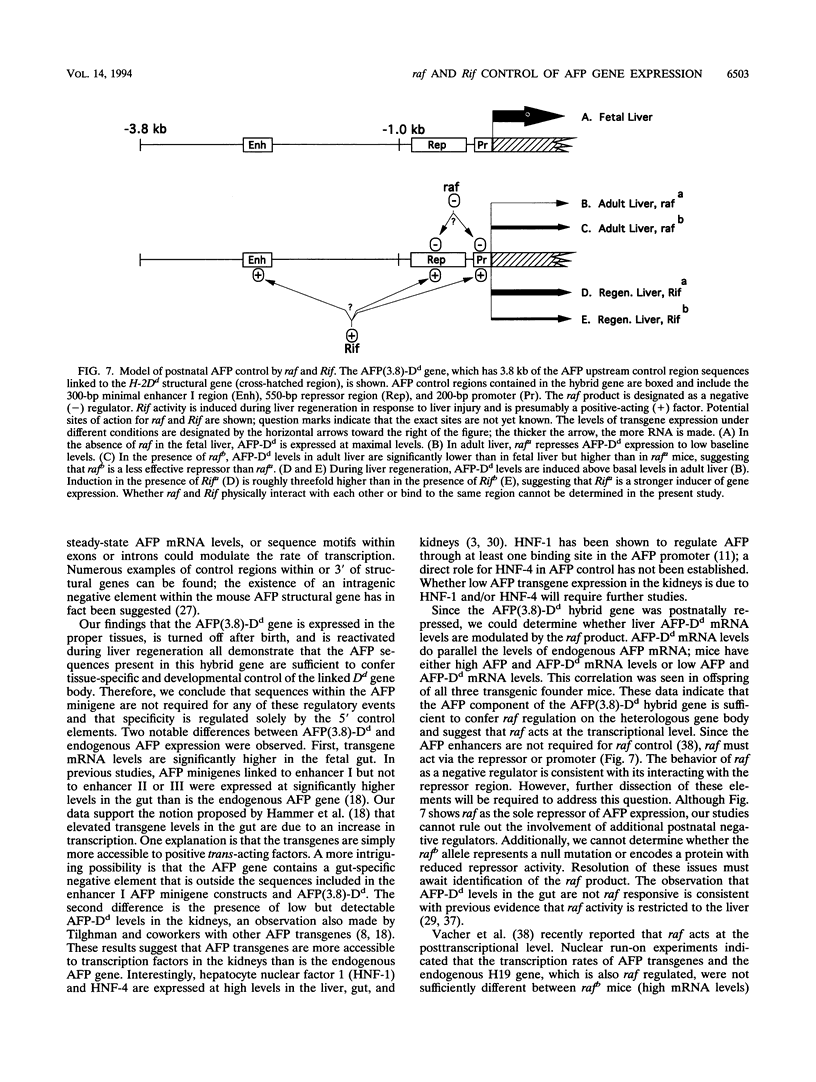
Abstract
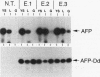
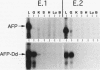
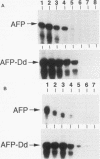
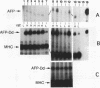
The mouse alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) gene is expressed at high levels in the yolk sac and fetal liver and at low levels in the fetal gut. AFP synthesis decreases dramatically shortly after birth to low levels that are maintained in the adult liver and gut. AFP expression can be reactivated in the adult liver upon renewed cell proliferation such as during liver regeneration or in hepatocellular carcinomas. Previously, two unlinked genetic loci that modulate postnatal AFP levels were identified. The raf locus controls, at least in part, basal steady-state AFP mRNA levels in adult liver. Rif influences the extent of AFP mRNA induction during liver regeneration. Transgenic mice were used to examine the role of 5' AFP regulatory regions in raf- and Rif-mediated control. A fragment of the AFP 5' region containing enhancer element I, the repressor, and the promoter was linked to the mouse class I H-2Dd structural gene. We demonstrate that this hybrid AFP-Dd transgene is expressed in the appropriate tissues. In addition, it is postnatally repressed and reactivated during liver regeneration in parallel with the endogenous AFP gene. Therefore, proper transcriptional control does not require the AFP structural gene. Furthermore, the AFP 5' control region is sufficient to confer raf and Rif responsiveness to the linked H-2Dd structural gene, suggesting that raf and Rif act at the level of transcriptional initiation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelev G. I. Alpha-fetoprotein in ontogenesis and its association with malignant tumors. Adv Cancer Res. 1971;14:295–358. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumhueter S., Mendel D. B., Conley P. B., Kuo C. J., Turk C., Graves M. K., Edwards C. A., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 shares three sequence motifs with the POU domain proteins and is identical to LF-B1 and APF. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):372–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belayew A., Tilghman S. M. Genetic analysis of alpha-fetoprotein synthesis in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1427–1435. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Flores O., Krauskopf A., Reinberg D., Aloni Y. Role of the mammalian transcription factors IIF, IIS, and IIX during elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1195–1206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernuau D., Poliard A., Feldmann G. In situ cellular analysis of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in regenerating rat liver after partial hepatectomy. Hepatology. 1988 Sep-Oct;8(5):997–1005. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenhorn E. P., Duncan R., Huppi K., Potter M. Chromosomal location of the regulator of mouse alpha-fetoprotein, Afr-1. Genetics. 1988 Jul;119(3):687–691. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.3.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper S. A., Tilghman S. M. Postnatal repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene is enhancer independent. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):537–546. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Margulies D. H., Shykind B., Seidman J. G., Ozato K. Exon shuffling: mapping polymorphic determinants on hybrid mouse transplantation antigens. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):755–757. doi: 10.1038/300755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreri K., Gill G., Montminy M. The cAMP-regulated transcription factor CREB interacts with a component of the TFIID complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1210–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerman M. H., Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Tissue-specific transcription of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene promoter is dependent on HNF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4204–4212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Burton Z., Greenblatt J., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. RNA polymerase II-associating protein 30 is an essential component of transcription factor IIF. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10812–10816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Pascal E., Tseng Z. H., Tjian R. A glutamine-rich hydrophobic patch in transcription factor Sp1 contacts the dTAFII110 component of the Drosophila TFIID complex and mediates transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):192–196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Tjian R. Eukaryotic coactivators associated with the TATA box binding protein. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Fine-structure mapping of the three mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R., Tilghman S. M. Multiple regulatory elements in the intergenic region between the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):477–487. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Hoey T., Thut C. J., Admon A., Tjian R. Drosophila TAFII40 interacts with both a VP16 activation domain and the basal transcription factor TFIIB. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):519–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90386-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Krumlauf R., Camper S. A., Brinster R. L., Tilghman S. M. Diversity of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in mice is generated by a combination of separate enhancer elements. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2432657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Lucito R. Elements required for transcription initiation of the human U2 snRNA gene coincide with elements required for snRNA 3' end formation. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3125–3134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L., Robertson E. J., Bikoff E. K. Developmental failure of chimeric embryos expressing high levels of H-2Dd transplantation antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5927–5931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalanko H. Alpha-fetoprotein and gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase in mice. Effect of Raf gene. Int J Cancer. 1979 Oct 15;24(4):394–397. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Hammer R. E., Tilghman S. M., Brinster R. L. Developmental regulation of alpha-fetoprotein genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1639–1648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty M., Das P. K., Mittal A., Nayak N. C. Cellular basis of induced alpha-fetoprotein synthesis by hepatocytes of adult mouse after hepatotoxic injury and partial hepatectomy. Int J Cancer. 1978 Aug 15;22(2):181–188. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molné M., Houart C., Szpirer J., Szpirer C. Combinatorial control of positive and negative, upstream and intragenic regulatory DNA domains of the mouse alpha 1-foetoprotein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3447–3457. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson M., Lindahl G., Ruoslahti E. Genetic control of alpha-fetoprotein synthesis in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1977 Apr 1;145(4):819–827. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.4.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachnis V., Belayew A., Tilghman S. M. Locus unlinked to alpha-fetoprotein under the control of the murine raf and Rif genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5523–5527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear B. T., Tilghman S. M. Role of alpha-fetoprotein regulatory elements in transcriptional activation in transient heterokaryons. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5047–5054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Belayew A. Transcriptional control of the murine albumin/alpha-fetoprotein locus during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5254–5257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M. The structure and regulation of the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1985;2:160–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuczek H. V., Fritz P., Wagner T., Braun U., Grau A., Wegner G. Synthesis of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and cell proliferation in regenerating livers of NMRI mice after partial hepatectomy. An immunohistochemical and autoradiographic study with 3H-thymidine. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;38(2):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF02892817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyner A. L., Godbout R., Compton R. S., Tilghman S. M. The ontogeny of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in the mouse gastrointestinal tract. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):915–927. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacher J., Camper S. A., Krumlauf R., Compton R. S., Tilghman S. M. raf regulates the postnatal repression of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene at the posttranscriptional level. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):856–864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacher J., Tilghman S. M. Dominant negative regulation of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene in adult liver. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1732–1735. doi: 10.1126/science.1702902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen P., Groupp E. R., Buzard G., Crawford N., Locker J. Enhancer, repressor, and promoter specificities combine to regulate the rat alpha-fetoprotein gene. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;10(7):525–536. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]