Abstract
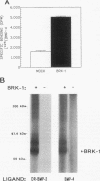
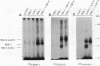
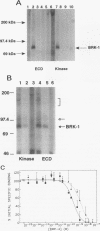
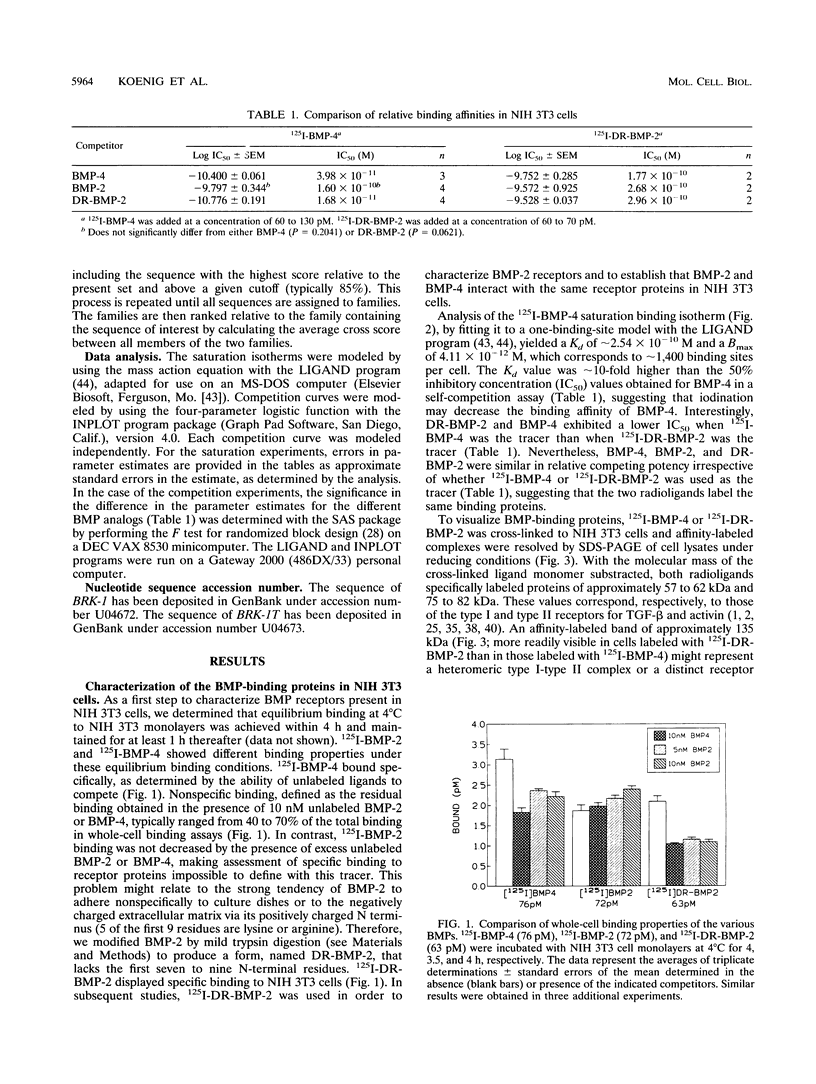
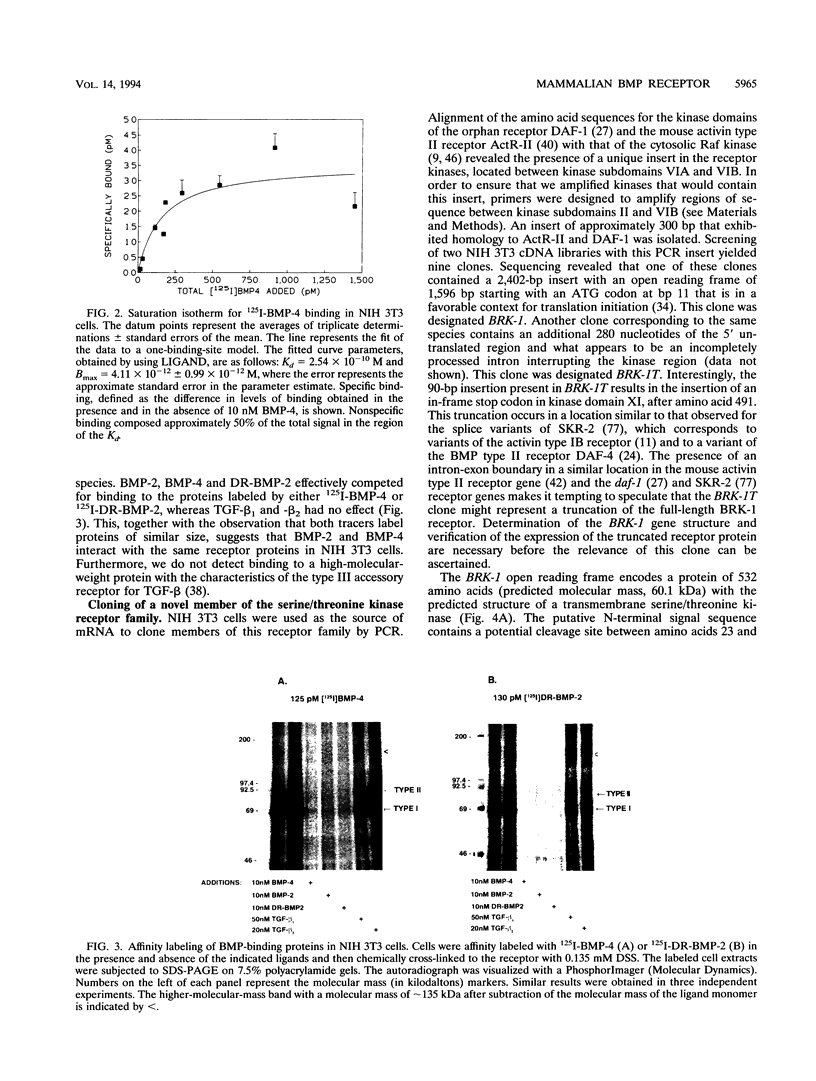
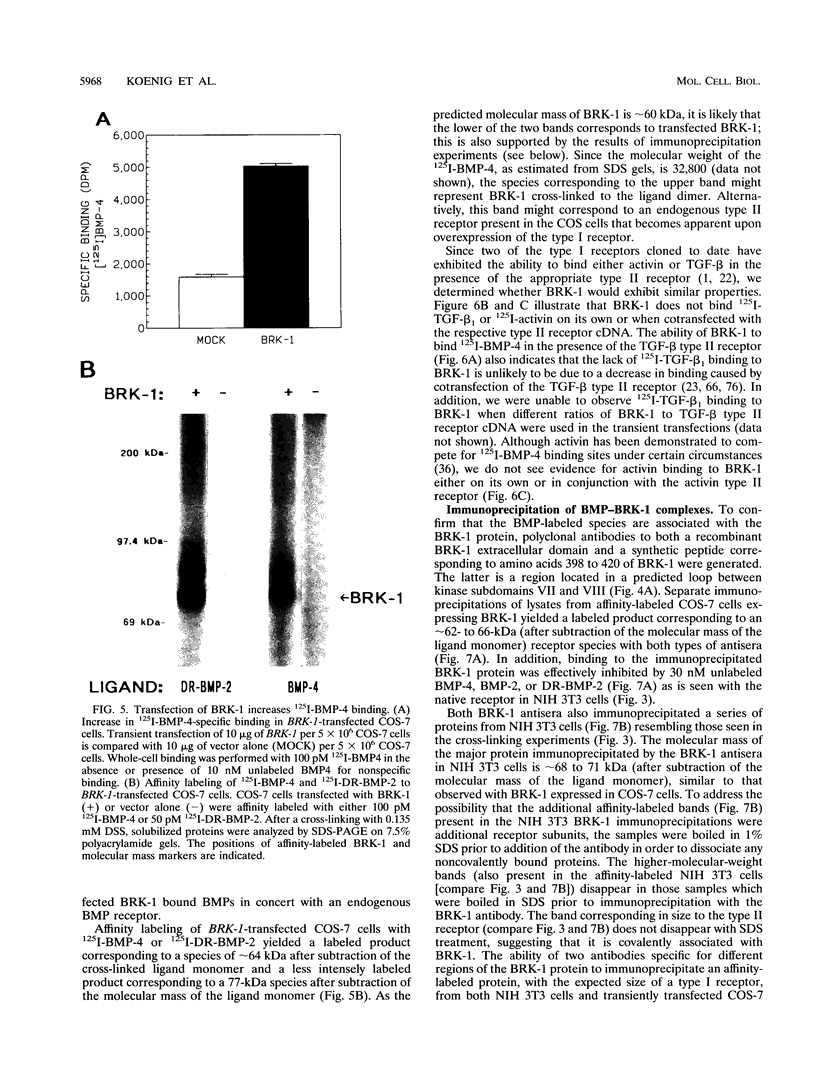
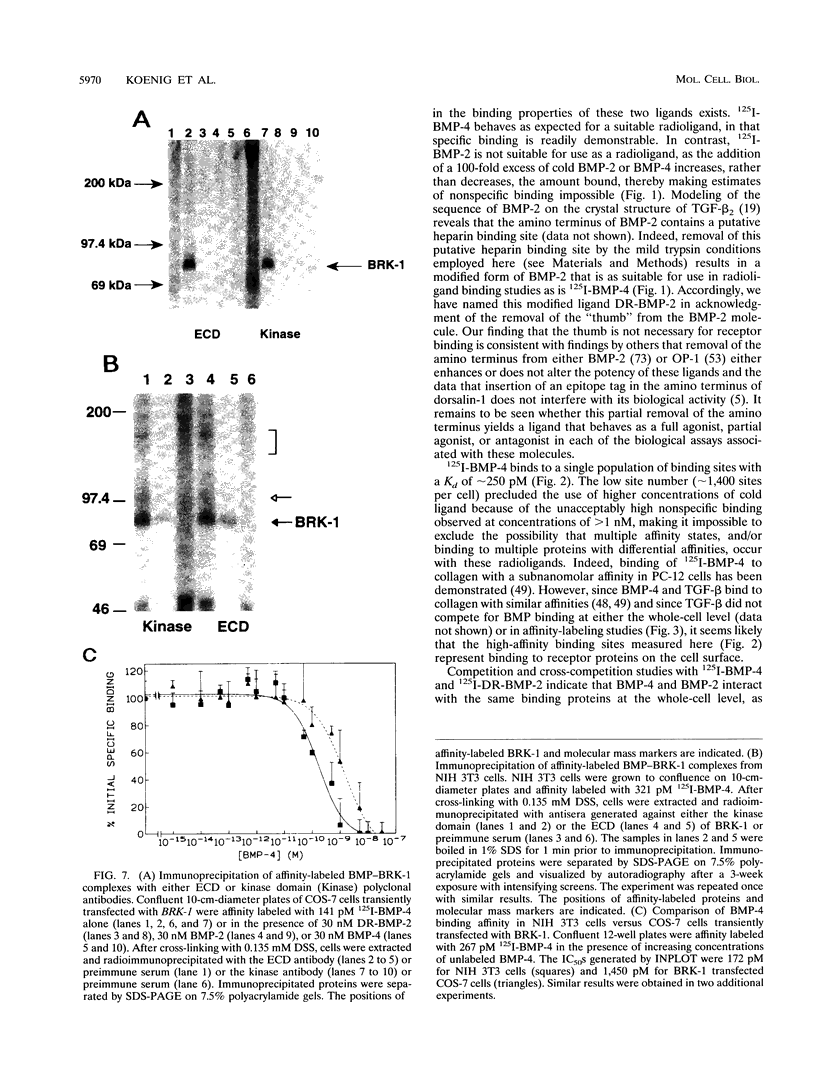
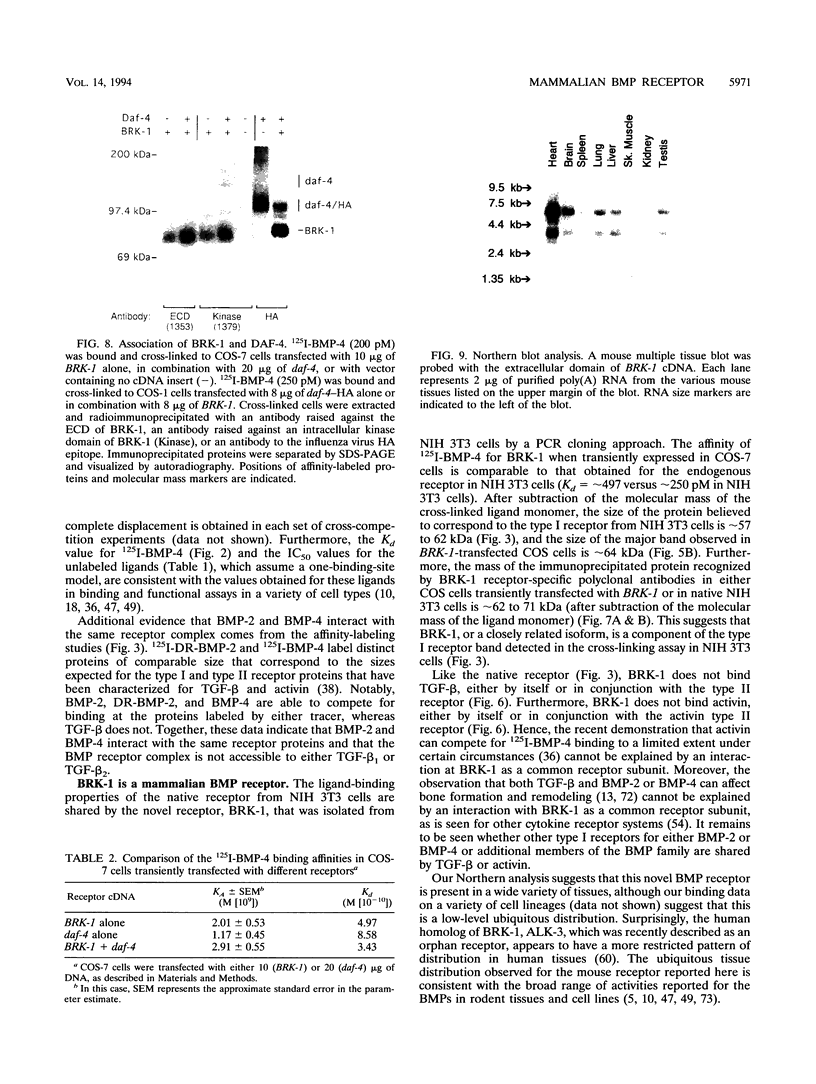
The bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a group of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)-related factors whose only receptor identified to date is the product of the daf-4 gene from Caenorhabditis elegans. Mouse embryonic NIH 3T3 fibroblasts display high-affinity 125I-BMP-4 binding sites. Binding assays are not possible with the isoform 125I-BMP-2 unless the positively charged N-terminal sequence is removed to create a modified BMP-2, 125I-DR-BMP-2. Cross-competition experiments reveal that BMP-2 and BMP-4 interact with the same binding sites. Affinity cross-linking assays show that both BMPs interact with cell surface proteins corresponding in size to the type I (57- to 62-kDa) and type II (75- to 82-kDa) receptor components for TGF-beta and activin. Using a PCR approach, we have cloned a cDNA from NIH 3T3 cells which encodes a novel member of the transmembrane serine/threonine kinase family most closely resembling the cloned type I receptors for TGF-beta and activin. Transient expression of this receptor in COS-7 cells leads to an increase in specific 125I-BMP-4 binding and the appearance of a major affinity-labeled product of approximately 64 kDa that can be labeled by either tracer. This receptor has been named BRK-1 in recognition of its ability to bind BMP-2 and BMP-4 and its receptor kinase structure. Although BRK-1 does not require cotransfection of a type II receptor in order to bind ligand in COS cells, complex formation between BRK-1 and the BMP type II receptor DAF-4 can be demonstrated when the two receptors are coexpressed, affinity labeled, and immunoprecipitated with antibodies to either receptor subunit. We conclude that BRK-1 is a putative BMP type I receptor capable of interacting with a known type II receptor for BMPs.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attisano L., Cárcamo J., Ventura F., Weis F. M., Massagué J., Wrana J. L. Identification of human activin and TGF beta type I receptors that form heteromeric kinase complexes with type II receptors. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90488-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attisano L., Wrana J. L., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Novel activin receptors: distinct genes and alternative mRNA splicing generate a repertoire of serine/threonine kinase receptors. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90209-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baarends W. M., van Helmond M. J., Post M., van der Schoot P. J., Hoogerbrugge J. W., de Winter J. P., Uilenbroek J. T., Karels B., Wilming L. G., Meijers J. H. A novel member of the transmembrane serine/threonine kinase receptor family is specifically expressed in the gonads and in mesenchymal cells adjacent to the müllerian duct. Development. 1994 Jan;120(1):189–197. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.1.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton G. J., Sternberg M. J. Flexible protein sequence patterns. A sensitive method to detect weak structural similarities. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 20;212(2):389–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Edlund T., Jessell T. M., Yamada T. Control of cell pattern in the neural tube: regulation of cell differentiation by dorsalin-1, a novel TGF beta family member. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):687–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90249-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassing C. H., Yingling J. M., Howe D. J., Wang T., He W. W., Gustafson M. L., Shah P., Donahoe P. K., Wang X. F. A transforming growth factor beta type I receptor that signals to activate gene expression. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):87–89. doi: 10.1126/science.8272871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier S. M., Goltzman D. Effect of protein and steroidal osteotropic agents on differentiation and epidermal growth factor-mediated growth of the CFK1 osseous cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Aug;152(2):317–327. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B. Nonreceptor tyrosine protein kinases. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2025–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Oppermann H., Seeburg P., Kerby S. B., Gunnell M. A., Young A. C., Rapp U. R. The complete coding sequence of the human raf oncogene and the corresponding structure of the c-raf-1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1009–1015. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin E. A., Ezzell R. M., Donahoe P. K., Gustafson M. L., Son E. V., MacLaughlin D. T. Identification of a receptor for human müllerian inhibiting substance. Endocrinology. 1993 Dec;133(6):3007–3013. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.6.8243329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centrella M., McCarthy T. L., Canalis E. Transforming growth factor-beta and remodeling of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991 Oct;73(9):1418–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs S. R., Wrana J. L., Arora K., Attisano L., O'Connor M. B., Massagué J. Identification of a Drosophila activin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9475–9479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. Erks: their fifteen minutes has arrived. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Feb;3(2):135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., McEwan R. N., Pearson M. L. Expression and amplification of engineered mouse dihydrofolate reductase minigenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):257–266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham N. S., Paralkar V., Reddi A. H. Osteogenin and recombinant bone morphogenetic protein 2B are chemotactic for human monocytes and stimulate transforming growth factor beta 1 mRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11740–11744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárcamo J., Weis F. M., Ventura F., Wieser R., Wrana J. L., Attisano L., Massagué J. Type I receptors specify growth-inhibitory and transcriptional responses to transforming growth factor beta and activin. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3810–3821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daopin S., Piez K. A., Ogawa Y., Davies D. R. Crystal structure of transforming growth factor-beta 2: an unusual fold for the superfamily. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):369–373. doi: 10.1126/science.1631557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bondt H. L., Rosenblatt J., Jancarik J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):595–602. doi: 10.1038/363595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doctor J. S., Jackson P. D., Rashka K. E., Visalli M., Hoffmann F. M. Sequence, biochemical characterization, and developmental expression of a new member of the TGF-beta superfamily in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1992 Jun;151(2):491–505. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90188-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebner R., Chen R. H., Lawler S., Zioncheck T., Derynck R. Determination of type I receptor specificity by the type II receptors for TGF-beta or activin. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):900–902. doi: 10.1126/science.8235612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebner R., Chen R. H., Shum L., Lawler S., Zioncheck T. F., Lee A., Lopez A. R., Derynck R. Cloning of a type I TGF-beta receptor and its effect on TGF-beta binding to the type II receptor. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1344–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.8388127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estevez M., Attisano L., Wrana J. L., Albert P. S., Massagué J., Riddle D. L. The daf-4 gene encodes a bone morphogenetic protein receptor controlling C. elegans dauer larva development. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):644–649. doi: 10.1038/365644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén P., ten Dijke P., Ichijo H., Yamashita H., Schulz P., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. Cloning of a TGF beta type I receptor that forms a heteromeric complex with the TGF beta type II receptor. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):681–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90489-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolik C. A., Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Sporn M. B. Characterization of a membrane receptor for transforming growth factor-beta in normal rat kidney fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10995–11000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgi L. L., Albert P. S., Riddle D. L. daf-1, a C. elegans gene controlling dauer larva development, encodes a novel receptor protein kinase. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):635–645. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90475-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Schwall R., Dudley A., Berkemeier L., Lai C., Lee J., Cunningham N., Reddi A. H., Wood W. I., Mason A. J. Bone-inducing activity of mature BMP-2b produced from a hybrid BMP-2a/2b precursor. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):149–155. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He W. W., Gustafson M. L., Hirobe S., Donahoe P. K. Developmental expression of four novel serine/threonine kinase receptors homologous to the activin/transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor family. Dev Dyn. 1993 Feb;196(2):133–142. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001960207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Moustakas A., Lin H. Y., Lodish H. F., Carr B. I. Growth inhibition by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) type I is restored in TGF-beta-resistant hepatoma cells after expression of TGF-beta receptor type II cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5359–5363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Weissinger E., Mischak H., Troppmair J., Showalter S. D., Lloyd P., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R. Probing structure and function of the raf protein kinase domain with monoclonal antibodies. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):713–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. Y., Wang X. F., Ng-Eaton E., Weinberg R. A., Lodish H. F. Expression cloning of the TGF-beta type II receptor, a functional transmembrane serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luyten F. P., Chen P., Paralkar V., Reddi A. H. Recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-4, transforming growth factor-beta 1, and activin A enhance the cartilage phenotype of articular chondrocytes in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Feb;210(2):224–229. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Laiho M., Ralph D. A., Weis F. M., Zentella A. Transforming growth factor-beta. Cancer Surv. 1992;12:81–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Identification of receptors for type-beta transforming growth factor. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:174–195. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Receptors for the TGF-beta family. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90627-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Vale W. W. Expression cloning of an activin receptor, a predicted transmembrane serine kinase. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90549-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki K., Xu J., Wang F., McKeehan W. L., Krummen L., Kan M. A widely expressed transmembrane serine/threonine kinase that does not bind activin, inhibin, transforming growth factor beta, or bone morphogenic factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12719–12723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzuk M. M., Bradley A. Structure of the mouse activin receptor type II gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):404–413. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81000-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. A collection of computer programs for the IBM PC. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida Y., Hata M., Ayaki T., Ryo H., Yamagata M., Shimizu K., Nishizuka Y. Proliferation of both somatic and germ cells is affected in the Drosophila mutants of raf proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):775–781. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paralkar V. M., Hammonds R. G., Reddi A. H. Identification and characterization of cellular binding proteins (receptors) for recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2B, an initiator of bone differentiation cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3397–3401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paralkar V. M., Vukicevic S., Reddi A. H. Transforming growth factor beta type 1 binds to collagen IV of basement membrane matrix: implications for development. Dev Biol. 1991 Feb;143(2):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90081-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paralkar V. M., Weeks B. S., Yu Y. M., Kleinman H. K., Reddi A. H. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2B stimulates PC12 cell differentiation: potentiation and binding to type IV collagen. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1721–1728. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasharma K., Li C. H. Characteristics of binding of human seminal alpha-inhibin-92 to human pituitary membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3595–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi A. H., Huggins C. Biochemical sequences in the transformation of normal fibroblasts in adolescent rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1601–1605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajjadi F. G., Pasquale E. B. Five novel avian Eph-related tyrosine kinases are differentially expressed. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1807–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampath T. K., Maliakal J. C., Hauschka P. V., Jones W. K., Sasak H., Tucker R. F., White K. H., Coughlin J. E., Tucker M. M., Pang R. H. Recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 (hOP-1) induces new bone formation in vivo with a specific activity comparable with natural bovine osteogenic protein and stimulates osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20352–20362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Yancopoulos G. D. The alphas, betas, and kinases of cytokine receptor complexes. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90506-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. C., Howlett B., Boyes D. C., Nasrallah M. E., Nasrallah J. B. Molecular cloning of a putative receptor protein kinase gene encoded at the self-incompatibility locus of Brassica oleracea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8816–8820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumitomo S., Saito T., Nohno T. A new receptor protein kinase from chick embryo related to type II receptor for TGF-beta. DNA Seq. 1993;3(5):297–302. doi: 10.3109/10425179309020827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Shioda N., Maeda T., Tada M., Ueno N. A mouse TGF-beta type I receptor that requires type II receptor for ligand binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 15;198(3):1063–1069. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Knighton D. R., Zheng J., Ten Eyck L. F., Sowadski J. M. Structural framework for the protein kinase family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:429–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tew D., Ortiz de Montellano P. R. The myoglobin protein radical. Coupling of Tyr-103 to Tyr-151 in the H2O2-mediated cross-linking of sperm whale myoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17880–17886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiesman J., Hart C. E. Identification of a soluble receptor for platelet-derived growth factor in cell-conditioned medium and human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9621–9628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias C. M., Howlett B., Nasrallah J. B. An Arabidopsis thaliana Gene with Sequence Similarity to the S-Locus Receptor Kinase of Brassica oleracea: Sequence and Expression. Plant Physiol. 1992 May;99(1):284–290. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.1.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida K., Lewis K. A., Mathews L. S., Vale W. W. Molecular characterization of rat transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 31;191(3):790–795. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida K., Mathews L. S., Vale W. W. Cloning and characterization of a transmembrane serine kinase that acts as an activin type I receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11242–11246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Mitchell P. J., Kas E., Chasin L. A., Funanage V. L., Myoda T. T., Hamlin J. Effect of gamma rays at the dihydrofolate reductase locus: deletions and inversions. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Nov;12(6):555–566. doi: 10.1007/BF01671941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C. Receptor-like protein kinase genes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1993 Mar;3(3):451–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.1993.tb00164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C., Zhang R. Relationship of a putative receptor protein kinase from maize to the S-locus glycoproteins of Brassica. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):743–746. doi: 10.1038/345743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Rosen V., D'Alessandro J. S., Bauduy M., Cordes P., Harada T., Israel D. I., Hewick R. M., Kerns K. M., LaPan P. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein induces bone formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2220–2224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J. M. Bone morphogenetic proteins. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(4):267–280. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J. M., Rosen V., Celeste A. J., Mitsock L. M., Whitters M. J., Kriz R. W., Hewick R. M., Wang E. A. Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1528–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.3201241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J. M. The bone morphogenetic protein family and osteogenesis. Mol Reprod Dev. 1992 Jun;32(2):160–167. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080320212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrana J. L., Attisano L., Cárcamo J., Zentella A., Doody J., Laiho M., Wang X. F., Massagué J. TGF beta signals through a heteromeric protein kinase receptor complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1003–1014. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90395-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrana J. L., Tran H., Attisano L., Arora K., Childs S. R., Massagué J., O'Connor M. B. Two distinct transmembrane serine/threonine kinases from Drosophila melanogaster form an activin receptor complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):944–950. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J., Knighton D. R., ten Eyck L. F., Karlsson R., Xuong N., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with MgATP and peptide inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 9;32(9):2154–2161. doi: 10.1021/bi00060a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dijke P., Ichijo H., Franzén P., Schulz P., Saras J., Toyoshima H., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. Activin receptor-like kinases: a novel subclass of cell-surface receptors with predicted serine/threonine kinase activity. Oncogene. 1993 Oct;8(10):2879–2887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dijke P., Yamashita H., Ichijo H., Franzén P., Laiho M., Miyazono K., Heldin C. H. Characterization of type I receptors for transforming growth factor-beta and activin. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):101–104. doi: 10.1126/science.8140412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]