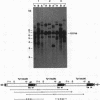
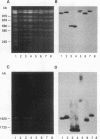
Abstract
Integration of the yeast retrotransposon Ty1 into the genome requires the self-encoded integrase (IN) protein and specific terminal nucleotides present on full-length Ty1 cDNA. Ty1 mutants with defects in IN, the conserved termini of Ty1 cDNA, or priming plus-strand DNA synthesis, however, were still able to efficiently insert into the genome when the elements were expressed from the GAL1 promoter present on a multicopy plasmid. As with normal transposition, formation of the exceptional insertions required an RNA intermediate, Ty1 reverse transcriptase, and Ty1 protease. In contrast to Ty1 transposition, at least 70% of the chromosomal insertions consisted of complex multimeric Ty1 elements. Ty1 cDNA was transferred to the inducing plasmid as well as to the genome, and transfer required the recombination and repair gene RAD52. Furthermore, multimeric insertions occurred without altering the levels of total Ty1 RNA, virus-like particle-associated RNA or cDNA, Ty1 capsid proteins, or IN. These results suggest that Ty1 cDNA is utilized much more efficiently for homologous recombination when IN-mediated integration is blocked.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. E., Mellor J., Gull K., Sim R. B., Tuite M. F., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. The functions and relationships of Ty-VLP proteins in yeast reflect those of mammalian retroviral proteins. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90761-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Eichinger D., Castrillon D., Fink G. R. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome contains functional and nonfunctional copies of transposon Ty1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1432–1442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SPT3 gene is required for transposition and transpositional recombination of chromosomal Ty elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3575–3581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiterman L. T., Monokian G. M., Eichinger D. J., Merbs S. L., Gabriel A., Boeke J. D. In-frame linker insertion mutagenesis of yeast transposon Ty1: phenotypic analysis. Gene. 1994 Feb 11;139(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90518-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns N. R., Saibil H. R., White N. S., Pardon J. F., Timmins P. A., Richardson S. M., Richards B. M., Adams S. E., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. Symmetry, flexibility and permeability in the structure of yeast retrotransposon virus-like particles. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1155–1164. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05156.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. Organization of DNA sequences and replication origins at yeast telomeres. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman K. B., Byström A. S., Boeke J. D. Initiator methionine tRNA is essential for Ty1 transposition in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3236–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curcio M. J., Garfinkel D. J. Single-step selection for Ty1 element retrotransposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):936–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curcio M. J., Hedge A. M., Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J. Ty RNA levels determine the spectrum of retrotransposition events that activate gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jan;220(2):213–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00260484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derr L. K., Strathern J. N. A role for reverse transcripts in gene conversion. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):170–173. doi: 10.1038/361170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derr L. K., Strathern J. N., Garfinkel D. J. RNA-mediated recombination in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski B. A., Feng Q., Mathias S. L., Sassaman D. M., Scott A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boeke J. D. An in vivo assay for the reverse transcriptase of human retrotransposon L1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4485–4492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger D. J., Boeke J. D. A specific terminal structure is required for Ty1 transposition. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):324–330. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger D. J., Boeke J. D. The DNA intermediate in yeast Ty1 element transposition copurifies with virus-like particles: cell-free Ty1 transposition. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):955–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid repair in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):70–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.70-102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Ty element transposition: reverse transcriptase and virus-like particles. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):507–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Hedge A. M., Youngren S. D., Copeland T. D. Proteolytic processing of pol-TYB proteins from the yeast retrotransposon Ty1. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4573–4581. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4573-4581.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Blackburn E. H. An alternative pathway for yeast telomere maintenance rescues est1- senescence. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90234-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo M. F., Weinstock K. G., Shafer B. K., Hedge A. M., Garfinkel D. J., Strathern J. N. Disruption of a silencer domain by a retrotransposon. Genetics. 1992 Jul;131(3):519–529. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed C., Nevo Y., Kupiec M. Involvement of cDNA in homologous recombination between Ty elements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1613–1620. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monokian G. M., Braiterman L. T., Boeke J. D. In-frame linker insertion mutagenesis of yeast transposon Ty1: mutations, transposition and dominance. Gene. 1994 Feb 11;139(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90517-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Brühl K. H., Freidel K., Kowallik K. V., Ciriacy M. Processing of TY1 proteins and formation of Ty1 virus-like particles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):421–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00331610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Laufer W., Pott U., Ciriacy M. Characterization of products of TY1-mediated reverse transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):145–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00273598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquin C. E., Williamson V. M. Temperature effects on the rate of ty transposition. Science. 1984 Oct 5;226(4670):53–55. doi: 10.1126/science.226.4670.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Mann C., Davis R. W. Reversion of a promoter deletion in yeast. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):815–819. doi: 10.1038/298815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Bieker J. J., Dumas L. B. Genetic transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with single-stranded circular DNA vectors. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A. M. Retroviral proteases: first glimpses at the anatomy of a processing machine. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):911–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90621-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J. N., Higgins D. R. Recovery of plasmids from yeast into Escherichia coli: shuttle vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:319–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton P. R., Liebman S. W. Rearrangements occurring adjacent to a single Ty1 yeast retrotransposon in the presence and absence of full-length Ty1 transcription. Genetics. 1992 Aug;131(4):833–850. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Origin of retroviruses from cellular moveable genetic elements. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voytas D. F., Boeke J. D. Yeast retrotransposon revealed. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):717–717. doi: 10.1038/358717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder R. Y., Walder J. A. Oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis using the yeast transformation system. Gene. 1986;42(2):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Doyle M. V., Mark D. F. Quantitation of mRNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock K. G., Mastrangelo M. F., Burkett T. J., Garfinkel D. J., Strathern J. N. Multimeric arrays of the yeast retrotransposon Ty. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2882–2892. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Durbin K. J., Fink G. R. The SPT3 gene is required for normal transcription of Ty elements in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90474-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H., Boeke J. D. Localization of sequences required in cis for yeast Ty1 element transposition near the long terminal repeats: analysis of mini-Ty1 elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2695–2702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimatsu T., Nagawa F. Control of gene expression by artificial introns in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1346–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.2544026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngren S. D., Boeke J. D., Sanders N. J., Garfinkel D. J. Functional organization of the retrotransposon Ty from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Ty protease is required for transposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1421–1431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A., Blanton H. M. Distribution of telomere-associated sequences on natural chromosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2257–2260. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]