Abstract
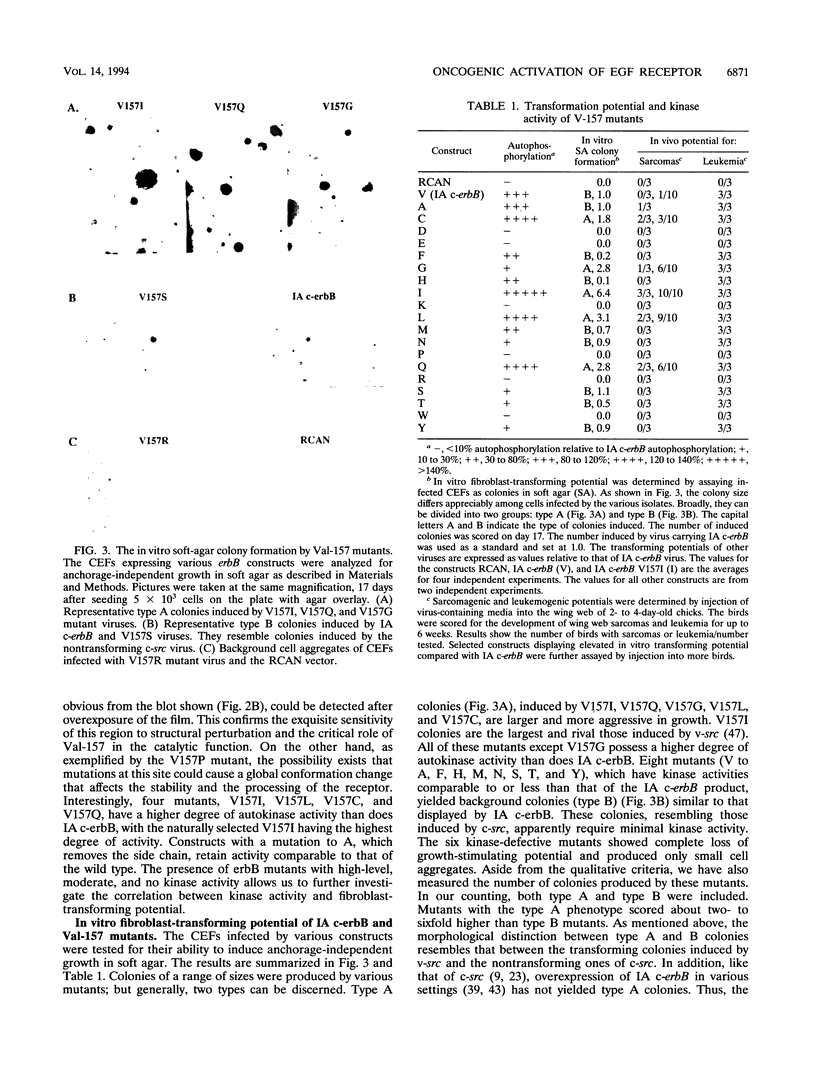
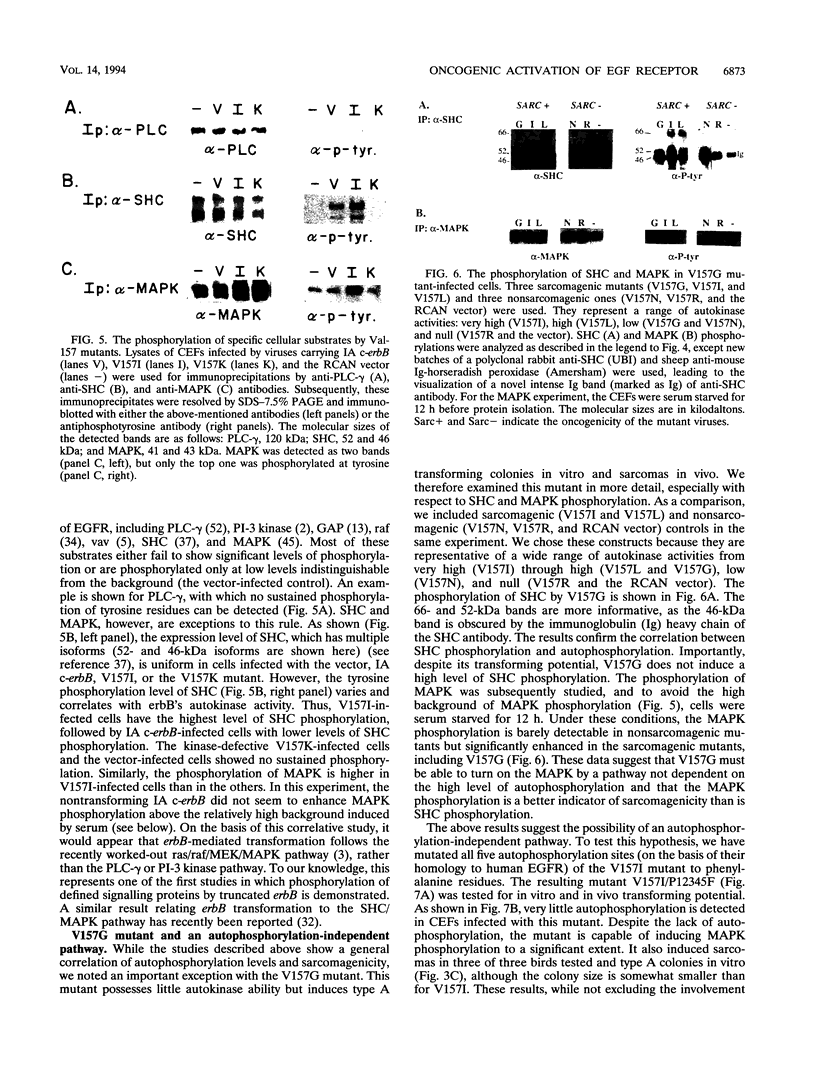
Avian c-erbB is activated to a leukemia oncogene following truncation of its amino-terminal ligand-binding domain by retroviral insertion. The insertionally activated transcripts encode protein products which have constitutive tyrosine kinase activity and can induce erythroleukemia but not sarcomas. We have previously found that a valine-to-isoleucine point mutation at position 157 (V157I mutant) within the tyrosine kinase domain of this truncated erbB can dramatically activate the sarcomagenic potential of the oncogene and increase the kinase activity of this oncoprotein. This mutation lies at position 157 of the insertionally activated c-erbB product, affecting a highly conserved valine residue of the glycine loop involved in ATP binding and phosphate transfer. To investigate the functional importance of this residue in the catalytic activity of kinases, we have introduced at this position, by site-directed mutagenesis, codons representing the remaining 18 amino acid residues. Most of the mutants have diminished activity, with six of them completely devoid of kinase activity, indicating the sensitivity of this region to conformational changes. Some of these mutants displayed increased kinase activity and greater transforming potential in comparison with IA c-erbB, but none had levels as high as those of the V157I mutant. In general, the sarcomagenic potential of the various erbB mutants correlated with their autophosphorylation state and their ability to cause phosphorylation of MAP kinase. However, there are important exceptions such as the V157G mutant, which lacks enhanced autophosphorylation but is highly sarcomagenic. Studies of this and other autophosphorylation site mutants point to the existence of an autophosphorylation-independent pathway in sarcomagenesis. The requirement for leukemogenic potential is much less stringent and correlates with positivity of kinase activity. When the valine-to-isoleucine substitution was put in context of the full-length erbB protein, the mutation relaxed the ligand dependence and had a positive effect on the transforming potential of the full-length c-erbB.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorge J. D., Chan T. O., Antczak M., Kung H. J., Fujita D. J. Activated type I phosphatidylinositol kinase is associated with the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor following EGF stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossemeyer D., Engh R. A., Kinzel V., Ponstingl H., Huber R. Phosphotransferase and substrate binding mechanism of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit from porcine heart as deduced from the 2.0 A structure of the complex with Mn2+ adenylyl imidodiphosphate and inhibitor peptide PKI(5-24). EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):849–859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05725.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustelo X. R., Ledbetter J. A., Barbacid M. Product of vav proto-oncogene defines a new class of tyrosine protein kinase substrates. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):68–71. doi: 10.1038/356068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrera A. C., Alexandrov K., Roberts T. M. The conserved lysine of the catalytic domain of protein kinases is actively involved in the phosphotransfer reaction and not required for anchoring ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Trainor C., Graf T., Beug H., Engel J. D. A single amino acid substitution in v-erbB confers a thermolabile phenotype to ts167 avian erythroblastosis virus-transformed erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1751–1759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens P. M., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Shalloway D. Restriction of the in vitro and in vivo tyrosine protein kinase activities of pp60c-src relative to pp60v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2753–2763. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90411-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flickinger T. W., Maihle N. J., Kung H. J. An alternatively processed mRNA from the avian c-erbB gene encodes a soluble, truncated form of the receptor that can block ligand-dependent transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):883–893. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Activation of the cellular oncogene c-erbB by LTR insertion: molecular basis for induction of erythroblastosis by avian leukosis virus. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Protein phosphorylation at tyrosine is induced by the v-erbB gene product in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hihara H., Yamamoto H., Shimohira H., Arai K., Shimizu T. Avian erythroblastosis virus isolated from chick erythroblastosis induced by lymphatic leukemia virus subgroup A. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 May;70(5):891–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Hormonal regulation of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene via a heterologous promoter defines a threshold dose for cellular transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Cadena D. L., Zheng J., Ten Eyck L. F., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M., Gill G. N. Structural features that specify tyrosine kinase activity deduced from homology modeling of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5001–5005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M., Perez C. F., Hardy C., Botchan M. Transformation mediated by the SV40 T antigens: separation of the overlapping SV40 early genes with a retroviral vector. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90503-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Johnson A., Howk R., Sap J., Bellot F., Winkler M., Ullrich A., Vennstrom B., Schlessinger J., Givol D. Chicken epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor: cDNA cloning, expression in mouse cells, and differential binding of EGF and transforming growth factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. B., Beug H., Hayman M. J. Mutational analysis of the role of the carboxy-terminal region of the v-erbB protein in erythroid cell transformation. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1317–1327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maihle N. J., Kung H. J. C-erbB and the epidermal growth-factor receptor: a molecule with dual identity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb;948(3):287–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B. L., Lax I., Kris R., Dombalagian M., Honegger A. M., Howk R., Givol D., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. All autophosphorylation sites of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor and HER2/neu are located in their carboxyl-terminal tails. Identification of a novel site in EGF receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10667–10671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoglia S., Gray A., Dull T. J., Munemitsu S., Kun H. J., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Epidermal growth factor receptor cytoplasmic domain mutations trigger ligand-independent transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3048–3055. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer S., LaBudda K., McGlade J., Hayman M. J. Analysis of the role of the Shc and Grb2 proteins in signal transduction by the v-ErbB protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3253–3262. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles B. D., Robinson H. L. High-frequency transduction of c-erbB in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):295–303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.295-303.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair N., Davis R. J., Robinson H. L. Protein tyrosine kinase activities of the epidermal growth factor receptor and ErbB proteins: correlation of oncogenic activation with altered kinetics. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2010–2016. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Crittenden L. B., Raines M. A., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in ALV-induced erythroblastosis: novel RNA processing and promoter insertion result in expression of an amino-truncated EGF receptor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci G., Lanfrancone L., Grignani F., McGlade J., Cavallo F., Forni G., Nicoletti I., Grignani F., Pawson T., Pelicci P. G. A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90536-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelley R. J., Maihle N. J., Boerkoel C., Shu H. K., Carter T. H., Moscovici C., Kung H. J. Disease tropism of c-erbB: effects of carboxyl-terminal tyrosine and internal mutations on tissue-specific transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7164–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelley R. J., Moscovici C., Hughes S., Kung H. J. Proviral-activated c-erbB is leukemogenic but not sarcomagenic: characterization of a replication-competent retrovirus containing the activated c-erbB. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1840–1844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1840-1844.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Variants of 3T3 cells lacking mitogenic response to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3918–3921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: clustered integration sites and the arrangement of provirus in the c-erbB alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2287–2291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Maihle N. J., Moscovici C., Crittenden L., Kung H. J. Mechanism of c-erbB transduction: newly released transducing viruses retain poly(A) tracts of erbB transcripts and encode C-terminally intact erbB proteins. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2437–2443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2437-2443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Maihle N. J., Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Kung H. J. Molecular characterization of three erbB transducing viruses generated during avian leukosis virus-induced erythroleukemia: extensive internal deletion near the kinase domain activates the fibrosarcoma- and hemangioma-inducing potentials of erbB. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2444–2452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2444-2452.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Tracy S. E., Nair N., Taglienti-Sian C., Gamett D. C. Characterization of an angiosarcoma-inducing mutation in the erbB oncogene. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):2025–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Payne D. M., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E., Nebreda A. R. Structural and functional properties of ras proteins. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2151–2163. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.10.2666231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H. K., Pelley R. J., Kung H. J. Dissecting the activating mutations in v-erbB of avian erythroblastosis virus strain R. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6173–6180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6173-6180.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H. K., Pelley R. J., Kung H. J. Tissue-specific transformation by epidermal growth factor receptor: a single point mutation within the ATP-binding pocket of the erbB product increases its intrinsic kinase activity and activates its sarcomagenic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9103–9107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theroux S. J., Taglienti-Sian C., Nair N., Countaway J. L., Robinson H. L., Davis R. J. Increased oncogenic potential of ErbB is associated with the loss of a COOH-terminal domain serine phosphorylation site. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):7967–7970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Jones G. A., Nishibe S., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Growth factor stimulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 activity. Comparative properties of control and activated enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10447–10456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Lemischka I. R., Nathan D. G., Mulligan R. C. Introduction of new genetic material into pluripotent haematopoietic stem cells of the mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):476–480. doi: 10.1038/310476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Hihara H., Nishida T., Kawai S., Toyoshima K. A new avian erythroblastosis virus, AEV-H, carries erbB gene responsible for the induction of both erythroblastosis and sarcomas. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nishida T., Miyajima N., Kawai S., Ooi T., Toyoshima K. The erbB gene of avian erythroblastosis virus is a member of the src gene family. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]