Abstract
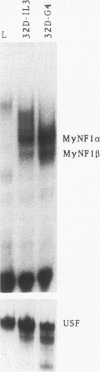
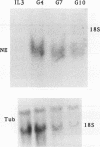
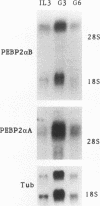
The myeloperoxidase (MPO) and neutrophil elastase genes are expressed specifically in immature myeloid cells. The integrity of a polyomavirus enhancer core sequence, 5'-AACCACA-3', is critical to the activity of the murine MPO proximal enhancer. This element binds two species, myeloid nuclear factors 1 alpha and 1 beta (MyNF1 alpha and -beta), present in 32D cl3 myeloid cell nuclear extracts. The levels of the MyNF1s increase during early 32D cl3 cell granulocytic differentiation. Both MyNF1 alpha and -beta supershift with an antiserum raised by using a peptide derived from the N terminus of polyomavirus enhancer-binding protein 2/core-binding factor (PEBP2/CBF) alpha subunit. The specific peptide inhibits these supershifts. In vitro-translated PEBP2/CBF DNA-binding domain binds the murine MPO PEBP2/CBF site. An alternate PEBP2/CBF consensus site, 5'-GACCGCA-3', but not a simian virus 40 enhancer core sequence, 5'-TTCCACA-3', binds the MyNF1s in vitro and activates a minimal murine MPO-thymidine kinase promoter in vivo. The murine neutrophil elastase gene 100-bp 5'-flanking sequences contain several functional elements, including potential binding sites for PU.1, C/EBP, c-Myb, and PEBP2/CBF. The functional element 5'-GGCCACA-3' located at positions -66 to 72 differs from the PEBP2/CBF consensus (5'-PuACCPuCA-3') only by an A-to-G transition at position 2. This DNA element binds MyNF1 alpha and -beta weakly. The N terminis of two PEBP2/CBF alpha subunit family members, PEBP2 alpha A and PEBP2 alpha B (murine AML1), are nearly identical, and 32D c13 cl3 cells contain both corresponding mRNAs. Since t(8;21), t(3;21), and inv(16), associated with myeloid leukemias, disrupt subunits of PEBP2/CBF, we speculate that the resulting oncoproteins, AML1-ETO, AML1-EAP, AML1-Evi1, and CBF beta-MYH11, inhibit early myeloid differentiation.
Full text
PDF


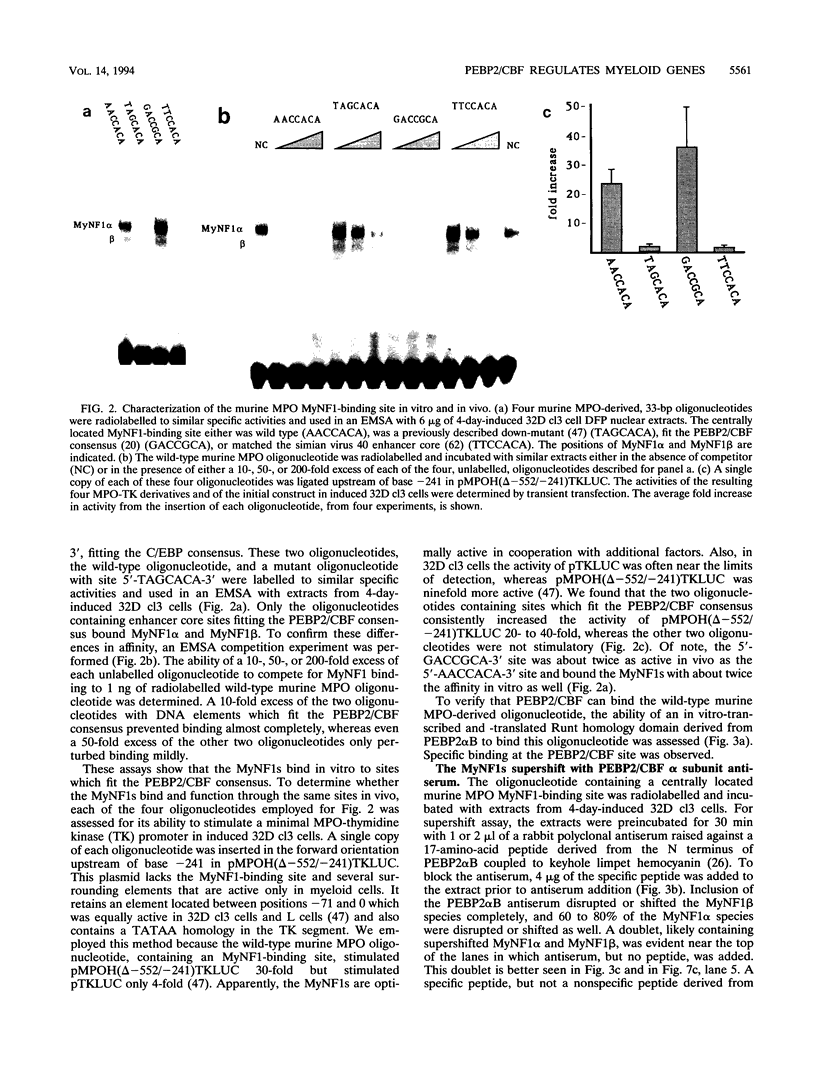



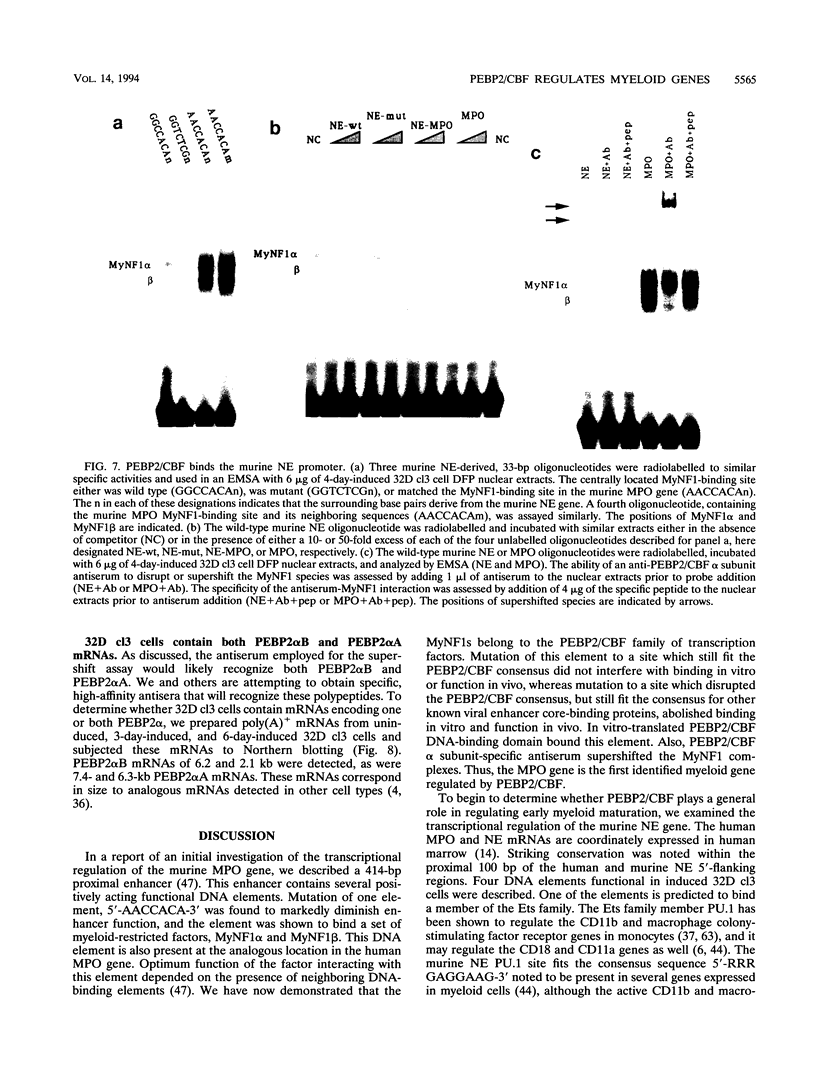



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida R. P., Melchior M., Campanelli D., Nathan C., Gabay J. E. Complementary DNA sequence of human neutrophil azurocidin, an antibiotic with extensive homology to serine proteases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 14;177(2):688–695. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91843-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae S. C., Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Oka H., Satake M., Shigesada K., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G., Ito Y. PEBP2 alpha B/mouse AML1 consists of multiple isoforms that possess differential transactivation potentials. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3242–3252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae S. C., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Inuzuka M., Kagoshima H., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y. Isolation of PEBP2 alpha B cDNA representing the mouse homolog of human acute myeloid leukemia gene, AML1. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttinger E. P., Shelley C. S., Farokhzad O. C., Arnaout M. A. The human beta 2 integrin CD18 promoter consists of two inverted Ets cis elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2604–2615. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Rosales R., Staub A., Chambon P. The HeLa cell protein TEF-1 binds specifically and cooperatively to two SV40 enhancer motifs of unrelated sequence. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson P., Gao J., Chang K. S., Look T., Whisenant E., Raimondi S., Lasher R., Trujillo J., Rowley J., Drabkin H. Identification of breakpoints in t(8;21) acute myelogenous leukemia and isolation of a fusion transcript, AML1/ETO, with similarity to Drosophila segmentation gene, runt. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1825–1831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouret P., du Bois R. M., Bernaudin J. F., Takahashi H., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Expression of the neutrophil elastase gene during human bone marrow cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):833–845. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Krieder B. L., Venturelli D., Rovera G. Transcriptional regulation of two myeloid-specific genes, myeloperoxidase and lactoferrin, during differentiation of the murine cell line 32D C13. Blood. 1991 Nov 1;78(9):2426–2432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Munain C., Krangel M. S. Regulation of the T-cell receptor delta enhancer by functional cooperation between c-Myb and core-binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):473–483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K., Gemperlein I., Hudson S., Shane S., Rovera G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the human myeloperoxidase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7985–7986. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgenson K. F., Antoun G. R., Zipf T. F. Chromatin structural analysis of the 5' end and contiguous flanking region of the myeloperoxidase gene. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):159–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamachi Y., Ogawa E., Asano M., Ishida S., Murakami Y., Satake M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Purification of a mouse nuclear factor that binds to both the A and B cores of the polyomavirus enhancer. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4808–4819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4808-4819.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kania M. A., Bonner A. S., Duffy J. B., Gergen J. P. The Drosophila segmentation gene runt encodes a novel nuclear regulatory protein that is also expressed in the developing nervous system. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1701–1713. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Bindereif A., Green M. R. A small-scale procedure for preparation of nuclear extracts that support efficient transcription and pre-mRNA splicing. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Mar-Apr;5(2):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Tarlé S. A., Hajra A., Claxton D. F., Marlton P., Freedman M., Siciliano M. J., Collins F. S. Fusion between transcription factor CBF beta/PEBP2 beta and a myosin heavy chain in acute myeloid leukemia. Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1041–1044. doi: 10.1126/science.8351518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert M., Miller C. W., Koeffler H. P. Changes of DNA methylation and chromatin structure in the human myeloperoxidase gene during myeloid differentiation. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):345–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio F., Karin M. Transcription factors AP-3 and AP-2 interact with the SV40 enhancer in a mutually exclusive manner. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1455–1460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers S., Downing J. R., Hiebert S. W. Identification of AML-1 and the (8;21) translocation protein (AML-1/ETO) as sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins: the runt homology domain is required for DNA binding and protein-protein interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6336–6345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitani K., Ogawa S., Tanaka T., Miyoshi H., Kurokawa M., Mano H., Yazaki Y., Ohki M., Hirai H. Generation of the AML1-EVI-1 fusion gene in the t(3;21)(q26;q22) causes blastic crisis in chronic myelocytic leukemia. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):504–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi H., Kozu T., Shimizu K., Enomoto K., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Kamada N., Ohki M. The t(8;21) translocation in acute myeloid leukemia results in production of an AML1-MTG8 fusion transcript. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2715–2721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi H., Shimizu K., Kozu T., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Ohki M. t(8;21) breakpoints on chromosome 21 in acute myeloid leukemia are clustered within a limited region of a single gene, AML1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10431–10434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natsuka S., Akira S., Nishio Y., Hashimoto S., Sugita T., Isshiki H., Kishimoto T. Macrophage differentiation-specific expression of NF-IL6, a transcription factor for interleukin-6. Blood. 1992 Jan 15;79(2):460–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Kowenz-Leutz E., Casini T., Graf T., Leutz A. Myb and NF-M: combinatorial activators of myeloid genes in heterologous cell types. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):749–759. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora G., Begy C. R., Erickson P., Drabkin H. A., Rowley J. D. The 3;21 translocation in myelodysplasia results in a fusion transcript between the AML1 gene and the gene for EAP, a highly conserved protein associated with the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7784–7788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa E., Inuzuka M., Maruyama M., Satake M., Naito-Fujimoto M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Molecular cloning and characterization of PEBP2 beta, the heterodimeric partner of a novel Drosophila runt-related DNA binding protein PEBP2 alpha. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):314–331. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Kagoshima H., Inuzuka M., Lu J., Satake M., Shigesada K., Ito Y. PEBP2/PEA2 represents a family of transcription factors homologous to the products of the Drosophila runt gene and the human AML1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6859–6863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryzwansky K. B., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. Immunocytochemical localization of myeloperoxidase, lactoferrin, lysozyme and neutral proteases in human monocytes and neutrophilic granulocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Sep;24(3):295–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagoh T., Yamada M. Transcriptional regulation of myeloperoxidase gene expression in myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells during differentiation into granulocytes and macrophages. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 May 1;262(2):599–604. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90411-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Inuzuka M., Shigesada K., Oikawa T., Ito Y. Differential expression of subspecies of polyomavirus and murine leukemia virus enhancer core binding protein, PEBP2, in various hematopoietic cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Jul;83(7):714–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb01971.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott L. M., Civin C. I., Rorth P., Friedman A. D. A novel temporal expression pattern of three C/EBP family members in differentiating myelomonocytic cells. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1725–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley C. S., Farokhzad O. C., Arnaout M. A. Identification of cell-specific and developmentally regulated nuclear factors that direct myeloid and lymphoid expression of the CD11a gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5364–5368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. In vitro mutagenesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:423–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobl H., Takimoto M., Majdic O., Fritsch G., Scheinecker C., Höcker P., Knapp W. Myeloperoxidase expression in CD34+ normal human hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1993 Oct 1;82(7):2069–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzow J., Friedman A. D. The murine myeloperoxidase promoter contains several functional elements, one of which binds a cell type-restricted transcription factor, myeloid nuclear factor 1 (MyNF1). Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2141–2151. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Nukiwa T., Basset P., Crystal R. G. Myelomonocytic cell lineage expression of the neutrophil elastase gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2543–2547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Nukiwa T., Yoshimura K., Quick C. D., States D. J., Holmes M. D., Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Crystal R. G. Structure of the human neutrophil elastase gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14739–14747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Differential protein binding in lymphocytes to a sequence in the enhancer of the mouse retrovirus SL3-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1625–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobler A., Miller C. W., Johnson K. R., Selsted M. E., Rovera G., Koeffler H. P. Regulation of gene expression of myeloperoxidase during myeloid differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Aug;136(2):215–225. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S., Bartelmez S., Heyman R., Damm K., Evans R., Collins S. J. A mutated retinoic acid receptor-alpha exhibiting dominant-negative activity alters the lineage development of a multipotent hematopoietic cell line. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2258–2269. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtieri M., Tweardy D. J., Caracciolo D., Johnson K., Mavilio F., Altmann S., Santoli D., Rovera G. Cytokine-dependent granulocytic differentiation. Regulation of proliferative and differentiative responses in a murine progenitor cell line. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3829–3835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venturelli D., Bittenbender S., Rovera G. Sequence of the murine myeloperoxidase (MPO) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7987–7988. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. W., Speck N. A. Purification of core-binding factor, a protein that binds the conserved core site in murine leukemia virus enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):89–102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Wang Q., Crute B. E., Melnikova I. N., Keller S. R., Speck N. A. Cloning and characterization of subunits of the T-cell receptor and murine leukemia virus enhancer core-binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3324–3339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L., Moore M. A., Metcalf D. A transplantable myelomonocytic leukemia in BALB-c mice: cytology, karyotype, and muramidase content. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Oct;43(4):963–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. G., Snable J. L., Griffith J. E., Scott R. W. Characterization of two azurphil granule proteases with active-site homology to neutrophil elastase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2038–2041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wotton D., Ghysdael J., Wang S., Speck N. A., Owen M. J. Cooperative binding of Ets-1 and core binding factor to DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):840–850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura K., Crystal R. G. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional modulation of human neutrophil elastase gene expression. Blood. 1992 May 15;79(10):2733–2740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D. E., Hetherington C. J., Chen H. M., Tenen D. G. The macrophage transcription factor PU.1 directs tissue-specific expression of the macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):373–381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zonneveld A. J., Curriden S. A., Loskutoff D. J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene: functional analysis and glucocorticoid regulation of its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5525–5529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]