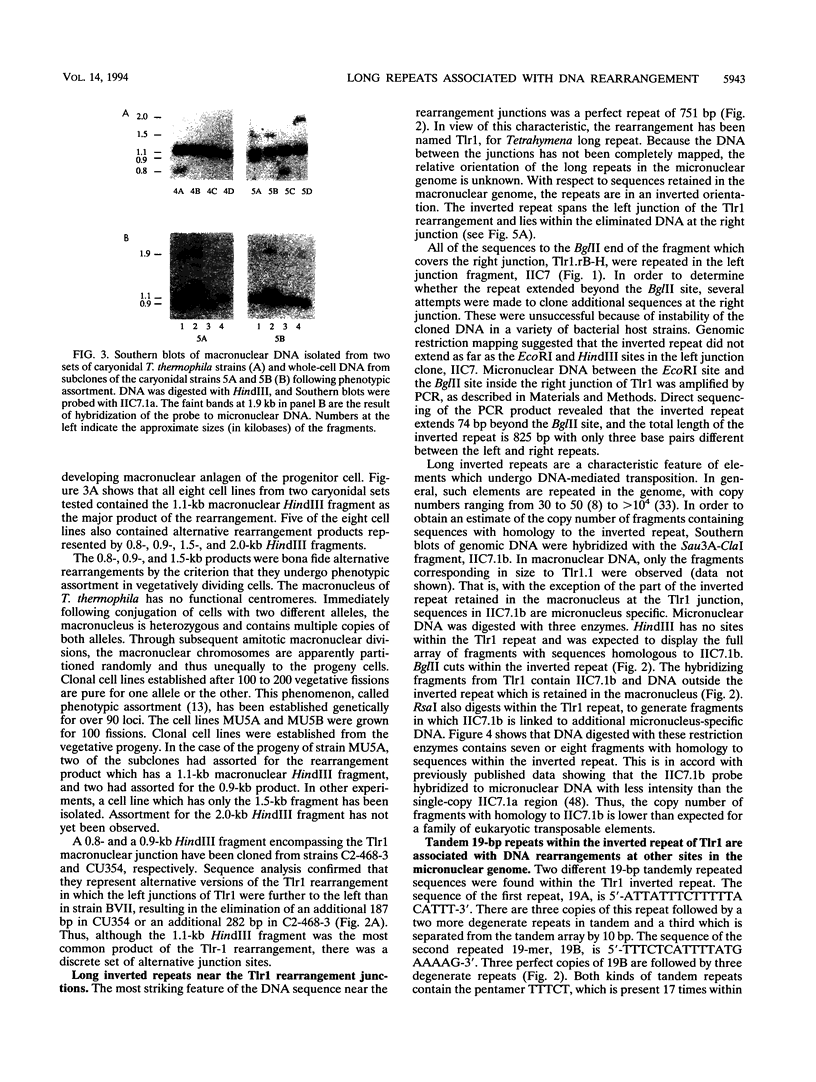
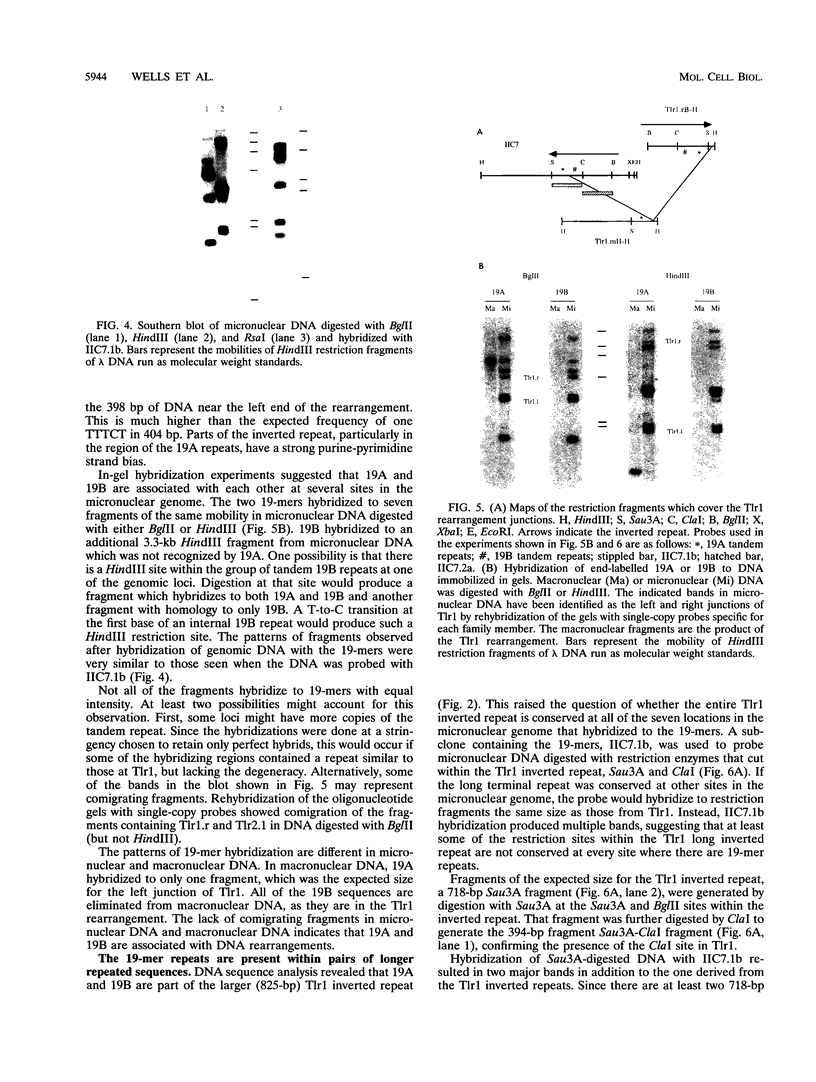
Abstract
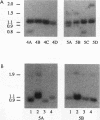
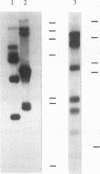
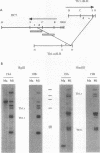
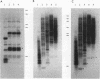
Extensive DNA rearrangement occurs during the development of the somatic macronucleus from the germ line micronucleus in ciliated protozoans. The micronuclear junctions and the macronuclear product of a developmentally regulated DNA rearrangement in Tetrahymena thermophila, Tlr1, have been cloned. The intrachromosomal rearrangement joins sequences that are separated by more than 13 kb in the micronucleus with the elimination of moderately repeated micronucleus-specific DNA sequences. There is a long, 825-bp, inverted repeat near the micronuclear junctions. The inverted repeat contains two different 19-bp tandem repeats. The 19-bp repeats are associated with each other and with DNA rearrangements at seven locations in the micronuclear genome. Southern blot analysis is consistent with the occurrence of the 19-bp repeats within pairs of larger repeated sequences. Another family member was isolated. The 19-mers in that clone are also in close proximity to a rearrangement junction. We propose that the 19-mers define a small family of developmentally regulated DNA rearrangements having elements with long inverted repeats near the junction sites. We discuss the possibility that transposable elements evolve by capture of molecular machinery required for essential cellular functions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allitto B. A., Karrer K. M. A family of DNA sequences is reproducibly rearranged in the somatic nucleus of Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8007–8025. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austerberry C. F., Allis C. D., Yao M. C. Specific DNA rearrangements in synchronously developing nuclei of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7383–7387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austerberry C. F., Snyder R. O., Yao M. C. Sequence microheterogeneity is generated at junctions of programmed DNA deletions in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7263–7272. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austerberry C. F., Yao M. C. Nucleotide sequence structure and consistency of a developmentally regulated DNA deletion in Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):435–443. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austerberry C. F., Yao M. C. Sequence structures of two developmentally regulated, alternative DNA deletion junctions in Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3947–3950. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird S. E., Fino G. M., Tausta S. L., Klobutcher L. A. Micronuclear genome organization in Euplotes crassus: a transposonlike element is removed during macronuclear development. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3793–3807. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M., Ferry K., d'Hulst M., Valgeirsdottir K., Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. Addition of telomere-associated HeT DNA sequences "heals" broken chromosome ends in Drosophila. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90478-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Kidwell M. G., Rubin G. M. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the role of the P element, a P-strain-specific transposon family. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):995–1004. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Conover R. K. Elimination of micronuclear specific DNA sequences early in anlagen development. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):93–98. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Tsao S. G., Diamond C. H., Ohashi P. S., Tsao N. N., Pearlman R. E. Reorganization of unique and repetitive sequences during nuclear development in Tetrahymena thermophila. Can J Biochem. 1982 Sep;60(9):847–853. doi: 10.1139/o82-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns P. J., Brussard T. B., Merriam E. V. Nullisomic Tetrahymena. II. a Set of Nullisomics Define the Germinal Chromosomes. Genetics. 1983 Jun;104(2):257–270. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R. C., Shalke G., Gorovsky M. A. Developmental rearrangements associated with a single type of expressed alpha-tubulin gene in Tetrahymena. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):441–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capowski E. E., Wells J. M., Harrison G. S., Karrer K. M. Molecular analysis of N6-methyladenine patterns in Tetrahymena thermophila nuclear DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2598–2605. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy-Hanley D., Yao M. C., Bruns P. J. A method for mapping germ line sequences in Tetrahymena thermophila using the polymerase chain reaction. Genetics. 1994 May;137(1):95–106. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. M., Blackburn E. H. The internally located telomeric sequences in the germ-line chromosomes of Tetrahymena are at the ends of transposon-like elements. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Woo S. L. Hybridization of genomic DNA to oligonucleotide probes in the presence of tetramethylammonium chloride. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doak T. G., Doerder F. P., Jahn C. L., Herrick G. A proposed superfamily of transposase genes: transposon-like elements in ciliated protozoa and a common "D35E" motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):942–946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiska R., James C., Yao M. C. A distant 10-bp sequence specifies the boundaries of a programmed DNA deletion in Tetrahymena. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2357–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiska R., Yao M. C. A programmed site-specific DNA rearrangement in Tetrahymena thermophila requires flanking polypurine tracts. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1237–1246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90688-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Yao M. C., Keevert J. B., Pleger G. L. Isolation of micro- and macronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;9(0):311–327. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinonen T. Y., Pearlman R. E. A germ line-specific sequence element in an intron in Tetrahymena thermophila. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17428–17433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick G., Cartinhour S., Dawson D., Ang D., Sheets R., Lee A., Williams K. Mobile elements bounded by C4A4 telomeric repeats in Oxytricha fallax. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. A., Blackburn E. H. Reproducible and variable genomic rearrangements occur in the developing somatic nucleus of the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2039–2050. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. J., Williams K., Cartinhour S., Herrick G. Precise excision of telomere-bearing transposons during Oxytricha fallax macronuclear development. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2101–2112. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. L., Doktor S. Z., Frels J. S., Jaraczewski J. W., Krikau M. F. Structures of the Euplotes crassus Tec1 and Tec2 elements: identification of putative transposase coding regions. Gene. 1993 Oct 29;133(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90226-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. L., Krikau M. F., Shyman S. Developmentally coordinated en masse excision of a highly repetitive element in E. crassus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1009–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaraczewski J. W., Jahn C. L. Elimination of Tec elements involves a novel excision process. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):95–105. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrer K. M. Germ line-specific DNA sequences are present on all five micronuclear chromosomes in Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):1909–1919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh M., Hirono M., Takemasa T., Kimura M., Watanabe Y. A micronucleus-specific sequence exists in the 5'-upstream region of calmodulin gene in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2409–2414. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Jahn C. L., Prescott D. M. Internal sequences are eliminated from genes during macronuclear development in the ciliated protozoan Oxytricha nova. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1045–1055. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Turner L. R., LaPlante J. Circular forms of developmentally excised DNA in Euplotes crassus have a heteroduplex junction. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):84–94. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Kitamura T., Sasaki H., Okada M. Two types of pole cells are present in the Drosophila embryo, one with and one without splicing activity for the third P-element intron. Development. 1993 Mar;117(3):885–893. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.3.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikau M. F., Jahn C. L. Tec2, a second transposon-like element demonstrating developmentally programmed excision in Euplotes crassus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4751–4759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Blackburn E. H. RNA-dependent polymerase motifs in EST1: tentative identification of a protein component of an essential yeast telomerase. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):529–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90653-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribas-Aparicio R. M., Sparkowski J. J., Proulx A. E., Mitchell J. D., Klobutcher L. A. Nucleic acid splicing events occur frequently during macronuclear development in the protozoan Oxytricha nova and involve the elimination of unique DNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):323–336. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein-Gavens S., Wells J. M., Karrer K. M. A germ line specific DNA sequence is transcribed in Tetrahymena. Dev Biol. 1987 Mar;120(1):259–269. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tausta S. L., Klobutcher L. A. Detection of circular forms of eliminated DNA during macronuclear development in E. crassus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. A spontaneously opened ring chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster has acquired He-T DNA sequences at both new telomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8116–8120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valgeirsdóttir K., Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. HeT DNA: a family of mosaic repeated sequences specific for heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7998–8002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K., Doak T. G., Herrick G. Developmental precise excision of Oxytricha trifallax telomere-bearing elements and formation of circles closed by a copy of the flanking target duplication. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4593–4601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., Wertman K. F. Host strains that alleviate underrepresentation of specific sequences: overview. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:173–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Choi J., Yokoyama S., Austerberry C. F., Yao C. H. DNA elimination in Tetrahymena: a developmental process involving extensive breakage and rejoining of DNA at defined sites. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Gorovsky M. A. Comparison of the sequences of macro- and micronuclear DNA of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Chromosoma. 1974;48(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00284863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C. Ribosomal RNA gene amplification in Tetrahymena may be associated with chromosome breakage and DNA elimination. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Yao C. H., Monks B. The controlling sequence for site-specific chromosome breakage in Tetrahymena. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):763–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Zheng K., Yao C. H. A conserved nucleotide sequence at the sites of developmentally regulated chromosomal breakage in Tetrahymena. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama R., Yao M. C. Internal micronuclear DNA regions which include sequences homologous to macronuclear telomeres are deleted during development in Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6103–6116. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]