Abstract
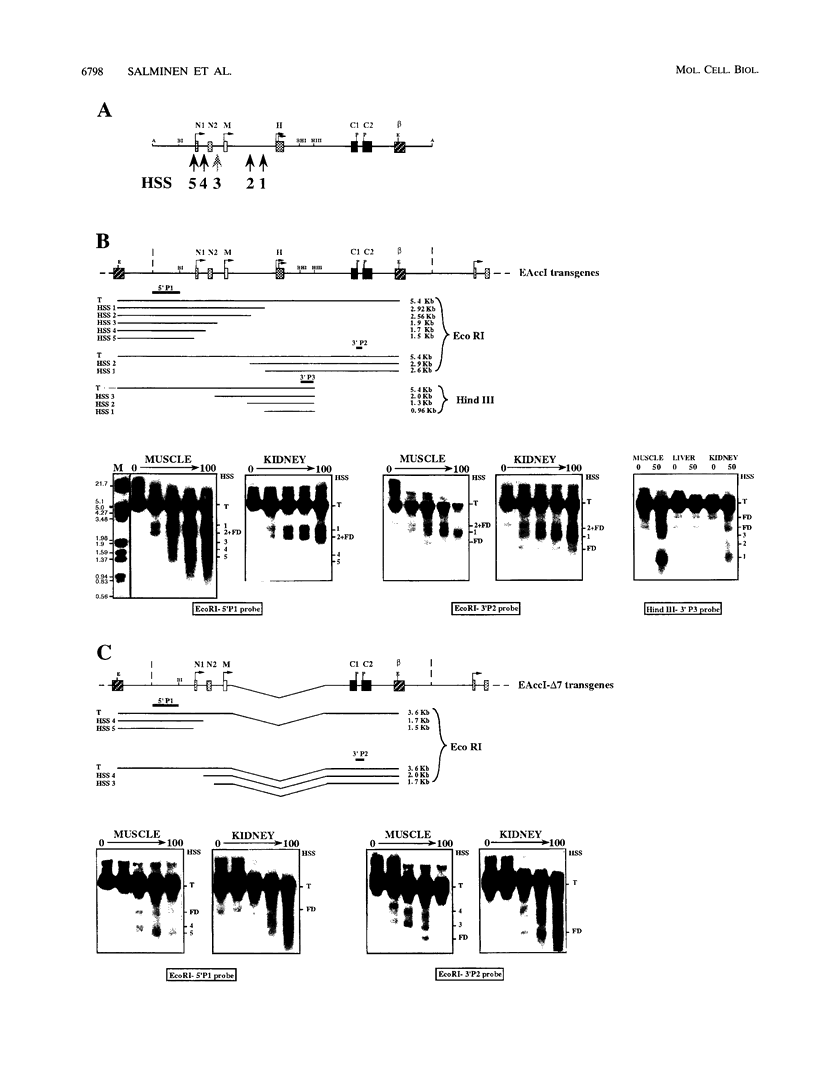
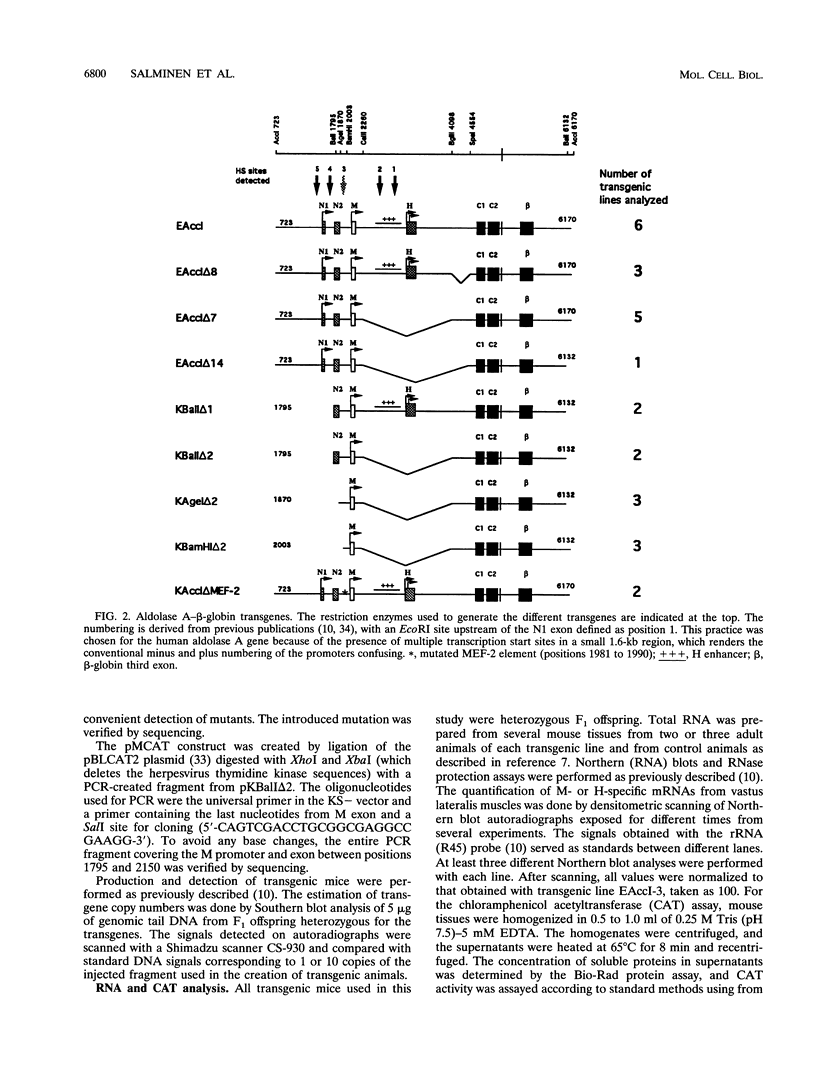
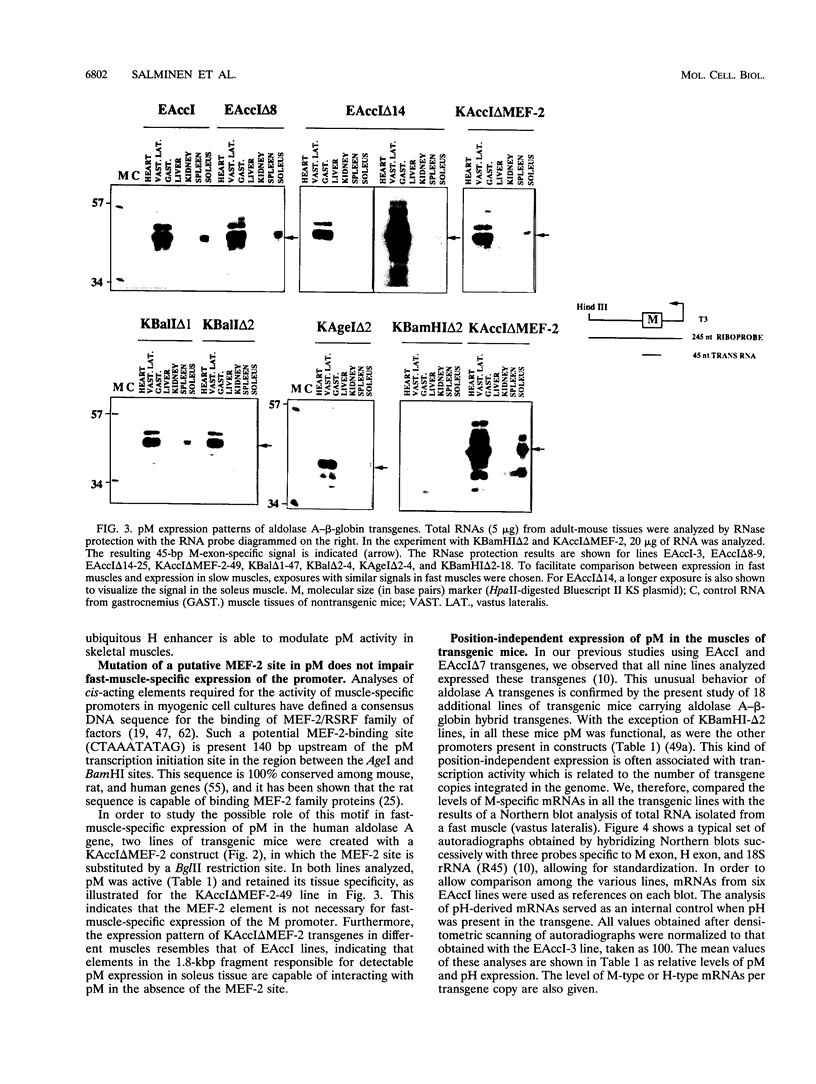
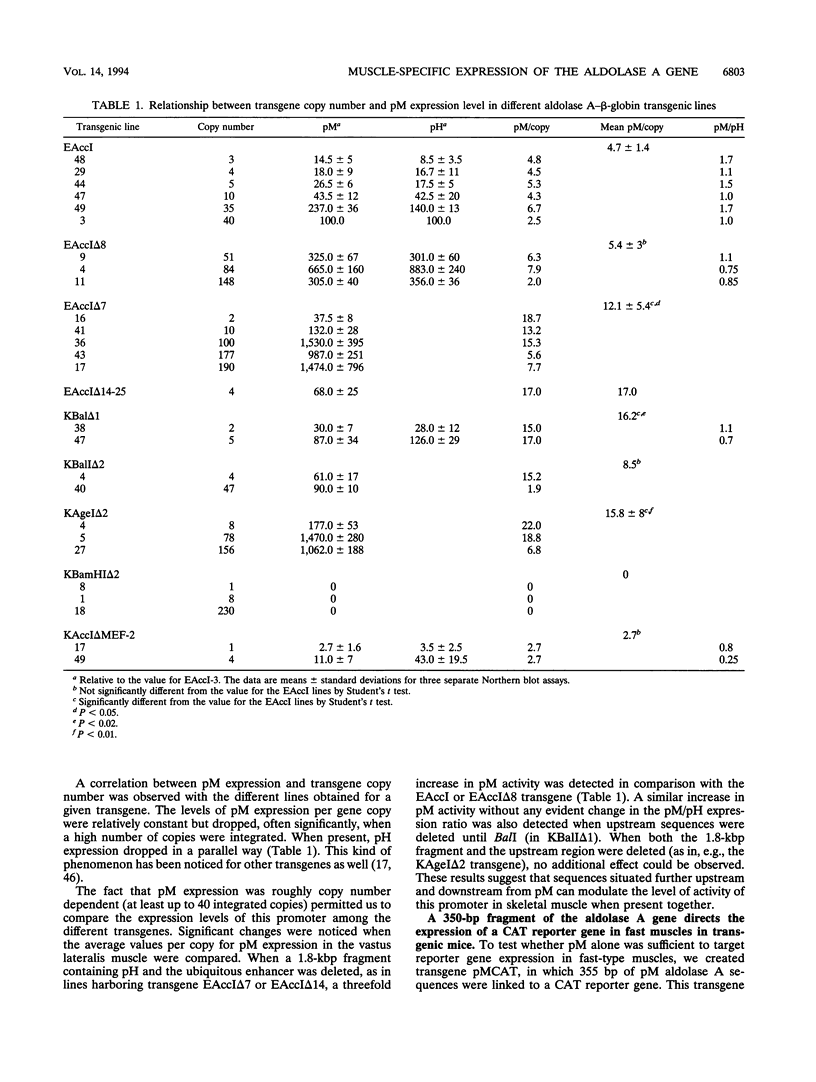
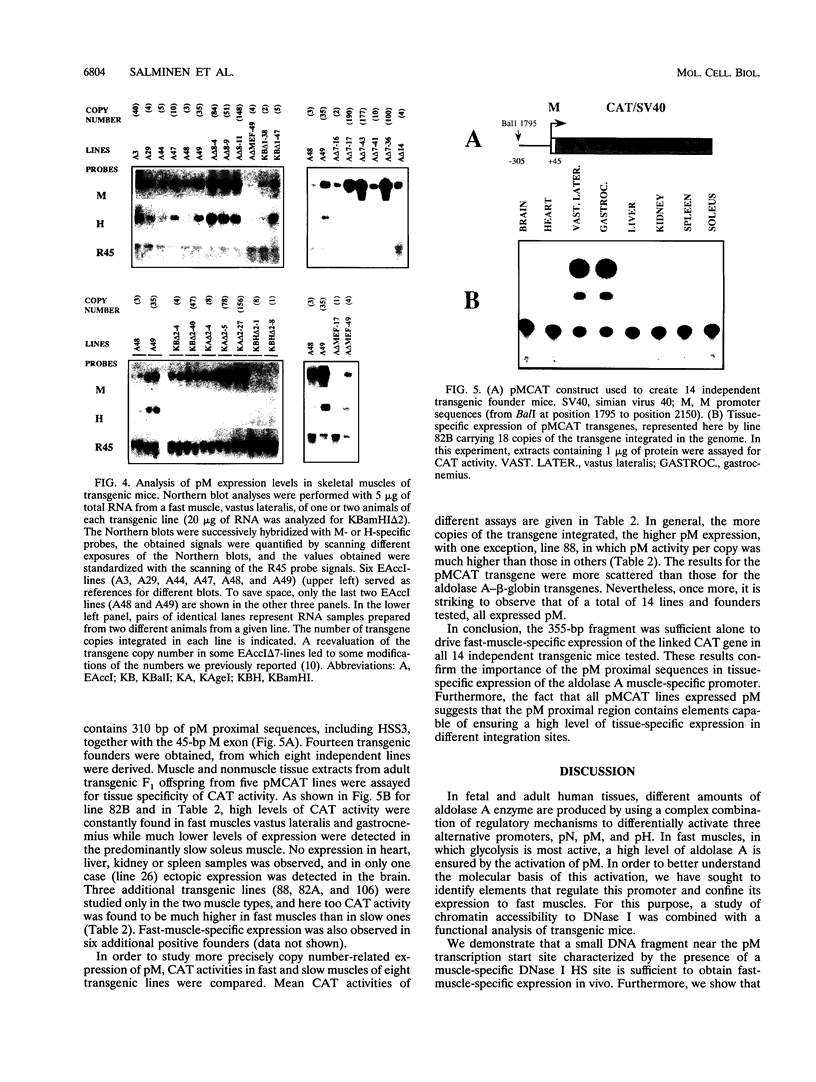
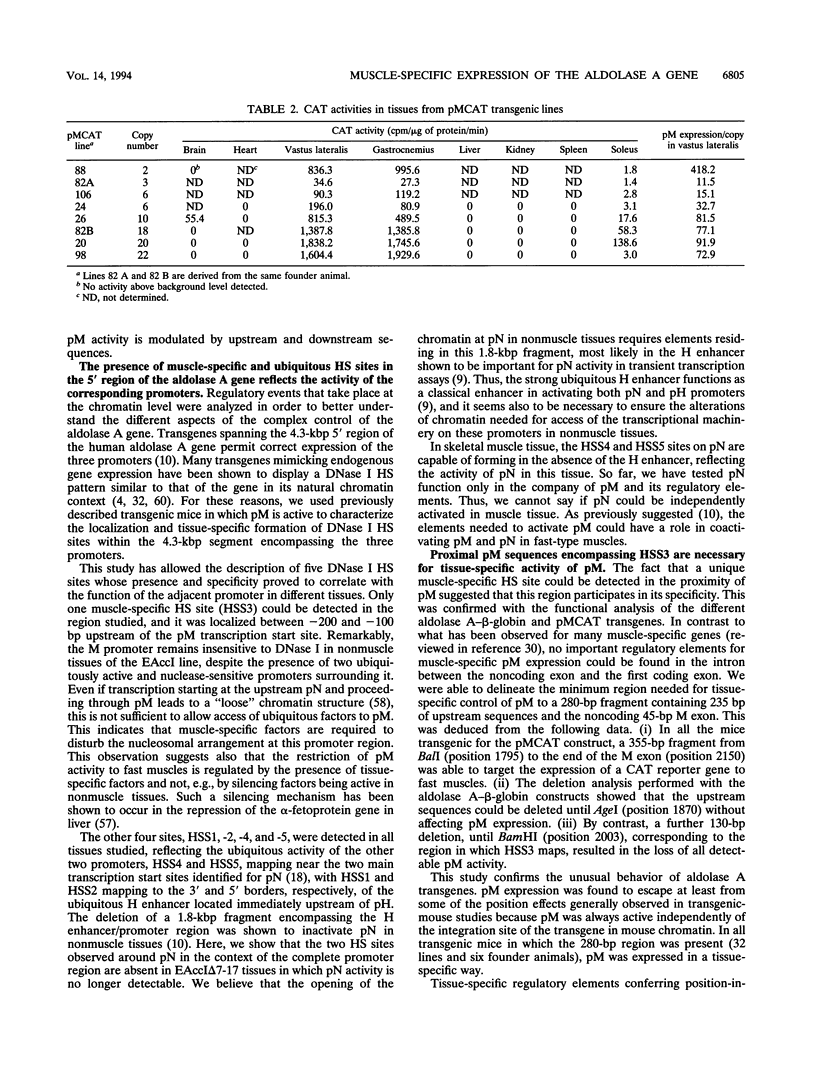
The expression of the human aldolase A gene is controlled by three alternative promoters. In transgenic mice, pN and pH are active in all tissues whereas pM is activated specifically in adult muscles composed mainly of fast, glycolytic fibers. To detect potential regulatory regions involved in the fast-muscle-specific activation of pM, we analyzed DNase I hypersensitivity in a 4.3-kbp fragment from the 5' end of the human aldolase A gene. Five hypersensitive sites were located near the transcription initiation site of each promoter in those transgenic-mouse tissues in which the corresponding promoter was active. Only one muscle-specific hypersensitive site was detected, mapping near pM. To functionally delimit the elements required for muscle-specific activity of pM, we performed a deletion analysis of the aldolase A 5' region in transgenic mice. Our results show that a 280-bp fragment containing 235 bp of pM proximal upstream sequences together with the noncoding M exon is sufficient for tissue-specific expression of pM. When a putative MEF-2-binding site residing in this proximal pM region is mutated, pM is still active and no change in its tissue specificity is detected. Furthermore, we observed a modulation of pM activity by elements lying further upstream and downstream from pM. Interestingly, pM was expressed in a tissue-specific way in all transgenic mice in which the 280-bp region was present (32 lines and six founder animals). This observation led us to suggest that the proximal pM region contains elements that are able to override to some extent the effects of the surrounding chromatin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronow B. J., Silbiger R. N., Dusing M. R., Stock J. L., Yager K. L., Potter S. S., Hutton J. J., Wiginton D. A. Functional analysis of the human adenosine deaminase gene thymic regulatory region and its ability to generate position-independent transgene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4170–4185. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandman E. Contractile protein isoforms in muscle development. Dev Biol. 1992 Dec;154(2):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90067-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bober E., Lyons G. E., Braun T., Cossu G., Buckingham M., Arnold H. H. The muscle regulatory gene, Myf-6, has a biphasic pattern of expression during early mouse development. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1255–1265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet D., Vaulont S., Tremp G., Ripoche M. A., Daegelen D., Jami J., Kahn A., Raymondjean M. DNase-I hypersensitivity analysis of the L-type pyruvate kinase gene in rats and transgenic mice. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 1;207(1):13–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. W., Vasavada H. A., Ganguly S., Weissman S. M. Identification of cis sequences controlling efficient position-independent tissue-specific expression of human major histocompatibility complex class I genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T. C., Wallace M. C., Merlie J. P., Olson E. N. Separable regulatory elements governing myogenin transcription in mouse embryogenesis. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):215–218. doi: 10.1126/science.8392225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert M. C., Ciejek-Baez E. The proximal promoter of the aldolase A gene remains active during myogenesis in vitro and muscle development in vivo. Dev Biol. 1992 Jan;149(1):66–79. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90264-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concordet J. P., Maire P., Kahn A., Daegelen D. A ubiquitous enhancer shared by two promoters in the human aldolase A gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4173–4180. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concordet J. P., Salminen M., Demignon J., Moch C., Maire P., Kahn A., Daegelen D. An opportunistic promoter sharing regulatory sequences with either a muscle-specific or a ubiquitous promoter in the human aldolase A gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):9–17. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley M., Orkin S. H. Regulation of the beta-globin locus. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):232–237. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90028-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M. J., Alvarez J. D., Merlie J. P., Sanes J. R. Fiber type- and position-dependent expression of a myosin light chain-CAT transgene detected with a novel histochemical stain for CAT. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):423–434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Cheng T. C., Cserjesi P., Chakraborty T., Olson E. N. Analysis of the myogenin promoter reveals an indirect pathway for positive autoregulation mediated by the muscle-specific enhancer factor MEF-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3665–3677. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. Helix-loop-helix proteins as regulators of muscle-specific transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):755–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epner E., Kim C. G., Groudine M. What does the locus control region control? Curr Biol. 1992 May;2(5):262–264. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90379-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P., Hurst J., Collis P., Grosveld F. DNaseI hypersensitive sites 1, 2 and 3 of the human beta-globin dominant control region direct position-independent expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3503–3508. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautron S., Maire P., Hakim V., Kahn A. Regulation of the multiple promoters of the human aldolase A gene: response of its two ubiquitous promoters to agents promoting cell proliferation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):767–774. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Wilson F. D., Lang G., Kioussis D. Human CD2 3'-flanking sequences confer high-level, T cell-specific, position-independent gene expression in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallauer P. L., Bradshaw H. L., Hastings K. E. Complex fiber-type-specific expression of fast skeletal muscle troponin I gene constructs in transgenic mice. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):691–701. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka K., Yamamoto I., Arai Y., Mukai T. The MEF-3 motif is required for MEF-2-mediated skeletal muscle-specific induction of the rat aldolase A gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6469–6478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Wood W. G., Jarman A. P., Sharpe J., Lida J., Pretorius I. M., Ayyub H. A major positive regulatory region located far upstream of the human alpha-globin gene locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1588–1601. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämäläinen N., Pette D. The histochemical profiles of fast fiber types IIB, IID, and IIA in skeletal muscles of mouse, rat, and rabbit. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 May;41(5):733–743. doi: 10.1177/41.5.8468455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo P., Costanzo P., Lupo A., Rippa E., Paolella G., Salvatore F. Human aldolase A gene. Structural organization and tissue-specific expression by multiple promoters and alternate mRNA processing. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):569–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Transgenic animals. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1468–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.3287623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Complex regulation of the muscle-specific contractile protein (troponin I) gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3065–3075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey C. H., Bodine D. M., Nienhuis A. W. Mechanism of DNase I hypersensitive site formation within the human globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1143–1147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Gautron S., Hakim V., Gregori C., Mennecier F., Kahn A. Characterization of three optional promoters in the 5' region of the human aldolase A gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 5;197(3):425–438. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90556-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor, a novel trans-acting factor governing muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4271–4283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Everitt E. A., Smith T. H., Block N. E., Dominov J. A. Cellular and molecular diversity in skeletal muscle development: news from in vitro and in vivo. Bioessays. 1993 Mar;15(3):191–196. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B. Myoblast diversity in skeletal myogenesis: how much and to what end? Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90111-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neznanov N., Thorey I. S., Ceceña G., Oshima R. G. Transcriptional insulation of the human keratin 18 gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2214–2223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Globin gene regulation and switching: circa 1990. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Bober E., Lyons G., Arnold H., Buckingham M. Early expression of the myogenic regulatory gene, myf-5, in precursor cells of skeletal muscle in the mouse embryo. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1097–1107. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Sandgren E. P., Koeller D. M., Brinster R. L. Distal regulatory elements from the mouse metallothionein locus stimulate gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5266–5275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette D., Staron R. S. Cellular and molecular diversities of mammalian skeletal muscle fibers. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;116:1–76. doi: 10.1007/3540528806_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Talbot D., Fraser P., Grosveld F. The beta-globin dominant control region: hypersensitive site 2. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2159–2167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2327–2341. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Identification of MRF4: a new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2050–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicki M. A., Braun T., Hinuma S., Jaenisch R. Inactivation of MyoD in mice leads to up-regulation of the myogenic HLH gene Myf-5 and results in apparently normal muscle development. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90508-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. A., Miller J. B., Stockdale F. E. Cell diversification within the myogenic lineage: in vitro generation of two types of myoblasts from a single myogenic progenitor cell. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):659–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90244-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. H., Block N. E., Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F., Miller J. B. A unique pattern of expression of the four muscle regulatory factor proteins distinguishes somitic from embryonic, fetal and newborn mouse myogenic cells. Development. 1993 Mar;117(3):1125–1133. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.3.1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer J. K., Ciejek-Baez E. Autonomous activity of the alternate aldolase A muscle promoter is maintained by a sequestering mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):327–336. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer J. K., Colbert M. C., Ciejek-Baez E. Nonconservative utilization of aldolase A alternative promoters. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11773–11782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockdale F. E. Myogenic cell lineages. Dev Biol. 1992 Dec;154(2):284–298. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90068-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacher J., Tilghman S. M. Dominant negative regulation of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene in adult liver. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1732–1735. doi: 10.1126/science.1702902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas P., Vickers M. A., Simmons D. L., Ayyub H., Craddock C. F., Higgs D. R. Cis-acting sequences regulating expression of the human alpha-globin cluster lie within constitutively open chromatin. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):781–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90290-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Sell S. M., Butler-Browne G. S., Schwartz K., Bouveret P., Pinset-Härstöm I. Three myosin heavy-chain isozymes appear sequentially in rat muscle development. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):805–809. doi: 10.1038/292805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw C. B., Harris S., McClenaghan M., Simons J. P., Clark A. J. Position-independent expression of the ovine beta-lactoglobulin gene in transgenic mice. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 15;286(Pt 1):31–39. doi: 10.1042/bj2860031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Rigby P. W. The regulation of myogenin gene expression during the embryonic development of the mouse. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1277–1289. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Breitbart R. E., Smoot L. B., Lee Y., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Human myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2 comprises a group of tissue-restricted MADS box transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1783–1798. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]