Abstract
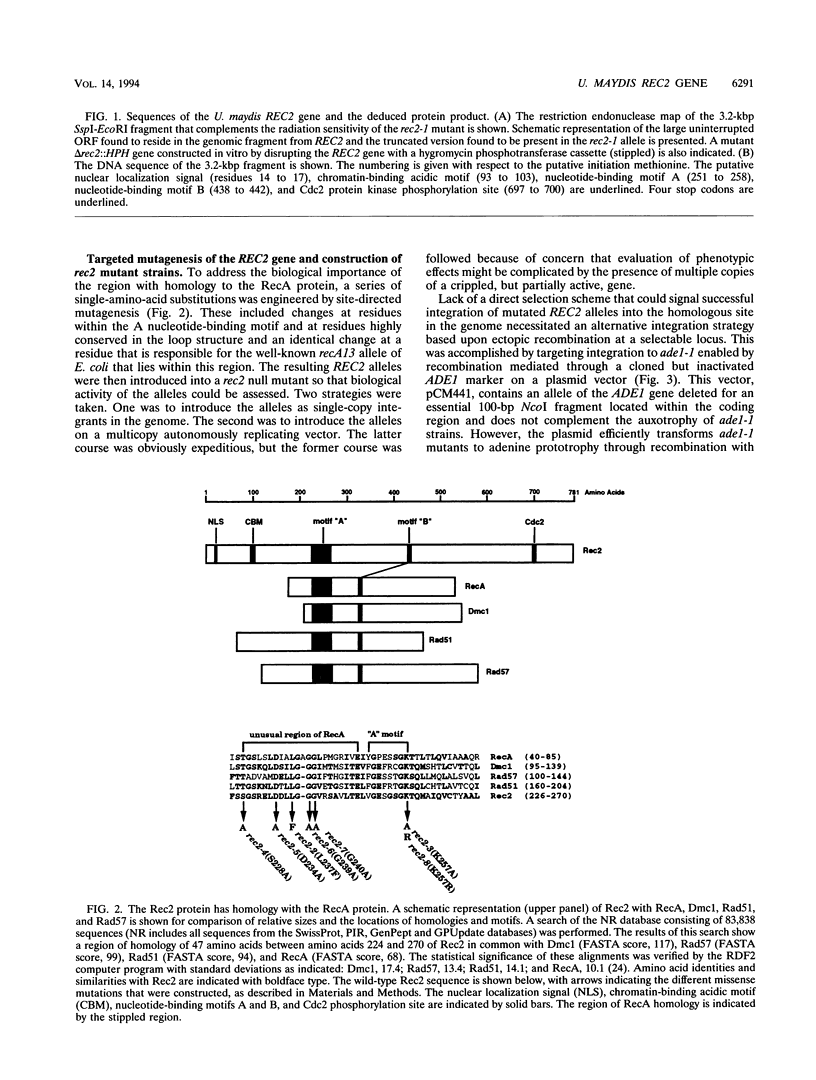
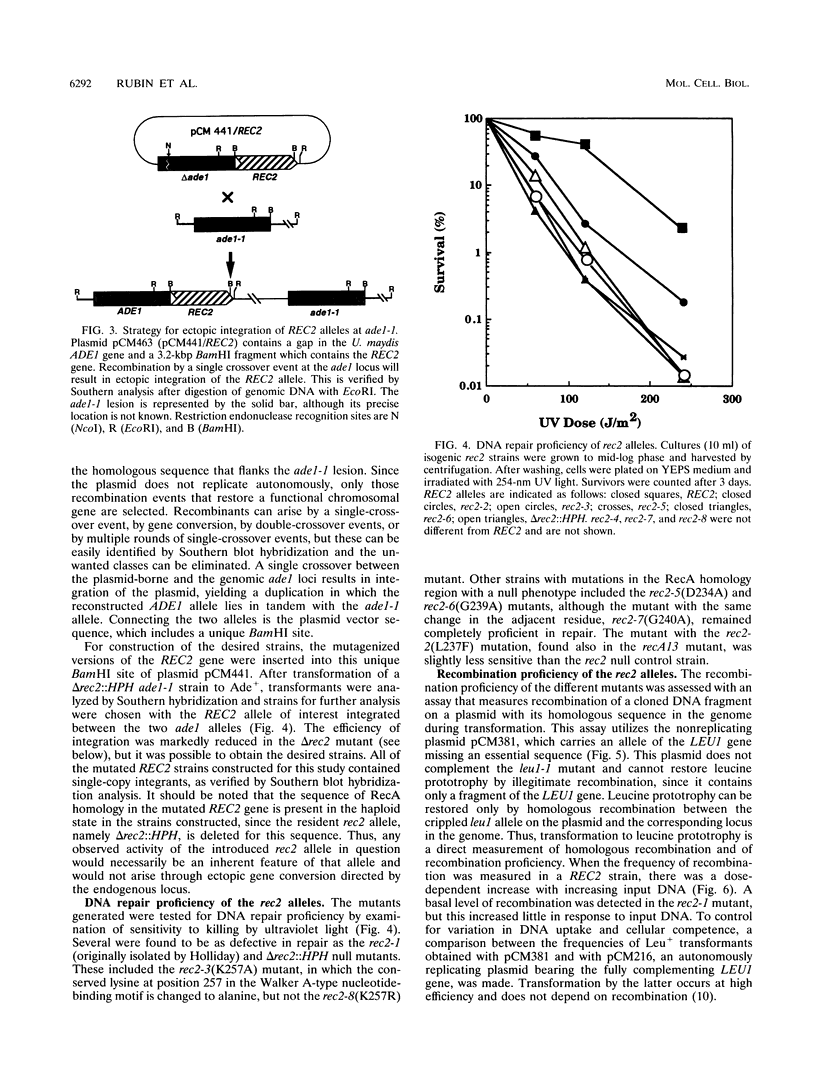
Mutation in the REC2 gene of Ustilago maydis leads to defects in DNA repair, recombination, and meiosis. Analysis of the primary sequence of the Rec2 protein reveals a region with significant homology to bacterial RecA protein and to the yeast recombination proteins Dmc1, Rad51, and Rad57. This homologous region in the U. maydis Rec2 protein was found to be functionally sensitive to mutation, lending support to the hypothesis that Rec2 has a functional RecA-like domain essential for activity in recombination and repair. Homologous recombination between plasmid and chromosomal DNA sequences is reduced substantially in the rec2 mutant following transformation. The frequency can be restored to a level approaching, but not exceeding, that observed in the wild-type strain if transformation is performed with cells containing multiple copies of REC2.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboussekhra A., Chanet R., Adjiri A., Fabre F. Semidominant suppressors of Srs2 helicase mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae map in the RAD51 gene, whose sequence predicts a protein with similarities to procaryotic RecA proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3224–3234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A. PROSITE: a dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2241–2245. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basile G., Aker M., Mortimer R. K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional regulation of the yeast recombinational repair gene RAD51. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3235–3246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauchwitz R., Holloman W. K. Isolation of the REC2 gene controlling recombination in Ustilago maydis. Gene. 1990 Dec 15;96(2):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90265-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. K., Park D., Xu L., Kleckner N. DMC1: a meiosis-specific yeast homolog of E. coli recA required for recombination, synaptonemal complex formation, and cell cycle progression. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):439–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90446-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formosa T., Alberts B. M. DNA synthesis dependent on genetic recombination: characterization of a reaction catalyzed by purified bacteriophage T4 proteins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):793–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90522-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham S., Holloman W. K. Cloning and disruption of Ustilago maydis genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4052–4055. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham S., Holloman W. K. Extrachromosomal recombination is deranged in the rec2 mutant of Ustilago maydis. Genetics. 1991 Dec;129(4):1052–1060. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham S., Holloman W. K. Pathways of transformation in Ustilago maydis determined by DNA conformation. Genetics. 1990 Apr;124(4):833–843. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. Altered recombination frequencies in radiation sensitivie strains of Ustilago. Mutat Res. 1967 May-Jun;4(3):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R., Halliwell R. E., Evans M. W., Rowell V. Genetic characterization of rec-1, a mutant of Ustilago maydis defective in repair and recombination. Genet Res. 1976 Jun;27(3):413–453. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300016621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. Radiation sensitive mutants of Ustilago maydis. Mutat Res. 1965 Dec;2(6):557–559. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(65)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kans J. A., Mortimer R. K. Nucleotide sequence of the RAD57 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1991 Aug 30;105(1):139–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90527-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C. Biochemical and biological function of Escherichia coli RecA protein: behavior of mutant RecA proteins. Biochimie. 1991 Feb-Mar;73(2-3):289–304. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90216-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaper S., Resnick M. A., Holliday R. Repair of double-strand breaks and lethal damage in DNA of Ustilago maydis. Genet Res. 1980 Jun;35(3):291–307. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan K. M., Knight K. L. Mutagenesis of the P-loop motif in the ATP binding site of the RecA protein from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1993 Aug 20;232(4):1048–1059. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Helical RecA nucleoprotein filaments mediate homologous pairing and strand exchange. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 7;1008(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(80)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehrauer W. M., Kowalczykowski S. C. Alteration of the nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) catalytic domain within Escherichia coli recA protein attenuates NTP hydrolysis but not joint molecule formation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1292–1297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. Nuclear location signal-mediated protein transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 14;1008(3):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca A. I., Cox M. M. The RecA protein: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(6):415–456. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy S., Choi J. K., Bagrodia S., Copeland T. D., Maller J. L., Shalloway D. Purified maturation promoting factor phosphorylates pp60c-src at the sites phosphorylated during fibroblast mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara A., Ogawa H., Ogawa T. Rad51 protein involved in repair and recombination in S. cerevisiae is a RecA-like protein. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90447-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Bishop D. K., Kleckner N., Steitz T. A. Structural relationship of bacterial RecA proteins to recombination proteins from bacteriophage T4 and yeast. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1892–1896. doi: 10.1126/science.8456313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. The structure of the E. coli recA protein monomer and polymer. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):318–325. doi: 10.1038/355318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M. P., Onel K., Holloman W. K. The REC1 gene of Ustilago maydis involved in the cellular response to DNA damage encodes an exonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):747–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Glynn S., Levi E., Mjolsness S., Hayday A. Use of a chemically modified T7 DNA polymerase for manual and automated sequencing of supercoiled DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):460–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang T., Copeland V., Bowden G. T. A set of cassette cloning vectors for rapid and versatile adaptation of restriction fragments. Biotechniques. 1991 Mar;10(3):330–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukuda T., Bauchwitz R., Holloman W. K. Isolation of the REC1 gene controlling recombination in Ustilago maydis. Gene. 1989 Dec 28;85(2):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukuda T., Carleton S., Fotheringham S., Holloman W. K. Isolation and characterization of an autonomously replicating sequence from Ustilago maydis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3703–3709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unrau P. The excision of pyrimidine dimers from the DNA of mutant and wild-type strains of Ustilago. Mutat Res. 1975 Jul;29(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Holden D. W., Leong S. A. Gene transfer system for the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):865–869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen L., Huang J. K., Johnson B. H., Reeck G. R. A human placental cDNA clone that encodes nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1197–1214. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonesaki T., Minagawa T. T4 phage gene uvsX product catalyzes homologous DNA pairing. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3321–3327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04083.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]