Abstract
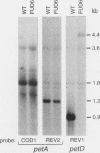
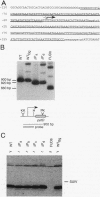
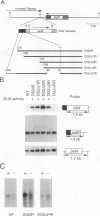
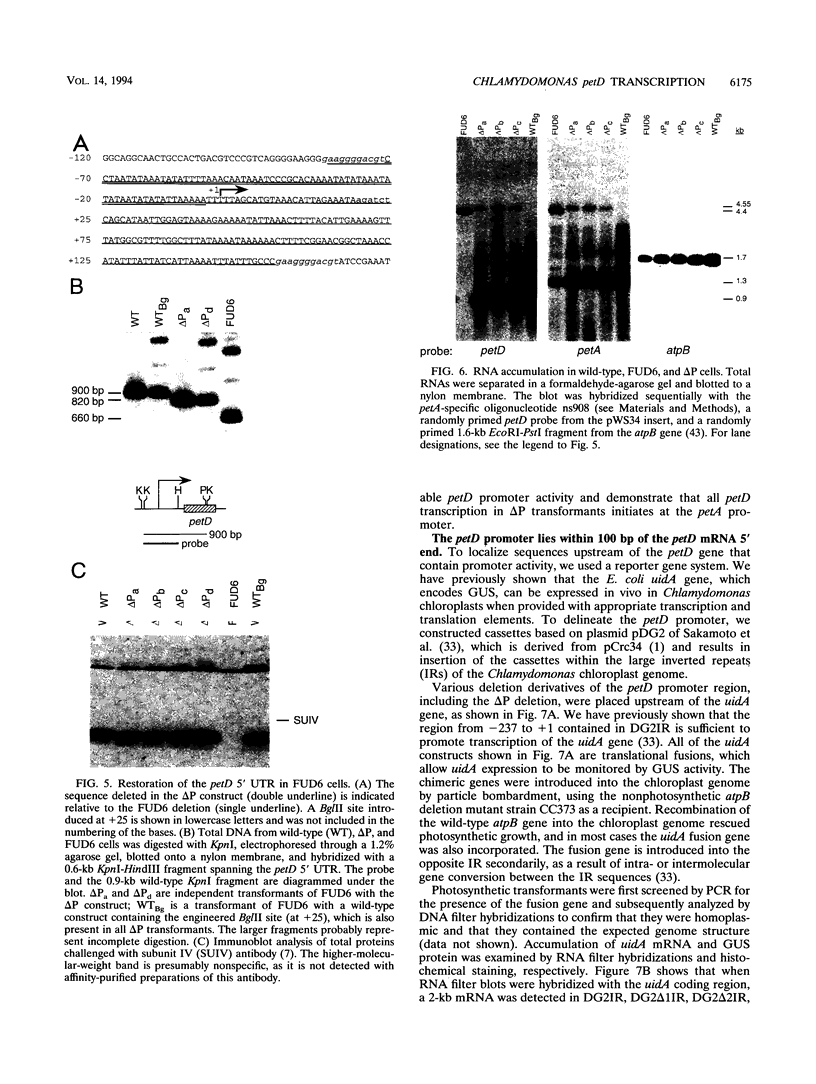
FUD6, a nonphotosynthetic mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, was previously found to be deficient in the synthesis of subunit IV of the cytochrome b6/f complex, the chloroplast petD gene product (C. Lemaire, J. Girard-Bascou, F.-A. Wollman, and P. Bennoun, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 851:229-238, 1986). The lesion in FUD6 is a 236-bp deletion between two 11-bp direct repeats in the chloroplast genome. It extends from 82 to 72 bp upstream of the 5' end of wild-type petD mRNA to 156 to 166 bp downstream of the 5' end. Thus, the deletion extends into the putative promoter and 5' untranslated region of petD. No petD mRNA of the normal size can be detected in FUD6 cells, but a low level of a dicistronic message accumulates, which contains the coding regions for subunit IV and cytochrome f, the product of the upstream petA gene. petD transcriptional activity in FUD6 is not significantly altered from the wild-type level. This transcriptional activity was eliminated by petA promoter disruptions, suggesting that it originates at the petA promoter. We conclude that the petD-coding portion of most cotranscripts is rapidly degraded in FUD6, possibly following processing events that generate the 3' end of petA mRNA. A chloroplast transformant was constructed in which only the sequence from -81 to -2 relative to the major 5' end of the petD transcript was deleted. Although this deletion eliminates all detectable petD promoter activity, the transformant grows phototrophically and accumulates high levels of monocistronic petD mRNA. We conclude that the petD gene can be transcribed by functionally redundant promoters. In the absence of a functional petD promoter, a lack of transcription termination allows the downstream petD gene to be cotranscribed with the petA coding region and thereby expressed efficiently.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blowers A. D., Ellmore G. S., Klein U., Bogorad L. Transcriptional analysis of endogenous and foreign genes in chloroplast transformants of Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1059–1070. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Klein U., Ellmore G. S., Bogorad L. Functional in vivo analyses of the 3' flanking sequences of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast rbcL and psaB genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Apr;238(3):339–349. doi: 10.1007/BF00291992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum B., Bakalara N., Simpson L. A model for RNA editing in kinetoplastid mitochondria: "guide" RNA molecules transcribed from maxicircle DNA provide the edited information. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90735-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W., Harris E. H., Hosler J. P., Johnson A. M., Jones A. R., Randolph-Anderson B. L., Robertson D., Klein T. M., Shark K. B. Chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas with high velocity microprojectiles. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1534–1538. doi: 10.1126/science.2897716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büschlen S., Choquet Y., Kuras R., Wollman F. A. Nucleotide sequences of the continuous and separated petA, petB and petD chloroplast genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 24;284(2):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80698-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. J., Orozco E. M., Jr Recognition of prokaryotic transcription terminators by spinach chloroplast RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8411–8431. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Kindle K., Stern D. Initiation codon mutations in the Chlamydomonas chloroplast petD gene result in temperature-sensitive photosynthetic growth. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3627–3635. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choquet Y., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Girard-Bascou J., Kück U., Bennoun P., Rochaix J. D. Mutant phenotypes support a trans-splicing mechanism for the expression of the tripartite psaA gene in the C. reinhardtii chloroplast. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90432-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S. E., Surzycki S. J. Organization and structure of plastome psbF, psbL, petG and ORF712 genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr Genet. 1992 May;21(6):527–530. doi: 10.1007/BF00351664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagné G., Guertin M. The early genetic response to light in the green unicellular alga Chlamydomonas eugametos grown under light/dark cycles involves genes that represent direct responses to light and photosynthesis. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Feb;18(3):429–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00040659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Girard-Bascou J., Choquet Y., Rochaix J. D. Trans-splicing mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(3):417–425. doi: 10.1007/BF00264448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M. Transgenic expression of aminoglycoside adenine transferase in the chloroplast: a selectable marker of site-directed transformation of chlamydomonas. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4083–4089. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guertin M., Bellemare G. Synthesis of chloroplast ribonucleic acid in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii toluene-treated cells. Eur J Biochem. 1979 May 2;96(1):125–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe G., Merchant S. The biosynthesis of membrane and soluble plastidic c-type cytochromes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is dependent on multiple common gene products. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2789–2801. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05346.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. H., Schmidt G. W. The psbB gene cluster of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast: sequence and transcriptional analyses of psbN and psbH. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Jul;22(4):645–658. doi: 10.1007/BF00047405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallas T., Spiller S., Malkin R. Characterization of two operons encoding the cytochrome b6-f complex of the cyanobacterium Nostoc PCC 7906. Highly conserved sequences but different gene organization than in chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14334–14342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Richards K. L., Stern D. B. Engineering the chloroplast genome: techniques and capabilities for chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1721–1725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein U., De Camp J. D., Bogorad L. Two types of chloroplast gene promoters in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3453–3457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuras R., Wollman F. A. The assembly of cytochrome b6/f complexes: an approach using genetic transformation of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1019–1027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kück U. The intron of a plastid gene from a green alga contains an open reading frame for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):257–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00331276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayers S. R., Dubbs J. M., Vass I., Hideg E., Nagy L., Barber J. Further characterization of the psbH locus of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: inactivation of psbH impairs QA to QB electron transport in photosystem 2. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 16;32(6):1454–1465. doi: 10.1021/bi00057a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod C., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Rochaix J. D. Accumulation of chloroplast psbB RNA requires a nuclear factor in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Feb;231(3):449–459. doi: 10.1007/BF00292715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. D. Contrasting modes and tempos of genome evolution in land plant organelles. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90125-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock C. D., Barkan A., Taylor W. C. The maize plastid psbB-psbF-petB-petD gene cluster: spliced and unspliced petB and petD RNAs encode alternative products. Curr Genet. 1987;12(1):69–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00420729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto W., Kindle K. L., Stern D. B. In vivo analysis of Chlamydomonas chloroplast petD gene expression using stable transformation of beta-glucuronidase translational fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):497–501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd H. S., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Mutations in nine chloroplast loci of Chlamydomonas affecting different photosynthetic functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1353–1357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression: 3' inverted repeats act as mRNA processing and stabilizing elements, but do not terminate transcription. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1145–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Kindle K. L. 3'end maturation of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast atpB mRNA is a two-step process. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2277–2285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Radwanski E. R., Kindle K. L. A 3' stem/loop structure of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast atpB gene regulates mRNA accumulation in vivo. Plant Cell. 1991 Mar;3(3):285–297. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M. The chloroplast genome. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):149–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00015612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Soen S. Y., Franzén L. G., Rochaix J. D. Directed chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: insertional inactivation of the psaC gene encoding the iron sulfur protein destabilizes photosystem I. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2033–2040. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turmel M., Boulanger J., Bergeron A. Nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast petD gene of Chlamydomonas eugametos. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3593–3593. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwoerd T. C., Dekker B. M., Hoekema A. A small-scale procedure for the rapid isolation of plant RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2362–2362. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Complex RNA maturation in chloroplasts. The psbB operon from spinach. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):551–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. P., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. The sequence of the chloroplast atpB gene and its flanking regions in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene. 1986;44(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu W., Spreitzer R. J. Sequences of trnR-ACG and petD that contain a tRNA-like element within the chloroplast genome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):957–957. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]