Kraemer R., Hanafusa H. Expression of the v-crk oncogene product in PC12 cells results in rapid differentiation by both nerve growth factor- and epidermal growth factor-dependent pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1964–1971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshikawa N., Kojima A., Yasuda A., Takayashiki E., Masuko S., Chiba J., Sata T., Kurata T. Role of the gag and pol genes of human immunodeficiency virus in the morphogenesis and maturation of retrovirus-like particles expressed by recombinant vaccinia virus: an ultrastructural study. J Gen Virol. 1991 Oct;72(Pt 10):2509–2517. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-10-2509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B. Q., Kaplan D., Kung H. F., Kamata T. Nerve growth factor stimulation of the Ras-guanine nucleotide exchange factor and GAP activities. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1456–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.1604323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Nagata S., Tanaka S., Nagashima K., Kurata T. Structural requirement of CRK SH2 region for binding to phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Evidence from reactivity to monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4441–4446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Tanaka S., Nagata S., Kojima A., Kurata T., Shibuya M. Two species of human CRK cDNA encode proteins with distinct biological activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3482–3489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Baltimore D. Signalling through SH2 and SH3 domains. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;3(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. The world according to GAP. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1281–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muroya K., Hattori S., Nakamura S. Nerve growth factor induces rapid accumulation of the GTP-bound form of p21ras in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. Oncogene. 1992 Feb;7(2):277–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier J. P., Raabe T., Henkemeyer M., Dickson B., Mbamalu G., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Hafen E., Pawson T. A Drosophila SH2-SH3 adaptor protein implicated in coupling the sevenless tyrosine kinase to an activator of Ras guanine nucleotide exchange, Sos. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90170-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Gish G. D. SH2 and SH3 domains: from structure to function. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazin M. J., Williams L. T. Triggering signaling cascades by receptor tyrosine kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90003-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichman C. T., Mayer B. J., Keshav S., Hanafusa H. The product of the cellular crk gene consists primarily of SH2 and SH3 regions. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Jul;3(7):451–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., Fernley R., Wade J., Pawson T., Bowtell D. The SH2 and SH3 domains of mammalian Grb2 couple the EGF receptor to the Ras activator mSos1. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):83–85. doi: 10.1038/363083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., McGlade J., Mbamalu G., Pelicci G., Daly R., Li W., Batzer A., Thomas S., Brugge J., Pelicci P. G. Association of the Shc and Grb2/Sem5 SH2-containing proteins is implicated in activation of the Ras pathway by tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):689–692. doi: 10.1038/360689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakafuku M., Kaziro Y. Function of Ras as a molecular switch in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24149–24152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suen K. L., Bustelo X. R., Pawson T., Barbacid M. Molecular cloning of the mouse grb2 gene: differential interaction of the Grb2 adaptor protein with epidermal growth factor and nerve growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5500–5512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Hattori S., Kurata T., Nagashima K., Fukui Y., Nakamura S., Matsuda M. Both the SH2 and SH3 domains of human CRK protein are required for neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4409–4415. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Morishita T., Hashimoto Y., Hattori S., Nakamura S., Shibuya M., Matuoka K., Takenawa T., Kurata T., Nagashima K. C3G, a guanine nucleotide-releasing protein expressed ubiquitously, binds to the Src homology 3 domains of CRK and GRB2/ASH proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3443–3447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]