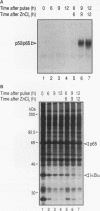
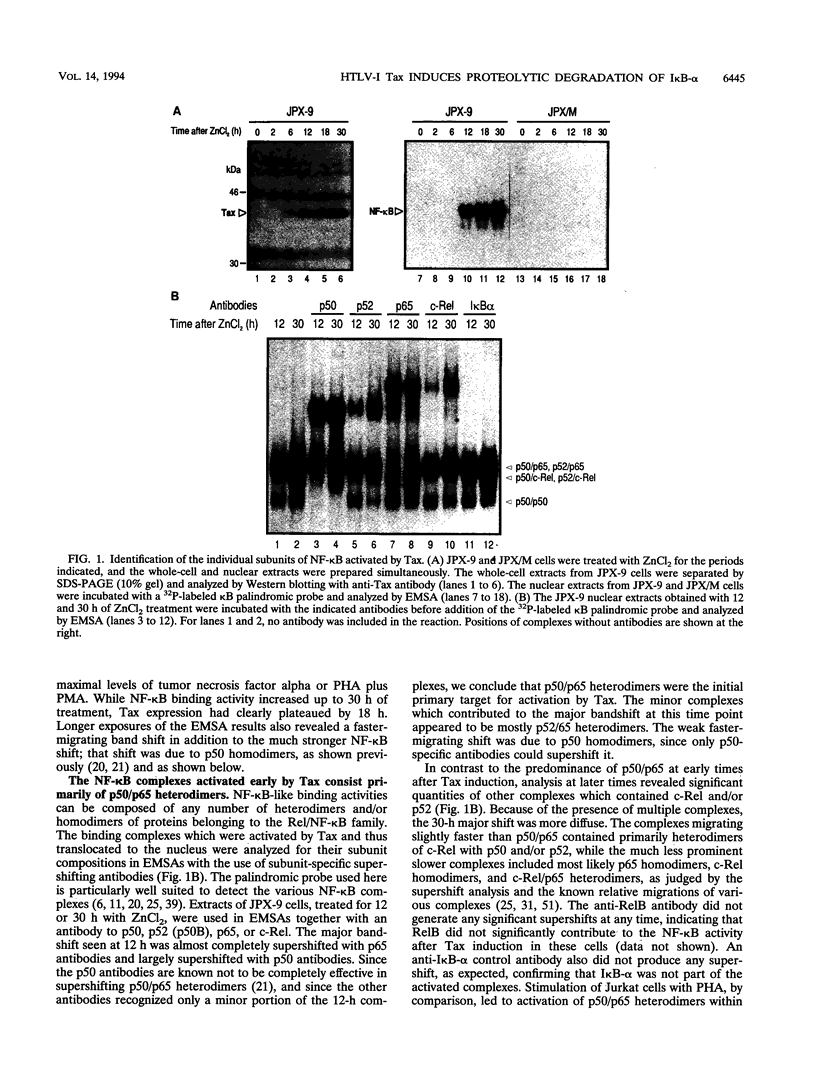
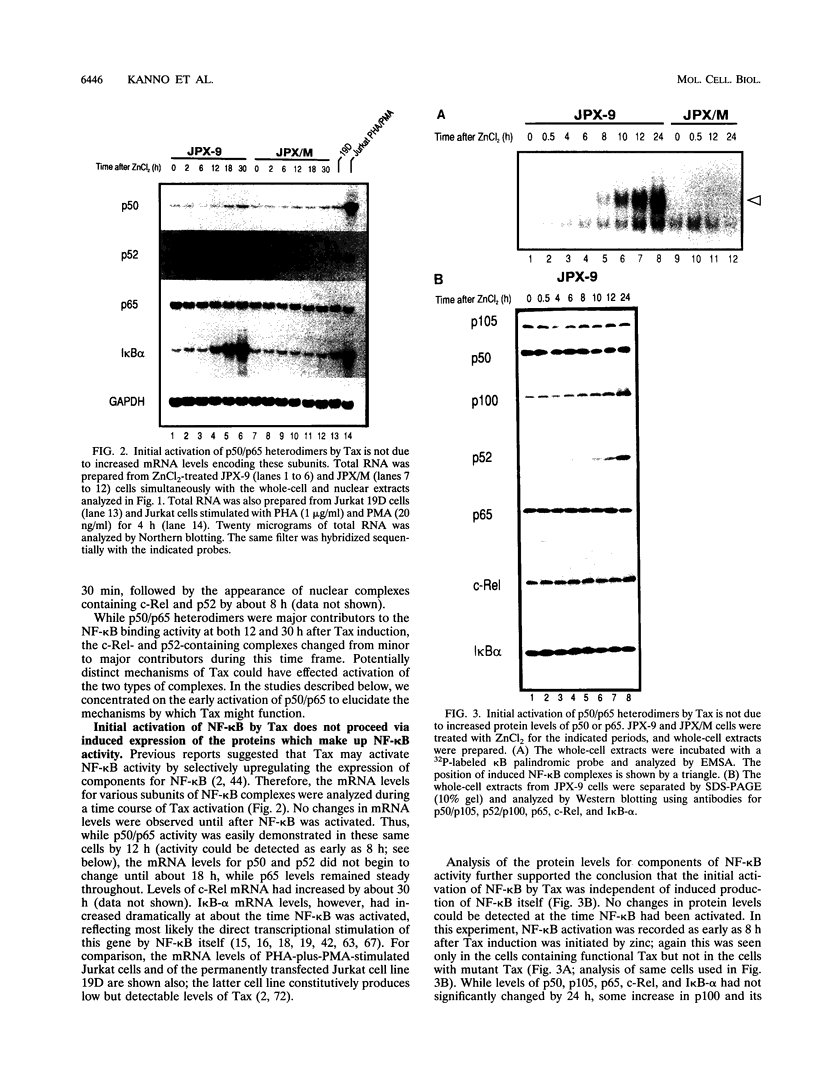
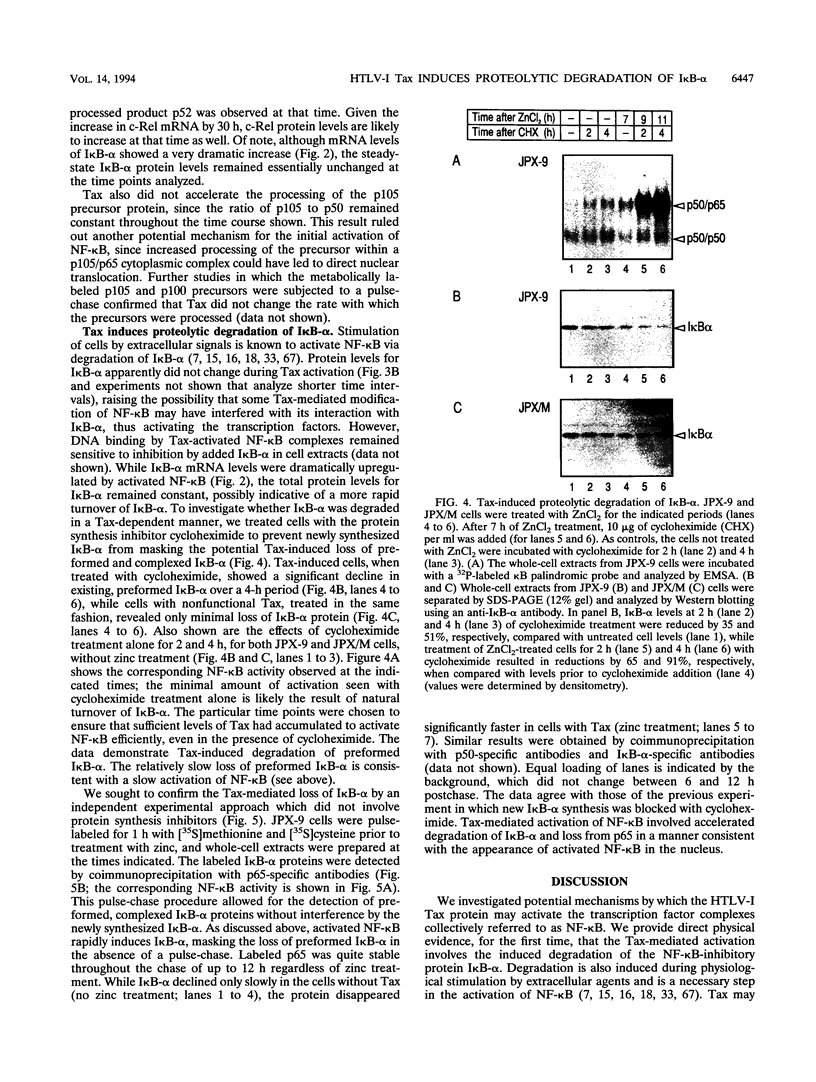
Abstract
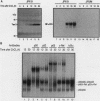
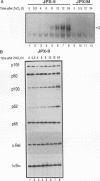
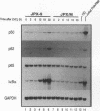
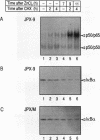
The human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) Tax protein induces the expression of cellular genes, at least in part, by activating the endogenous NF-kappa B transcription factors. Induced expression of cellular genes is thought to be important for transformation of T cells to continued growth, a prelude to the establishment of adult T-cell leukemia. However, neither underlying mechanisms nor kinetics of the Tax-mediated activation of NF-kappa B are understood. We have analyzed a permanently transfected Jurkat T-cell line in which the expression of Tax is entirely dependent on addition of heavy metals. The initial NF-kappa B binding activity seen after induction of Tax is due almost exclusively to p50/p65 heterodimers. At later times, NF-kappa B complexes containing c-Rel and/or p52 accumulate. The early activation of p50/p65 complexes is a posttranslational event, since neither mRNA nor protein levels of NF-kappa B subunits had increased at that time. We demonstrate for the first time a Tax-induced proteolytic degradation of the NF-kappa B inhibitor, I kappa B-alpha, which may trigger the initial nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B. As nuclear NF-kappa B rapidly and potently stimulates resynthesis of I kappa B-alpha, the steady-state level of I kappa B-alpha does not significantly change. Thus, the dramatic Tax-induced increase in the I kappa B-alpha turnover may continually weaken inhibition and activate NF-kappa B. Additional, distinct actions of Tax may contribute further to the high levels of NF-kappa B activity seen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arima N., Molitor J. A., Smith M. R., Kim J. H., Daitoku Y., Greene W. C. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax induces expression of the Rel-related family of kappa B enhancer-binding proteins: evidence for a pretranslational component of regulation. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6892–6899. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6892-6899.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong A. P., Franklin A. A., Uittenbogaard M. N., Giebler H. A., Nyborg J. K. Pleiotropic effect of the human T-cell leukemia virus Tax protein on the DNA binding activity of eukaryotic transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7303–7307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Wano Y., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Bogerd H., Doerre S., Stein B., Greene W. C. The 65-kDa subunit of human NF-kappa B functions as a potent transcriptional activator and a target for v-Rel-mediated repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1875–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Finco T. S., Nantermet P. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3301–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Burd P. R., Brown K., Villalobos J., Park S., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. A novel mitogen-inducible gene product related to p50/p105-NF-kappa B participates in transactivation through a kappa B site. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):685–695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Franzoso G., Azarenko V., Park S., Kanno T., Brown K., Siebenlist U. The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly transactivates through kappa B motifs via association with DNA-binding p50B homodimers. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90401-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Franzoso G., Brown K., Park S., Azarenko V., Tomita-Yamaguchi M., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Lymphocyte activation and the family of NF-kappa B transcription factor complexes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;182:411–420. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77633-5_52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Villalobos J., Burd P. R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Cloning of a mitogen-inducible gene encoding a kappa B DNA-binding protein with homology to the rel oncogene and to cell-cycle motifs. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):76–80. doi: 10.1038/348076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K., Park S., Kanno T., Franzoso G., Siebenlist U. Mutual regulation of the transcriptional activator NF-kappa B and its inhibitor, I kappa B-alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2532–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béraud C., Lombard-Platet G., Michal Y., Jalinot P. Binding of the HTLV-I Tax1 transactivator to the inducible 21 bp enhancer is mediated by the cellular factor HEB1. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3795–3803. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béraud C., Sun S. C., Ganchi P., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax associates with and is negatively regulated by the NF-kappa B2 p100 gene product: implications for viral latency. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Lowenthal J. W., Rimsky L., Bogérd H., Hoffman J., Wano Y., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. Stimulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax gene product involves the action of inducible cellular proteins. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1578–1586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1578-1586.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiao P. J., Miyamoto S., Verma I. M. Autoregulation of I kappa B alpha activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):28–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordle S. R., Donald R., Read M. A., Hawiger J. Lipopolysaccharide induces phosphorylation of MAD3 and activation of c-Rel and related NF-kappa B proteins in human monocytic THP-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11803–11810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzoso G., Bours V., Azarenko V., Park S., Tomita-Yamaguchi M., Kanno T., Brown K., Siebenlist U. The oncoprotein Bcl-3 can facilitate NF-kappa B-mediated transactivation by removing inhibiting p50 homodimers from select kappa B sites. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3893–3901. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzoso G., Bours V., Park S., Tomita-Yamaguchi M., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. The candidate oncoprotein Bcl-3 is an antagonist of p50/NF-kappa B-mediated inhibition. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):339–342. doi: 10.1038/359339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. c-fos promoter trans-activation by the tax1 protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8526–8530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Tsuchiya H., Chuhjo T., Akizawa T., Seiki M. Interaction of HTLV-1 Tax1 with p67SRF causes the aberrant induction of cellular immediate early genes through CArG boxes. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2066–2076. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Toita M., Yoshimura T., Yoshida M. The indirect association of human T-cell leukemia virus tax protein with DNA results in transcriptional activation. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4525–4528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4525-4528.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganchi P. A., Sun S. C., Greene W. C., Ballard D. W. A novel NF-kappa B complex containing p65 homodimers: implications for transcriptional control at the level of subunit dimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7826–7835. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen J. L., Minnaar R. P., Boom R., van der Noordaa J., Goudsmit J. Heat-shock induction of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. J Gen Virol. 1988 Nov;69(Pt 11):2913–2917. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-11-2913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh W. C., Sodroski J., Rosen C., Essex M., Haseltine W. A. Subcellular localization of the product of the long open reading frame of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1227–1228. doi: 10.1126/science.2983419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassmann R., Dengler C., Müller-Fleckenstein I., Fleckenstein B., McGuire K., Dokhelar M. C., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Transformation to continuous growth of primary human T lymphocytes by human T-cell leukemia virus type I X-region genes transduced by a Herpesvirus saimiri vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3351–3355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm S., Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription factor NF-kappa B: structure-function relationship of its protein subunits. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 1;290(Pt 2):297–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2900297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S. K., Nerlov C., Zabel U., Verde P., Johnsen M., Baeuerle P. A., Blasi F. A novel complex between the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B and c-Rel binds to a DNA element involved in the phorbol ester induction of the human urokinase gene. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):205–213. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05043.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Beg A. A., Tompkins S. M., Morris J. S., Yurochko A. D., Sampson-Johannes A., Mondal K., Ralph P., Baldwin A. S., Jr Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Machleidt T., Alkalay I., Krönke M., Ben-Neriah Y., Baeuerle P. A. Rapid proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha is necessary for activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):182–185. doi: 10.1038/365182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos B., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Siekevitz M., Greene W. C. Kappa B-specific DNA binding proteins: role in the regulation of human interleukin-2 gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):457–460. doi: 10.1126/science.2497518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Bengal E., Hunter T., Verma I. M. c-rel activates but v-rel suppresses transcription from kappa B sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Boros I., Brady J., Radonovich M., Khoury G. Characterization of cellular factors that interact with the human T-cell leukemia virus type I p40x-responsive 21-base-pair sequence. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4499–4509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4499-4509.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa T., Kawaguchi T., Seiki M., Yoshida M. Association of the pX gene product of human T-cell leukemia virus type-I with nucleus. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):462–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Selection of optimal kappa B/Rel DNA-binding motifs: interaction of both subunits of NF-kappa B with DNA is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4412–4421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste J., Cohen L., Hiscott J. NF-kappa B activity in T cells stably expressing the Tax protein of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):553–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90425-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanoix J., Lacoste J., Pepin N., Rice N., Hiscott J. Overproduction of NFKB2 (lyt-10) and c-Rel: a mechanism for HTLV-I Tax-mediated trans-activation via the NF-kappa B signalling pathway. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):841–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bail O., Schmidt-Ullrich R., Israël A. Promoter analysis of the gene encoding the I kappa B-alpha/MAD3 inhibitor of NF-kappa B: positive regulation by members of the rel/NF-kappa B family. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5043–5049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06197.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. C., Ruscetti F. W., Rice N. R., Chen E., Yang N. S., Mikovits J., Longo D. L. Differential expression of Rel family members in human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected cells: transcriptional activation of c-rel by Tax protein. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4205–4213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4205-4213.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm P. F., Marriott S. J., Gitlin S. D., Bohan C. A., Brady J. N. Induction of nuclear NF-kappa B DNA binding activity after exposure of lymphoid cells to soluble tax1 protein. New Biol. 1990 Nov;2(11):1034–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm P. F., Reid R. L., Brady J. N. Extracellular Tax1 protein stimulates tumor necrosis factor-beta and immunoglobulin kappa light chain expression in lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1294–1302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1294-1302.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio F., DiDonato J. A., Rosette C., Karin M. p105 and p98 precursor proteins play an active role in NF-kappa B-mediated signal transduction. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):705–718. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Chiao P. J., Verma I. M. Enhanced I kappa B alpha degradation is responsible for constitutive NF-kappa B activity in mature murine B-cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3276–3282. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B: a family of inducible and differentially expressed enhancer-binding proteins in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10028–10032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Ohtani K., Nakamura M., Sugamura K. Activation of endogenous c-fos proto-oncogene expression by human T-cell leukemia virus type I-encoded p40tax protein in the human T-cell line, Jurkat. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3220–3226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3220-3226.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Shimizu H., Mitomo K., Watanabe T., Okamoto S., Yamamoto K. A lymphoid cell-specific nuclear factor containing c-Rel-like proteins preferentially interacts with interleukin-6 kappa B-related motifs whose activities are repressed in lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1736–1746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann M., Nieters A., Hatada E. N., Scheidereit C. NF-kappa B precursor p100 inhibits nuclear translocation and DNA binding of NF-kappa B/rel-factors. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2275–2281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann M., Wulczyn F. G., Scheidereit C. The NF-kappa B precursor p105 and the proto-oncogene product Bcl-3 are I kappa B molecules and control nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):213–222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05647.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerenberg M., Hinrichs S. H., Reynolds R. K., Khoury G., Jay G. The tat gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 induces mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1324–1329. doi: 10.1126/science.2888190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani K., Nakamura M., Saito S., Nagata K., Sugamura K., Hinuma Y. Electroporation: application to human lymphoid cell lines for stable introduction of a transactivator gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1589–1604. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., MacKichan M. L., Israël A. The precursor of NF-kappa B p50 has I kappa B-like functions. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90353-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Poteat H., Tan T. H., Kawakami K., Roeder R., Haseltine W., Rosen C. A. Cellular transcription factors and regulation of IL-2 receptor gene expression by HTLV-I tax gene product. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.2838905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bull P., Takamiya M., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Dobrzanski P., Bravo R. RelB, a new Rel family transcription activator that can interact with p50-NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):674–684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman R. I., Beg A. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr NF-kappa B p100 (Lyt-10) is a component of H2TF1 and can function as an I kappa B-like molecule. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6089–6101. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Baeuerle P. A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3805–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Grassmann R., Fleckenstein B., Baeuerle P. A. Antioxidants selectively suppress activation of NF-kappa B by human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6288–6293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6288-6293.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. L., Fujita T., Liou H. C., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. The p65 subunit of NF-kappa B regulates I kappa B by two distinct mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1266–1276. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semmes O. J., Jeang K. T. Mutational analysis of human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax: regions necessary for function determined with 47 mutant proteins. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7183–7192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7183-7192.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Greene W. C. Identification of HTLV-I tax trans-activator mutants exhibiting novel transcriptional phenotypes. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1875–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Greene W. C. Molecular biology of the type I human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) and adult T-cell leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):761–766. doi: 10.1172/JCI115078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Ganchi P. A., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1912–1915. doi: 10.1126/science.8096091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Ganchi P. A., Béraud C., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. Autoregulation of the NF-kappa B transactivator RelA (p65) by multiple cytoplasmic inhibitors containing ankyrin motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1346–1350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Fujisawa J. I., Toita M., Yoshida M. The trans-activator tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) interacts with cAMP-responsive element (CRE) binding and CRE modulator proteins that bind to the 21-base-pair enhancer of HTLV-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):610–614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Hirai H., Fujisawa J., Fujita T., Yoshida M. A trans-activator Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 binds to NF-kappa B p50 and serum response factor (SRF) and associates with enhancer DNAs of the NF-kappa B site and CArG box. Oncogene. 1993 Sep;8(9):2391–2397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner S., Green M. R. HTLV-I Tax protein stimulation of DNA binding of bZIP proteins by enhancing dimerization. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):395–399. doi: 10.1126/science.8211160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wano Y., Feinberg M., Hosking J. B., Bogerd H., Greene W. C. Stable expression of the tax gene of type I human T-cell leukemia virus in human T cells activates specific cellular genes involved in growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9733–9737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L. J., Giam C. Z. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) transcriptional activator, Tax, enhances CREB binding to HTLV-I 21-base-pair repeats by protein-protein interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7070–7074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L. J., Giam C. Z. Interaction of the human T-cell lymphotrophic virus type I (HTLV-I) transcriptional activator Tax with cellular factors that bind specifically to the 21-base-pair repeats in the HTLV-I enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11445–11449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martin R., Vanhove B., Cheng Q., Hofer E., Csizmadia V., Winkler H., Bach F. H. Cytokine-inducible expression in endothelial cells of an I kappa B alpha-like gene is regulated by NF kappa B. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2773–2779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]