Abstract
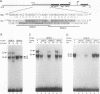
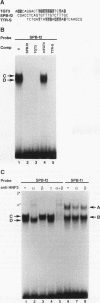
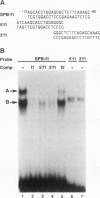
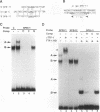
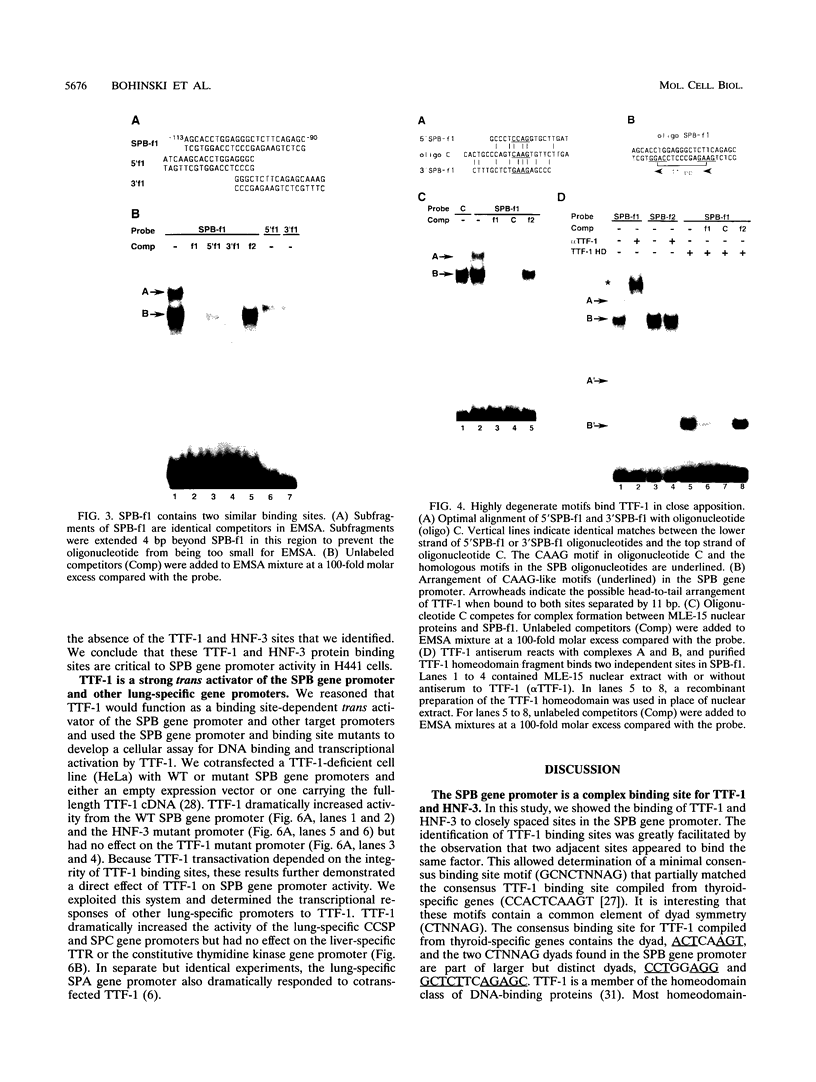
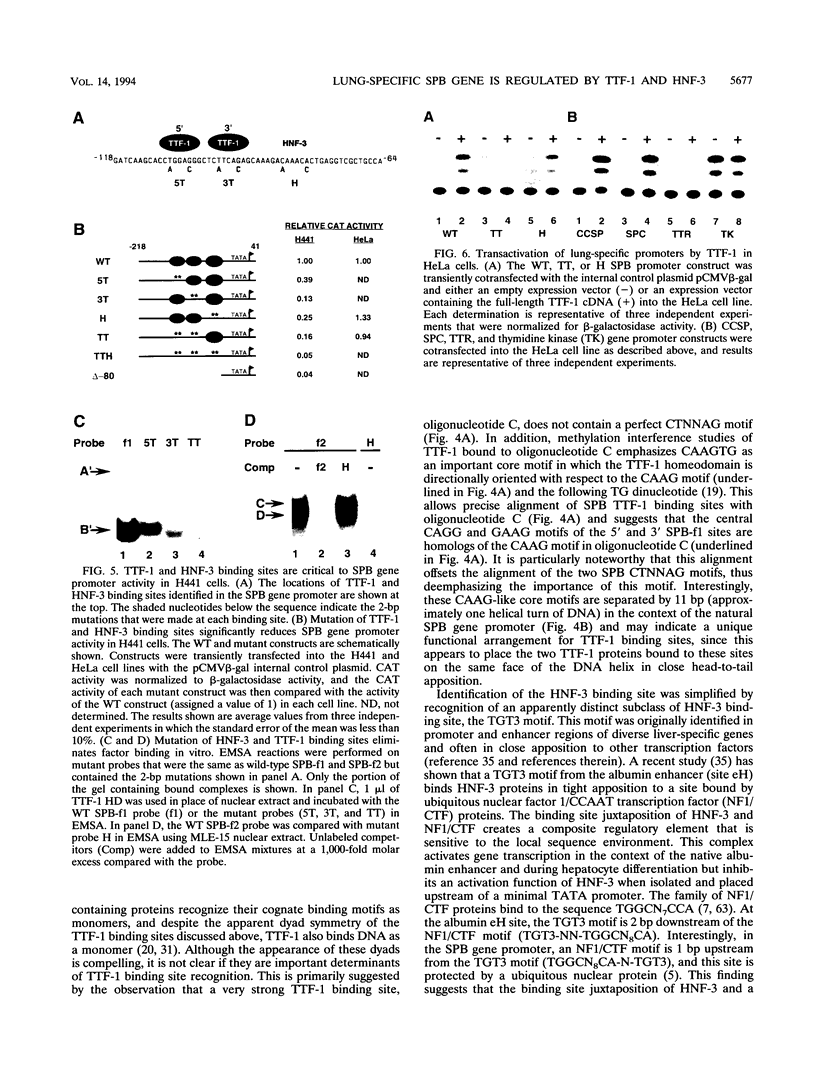
We used the lung epithelial cell-specific surfactant protein B (SPB) gene promoter as a model with which to investigate mechanisms involved in transcriptional control of lung-specific genes. In a previous study, we showed that the SPB promoter specifically activated expression of a linked reporter gene in the continuous H441 lung cell line and that H441 nuclear proteins specifically protected a region of this promoter from bp -111 to -73. In this study, we further show that this region is a complex binding site for thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1) and hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 (HNF-3). Whereas TTF-1 bound two highly degenerate and closely spaced sites, HNF-3 proteins bound a TGT3 motif (TGTTTGT) that is also found in several liver-specific gene regulatory regions, where it appears to be a weak affinity site for HNF-3. Point mutations of these binding sites eliminated factor binding and resulted in significant decreases in transfected SPB promoter activity. In addition, we developed a cotransfection assay and showed that a family of lung-specific gene promoters that included the SPB, SPC, SPA, and Clara cell secretory protein (CCSP) gene promoters were specifically activated by cotransfected TTF-1. We conclude that TTF-1 and HNF-3 are major activators of lung-specific genes and propose that these factors are involved in a general mechanism of lung-specific gene transcription. Importantly, these data also show that common factors are involved in organ-specific gene expression along the mammalian foregut axis.
Full text
PDF



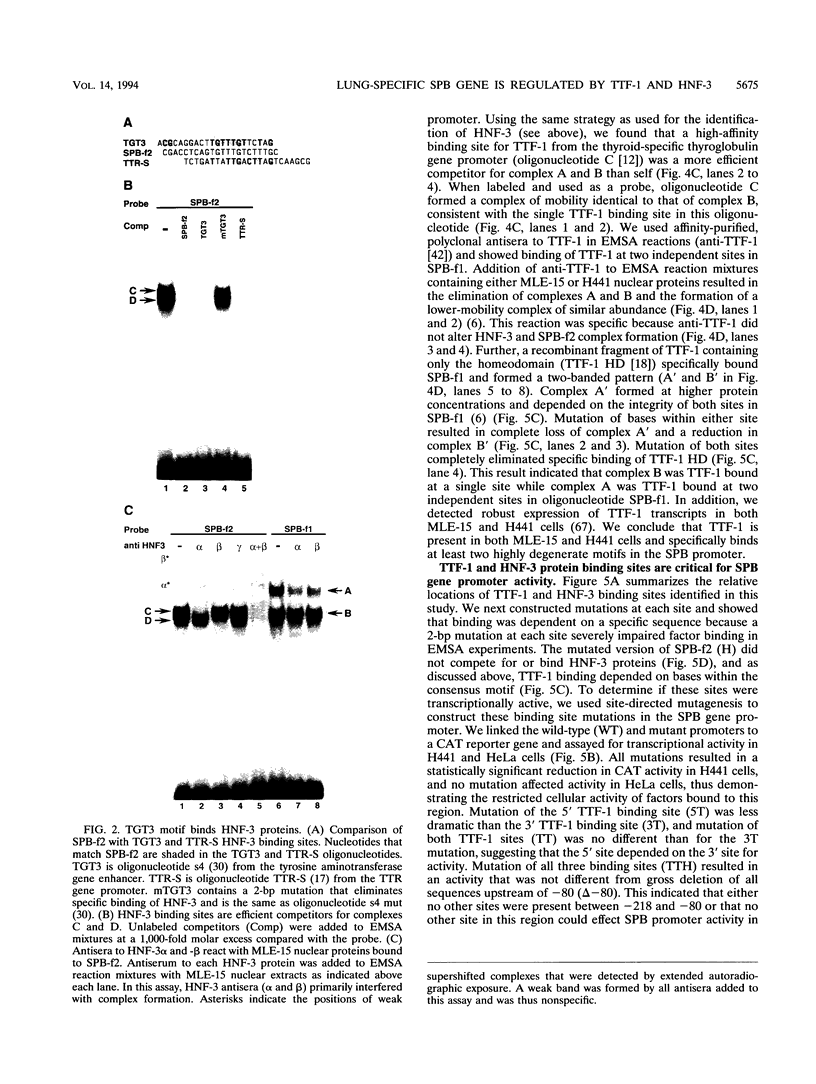




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ang S. L., Wierda A., Wong D., Stevens K. A., Cascio S., Rossant J., Zaret K. S. The formation and maintenance of the definitive endoderm lineage in the mouse: involvement of HNF3/forkhead proteins. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1301–1315. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avvedimento V. E., Musti A. M., Ueffing M., Obici S., Gallo A., Sanchez M., DeBrasi D., Gottesman M. E. Reversible inhibition of a thyroid-specific trans-acting factor by Ras. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):22–28. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingle C. D., Gitlin J. D. Identification of hepatocyte nuclear factor-3 binding sites in the Clara cell secretory protein gene. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 1;295(Pt 1):227–232. doi: 10.1042/bj2950227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld M., Maury M., Chouard T., Yaniv M., Condamine H. Hepatic nuclear factor 1 (HNF1) shows a wider distribution than products of its known target genes in developing mouse. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):589–599. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohinski R. J., Huffman J. A., Whitsett J. A., Lattier D. L. Cis-active elements controlling lung cell-specific expression of human pulmonary surfactant protein B gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11160–11166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgmeyer U., Nowock J., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA-binding protein: a eukaryotic nuclear protein recognizing a symmetrical sequence on double-stranded linear DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4295–4311. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Klüppel M., Schmidt A., Schütz G., Luckow B. Reporter constructs with low background activity utilizing the cat gene. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):129–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90456-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botas J. Control of morphogenesis and differentiation by HOM/Hox genes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;5(6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascio S., Zaret K. S. Hepatocyte differentiation initiates during endodermal-mesenchymal interactions prior to liver formation. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):217–225. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civitareale D., Lonigro R., Sinclair A. J., Di Lauro R. A thyroid-specific nuclear protein essential for tissue-specific expression of the thyroglobulin promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. L., Halay E. D., Lai E., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):412–420. doi: 10.1038/364412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevidence D. E., Overdier D. G., Tao W., Qian X., Pani L., Lai E., Costa R. H. Identification of nine tissue-specific transcription factors of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/forkhead DNA-binding-domain family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3948–3952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damante G., Di Lauro R. Several regions of Antennapedia and thyroid transcription factor 1 homeodomains contribute to DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5388–5392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damante G., Tell G., Formisano S., Fabbro D., Pellizzari L., Di Lauro R. Effect of salt concentration on TTF-1 HD binding to specific and non-specific DNA sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 15;197(2):632–638. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., Cortese R. Transcriptional regulation of liver-specific gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):960–965. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90114-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewes T., Klein-Hitpass L., Ryffel G. U. Liver specific transcription factors of the HNF3-, C/EBP- and LFB1-families interact with the A-activator binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6383–6389. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis-Lang H., Price M., Polycarpou-Schwarz M., Di Lauro R. Cell-type-specific expression of the rat thyroperoxidase promoter indicates common mechanisms for thyroid-specific gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):576–588. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis-Lang H., Zannini M., De Felice M., Berlingieri M. T., Fusco A., Di Lauro R. Multiple mechanisms of interference between transformation and differentiation in thyroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5793–5800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Linnoila R. I., Kurita Y., Oie H. K., Mulshine J. L., Clark J. C., Whitsett J. A. Peripheral airway cell differentiation in human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17):5481–5487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Roux J., Rigaud G., Pictet R. Cell-type specific activity of two glucocorticoid responsive units of rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene is associated with multiple binding sites for C/EBP and a novel liver-specific nuclear factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guazzi S., Price M., De Felice M., Damante G., Mattei M. G., Di Lauro R. Thyroid nuclear factor 1 (TTF-1) contains a homeodomain and displays a novel DNA binding specificity. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3631–3639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen B. R., Wood W. M., Gordon D. F., Ridgway E. C. A thyrotrope-specific variant of Pit-1 transactivates the thyrotropin beta promoter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20818–20824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L., Lubon H. Interaction of protein with DNA in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:721–735. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Rowader K. E., Stevens K., Jiang C., Milos P., Zaret K. S. Modulation of liver-specific transcription by interactions between hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 and nuclear factor 1 binding DNA in close apposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2401–2410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Transgenic animals. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1468–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.3287623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapiloff M. S., Farkash Y., Wegner M., Rosenfeld M. G. Variable effects of phosphorylation of Pit-1 dictated by the DNA response elements. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):786–789. doi: 10.1126/science.1652153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. J., Conley P. B., Chen L., Sladek F. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Crabtree G. R. A transcriptional hierarchy involved in mammalian cell-type specification. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):457–461. doi: 10.1038/355457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzaro D., Price M., de Felice M., Di Lauro R. The transcription factor TTF-1 is expressed at the onset of thyroid and lung morphogenesis and in restricted regions of the foetal brain. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1093–1104. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Fujii H., Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A novel B cell-derived coactivator potentiates the activation of immunoglobulin promoters by octamer-binding transcription factors. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90352-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Caskey C. T. Construction of plasmids that express E. coli beta-galactosidase in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2365–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson C. E., Shim E. Y., Friedman D. S., Zaret K. S. An active tissue-specific enhancer and bound transcription factors existing in a precisely positioned nucleosomal array. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80079-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milos P. M., Zaret K. S. A ubiquitous factor is required for C/EBP-related proteins to form stable transcription complexes on an albumin promoter segment in vitro. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):991–1004. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Miller J. B., Wold B. J. Skeletal muscle phenotypes initiated by ectopic MyoD in transgenic mouse heart. Development. 1992 Apr;114(4):853–860. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.4.853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan A. P., Kaestner K. H., Grau E., Schütz G. Postimplantation expression patterns indicate a role for the mouse forkhead/HNF-3 alpha, beta and gamma genes in determination of the definitive endoderm, chordamesoderm and neuroectoderm. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):567–578. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerlov C., Ziff E. B. Three levels of functional interaction determine the activity of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-alpha on the serum albumin promoter. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 1;8(3):350–362. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.3.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch D., Boshart M., Schütz G. Activation of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene is dependent on synergy between liver-specific and hormone-responsive elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5479–5483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch D., Boshart M., Schütz G. Extinction of tyrosine aminotransferase gene activity in somatic cell hybrids involves modification and loss of several essential transcriptional activators. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):308–319. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M. A., Gazdar A. F., Morris R. E., Whitsett J. A. Differential effects of glucocorticoid on expression of surfactant proteins in a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 30;970(2):194–204. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overdier D. G., Porcella A., Costa R. H. The DNA-binding specificity of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/forkhead domain is influenced by amino-acid residues adjacent to the recognition helix. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2755–2766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pani L., Quian X. B., Clevidence D., Costa R. H. The restricted promoter activity of the liver transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 beta involves a cell-specific factor and positive autoactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):552–562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Floros J. Localization of pulmonary surfactant proteins using immunohistochemistry and tissue in situ hybridization. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Nov-Dec;17(6):985–995. doi: 10.3109/01902149109064330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plachov D., Chowdhury K., Walther C., Simon D., Guenet J. L., Gruss P. Pax8, a murine paired box gene expressed in the developing excretory system and thyroid gland. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):643–651. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., Finch J. T., Graziano V., Lee P. L., Sweet R. M. Crystal structure of globular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):219–223. doi: 10.1038/362219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. In vivo footprinting of rat TAT gene: dynamic interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and a liver-specific factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90370-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Identification of regulatory elements of cloned genes with functional assays. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:704–720. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp R. A., Kruse U., Multhaup G., Göbel U., Beyreuther K., Sippel A. E. Chicken NFI/TGGCA proteins are encoded by at least three independent genes: NFI-A, NFI-B and NFI-C with homologues in mammalian genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2607–2616. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Hogan B. L. Differential expression of multiple fork head related genes during gastrulation and axial pattern formation in the mouse embryo. Development. 1993 May;118(1):47–59. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawaya P. L., Stripp B. R., Whitsett J. A., Luse D. S. The lung-specific CC10 gene is regulated by transcription factors from the AP-1, octamer, and hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 families. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3860–3871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. M., Voss J. W., Ingraham H. A., Holloway J. M., Broide R. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Swanson L. W. Pituitary cell phenotypes involve cell-specific Pit-1 mRNA translation and synergistic interactions with other classes of transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):695–711. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver T. E., Whitsett J. A. Function and regulation of expression of pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 15;273(Pt 2):249–264. doi: 10.1042/bj2730249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Adam M. A., Lassar A. B., Miller A. D. Activation of muscle-specific genes in pigment, nerve, fat, liver, and fibroblast cell lines by forced expression of MyoD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wert S. E., Glasser S. W., Korfhagen T. R., Whitsett J. A. Transcriptional elements from the human SP-C gene direct expression in the primordial respiratory epithelium of transgenic mice. Dev Biol. 1993 Apr;156(2):426–443. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikenheiser K. A., Vorbroker D. K., Rice W. R., Clark J. C., Bachurski C. J., Oie H. K., Whitsett J. A. Production of immortalized distal respiratory epithelial cell lines from surfactant protein C/simian virus 40 large tumor antigen transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11029–11033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikenheiser K. A., Wert S. E., Wispé J. R., Stahlman M., D'Amore-Bruno M., Singh G., Katyal S. L., Whitsett J. A. Distinct effects of oxygen on surfactant protein B expression in bronchiolar and alveolar epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):L32–L39. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.1.L32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthopoulos K. G., Prezioso V. R., Chen W. S., Sladek F. M., Cortese R., Darnell J. E., Jr The different tissue transcription patterns of genes for HNF-1, C/EBP, HNF-3, and HNF-4, protein factors that govern liver-specific transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3807–3811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannini M., Francis-Lang H., Plachov D., Di Lauro R. Pax-8, a paired domain-containing protein, binds to a sequence overlapping the recognition site of a homeodomain and activates transcription from two thyroid-specific promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4230–4241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]