Abstract
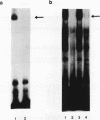
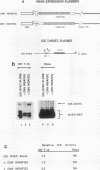
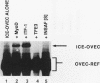
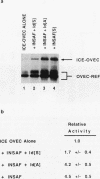
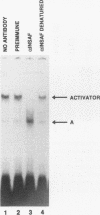
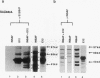
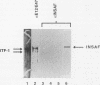
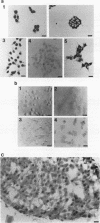
Pancreatic beta-cell-type-specific transcription of the insulin gene is principally regulated by a single cis-acting DNA sequence element, termed the insulin control element (ICE), which is found within the 5'-flanking region of the gene. The ICE activator is a heteromeric complex composed of an islet alpha/beta-cell-specific factor associated with the ubiquitously distributed E2A-encoded proteins (E12, E47, and E2-5). We describe the isolation and characterization of a cDNA for a protein present in alpha and beta cells, termed INSAF for insulin activator factor, which binds to and activates ICE-mediated expression. INSAF was isolated from a human insulinoma cDNA library. Transfection experiments demonstrated that INSAF activates ICE expression in insulin-expressing cells but not in non-insulin-expressing cells. Cotransfection experiments showed that activation by INSAF was inhibited by Id, a negative regulator of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) protein function. INSAF was also shown to associate in vitro with the bHLH protein E12. In addition, affinity-purified INSAF antiserum abolished the formation of the activator-specific ICE-binding complex. Immunohistochemical studies indicate that INSAF is restricted in terms of its expression pattern, in that INSAF appears to be detected only within the nuclei of islet pancreatic alpha and beta cells. All of these data are consistent with the proposal that INSAF is either part of the ICE activator or is antigenically related to the specific activator required for insulin gene transcription.
Full text
PDF


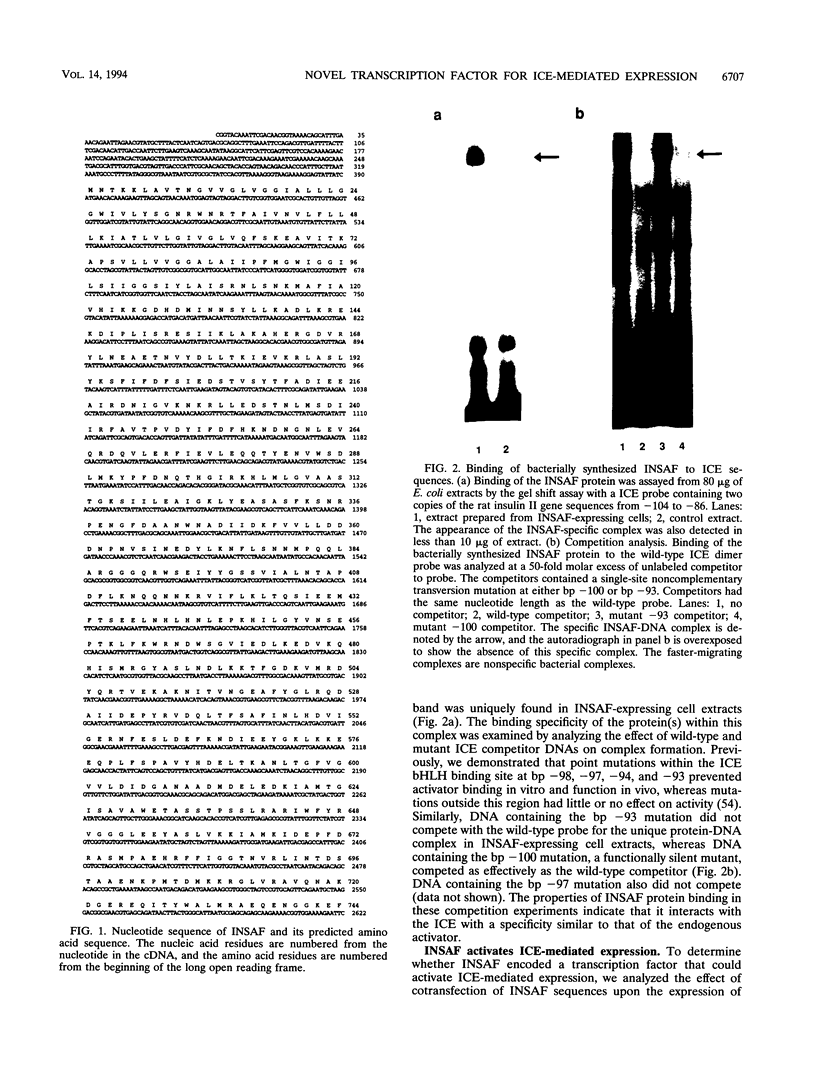

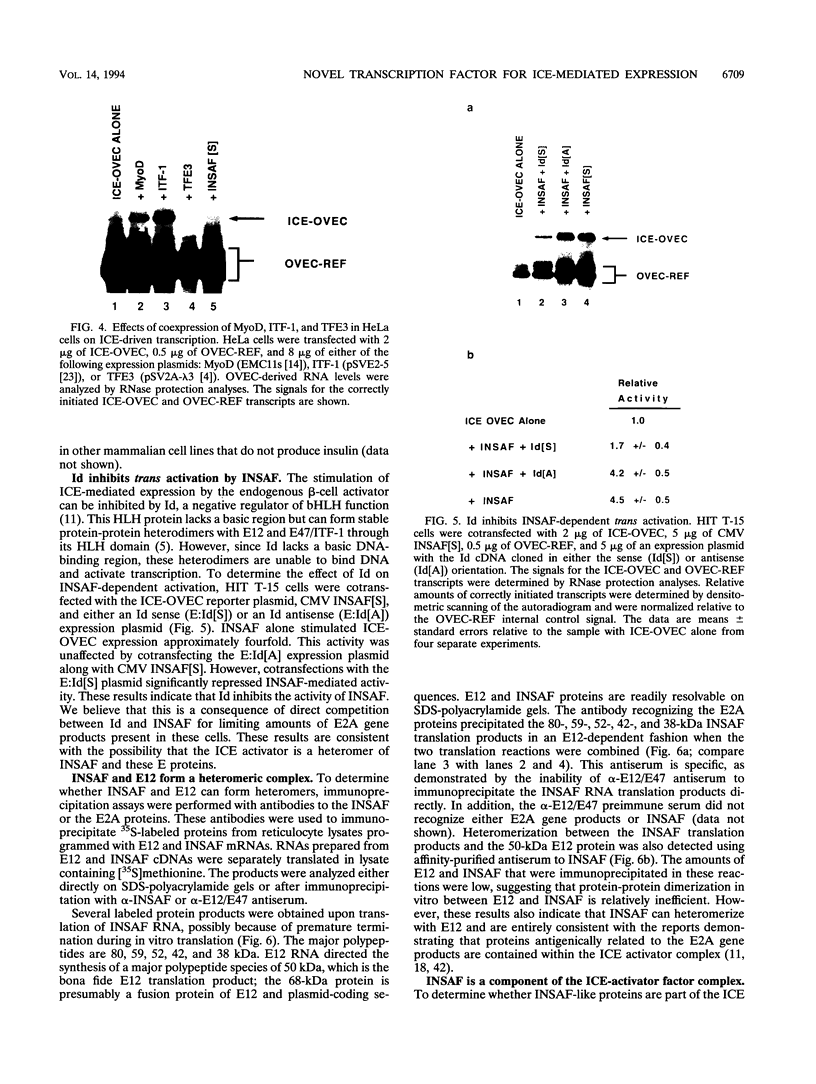
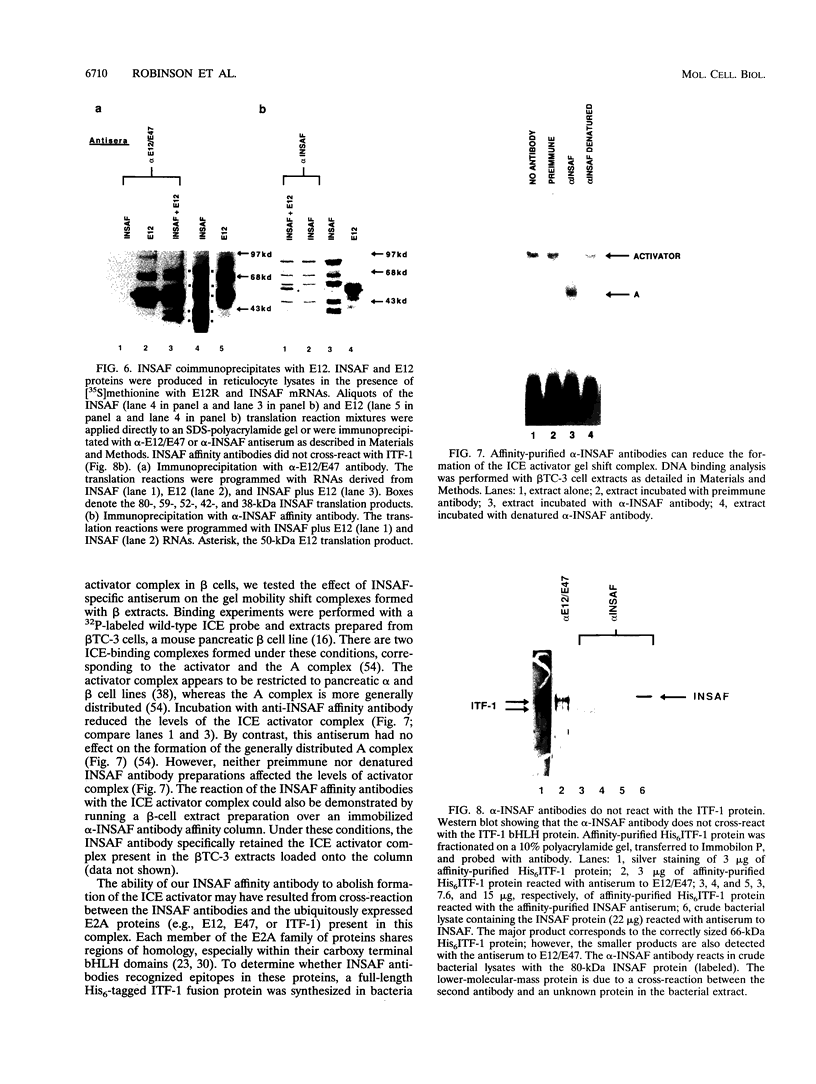




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S., Hanahan D., Teitelman G. Hybrid insulin genes reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cells and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Ransone L., Scharfmann R., Dwarki V. J., Tapscott S. J., Weintraub H., Verma I. M. Functional antagonism between c-Jun and MyoD proteins: a direct physical association. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90187-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Cory S., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Adams J. M. Sequence of the murine and human cellular myc oncogenes and two modes of myc transcription resulting from chromosome translocation in B lymphoid tumours. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2375–2383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedler J. L., Helson L., Spengler B. A. Morphology and growth, tumorigenicity, and cytogenetics of human neuroblastoma cells in continuous culture. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2643–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucchini D., Ripoche M. A., Stinnakre M. G., Desbois P., Lorès P., Monthioux E., Absil J., Lepesant J. A., Pictet R., Jami J. Pancreatic expression of human insulin gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2511–2515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordle S. R., Henderson E., Masuoka H., Weil P. A., Stein R. Pancreatic beta-cell-type-specific transcription of the insulin gene is mediated by basic helix-loop-helix DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1734–1738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordle S. R., Whelan J., Henderson E., Masuoka H., Weil P. A., Stein R. Insulin gene expression in nonexpressing cells appears to be regulated by multiple distinct negative-acting control elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2881–2886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe D. T., Tsai M. J. Mutagenesis of the rat insulin II 5'-flanking region defines sequences important for expression in HIT cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1784–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Linde S., Kofod H., Spector D., Delannoy M., Grant S., Hanahan D., Baekkeskov S. Beta-cell lines derived from transgenic mice expressing a hybrid insulin gene-oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9037–9041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromont-Racine M., Bucchini D., Madsen O., Desbois P., Linde S., Nielsen J. H., Saulnier C., Ripoche M. A., Jami J., Pictet R. Effect of 5'-flanking sequence deletions on expression of the human insulin gene in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 May;4(5):669–677. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-5-669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Blanar M. A., Nelson C., Moss L. G., Rutter W. J. Two related helix-loop-helix proteins participate in separate cell-specific complexes that bind the insulin enhancer. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):292–299. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi K., Leiter E. H. Comparison of cytokine effects on mouse pancreatic alpha-cell and beta-cell lines. Viability, secretory function, and MHC antigen expression. Diabetes. 1990 Apr;39(4):415–425. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Stein R. c-jun inhibits transcriptional activation by the insulin enhancer, and the insulin control element is the target of control. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):655–662. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwung Y. P., Gu Y. Z., Tsai M. J. Cooperativity of sequence elements mediates tissue specificity of the rat insulin II gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1784–1788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Edlund T., Moss J. B., Rutter W. J., Walker M. D. A mutational analysis of the insulin gene transcription control region: expression in beta cells is dependent on two related sequences within the enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8819–8823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J., Edlund T. Individual protein-binding domains of the insulin gene enhancer positively activate beta-cell-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):823–827. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J. Regulation of rat insulin 1 gene expression: evidence for negative regulation in nonpancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Thor S., Edlund T. Novel insulin promoter- and enhancer-binding proteins that discriminate between pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):897–904. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. W., Walker M. D. Subunit structure of cell-specific E box-binding proteins analyzed by quantitation of electrophoretic mobility shift. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15642–15649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peshavaria M., Gamer L., Henderson E., Teitelman G., Wright C. V., Stein R. XIHbox 8, an endoderm-specific Xenopus homeodomain protein, is closely related to a mammalian insulin gene transcription factor. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Jun;8(6):806–816. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.6.7935494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Drucker D. J., Knepel W., Jepeal L., Misulovin Z., Habener J. F. Alpha-cell-specific expression of the glucagon gene is conferred to the glucagon promoter element by the interactions of DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4877–4888. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. L., Peshavaria M., Henderson E., Shieh S. Y., Tsai M. J., Teitelman G., Stein R. Expression of the trans-active factors that stimulate insulin control element-mediated activity appear to precede insulin gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2452–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Skośkiewicz M. J., Howie K. B., Russell P. S., Goodman H. M. Regulation of human insulin gene expression in transgenic mice. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):525–528. doi: 10.1038/321525a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A., Stein R. Glucose-induced transcription of the insulin gene is mediated by factors required for beta-cell-type-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):871–879. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen G. H., Grundemar L., Zukowska-Grojec Z., Håkanson R., Wahlestedt C. C-terminal neuropeptide Y fragments are mast cell-dependent vasodepressor agents. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov 12;204(3):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90849-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh S. Y., Tsai M. J. Cell-specific and ubiquitous factors are responsible for the enhancer activity of the rat insulin II gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16708–16714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Chan S. J., Welsh J. M., Kwok S. C. Structure and evolution of the insulin gene. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:463–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler F., Håkanson R., Larsson L. I. Ontogeny of rat pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Mar 16;178(3):303–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00218694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Linkage of the brain-skin-gut axis: islet cells originate from dopaminergic precursors. Peptides. 1981;2 (Suppl 2):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(81)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Lee J. K. Cell lineage analysis of pancreatic islet development: glucagon and insulin cells arise from catecholaminergic precursors present in the pancreatic duct. Dev Biol. 1987 Jun;121(2):454–466. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. Positive autoregulation of the myogenic determination gene MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90838-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Gerster T., Müller M. M., Schaffner G., Schaffner W. OVEC, a versatile system to study transcription in mammalian cells and cell-free extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6787–6798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Cordle S. R., Henderson E., Weil P. A., Stein R. Identification of a pancreatic beta-cell insulin gene transcription factor that binds to and appears to activate cell-type-specific expression: its possible relationship to other cellular factors that bind to a common insulin gene sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1564–1572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Poon D., Weil P. A., Stein R. Pancreatic beta-cell-type-specific expression of the rat insulin II gene is controlled by positive and negative cellular transcriptional elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3253–3259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]