Abstract
The activity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain (IgH) enhancer is restricted to B cells, although it binds both B-cell-restricted and ubiquitous transcription factors. Activation of the enhancer in non-B cells upon overexpression of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) protein E2A appears to be mediated not only by the binding of E2A to its cognate E box but also by the resulting displacement of a repressor from that same site. We have identified a "two-handed" zinc finger protein, denoted ZEB, the DNA-binding specificity of which mimics that of the cellular repressor. By employing a derivative E box that binds ZEB but not E2A, we have shown that the repressor is active in B cells and the IgH enhancer is silenced in the absence of binding competition by bHLH proteins. Hence, we propose that a necessary prerequisite of enhancer activity is the B-cell-specific displacement of a ZEB-like repressor by bHLH proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
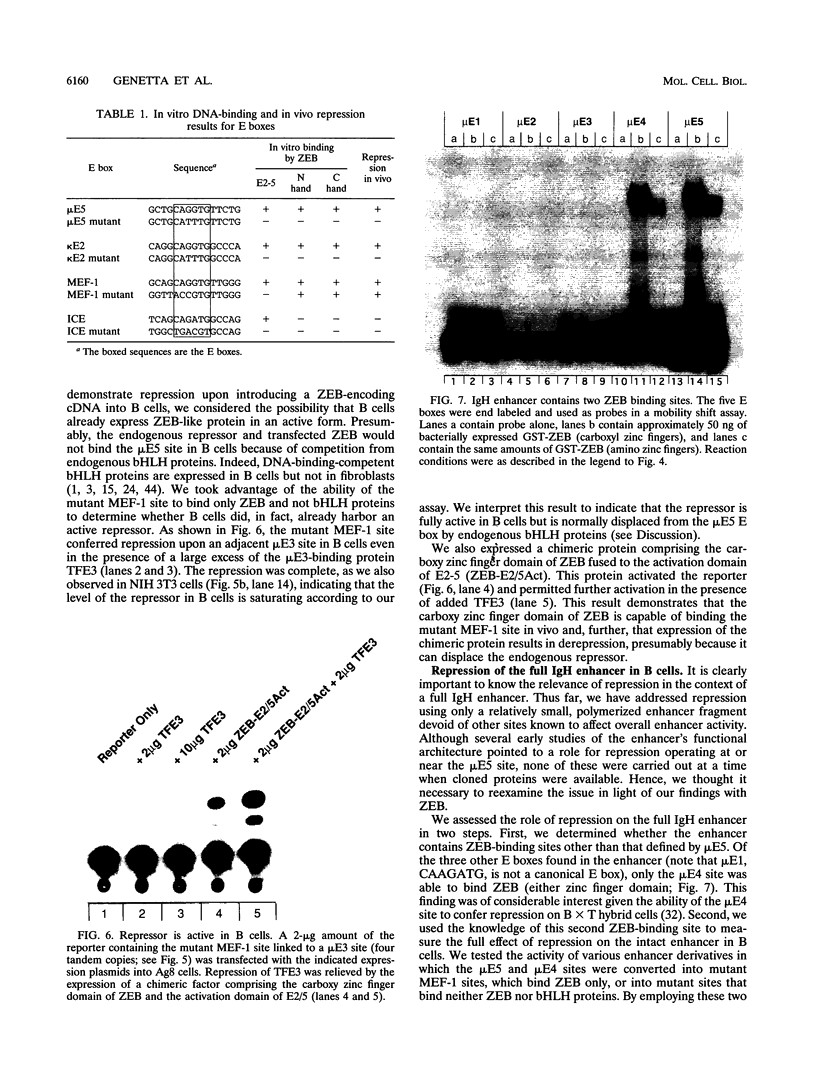
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronheim A., Ohlsson H., Park C. W., Edlund T., Walker M. D. Distribution and characterization of helix-loop-helix enhancer-binding proteins from pancreatic beta cells and lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3893–3899. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bain G., Gruenwald S., Murre C. E2A and E2-2 are subunits of B-cell-specific E2-box DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3522–3529. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Identification of a myocyte nuclear factor that binds to the muscle-specific enhancer of the mouse muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2627–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. S., Sharp P. A. A helix-loop-helix protein related to the immunoglobulin E box-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4384–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P. S., Raducha M., Edwards Y. H., Weiss M. J., Slaughter C., Lafferty M. A., Harris H. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of human intestinal alkaline phosphatase: close homology to placental alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1234–1238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. S., Olson E. N., Kingston R. E. HEB, a helix-loop-helix protein related to E2A and ITF2 that can modulate the DNA-binding ability of myogenic regulatory factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1031–1042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. F., Lüscher B., Admon A., Mermod N., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-4 contains multiple dimerization domains that regulate dimer specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1741–1752. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs Y., Vierra C., Nelson C. E2A expression, nuclear localization, and in vivo formation of DNA- and non-DNA-binding species during B-cell development. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7321–7333. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenuwein T., Grosschedl R. Complex pattern of immunoglobulin mu gene expression in normal and transgenic mice: nonoverlapping regulatory sequences govern distinct tissue specificities. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):932–943. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Zervos P., Ruezinsky D. Functional analysis of the murine IgH enhancer: evidence for negative control of cell-type specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8209–8221. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Su L. K., Kadesch T. Identification and characterization of two functional domains within the murine heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D. B-cell- and myocyte-specific E2-box-binding factors contain E12/E47-like subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1156–1160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen B., Tian G., Erman B., Gregoire J., Maki R., Graves B., Sen R. Regulation of lymphoid-specific immunoglobulin mu heavy chain gene enhancer by ETS-domain proteins. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):82–86. doi: 10.1126/science.8316859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Shen L. P., Meister A., Fodor E., Rutter W. J. Pan: a transcriptional regulator that binds chymotrypsin, insulin, and AP-4 enhancer motifs. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1035–1043. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K., Atchison M. L. Isolation of a candidate repressor/activator, NF-E1 (YY-1, delta), that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain mu E1 site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9804–9808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera R. R., Stuiver M. H., Steenbergen R., Murre C. Ets proteins: new factors that regulate immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7163–7169. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruezinsky D., Beckmann H., Kadesch T. Modulation of the IgH enhancer's cell type specificity through a genetic switch. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):29–37. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Lieberman S., Eckhardt L. A. The octamer/mu E4 region of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer mediates gene repression in myeloma x T-lymphoma hybrids. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3530–3540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Seto E., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. M., Burden S. J. An E box mediates activation and repression of the acetylcholine receptor delta-subunit gene during myogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5133–5140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Lenardo M. J. Immunoglobulin gene transcription. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:373–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Baltimore D. Id proteins Id1 and Id2 selectively inhibit DNA binding by one class of helix-loop-helix proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5603–5611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Park C. W., Rosen A., Aronheim A. A cDNA from a mouse pancreatic beta cell encoding a putative transcription factor of the insulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Cordle S. R., Henderson E., Weil P. A., Stein R. Identification of a pancreatic beta-cell insulin gene transcription factor that binds to and appears to activate cell-type-specific expression: its possible relationship to other cellular factors that bind to a common insulin gene sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1564–1572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. M., Moolten D., Burlein J., Romano J., Bhaerman R., Godillot A., Mellon M., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Kant J. A. Identification of a zinc finger protein that inhibits IL-2 gene expression. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1791–1794. doi: 10.1126/science.1840704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. B., Kiledjian M., Shen C. P., Benezra R., Zwollo P., Dymecki S. M., Desiderio S. V., Kadesch T. Repression of immunoglobulin enhancers by the helix-loop-helix protein Id: implications for B-lymphoid-cell development. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6185–6191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Porton B., Shen L. Y., Eckhardt L. A. Role of the octamer motif in hybrid cell extinction of immunoglobulin gene expression: extinction is dominant in a two enhancer system. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]