Abstract
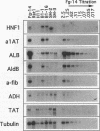
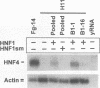
A hierarchy of liver-enriched transcription factors plays an important role in activating expression of many hepatic genes. In particular, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 (HNF-4) is a major activator of the gene encoding HNF-1, and HNF-1 itself activates expression of more than 20 liver genes. To dissect this activation pathway genetically, we prepared somatic cell variants that were deficient in expression of the liver-specific alpha 1-antitrypsin (alpha 1AT) gene, which requires both HNF-1 and HNF-4 for high-level gene activity. This was accomplished in two steps. First, hepatoma transfectants that stably expressed two selectable markers under alpha 1AT promoter control were prepared; second, variant sublines that could no longer express either transgene were isolated by direct selection. In this report, we demonstrate that the variants contain defects in the HNF-4/HNF-1 activation pathway. These defects functioned in trans, as expression of many liver genes was affected, but the variant phenotypes were recessive to wild type in somatic cell hybrids. Three different variant classes could be discriminated by their phenotypic responses to ectopic expression of either HNF-4 or HNF-1. Two variant clones appeared specifically deficient in HNF-4 expression, as transfection with an HNF-4 expression cassette fully restored their hepatic phenotypes. Another line activated HNF-1 in response to forced HNF-4 expression, but activation of downstream genes failed to occur. One clone was unresponsive to either HNF-1 or HNF-4. Using the variants, we demonstrate further that the chromosomal genes encoding alpha 1AT, aldolase B, and alpha-fibrinogen display strict requirements for HNF-1 activation in vivo, while other liver genes were unaffected by the presence or absence of HNF-1 or HNF-4. We also provide evidence for the existence of an autoregulatory loop in which HNF-1 regulates its own expression through activation of HNF-4.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumhueter S., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. A variant nuclear protein in dedifferentiated hepatoma cells binds to the same functional sequences in the beta fibrinogen gene promoter as HNF-1. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2485–2493. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla G. A., DeSimone V., Cortese R., Fournier R. E. Extinction of alpha 1-antitrypsin gene expression in somatic cell hybrids: evidence for multiple controls. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):316–327. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
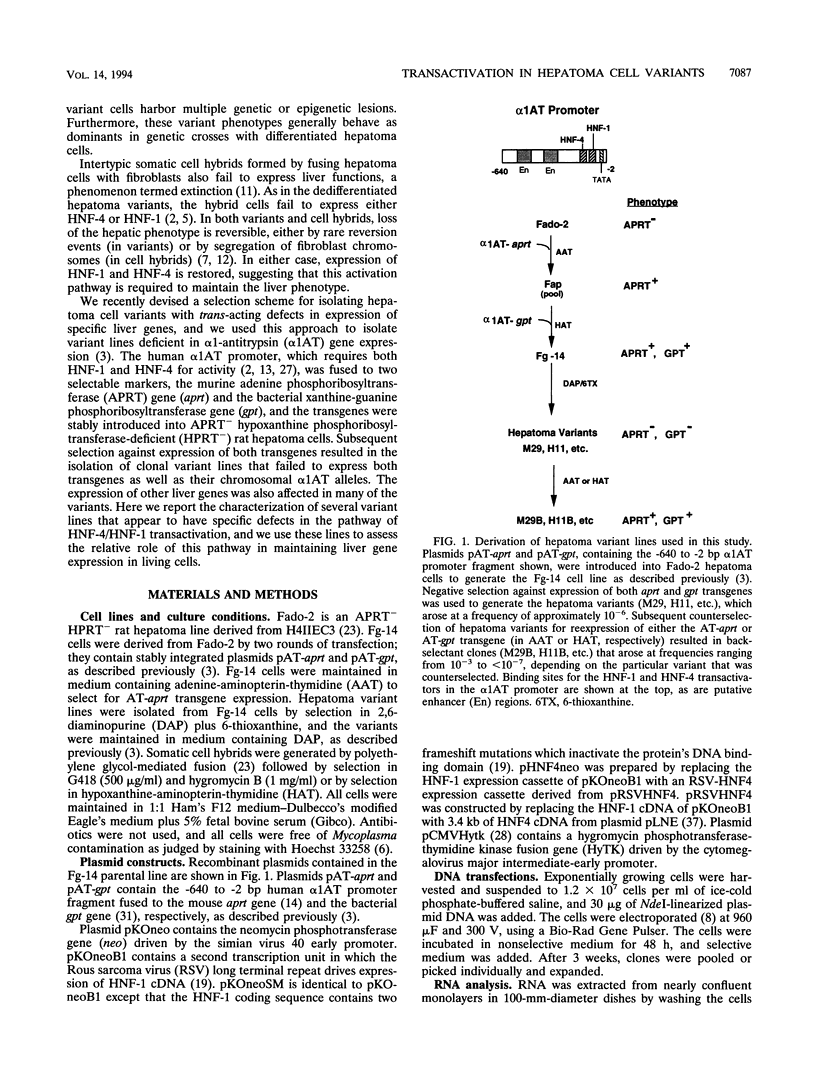
- Bulla G. A., Fournier R. E. Direct selection of hepatoma cell variants deficient in alpha 1-antitrypsin gene expression. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;18(4):361–370. doi: 10.1007/BF01235759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Yaniv M., Cortese R. Hepatocyte dedifferentiation and extinction is accompanied by a block in the synthesis of mRNA coding for the transcription factor HNF1/LFB1. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2257–2263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. R. In situ detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by fluorescent Hoechst 33258 stain. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Feb;104(2):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
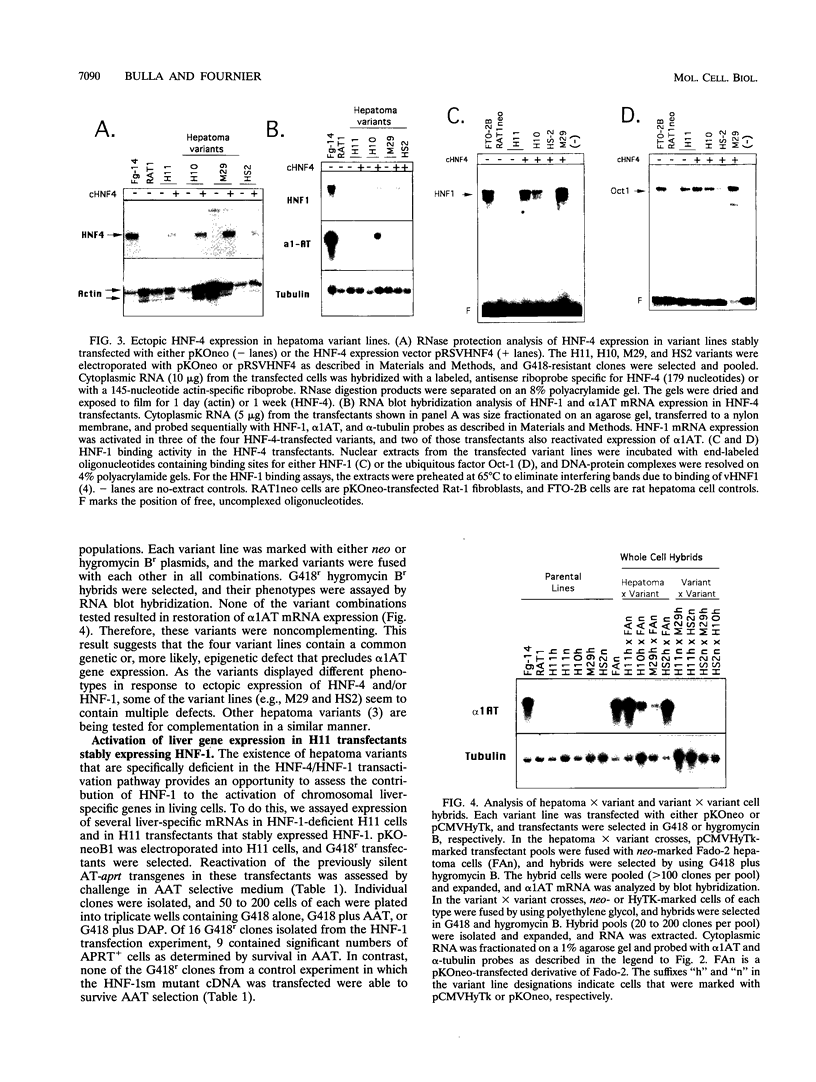
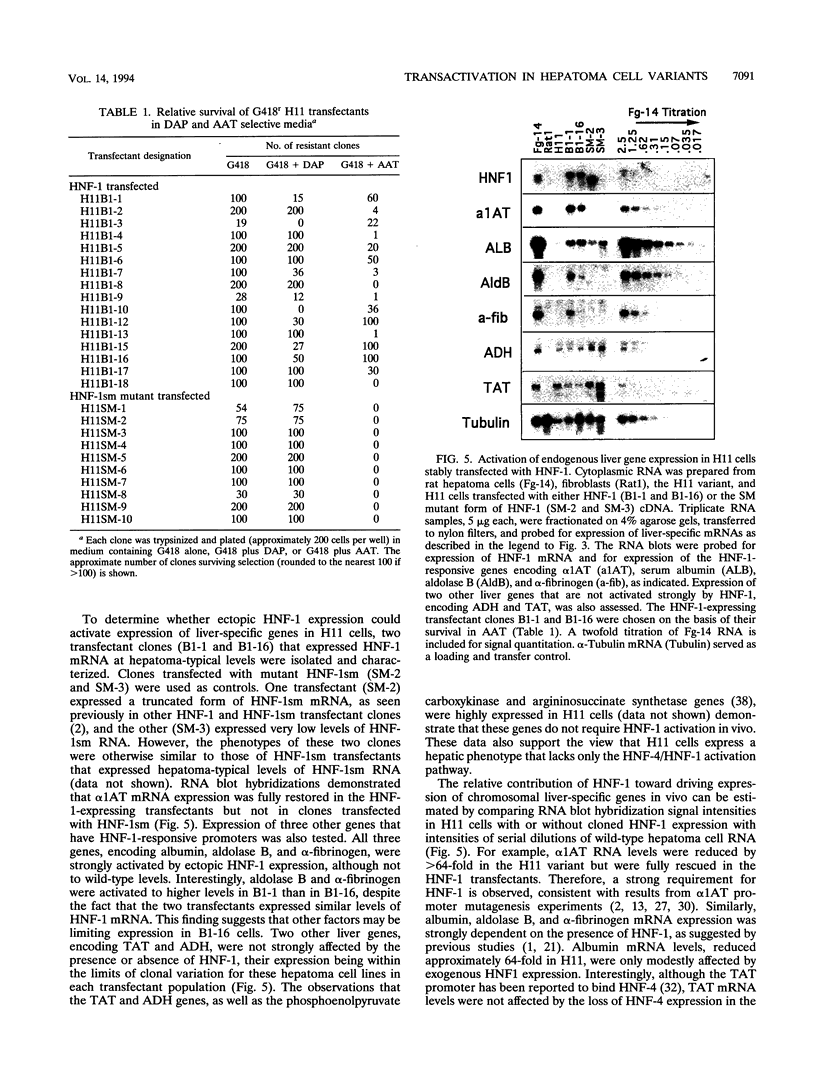
- Chin A. C., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-regulation of 16 liver-specific genes in hepatoma-fibroblast hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1614–1618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan N. J., Dobner P. R., Fuchs E. V., Cleveland D. W. Expression of human alpha-tubulin genes: interspecies conservation of 3' untranslated regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1738–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Ephrussi B., Yamamoto K. Regulation of pigment synthesis in mammalian cells, as studied by somatic hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1437–1440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., Ciliberto G., Hardon E., Paonessa G., Palla F., Lundberg L., Cortese R. Cis- and trans-acting elements responsible for the cell-specific expression of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2759–2766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschatrette J., Moore E. E., Dubois M., Weiss M. C. Dedifferentiated variants of a rat hepatoma:reversion analysis. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dush M. K., Sikela J. M., Khan S. A., Tischfield J. A., Stambrook P. J. Nucleotide sequence and organization of the mouse adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene: presence of a coding region common to animal and bacterial phosphoribosyltransferases that has a variable intron/exon arrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2731–2735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Activation of the human beta-interferon gene requires an interferon-inducible factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):801–810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerman M. H., Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Tissue-specific transcription of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene promoter is dependent on HNF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4204–4212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourdeau H., Fournier R. E. Genetic analysis of mammalian cell differentiation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregori C., Kahn A., Pichard A. L. Competition between transcription factors HNF1 and HNF3, and alternative cell-specific activation by DBP and C/EBP contribute to the regulation of the liver-specific aldolase B promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 25;21(4):897–903. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Rollier A., Tronche F., Ott M. O., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. The rat albumin promoter is composed of six distinct positive elements within 130 nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4750–4758. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killary A. M., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-dominant loci regulate expression of liver-specific traits in hepatoma hybrid cells. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. J., Conley P. B., Chen L., Sladek F. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Crabtree G. R. A transcriptional hierarchy involved in mammalian cell-type specification. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):457–461. doi: 10.1038/355457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in hepatocytes: a window on development. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):427–430. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90169-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzaro D., De Simone V., De Magistris L., Lehtonen E., Cortese R. LFB1 and LFB3 homeoproteins are sequentially expressed during kidney development. Development. 1992 Feb;114(2):469–479. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.2.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Shen R. F., Tsai S. Y., Woo S. L. Multiple hepatic trans-acting factors are required for in vitro transcription of the human alpha-1-antitrypsin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4362–4369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupton S. D., Brunton L. L., Kalberg V. A., Overell R. W. Dominant positive and negative selection using a hygromycin phosphotransferase-thymidine kinase fusion gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3374–3378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Factors governing the expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 May;1(5):449–459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.5.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch D., Boshart M., Schütz G. Extinction of tyrosine aminotransferase gene activity in somatic cell hybrids involves modification and loss of several essential transcriptional activators. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):308–319. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Wu J. R., Sala-Trepat J. M., Wallace R. B., Reyes A. A., Bonner J. The rat serum albumin gene: analysis of cloned sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3256–3260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Schmid W., Strange C. M., Röwekamp W., Schütz G. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for rat tyrosine aminotransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7205–7208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. P., Besmond C., Cottreau D., Weber A., Chaumet-Riffaud P., Dreyfus J. C., Trépat J. S., Marie J., Kahn A. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat L-type pyruvate kinase and aldolase B. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14576–14584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surh L. C., Morris S. M., O'Brien W. E., Beaudet A. L. Nucleotide sequence of the cDNA encoding the rat argininosuccinate synthetase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9352–9352. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian J. M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific expression of the gene encoding hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 may involve hepatocyte nuclear factor 4. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2225–2234. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronche F., Yaniv M. HNF1, a homeoprotein member of the hepatic transcription regulatory network. Bioessays. 1992 Sep;14(9):579–587. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]