Abstract
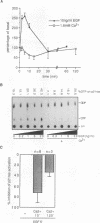
Human primary keratinocytes are an elegant model system to study the balance between proliferation and differentiation. Both epidermal growth factor (EGF) and extracellular calcium have been implicated to function in the control of this balance, although the molecular mechanism underlying this process is poorly understood. In this study, we measured the effect of both EGF and calcium treatment on activation of p21ras and ERK2. We found that addition of EGF stimulated the activity of ERK2. This stimulation was dependent on p21ras activity, since it was completely abolished by expression of a dominant negative mutant of p21ras (p21ras(Asn-17)). Raising the level of extracellular calcium (1.8 mM) did not result in activation of ERK2. On the contrary, calcium treatment inhibited EGF-induced stimulation of ERK2 activity. In order to determine the site at which calcium treatment interferes in EGF-induced signaling, we analyzed the effect of calcium on the various steps that are involved in EGF-induced, p21ras-dependent activation of ERK2. We observed that calcium treatment inhibited EGF-induced p21ras activation. Calcium treatment, however, did not interfere with EGF-induced EGF receptor autophosphorylation or association of mammalian SOS with the EGF receptor and Shc. This, together with the observation that calcium treatment alone decreased the basal level of p21ras activity, indicates that calcium treatment interferes in EGF-mediated signaling at the level of p21ras. This type of cross talk may play a role in the decision between proliferation and differentiation in human primary keratinocytes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balmain A., Pragnell I. B. Mouse skin carcinomas induced in vivo by chemical carcinogens have a transforming Harvey-ras oncogene. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):72–74. doi: 10.1038/303072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balmain A., Ramsden M., Bowden G. T., Smith J. Activation of the mouse cellular Harvey-ras gene in chemically induced benign skin papillomas. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):658–660. doi: 10.1038/307658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfini L., Karlovich C. A., Dasgupta C., Banerjee U. The Son of sevenless gene product: a putative activator of Ras. Science. 1992 Jan 31;255(5044):603–606. doi: 10.1126/science.1736363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D., Fu P., Simon M., Senior P. Identification of murine homologues of the Drosophila son of sevenless gene: potential activators of ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce S. T., Ham R. G. Calcium-regulated differentiation of normal human epidermal keratinocytes in chemically defined clonal culture and serum-free serial culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):33s–40s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90146-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates the exchange rate of guanine nucleotides on p21ras in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1903–1910. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., Pronk G. J., van Weeren P. C., Chardin P., Bos J. L. cAMP antagonizes p21ras-directed activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 and phosphorylation of mSos nucleotide exchange factor. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4211–4220. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., de Vries-Smits A. M., Medema R. H., van Weeren P. C., Tertoolen L. G., Bos J. L. Epidermal growth factor induces phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 via multiple pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7248–7256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., McCormick F. Inhibition by cAMP of Ras-dependent activation of Raf. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1069–1072. doi: 10.1126/science.7694367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Rubinfeld B., Albert I., McCormick F. RapV12 antagonizes Ras-dependent activation of ERK1 and ERK2 by LPA and EGF in Rat-1 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3475–3485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Falco J., Borrello I., Weissman B., Aaronson S. A. The calcium signal for BALB/MK keratinocyte terminal differentiation counteracts epidermal growth factor (EGF) very early in the EGF-induced proliferative pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):557–563. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J. D., Warne P. H., Rayter S., Cantrell D. A. Stimulation of p21ras upon T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):719–723. doi: 10.1038/346719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drozdoff V., Pledger W. J. Commitment to differentiation and expression of early differentiation markers in murine keratinocytes in vitro are regulated independently of extracellular calcium concentrations. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):909–919. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duden R., Franke W. W. Organization of desmosomal plaque proteins in cells growing at low calcium concentrations. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1049–1063. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Giddings B. W., Brooks M. W., Buday L., Sizeland A. M., Weinberg R. A. Association of Sos Ras exchange protein with Grb2 is implicated in tyrosine kinase signal transduction and transformation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):45–51. doi: 10.1038/363045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Inhibition of NIH 3T3 cell proliferation by a mutant ras protein with preferential affinity for GDP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3235–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filvaroff E., Calautti E., McCormick F., Dotto G. P. Specific changes of Ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and a GAP-associated p62 protein during calcium-induced keratinocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5319–5328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale N. W., Kaplan S., Lowenstein E. J., Schlessinger J., Bar-Sagi D. Grb2 mediates the EGF-dependent activation of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ras. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):88–92. doi: 10.1038/363088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs S., Lohman F., Teubel W., van de Putte P., Backendorf C. Characterization of the human spr2 promoter: induction after UV irradiation or TPA treatment and regulation during differentiation of cultured primary keratinocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4401–4407. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves L. M., Bornfeldt K. E., Raines E. W., Potts B. C., Macdonald S. G., Ross R., Krebs E. G. Protein kinase A antagonizes platelet-derived growth factor-induced signaling by mitogen-activated protein kinase in human arterial smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10300–10304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohl D., Lichti U., Breitkreutz D., Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Transcription of the human loricrin gene in vitro is induced by calcium and cell density and suppressed by retinoic acid. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Apr;96(4):414–418. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12469779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata M., Matsui Y., Kondo J., Hishida T., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. A novel small molecular weight GTP-binding protein with the same putative effector domain as the ras proteins in bovine brain membranes. Purification, determination of primary structure, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18965–18971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama H., Sugimoto Y., Matsuzaki T., Ikawa Y., Noda M. A ras-related gene with transformation suppressor activity. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90985-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Allemain G., Her J. H., Wu J., Sturgill T. W., Weber M. J. Growth factor-induced activation of a kinase activity which causes regulatory phosphorylation of p42/microtubule-associated protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2222–2229. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchese C., Rubin J., Ron D., Faggioni A., Torrisi M. R., Messina A., Frati L., Aaronson S. A. Human keratinocyte growth factor activity on proliferation and differentiation of human keratinocytes: differentiation response distinguishes KGF from EGF family. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Aug;144(2):326–332. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema R. H., de Vries-Smits A. M., van der Zon G. C., Maassen J. A., Bos J. L. Ras activation by insulin and epidermal growth factor through enhanced exchange of guanine nucleotides on p21ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):155–162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie S. A., Willumsen B. M., Weber M. J., Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.8503013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci G., Lanfrancone L., Grignani F., McGlade J., Cavallo F., Forni G., Nicoletti I., Grignani F., Pawson T., Pelicci P. G. A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90536-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai S., Bikle D. D., Mancianti M. L., Cline P., Hincenbergs M. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of normal human keratinocytes: modulation of differentiation competence by stages of growth and extracellular calcium. J Cell Physiol. 1990 May;143(2):294–302. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041430213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittelkow M. R., Wille J. J., Jr, Scott R. E. Two functionally distinct classes of growth arrest states in human prokeratinocytes that regulate clonogenic potential. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Apr;86(4):410–417. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizon V., Chardin P., Lerosey I., Olofsson B., Tavitian A. Human cDNAs rap1 and rap2 homologous to the Drosophila gene Dras3 encode proteins closely related to ras in the 'effector' region. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponec M., Kempenaar J. A., De Kloet E. R. Corticoids and cultured human epidermal keratinocytes: specific intracellular binding and clinical efficacy. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Mar;76(3):211–214. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronk G. J., de Vries-Smits A. M., Buday L., Downward J., Maassen J. A., Medema R. H., Bos J. L. Involvement of Shc in insulin- and epidermal growth factor-induced activation of p21ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1575–1581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase is phosphorylated on tyrosine and threonine in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read J., Watt F. M. A model for in vitro studies of epidermal homeostasis: proliferation and involucrin synthesis by cultured human keratinocytes during recovery after stripping off the suprabasal layers. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 May;90(5):739–743. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12560940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Green H. Epidermal growth factor and the multiplication of cultured human epidermal keratinocytes. Nature. 1977 Feb 3;265(5593):421–424. doi: 10.1038/265421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., Fernley R., Wade J., Pawson T., Bowtell D. The SH2 and SH3 domains of mammalian Grb2 couple the EGF receptor to the Ras activator mSos1. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):83–85. doi: 10.1038/363083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. D., Pittelkow M. R. Control of growth and differentiation in vitro of human keratinocytes cultured in serum-free medium. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Nov;123(11):1541a–1544a. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao M. C., Walthall B. J., Ham R. G. Clonal growth of normal human epidermal keratinocytes in a defined medium. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Feb;110(2):219–229. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aelst L., Barr M., Marcus S., Polverino A., Wigler M. Complex formation between RAS and RAF and other protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6213–6217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warne P. H., Viciana P. R., Downward J. Direct interaction of Ras and the amino-terminal region of Raf-1 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):352–355. doi: 10.1038/364352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt G. A surgical care study. NATNEWS. 1984 Feb;21(2):16–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke M. S., Hsu B. M., Wille J. J., Jr, Pittelkow M. R., Scott R. E. Biologic mechanisms for the regulation of normal human keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation. Am J Pathol. 1988 Apr;131(1):171–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille J. J., Jr, Pittelkow M. R., Shipley G. D., Scott R. E. Integrated control of growth and differentiation of normal human prokeratinocytes cultured in serum-free medium: clonal analyses, growth kinetics, and cell cycle studies. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Oct;121(1):31–44. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Dent P., Jelinek T., Wolfman A., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Inhibition of the EGF-activated MAP kinase signaling pathway by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1065–1069. doi: 10.1126/science.7694366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. F., Settleman J., Kyriakis J. M., Takeuchi-Suzuki E., Elledge S. J., Marshall M. S., Bruder J. T., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Normal and oncogenic p21ras proteins bind to the amino-terminal regulatory domain of c-Raf-1. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):308–313. doi: 10.1038/364308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries-Smits A. M., Burgering B. M., Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J., Bos J. L. Involvement of p21ras in activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):602–604. doi: 10.1038/357602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]