Abstract
The African trypanosomes express two major surface proteins, the variant surface glycoprotein (VSG) and the procyclic acidic repetitive protein (PARP). The RNA polymerase that transcribes the VSG and PARP genes shares many characteristics with RNA polymerase I. We show that although there is very little similarity in nucleotide sequence, the functional structure of a trypanosome rRNA promoter is almost identical to that of the PARP promoter. Further, domains from the PARP promoter can functionally substitute for the corresponding parts of the rRNA promoter, and vice versa.
Full text
PDF
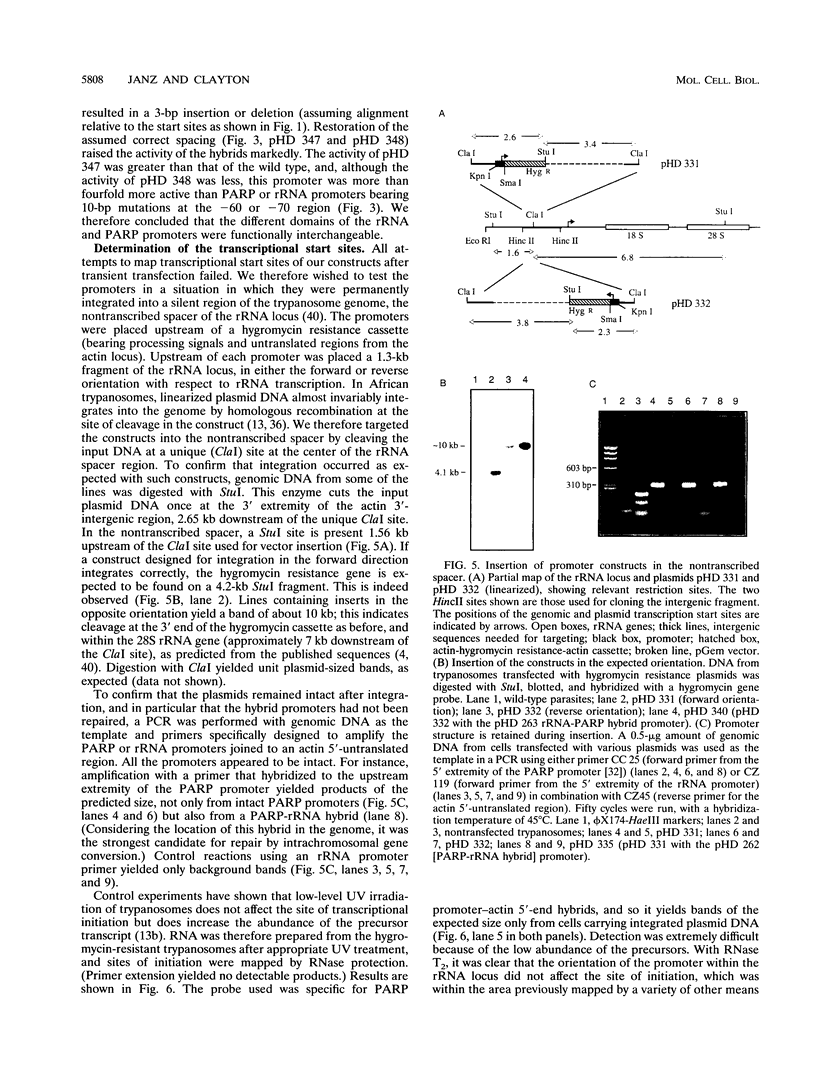



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beverley S. M., Clayton C. E. Transfection of Leishmania and Trypanosoma brucei by electroporation. Methods Mol Biol. 1993;21:333–348. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-239-6:333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringaud F., Baltz T. Differential regulation of two distinct families of glucose transporter genes in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1146–1154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
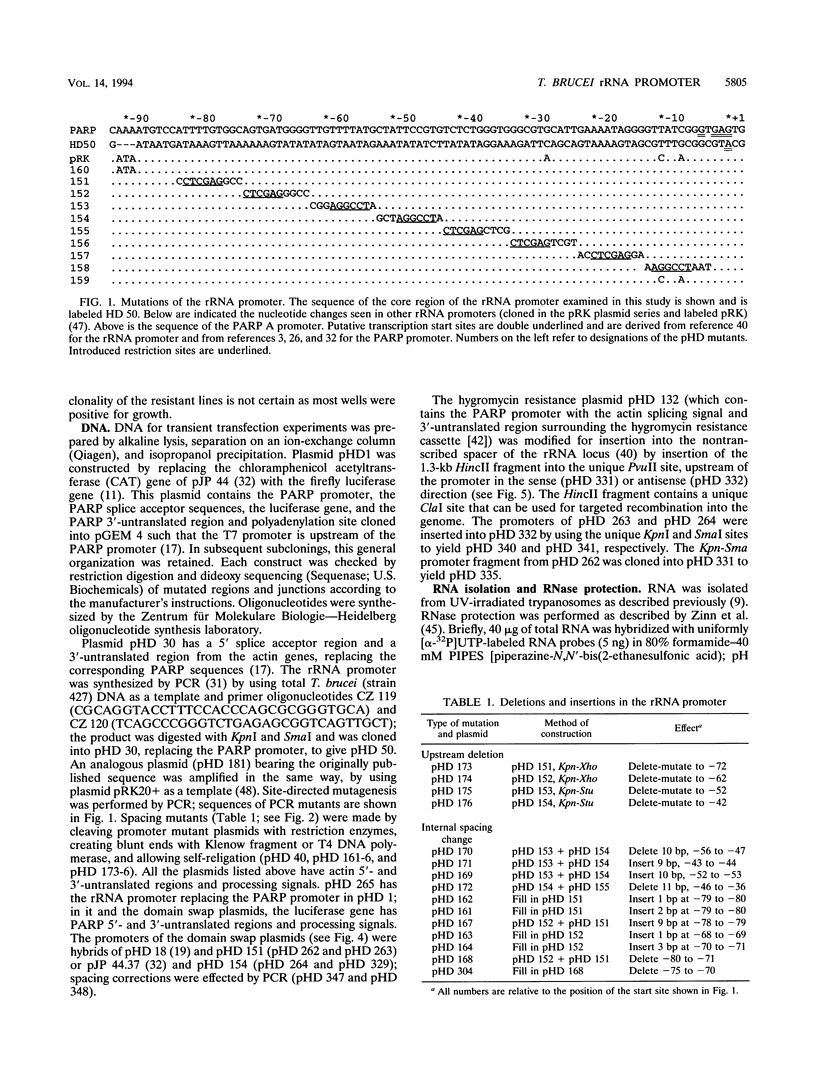
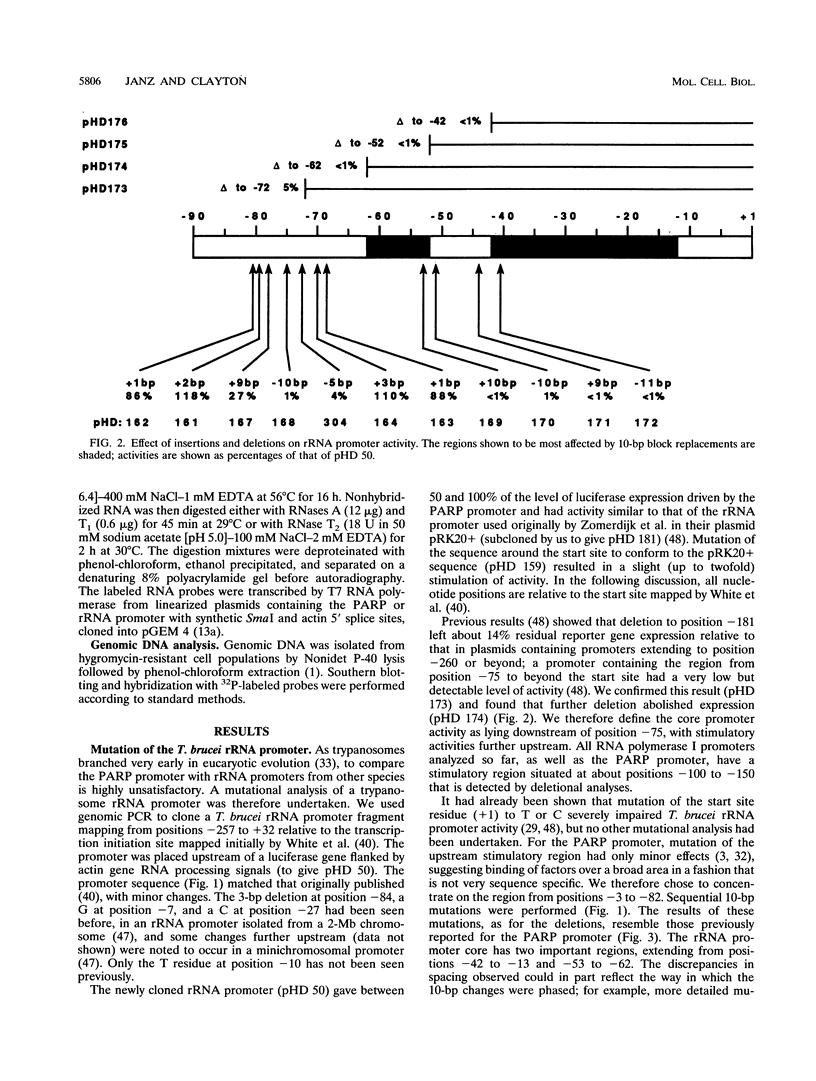
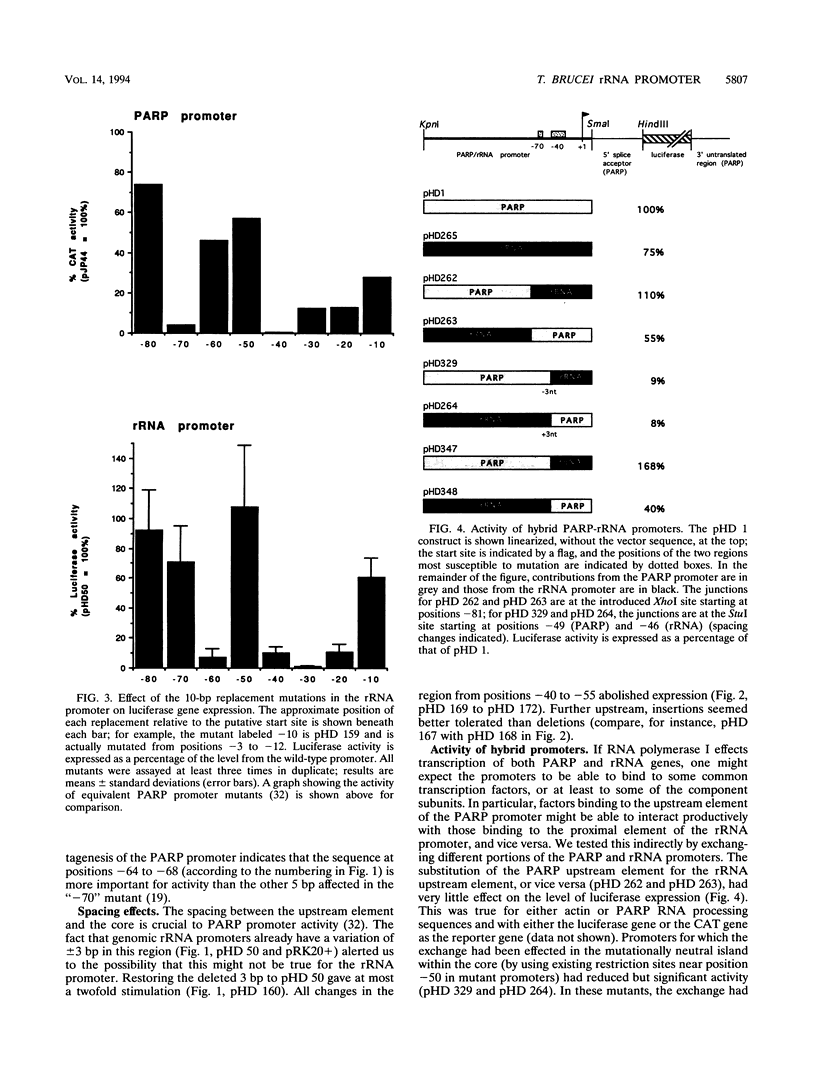
- Brown S. D., Huang J., Van der Ploeg L. H. The promoter for the procyclic acidic repetitive protein (PARP) genes of Trypanosoma brucei shares features with RNA polymerase I promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2644–2652. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A., Kubo K., Clark C. G., Boothroyd J. C. Precise identification of cleavage sites involved in the unusual processing of trypanosome ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90514-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe S. Y., Schultz M. C., Reeder R. H. In vitro definition of the yeast RNA polymerase I promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):279–285. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H. M., Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. RNA polymerase I-mediated protein-coding gene expression in Trypanosoma brucei. Parasitol Today. 1992 Dec;8(12):414–418. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(92)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Fueri J. P., Itzhaki J. E., Bellofatto V., Sherman D. R., Wisdom G. S., Vijayasarathy S., Mowatt M. R. Transcription of the procyclic acidic repetitive protein genes of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3036–3047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E. Structure and regulated expression of genes encoding fructose biphosphate aldolase in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2997–3003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. Developmental regulation of nuclear gene expression in Trypanosoma brucei. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1992;43:37–66. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)61043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Cellular and genetic aspects of antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:83–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eid J. E., Sollner-Webb B. Homologous recombination in the tandem calmodulin genes of Trypanosoma brucei yields multiple products: compensation for deleterious deletions by gene amplification. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2024–2032. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. C., Swinkels B. W., Borst P. Post-transcriptional control of the differential expression of phosphoglycerate kinase genes in Trypanosoma brucei. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 20;201(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesdiener K., Chung H. M., Brown S. D., Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. Characterization of VSG gene expression site promoters and promoter-associated DNA rearrangement events. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2467–2480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grondal E. J., Evers R., Kosubek K., Cornelissen A. W. Characterization of the RNA polymerases of Trypanosoma brucei: trypanosomal mRNAs are composed of transcripts derived from both RNA polymerase II and III. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3383–3389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug M., Carruthers V. B., Hartmann C., Sherman D. S., Cross G. A., Clayton C. A possible role for the 3'-untranslated region in developmental regulation in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Sep;61(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90161-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferies D., Tebabi P., Pays E. Transient activity assays of the Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein gene promoter: control of gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):338–343. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. H., Learned R. M., Tjian R. Analysis of clustered point mutations in the human ribosomal RNA gene promoter by transient expression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooter J. M., Borst P. Alpha-amanitin-insensitive transcription of variant surface glycoprotein genes provides further evidence for discontinuous transcription in trypanosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9457–9472. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkens T., Riggs D. L., Heck J. D., Planta R. J., Nomura M. The yeast RNA polymerase I promoter: ribosomal DNA sequences involved in transcription initiation and complex formation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5363–5370. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musters W., Knol J., Maas P., Dekker A. F., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. Linker scanning of the yeast RNA polymerase I promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9661–9678. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E., Coquelet H., Tebabi P., Pays A., Jefferies D., Steinert M., Koenig E., Williams R. O., Roditi I. Trypanosoma brucei: constitutive activity of the VSG and procyclin gene promoters. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3145–3151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Regulatory elements of the generic ribosomal gene. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;1(3):466–474. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roditi I., Schwarz H., Pearson T. W., Beecroft R. P., Liu M. K., Richardson J. P., Bühring H. J., Pleiss J., Bülow R., Williams R. O. Procyclin gene expression and loss of the variant surface glycoprotein during differentiation of Trypanosoma brucei. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):737–746. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Chung H. M., Pham V. P., Van der Ploeg L. H. RNA polymerase I can mediate expression of CAT and neo protein-coding genes in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3387–3397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. The PARP and VSG genes of Trypanosoma brucei do not resemble RNA polymerase II transcription units in sensitivity to Sarkosyl in nuclear run-on assays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):303–306. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. R., Janz L., Hug M., Clayton C. Anatomy of the parp gene promoter of Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3379–3386. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Elwood H. J., Gunderson J. H. Evolutionary diversity of eukaryotic small-subunit rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Mougey E. B. News from the nucleolus: rRNA gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Feb;16(2):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90025-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Milhausen M., Rutter W. J., Agabian N. Tubulin genes are tandemly linked and clustered in the genome of trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi C., Young A. S., Ruben L., Patton C. L., Richards F. F. Calmodulin genes in trypanosomes are tandemly repeated and produce multiple mRNAs with a common 5' leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayasarathy S., Ernest I., Itzhaki J. E., Sherman D., Mowatt M. R., Michels P. A., Clayton C. E. The genes encoding fructose bisphosphate aldolase in Trypanosoma brucei are interspersed with unrelated genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2967–2975. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. C., Rudenko G., Borst P. Three small RNAs within the 10 kb trypanosome rRNA transcription unit are analogous to domain VII of other eukaryotic 28S rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9471–9489. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle J. J., Sollner-Webb B. Two distant and precisely positioned domains promote transcription of Xenopus laevis rRNA genes: analysis with linker-scanning mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4585–4593. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. Q., Rothblum L. I. Domains of the rat rDNA promoter must be aligned stereospecifically. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1266–1275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegelbauer K., Quinten M., Schwarz H., Pearson T. W., Overath P. Synchronous differentiation of Trypanosoma brucei from bloodstream to procyclic forms in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):373–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomerdijk J. C., Kieft R., Borst P. A ribosomal RNA gene promoter at the telomere of a mini-chromosome in Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2725–2734. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomerdijk J. C., Kieft R., Borst P. Efficient production of functional mRNA mediated by RNA polymerase I in Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):772–775. doi: 10.1038/353772a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomerdijk J. C., Kieft R., Shiels P. G., Borst P. Alpha-amanitin-resistant transcription units in trypanosomes: a comparison of promoter sequences for a VSG gene expression site and for the ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5153–5158. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Asbroek A. L., Mol C. A., Kieft R., Borst P. Stable transformation of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 May;59(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90014-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Asbroek A. L., Ouellette M., Borst P. Targeted insertion of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene into the tubulin gene cluster of Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):174–175. doi: 10.1038/348174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]