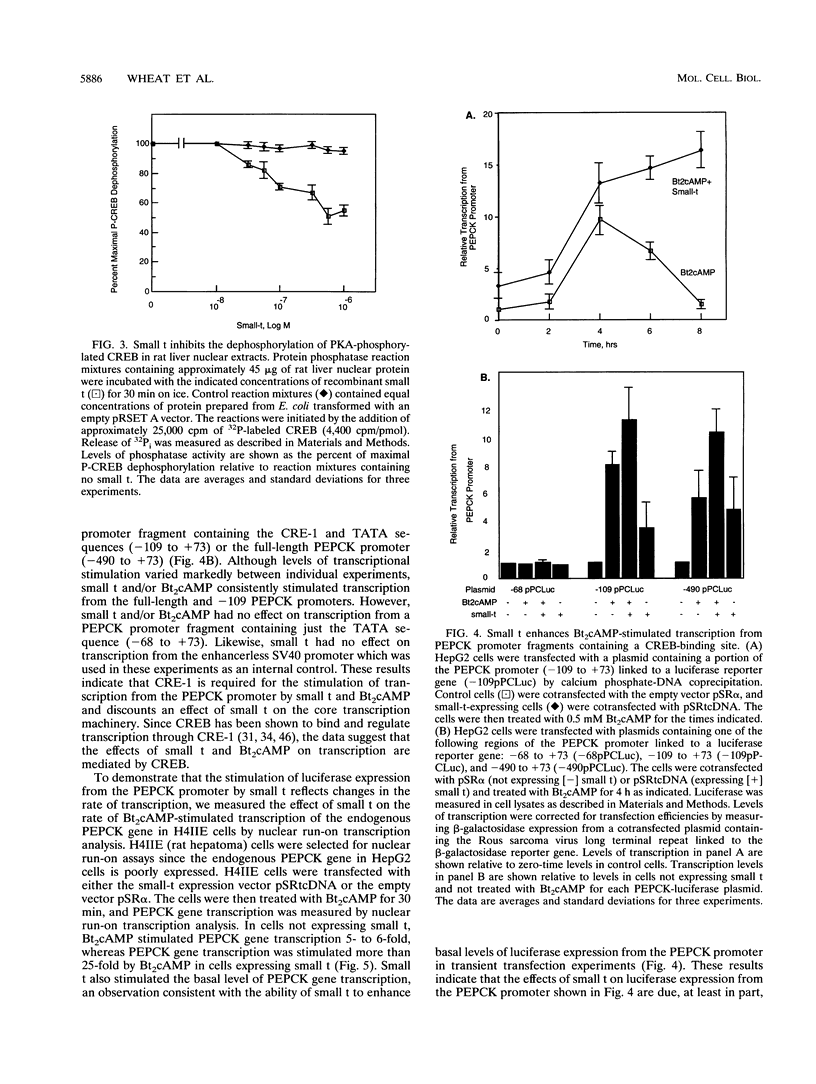
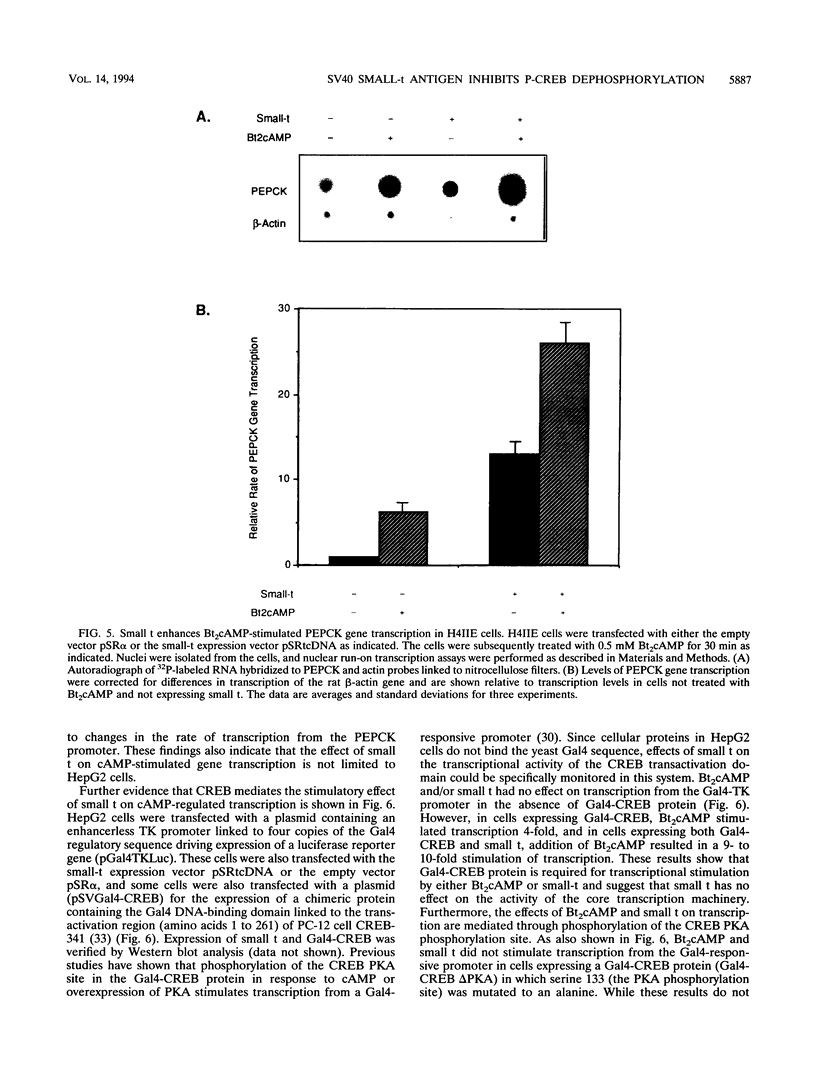
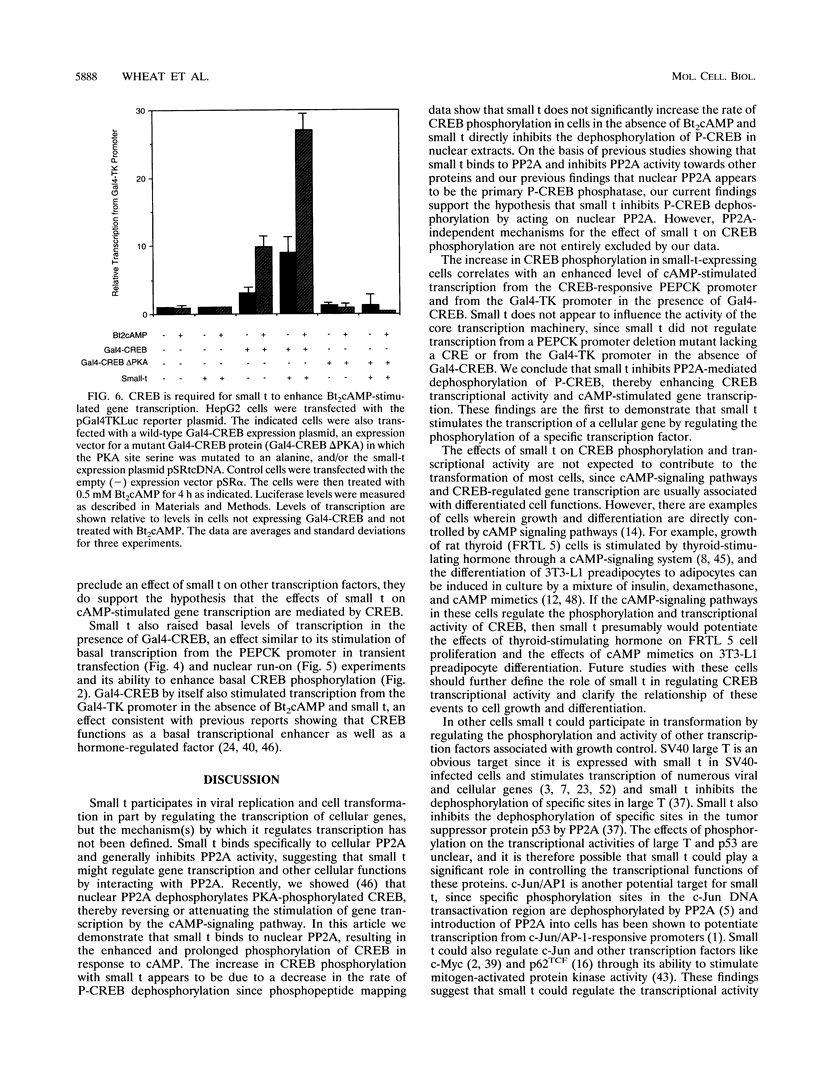
Abstract
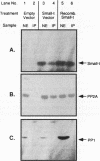
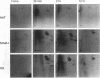
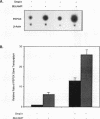
We report that the small tumor (small-t) antigen of simian virus 40 (SV40) forms complexes with nuclear protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and regulates the phosphorylation and transcriptional transactivation function of the cyclic AMP (cAMP)-regulatory element binding protein (CREB). PP2A coimmunoprecipitated with small t from nuclear extracts from HepG2 cells expressing small t or from rat liver nuclear extracts to which recombinant small t was added. Protein phosphatase 1 was not detected in small-t immunoprecipitates. In HepG2 cells expressing small t, dibutyryl-cAMP (Bt2cAMP) stimulated the phosphorylation of CREB 65-fold, whereas CREB phosphorylation was stimulated only 5- to 8-fold by Bt2cAMP in cells not expressing small t. Small t also inhibited the dephosphorylation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA)-phosphorylated CREB in rat liver nuclear extracts. In cells expressing small t, Bt2cAMP-stimulated transcription from the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) gene promoter was enhanced over the level of transcription from the PEPCK promoter in cells not expressing small t. Small t also enhanced Bt2cAMP-stimulated transcription from a Gal4-responsive promoter in cells expressing a chimeric protein containing the Gal4 DNA-binding domain linked to the CREB transactivation domain. However, small t did not stimulate transcription either from a 5' deletion mutant of the PEPCK promoter that is not able to bind CREB or from the Gal4-responsive promoter in the absence of the Gal4-CREB protein. These data suggest that small t enhances Bt2cAMP-stimulated gene transcription by inhibiting the dephosphorylation of PKA-phosphorylated CREB by nuclear PP2A. These findings support previous observations that nuclear PP2A is the primary phosphatase that dephosphorylates PKA-phosphorylated CREB.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. S., Deng T., Lin A., Meinkoth J. L., Schönthal A., Mumby M. C., Karin M., Feramisco J. R. Protein phosphatase 2A potentiates activity of promoters containing AP-1-binding elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2104–2112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C. Transient gene expression control: effects of transfected DNA stability and trans-activation by viral early proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1034–1042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias J. A., Peterson S. R., Dynan W. S. Promoter-dependent phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by a template-bound kinase. Association with transcriptional initiation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8055–8061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikel I., Montano X., Agha M. E., Brown M., McCormack M., Boltax J., Livingston D. M. SV40 small t antigen enhances the transformation activity of limiting concentrations of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90435-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black E. J., Street A. J., Gillespie D. A. Protein phosphatase 2A reverses phosphorylation of c-Jun specified by the delta domain in vitro: correlation with oncogenic activation and deregulated transactivation activity of v-Jun. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):1949–1958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossert A., Mulgaonkar P., Rundell K. Interaction of simian virus 40 small-T antigen produced in bacteria with 56K and 32K proteins of animal cells. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):325–327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.325-327.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Khoury G. trans Activation of the simian virus 40 late transcription unit by T-antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner-Gati L., Berg K. A., Gershengorn M. C. Insulin-like growth factor-I potentiates thyrotropin stimulation of adenylyl cyclase in FRTL-5 cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1315–1320. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone M., Hauser J., Carty M. P., Rundell K., Dixon K., Levine A. S. Simian virus 40 (SV40) small t antigen inhibits SV40 DNA replication in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1804–1808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1804-1808.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Lee I. C., Ross S. R. Requirement for the simian virus 40 small tumor antigen in tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3382–3390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. S., Lucas J. J., Sibley E., Bolanowski M. A., Christy R. J., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Expression of the differentiation-induced gene for fatty acid-binding protein is activated by glucocorticoid and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2949–2953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. E., Jauniaux J. C., Roger P. P. The cyclic AMP-mediated stimulation of cell proliferation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feunteun J., Kress M., Gardes M., Monier R. Viable deletion mutants in the simian virus 40 early region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):414–417. doi: 10.1038/358414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Graessmann M., Tjian R., Topp W. C. Simian virus 40 small-t protein is required for loss of actin cable networks in rat cells. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1182–1191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1182-1191.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D., Andreone T., Sasaki K., Beale E. Inhibition of transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene by insulin. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):549–551. doi: 10.1038/305549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara M., Alberts A., Brindle P., Meinkoth J., Feramisco J., Deng T., Karin M., Shenolikar S., Montminy M. Transcriptional attenuation following cAMP induction requires PP-1-mediated dephosphorylation of CREB. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90537-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J. B., Defendi V. Simian virus 40 gene A regulation of cellular DNA synthesis. II. In nonpermissive cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):802–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.802-812.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm D. J., Roesler W. J., Liu J. S., Park E. A., Hanson R. W. In vitro analysis of promoter elements regulating transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):480–485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Q., Yun Y. D., Hoeffler J. P., Habener J. F. Cyclic-AMP-responsive transcriptional activation of CREB-327 involves interdependent phosphorylated subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4455–4465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Loeken M., Bikel I., Livingston D. M., Brady J. trans-activation of RNA polymerase II and III promoters by SV40 small t antigen. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1171–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson M. A., Quinn P. G., Granner D. K. Multihormonal regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase fusion genes. Insulin's effects oppose those of cAMP and dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14917–14920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Setlow V. P., Edwards C. A., Vembu D. The roles of the simian virus 40 tumor antigens in transformation of Chinese hamster lung cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Shahrik L. K., Martin B. L., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Brautigan D. L., Roberts T. M. Polyoma small and middle T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90726-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. A., Roesler W. J., Liu J., Klemm D. J., Gurney A. L., Thatcher J. D., Shuman J., Friedman A., Hanson R. W. The role of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein in the transcriptional regulation of the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6264–6272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. G., Granner D. K. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase regulates transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene but not binding of nuclear factors to the cyclic AMP regulatory element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3357–3364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., McFie P. J., Puttick D. M. Evidence for the involvement of at least two distinct transcription factors, one of which is liver-enriched, for the activation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene promoter by cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3791–3796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H., Figge J., Bladon M. T., Chen L. B., Ellman M., Bikel I., Farrell M., Livingston D. M. Role of small t antigen in the acute transforming activity of SV40. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K., Cox J. Simian virus 40 t antigen affects the sensitivity of cellular DNA synthesis to theophylline. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):394–396. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.394-396.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Mumby M. C., Rundell K., Walter G. Dephosphorylation of simian virus 40 large-T antigen and p53 protein by protein phosphatase 2A: inhibition by small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1996–2003. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif R., Martin R. G. Simian virus 40 small t antigen is not required for the maintenance of transformation but may act as a promoter (cocarcinogen) during establishment of transformation in resting rat cells. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):979–988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.979-988.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Alvarez E., Gupta S., Davis R. J. A phosphorylation site located in the NH2-terminal domain of c-Myc increases transactivation of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23521–23524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Wynshaw-Boris A., Short H. P., Hanson R. W. Characterization of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) promoter-regulatory region. II. Identification of cAMP and glucocorticoid regulatory domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9721–9726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J., Topp W. C., Hanich R., Sambrook J. F. Mutants of SV40 with an altered small t protein are reduced in their ability to transform cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. A simian virus 40 dl884/tsA58 double mutant is temperature sensitive for abortive transformation. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):620–625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.620-625.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontag E., Fedorov S., Kamibayashi C., Robbins D., Cobb M., Mumby M. The interaction of SV40 small tumor antigen with protein phosphatase 2A stimulates the map kinase pathway and induces cell proliferation. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90533-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontano D., Moses A. C., Veneziani B. M., Ingbar S. H. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate mediates both the mitogenic effect of thyrotropin and its ability to amplify the response to insulin-like growth factor I in FRTL5 cells. Endocrinology. 1988 Jan;122(1):127–132. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadzinski B. E., Wheat W. H., Jaspers S., Peruski L. F., Jr, Lickteig R. L., Johnson G. L., Klemm D. J. Nuclear protein phosphatase 2A dephosphorylates protein kinase A-phosphorylated CREB and regulates CREB transcriptional stimulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2822–2834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Ruediger R., Slaughter C., Mumby M. Association of protein phosphatase 2A with polyoma virus medium tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2521–2525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams I. H., Polakis S. E. Differentiation of 3T3-L1 fibroblasts to adipocytes. The effect of indomethacin, prostaglandin E1 and cyclic AMP on the process of differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):175–186. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. I., Lickteig R. L., Estes R., Rundell K., Walter G., Mumby M. C. Control of protein phosphatase 2A by simian virus 40 small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1988–1995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo-Warren H., Monahan J. E., Short J., Short H., Bruzel A., Wynshaw-Boris A., Meisner H. M., Samols D., Hanson R. W. Isolation and characterization of the gene coding for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) from the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3656–3660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Rice P. W., Chamberlain M., Cole C. N. Mapping the transcriptional transactivation function of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2778–2790. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2778-2790.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]