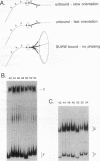
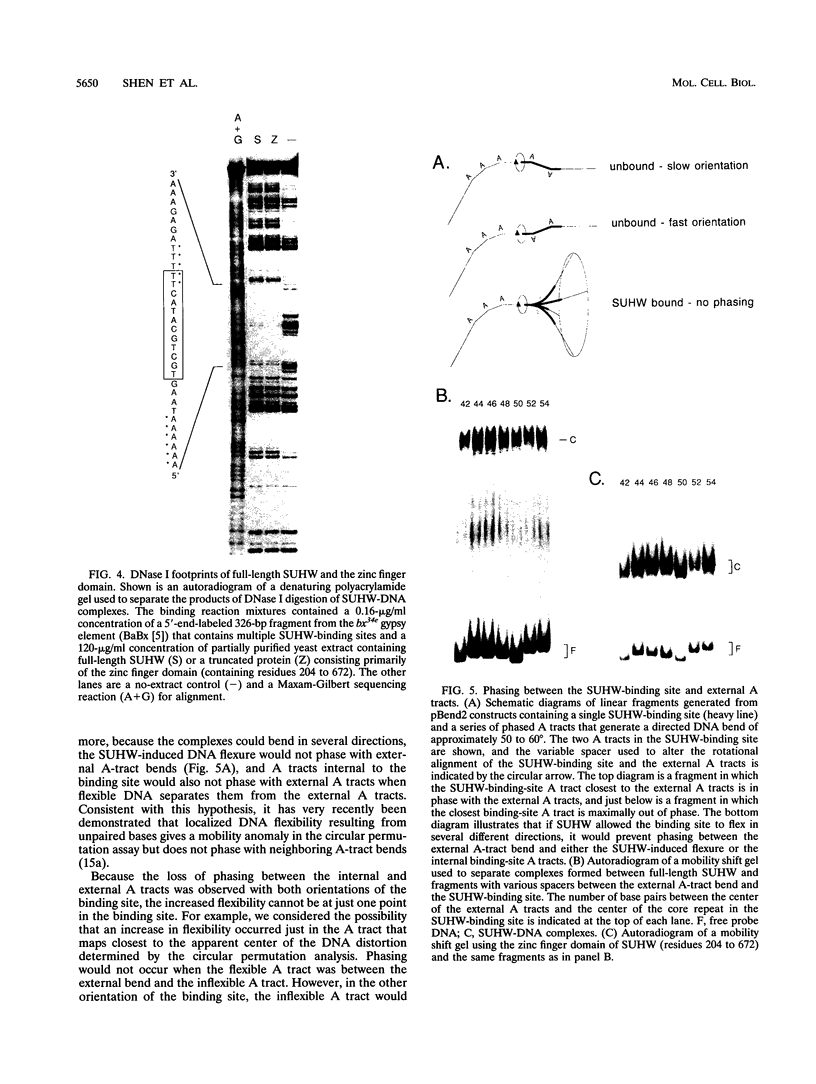
Abstract
Insertion of the gypsy retrotransposon of Drosophila melanogaster into a gene control region can repress gene expression. The zinc finger protein (SUHW) encoded by the suppressor of Hairy-wing [su(Hw)] gene binds to gypsy and prevents gene enhancers from activating transcription. SUHW blocks an enhancer only when positioned between the enhancer and promoter. Although position dependent, SUHW enhancer blocking is distance independent. These properties indicate that SUHW does not interact with the transcription activator proteins that bind to enhancers. To explore if DNA distortions are involved in enhancer blocking, the ability of SUHW to alter DNA structure was examined in gel mobility assays. Indeed, SUHW induces an unusual change in the structure of the binding-site DNA. The change is not a directed DNA bend but correlates with loss of sequence-directed bends in the unbound DNA. The DNA distortion requires a SUHW protein domain not required for DNA binding, and mutant proteins that fail to alter DNA structure also fail to eliminate the sequence-directed bends. These results suggest that SUHW increases DNA flexibility. The DNA distortion is not sufficient to block enhancers, and therefore it is suggested that increased DNA flexibility may help SUHW interact and interfere with proteins that support long-distance enhancer-promoter interactions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. Localized melting and structural changes in the SV40 origin of replication induced by T-antigen. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3149–3158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Zhang L., Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. DNA supercoiling promotes formation of a bent repression loop in lac DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. Duplex opening by dnaA protein at novel sequences in initiation of replication at the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):743–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A bacterial repressor protein or a yeast transcriptional terminator can block upstream activation of a yeast gene. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):612–615. doi: 10.1038/312612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsett D. Distance-independent inactivation of an enhancer by the suppressor of Hairy-wing DNA-binding protein of Drosophila. Genetics. 1993 Aug;134(4):1135–1144. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.4.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsett D. Potentiation of a polyadenylylation site by a downstream protein-DNA interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4373–4377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsett D., Viglianti G. A., Rutledge B. J., Meselson M. Alteration of hsp82 gene expression by the gypsy transposon and suppressor genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):454–468. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Giniger E., Maniatis T., Ptashne M. GAL4 activates transcription in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):853–856. doi: 10.1038/332853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Ampe C., Steitz T. A., Crothers D. M. Molecular characterization of the GCN4-DNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6034–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Corces V. G. DNA position-specific repression of transcription by a Drosophila zinc finger protein. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1865–1873. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Green M. M., Corces V. G. Tissue-specific transcriptional enhancers may act in trans on the gene located in the homologous chromosome: the molecular basis of transvection in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2247–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Noble S. M., Grindley N. D. The gamma delta resolvase induces an unusual DNA structure at the recombinational crossover point. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90760-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdridge C., Dorsett D. Repression of hsp70 heat shock gene transcription by the suppressor of hairy-wing protein of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1894–1900. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. W. Molecular organization of the cut locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):869–876. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J., Dorsett D., Delotto Y., Liu S. Expression of the cut locus in the Drosophila wing margin is required for cell type specification and is regulated by a distant enhancer. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):735–747. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Yun E., Crothers D. M. Detection of localized DNA flexibility. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):163–166. doi: 10.1038/368163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. DNA bending by Fos and Jun: the flexible hinge model. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1210–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.1957173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Shen B., Dorsett D. The Drosophila melanogaster suppressor of Hairy-wing zinc finger protein has minimal effects on gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1993 Oct;135(2):343–355. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Khan S. A. Static and initiator protein-enhanced bending of DNA at a replication origin. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1316–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.3749879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Bender W., Meselson M. Drosophila melanogaster mutations suppressible by the suppressor of Hairy-wing are insertions of a 7.3-kilobase mobile element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1678–1682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S., Patel I., Bastia D. Conformational changes in a replication origin induced by an initiator protein. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst S. M., Harrison D. A., Remington M. P., Spana C., Kelley R. L., Coyne R. S., Corces V. G. The Drosophila su(Hw) gene, which controls the phenotypic effect of the gypsy transposable element, encodes a putative DNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1205–1215. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Bender W. Sequences of the gypsy transposon of Drosophila necessary for its effects on adjacent genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9650–9654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. A., Nash H. A. Bending of the bacteriophage lambda attachment site by Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3554–3557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F., Zaballos A., Salas M. Bend induced by the phage phi 29 transcriptional activator in the viral late promoter is required for activation. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):713–725. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90072-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutledge B. J., Mortin M. A., Schwarz E., Thierry-Mieg D., Meselson M. Genetic interactions of modifier genes and modifiable alleles in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Jun;119(2):391–397. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. Helical phasing between DNA bends and the determination of bend direction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9771–9779. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder U. K., Thompson J. F., Landy A. Phasing of protein-induced DNA bends in a recombination complex. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):255–257. doi: 10.1038/341255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spana C., Corces V. G. DNA bending is a determinant of binding specificity for a Drosophila zinc finger protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1505–1515. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Sentenac A. Asymmetric DNA bending induced by the yeast multifunctional factor TUF. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8463–8466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Binding and bending of the lambda replication origin by the phage O protein. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3605–3616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet P. C., Verrijzer C. P. Bending of DNA by transcription factors. Bioessays. 1993 Jan;15(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]