Abstract
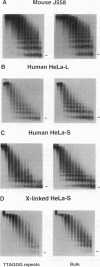
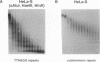
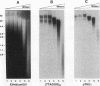
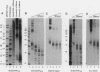
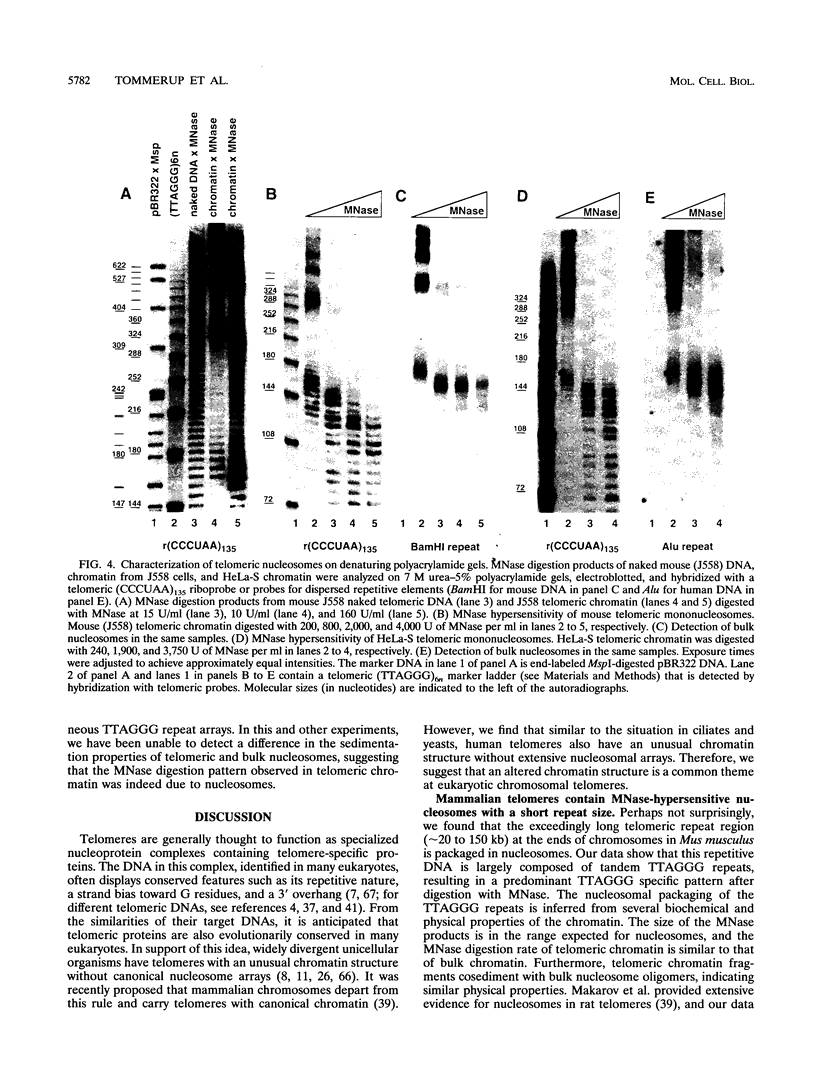
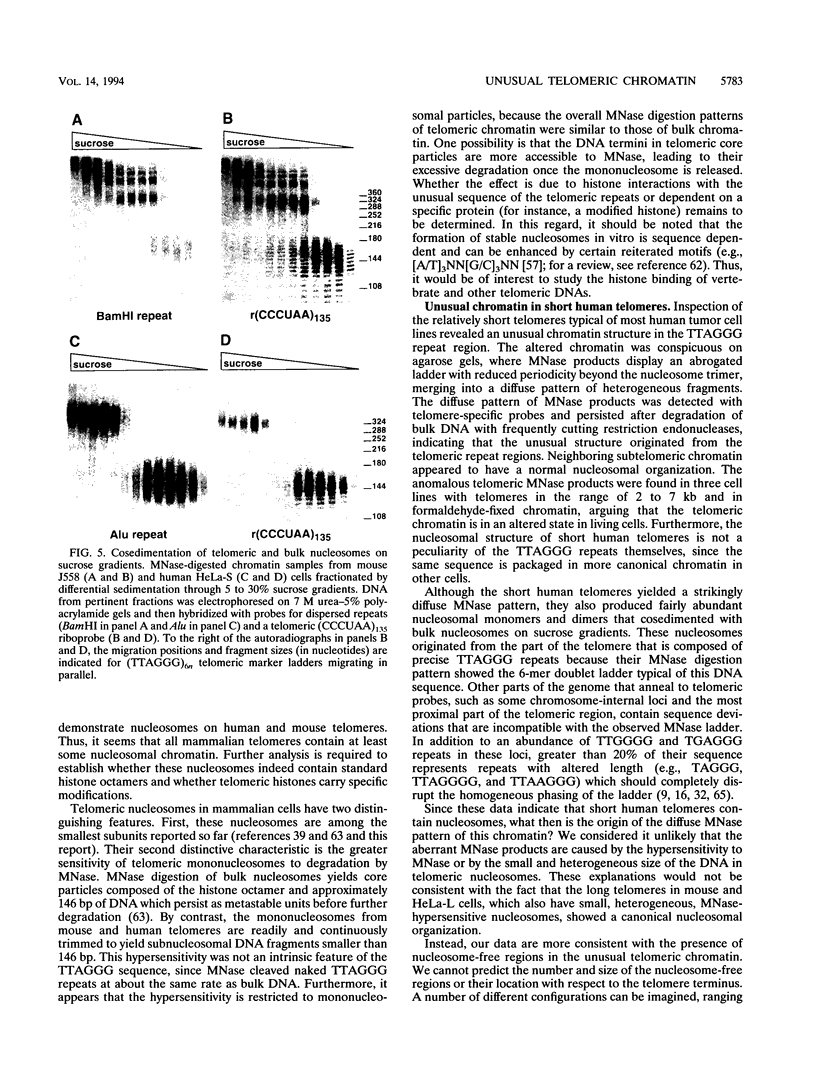
We report that human telomeres have an unusual chromatin structure characterized by diffuse micrococcal nuclease patterns. The altered chromatin manifested itself only in human telomeres that are relatively short (2 to 7 kb). In contrast, human and mouse telomeres with telomeric repeat arrays of 14 to 150 kb displayed a more canonical chromatin structure with extensive arrays of tightly packed nucleosomes. All telomeric nucleosomes showed a shorter repeat size than bulk nucleosomes, and telomeric mononucleosomal particles were found to be hypersensitive to micrococcal nuclease. However, telomeric nucleosomes were similar to bulk nucleosomes in the rate at which they sedimented through sucrose gradients. We speculate that mammalian telomeres have a bipartite structure with unusual chromatin near the telomere terminus and a more canonical nucleosomal organization in the proximal part of the telomere.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allshire R. C., Dempster M., Hastie N. D. Human telomeres contain at least three types of G-rich repeat distributed non-randomly. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4611–4627. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J., Tachibana C. Y., Tye B. K. Identification of a telomere-binding activity from yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3713–3717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards A., van Harten-Loosbroek N., Borst P. Modification of telomeric DNA in Trypanosoma brucei; a role in antigenic variation? Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4153–4170. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M., Ferry K., d'Hulst M., Valgeirsdottir K., Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. Addition of telomere-associated HeT DNA sequences "heals" broken chromosome ends in Drosophila. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90478-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Chiou S. S. Non-nucleosomal packaging of a tandemly repeated DNA sequence at termini of extrachromosomal DNA coding for rRNA in Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2263–2267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Gall J. G. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):33–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., MacKinnon P. J., Villasanté A., Spurr N., Buckle V. J., Dobson M. J. Structure and polymorphism of human telomere-associated DNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90293-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budarf M. L., Blackburn E. H. Chromatin structure of the telomeric region and 3'-nontranscribed spacer of Tetrahymena ribosomal RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):363–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Bianchi A., de Lange T. A Xenopus egg factor with DNA-binding properties characteristic of terminus-specific telomeric proteins. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):883–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. F., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Isolation and characterization of a human telomere. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6109–6127. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Wright J. H., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. RAP1 protein interacts with yeast telomeres in vivo: overproduction alters telomere structure and decreases chromosome stability. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90140-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S., Lindsey J., Fantes J., McKay S., McGill N., Cooke H. The structure of a subterminal repeated sequence present on many human chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6649–6657. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Size and structure of the highly repetitive BAM HI element in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5073–5091. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B. M., Fangman W. L. A position effect on the time of replication origin activation in yeast. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90474-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gommers-Ampt J. H., Van Leeuwen F., de Beer A. L., Vliegenthart J. F., Dizdaroglu M., Kowalak J. A., Crain P. F., Borst P. beta-D-glucosyl-hydroxymethyluracil: a novel modified base present in the DNA of the parasitic protozoan T. brucei. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90322-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Aparicio O. M., Billington B. L., Zakian V. A. Position effect at S. cerevisiae telomeres: reversible repression of Pol II transcription. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):751–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90141-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Chromatin structure of the molecular ends of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA: phased nucleosomes and a telomeric complex. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):501–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90505-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E. Telomere-proximal DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is refractory to methyltransferase activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4062–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Zakian V. A. Telomere proteins: specific recognition and protection of the natural termini of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W. Telomeres. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;3(3):444–451. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2643–2658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IJdo J. W., Baldini A., Ward D. C., Reeders S. T., Wells R. A. Origin of human chromosome 2: an ancestral telomere-telomere fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9051–9055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipling D., Cooke H. J. Hypervariable ultra-long telomeres in mice. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):400–402. doi: 10.1038/347400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein F., Laroche T., Cardenas M. E., Hofmann J. F., Schweizer D., Gasser S. M. Localization of RAP1 and topoisomerase II in nuclei and meiotic chromosomes of yeast. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):935–948. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M. Analysis of splicing complexes and small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by native gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:442–453. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyrion G., Liu K., Liu C., Lustig A. J. RAP1 and telomere structure regulate telomere position effects in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1146–1159. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R. W., Ganesan R., Houtchens K., Tolar L. A., Sheen F. M. Transposons in place of telomeric repeats at a Drosophila telomere. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90318-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Kurtz S., Shore D. Involvement of the silencer and UAS binding protein RAP1 in regulation of telomere length. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2237406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makarov V. L., Lejnine S., Bedoyan J., Langmore J. P. Nucleosomal organization of telomere-specific chromatin in rat. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):775–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90256-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The Stability of Broken Ends of Chromosomes in Zea Mays. Genetics. 1941 Mar;26(2):234–282. doi: 10.1093/genetics/26.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEachern M. J., Hicks J. B. Unusually large telomeric repeats in the yeast Candida albicans. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):551–560. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyne J., Baker R. J., Hobart H. H., Hsu T. C., Ryder O. A., Ward O. G., Wiley J. E., Wurster-Hill D. H., Yates T. L., Moyzis R. K. Distribution of non-telomeric sites of the (TTAGGG)n telomeric sequence in vertebrate chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1990 Apr;99(1):3–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01737283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Moyzis R. K. Conservation of the human telomere sequence (TTAGGG)n among vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7049–7053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. Recognition of a chromosome truncation site associated with alpha-thalassaemia by human telomerase. Nature. 1991 Oct 3;353(6343):454–456. doi: 10.1038/353454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll H., Noll M. Sucrose gradient techniques and applications to nucleosome structure. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:55–116. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)70043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polizzi C., Clarke L. The chromatin structure of centromeres from fission yeast: differentiation of the central core that correlates with function. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(2):191–201. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M. Centromeres and telomeres. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):379–384. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90002-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M. Telomere structure in Euplotes crassus: characterization of DNA-protein interactions and isolation of a telomere-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3421–3431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse K. R., Avilion A. A., Greider C. W. Identification of a nonprocessive telomerase activity from mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1493–1497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renauld H., Aparicio O. M., Zierath P. D., Billington B. L., Chhablani S. K., Gottschling D. E. Silent domains are assembled continuously from the telomere and are defined by promoter distance and strength, and by SIR3 dosage. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1133–1145. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltman D., Morgan R., Cleary M. L., de Lange T. Telomeric structure in cells with chromosome end associations. Chromosoma. 1993 Jan;102(2):121–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00356029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandell L. L., Zakian V. A. Loss of a yeast telomere: arrest, recovery, and chromosome loss. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90493-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandell L. L., Zakian V. A. Telomeric position effect in yeast. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;2(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90138-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrader T. E., Crothers D. M. Artificial nucleosome positioning sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7418–7422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. A., Jackson V., Chalkley R. Two-stage maturation process for newly replicated chromatin. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 27;23(7):1576–1581. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadafora C., Oudet P., Chambon P. Rearrangement of chromatin structure induced by increasing ionic strength and temperature. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):225–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starling J. A., Maule J., Hastie N. D., Allshire R. C. Extensive telomere repeat arrays in mouse are hypervariable. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6881–6888. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A., Künzler P. Histone H5 can correctly align randomly arranged nucleosomes in a defined in vitro system. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):548–550. doi: 10.1038/302548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F. Nucleosome positioning. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 28;1130(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90455-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weischet W. O. On the de novo formation of compact oligonucleosomes at high ionic strength. Evidence for nucleosomal sliding in high salt. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):291–304. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. A., Germino G. G., Krishna S., Buckle V. J., Reeders S. T. Telomere-related sequences at interstitial sites in the human genome. Genomics. 1990 Dec;8(4):699–704. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90257-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. H., Gottschling D. E., Zakian V. A. Saccharomyces telomeres assume a non-nucleosomal chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):197–210. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Shiue L., Kaplan S., de Lange T. A mammalian factor that binds telomeric TTAGGG repeats in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4834–4843. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T. Activation of telomerase in a human tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):2882–2885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T. Human telomeres are attached to the nuclear matrix. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):717–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05104.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T., Shiue L., Myers R. M., Cox D. R., Naylor S. L., Killery A. M., Varmus H. E. Structure and variability of human chromosome ends. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):518–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]