Abstract
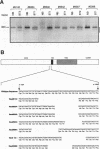
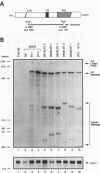
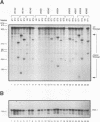
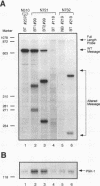
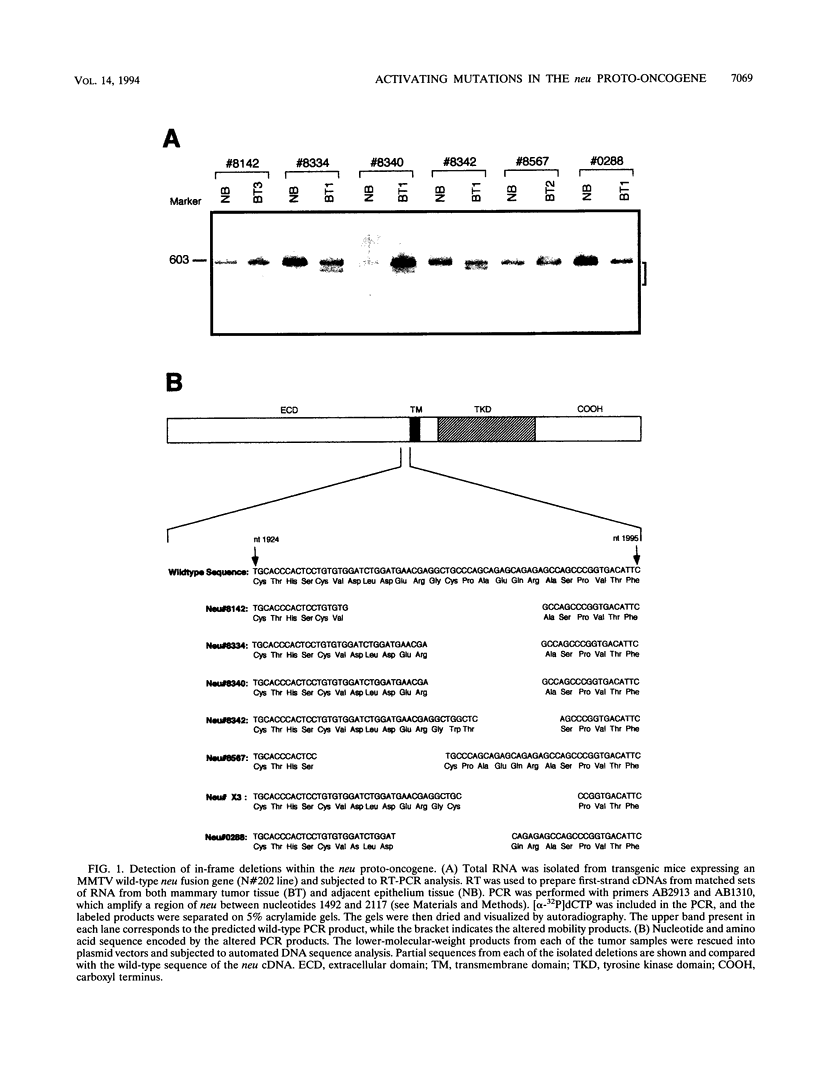
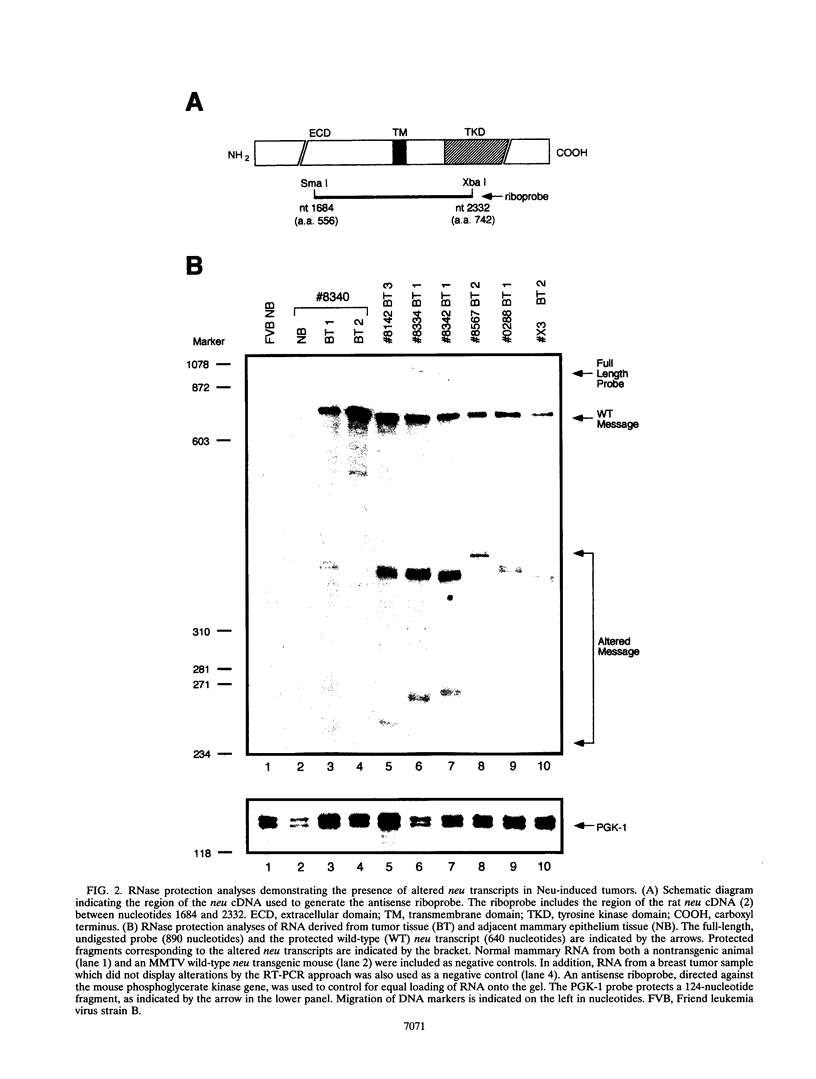
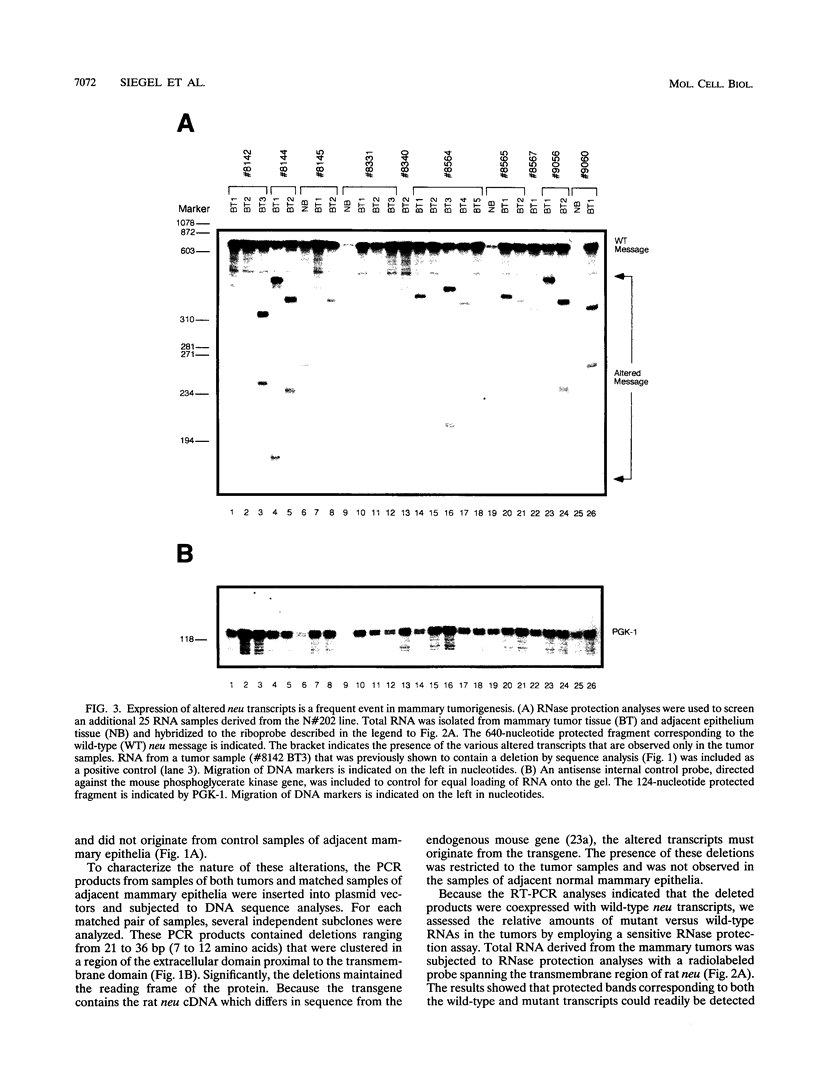
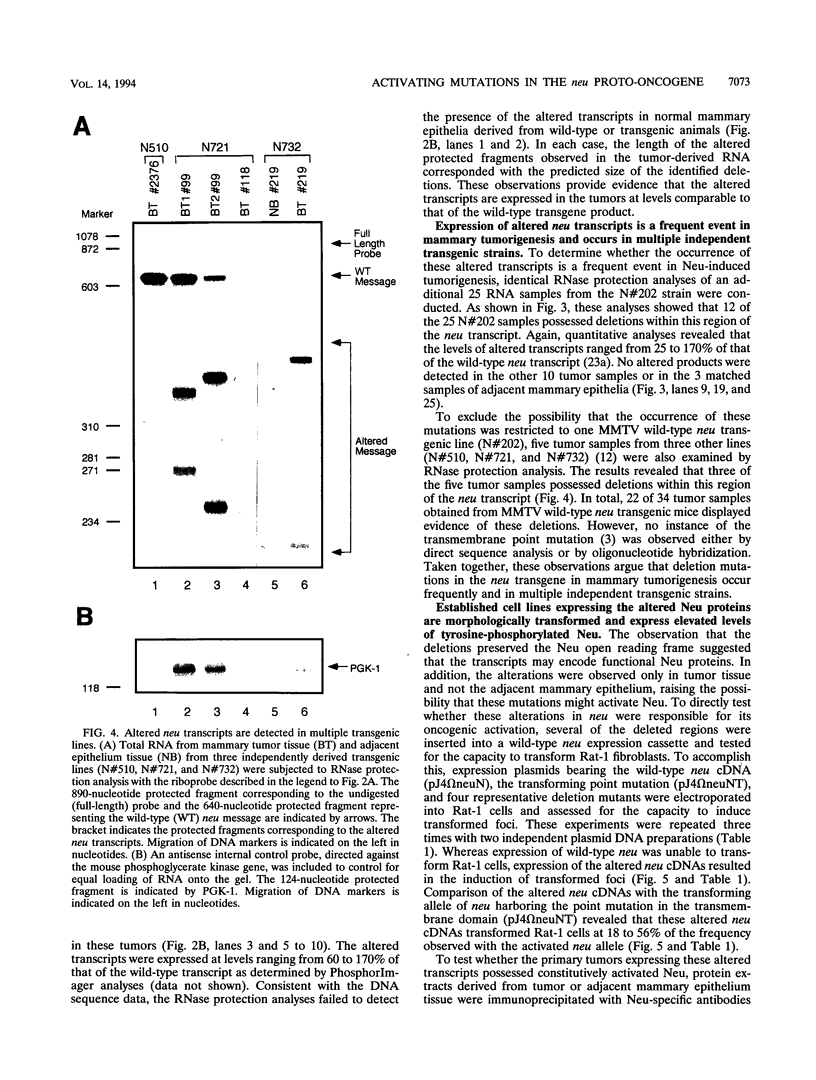
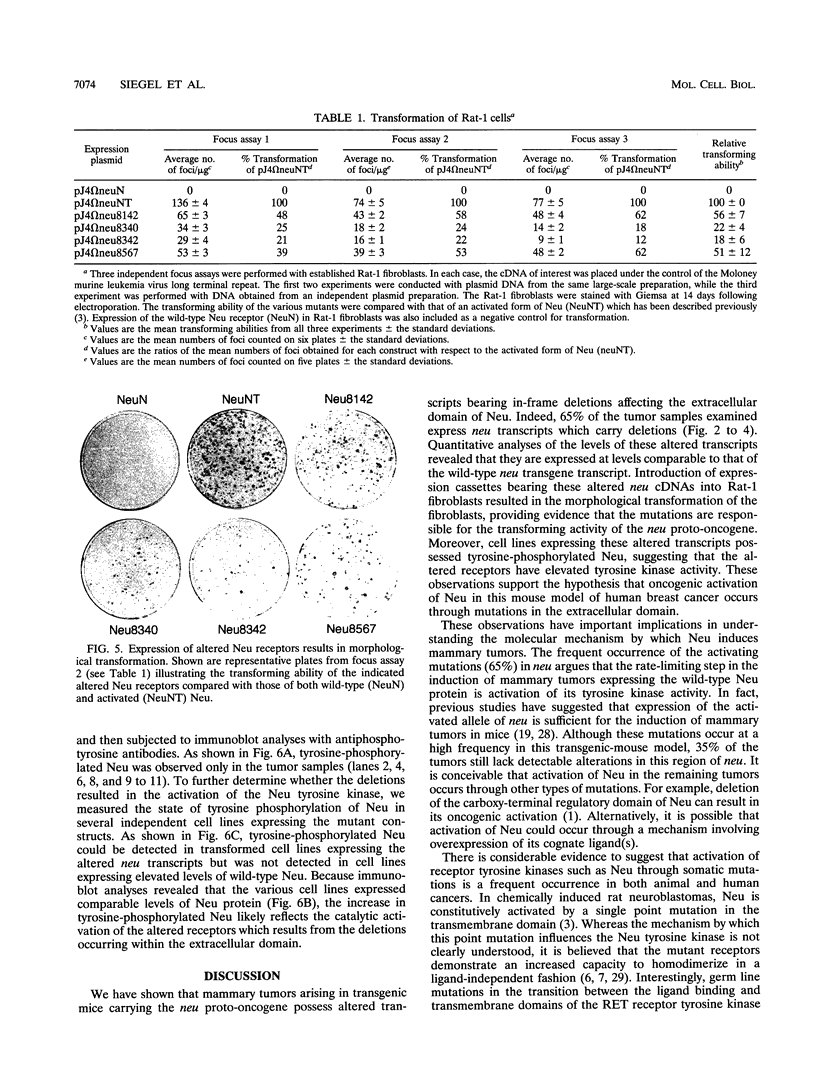
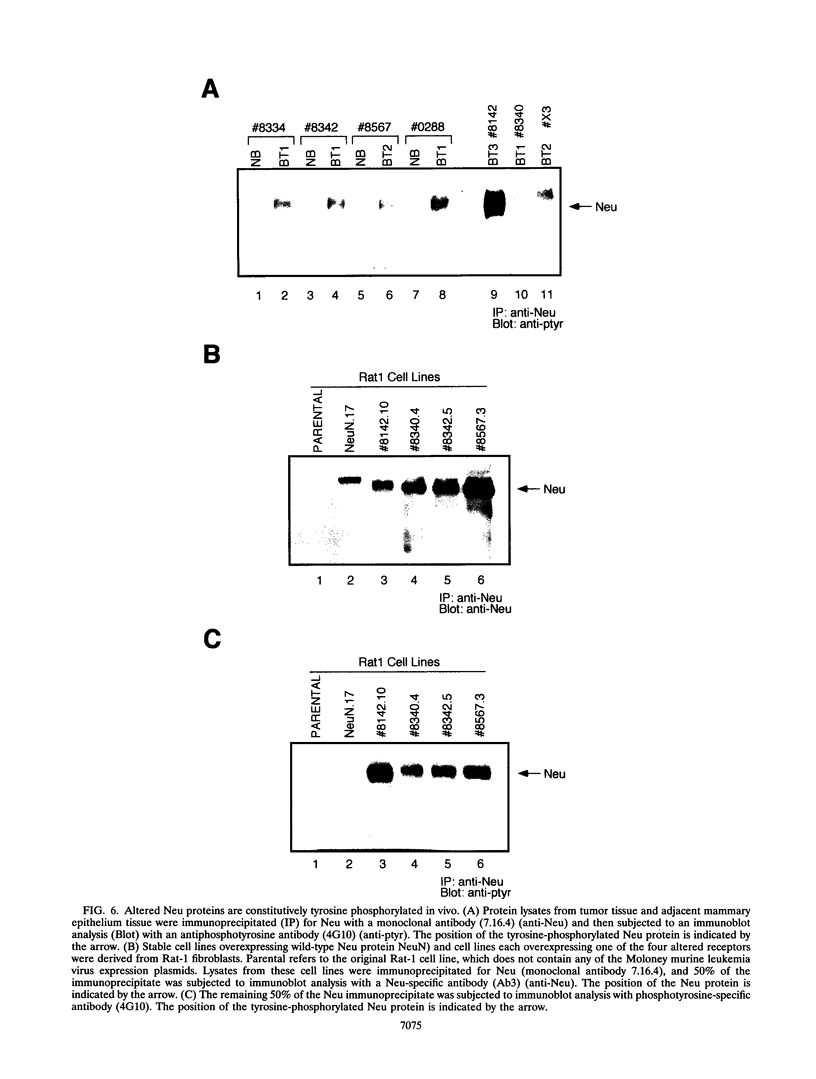
Amplification of the Neu/c-erbB-2 receptor tyrosine kinase has been implicated as an important event in the genesis of human breast cancer. Indeed, transgenic mice bearing either an activated form of neu or the wild-type proto-oncogene under the transcriptional control of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter-enhancer frequently develop mammary carcinomas (L. Bouchard, L. Lamarre, P. J. Tremblay, and P. Jolicoeur, Cell 57:931-936, 1989; C. T. Guy, M. A. Webster, M. Schaller, T. J. Parson, R. D. Cardiff, and W. J. Muller, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:10578-10582, 1992; W. J. Muller, E. Sinn, R. Wallace, P. K. Pattengale, and P. Leder, Cell 54:105-115, 1988). Induction of mammary tumors in transgenic mice expressing the wild-type Neu receptor is associated with activation of the receptor's intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity (Guy et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:10578-10582, 1992). Here, we demonstrate that activation of Neu in these transgenic mice occurs through somatic mutations located within the transgene itself. Sequence analyses of these mutations revealed that they contain in-frame deletions of 7 to 12 amino acids in the extracellular region proximal to the transmembrane domain. Introduction of these mutations into a wild-type neu cDNA results in an increased transforming ability of the altered Neu tyrosine kinase. These observations suggest that oncogenic activation of Neu in mammary tumorigenesis frequently occurs by somatic mutation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Matsuda S., Namba Y., Saito T., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. The transforming potential of the c-erbB-2 protein is regulated by its autophosphorylation at the carboxyl-terminal domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):833–842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):226–230. doi: 10.1038/319226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A. Oncogenic activation of the neu-encoded receptor protein by point mutation and deletion. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2043–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard L., Lamarre L., Tremblay P. J., Jolicoeur P. Stochastic appearance of mammary tumors in transgenic mice carrying the MMTV/c-neu oncogene. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):931–936. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90331-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt-Rauf P. W., Rackovsky S., Pincus M. R. Correlation of the structure of the transmembrane domain of the neu oncogene-encoded p185 protein with its function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8660–8664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao H., Bangalore L., Bormann B. J., Stern D. F. A subdomain in the transmembrane domain is necessary for p185neu* activation. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):923–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Yang-Feng T. L., Liao Y. C., Chen E., Gray A., McGrath J., Seeburg P. H., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J., Francke U. Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1132–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2999974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drebin J. A., Stern D. F., Link V. C., Weinberg R. A., Greene M. I. Monoclonal antibodies identify a cell-surface antigen associated with an activated cellular oncogene. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):545–548. doi: 10.1038/312545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Love S. B., Wright C., Barnes D. M., Gusterson B., Harris A. L., Altman D. G. c-erbB-2 protein overexpression in breast cancer is a risk factor in patients with involved and uninvolved lymph nodes. Br J Cancer. 1991 Mar;63(3):434–438. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy C. T., Webster M. A., Schaller M., Parsons T. J., Cardiff R. D., Muller W. J. Expression of the neu protooncogene in the mammary epithelium of transgenic mice induces metastatic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10578–10582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra R. M., Landsvater R. M., Ceccherini I., Stulp R. P., Stelwagen T., Luo Y., Pasini B., Höppener J. W., van Amstel H. K., Romeo G. A mutation in the RET proto-oncogene associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B and sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma. Nature. 1994 Jan 27;367(6461):375–376. doi: 10.1038/367375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Aaronson S. A. Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):974–976. doi: 10.1126/science.2992089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine N. R., Staddon S., Dickson C., Barnes D. M., Gullick W. J. Absence of activating transmembrane mutations in the c-erbB-2 proto-oncogene in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 1990 Feb;5(2):237–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. A series of mammalian expression vectors and characterisation of their expression of a reporter gene in stably and transiently transfected cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1068–1068. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Singer-Sam J., Lee C. Y., Riggs A. D. The nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone containing the entire coding region for mouse X-chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase. Gene. 1986;45(3):275–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Sinn E., Pattengale P. K., Wallace R., Leder P. Single-step induction of mammary adenocarcinoma in transgenic mice bearing the activated c-neu oncogene. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L. M., Kwok J. B., Healey C. S., Elsdon M. J., Eng C., Gardner E., Love D. R., Mole S. E., Moore J. K., Papi L. Germ-line mutations of the RET proto-oncogene in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):458–460. doi: 10.1038/363458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthuswamy S. K., Siegel P. M., Dankort D. L., Webster M. A., Muller W. J. Mammary tumors expressing the neu proto-oncogene possess elevated c-Src tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):735–743. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson M. C., Dietrich K. D., Danyluk J., Paterson A. H., Lees A. W., Jamil N., Hanson J., Jenkins H., Krause B. E., McBlain W. A. Correlation between c-erbB-2 amplification and risk of recurrent disease in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 15;51(2):556–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Downing J. R., Rettenmier C. W., Sherr C. J. A point mutation in the extracellular domain of the human CSF-1 receptor (c-fms proto-oncogene product) activates its transforming potential. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):979–988. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger F., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Torso receptor activity is regulated by a diffusible ligand produced at the extracellular terminal regions of the Drosophila egg. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):987–1001. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90394-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Kennan W. S., Yasukawa-Barnes J., Lindstrom M. J., Gould M. N. Frequent induction of mammary carcinomas following neu oncogene transfer into in situ mammary epithelial cells of susceptible and resistant rat strains. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 15;51(20):5649–5654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Liu J., Cohen J. A., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. A point mutation in the neu oncogene mimics ligand induction of receptor aggregation. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):230–231. doi: 10.1038/339230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford J., McAuliffe A., Rohrschneider L. R. Activation of the feline c-fms proto-oncogene: multiple alterations are required to generate a fully transformed phenotype. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):965–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M., van de Bersselaar R., Devilee P., Cornelisse C., Peterse J., Nusse R. Amplification of the neu (c-erbB-2) oncogene in human mammmary tumors is relatively frequent and is often accompanied by amplification of the linked c-erbA oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]