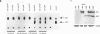Abstract
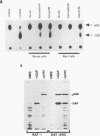
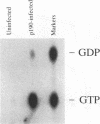
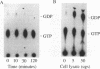
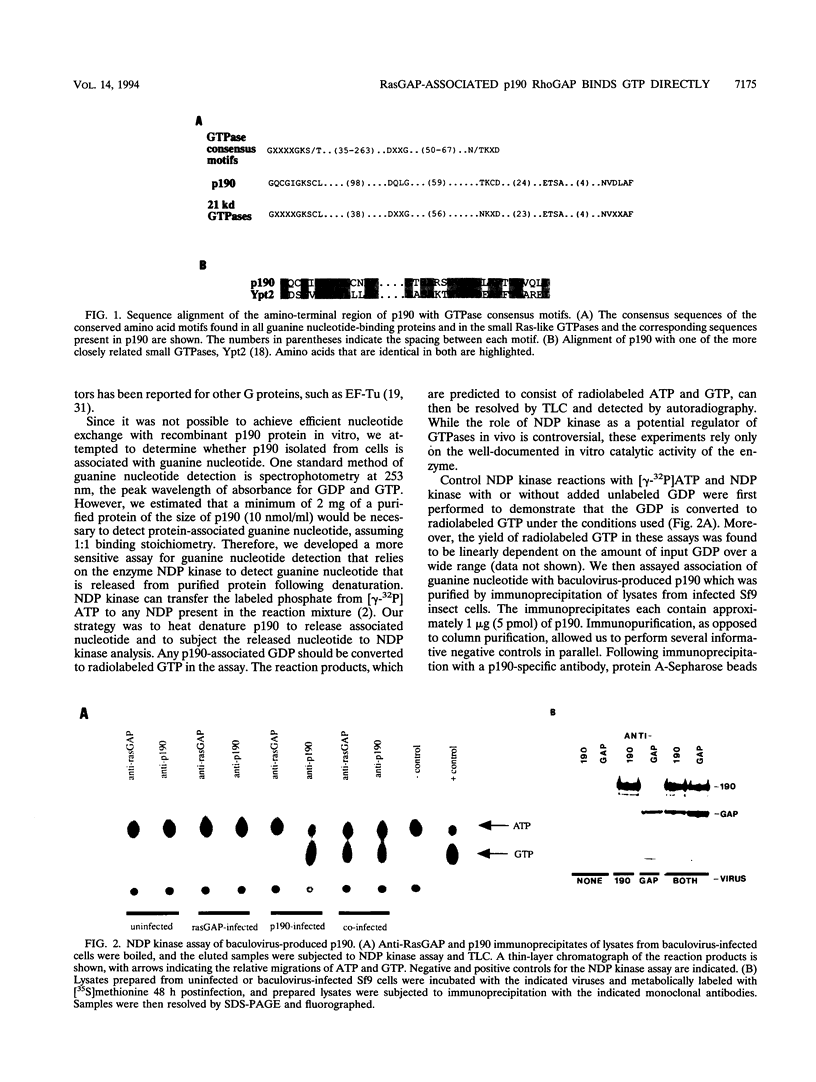
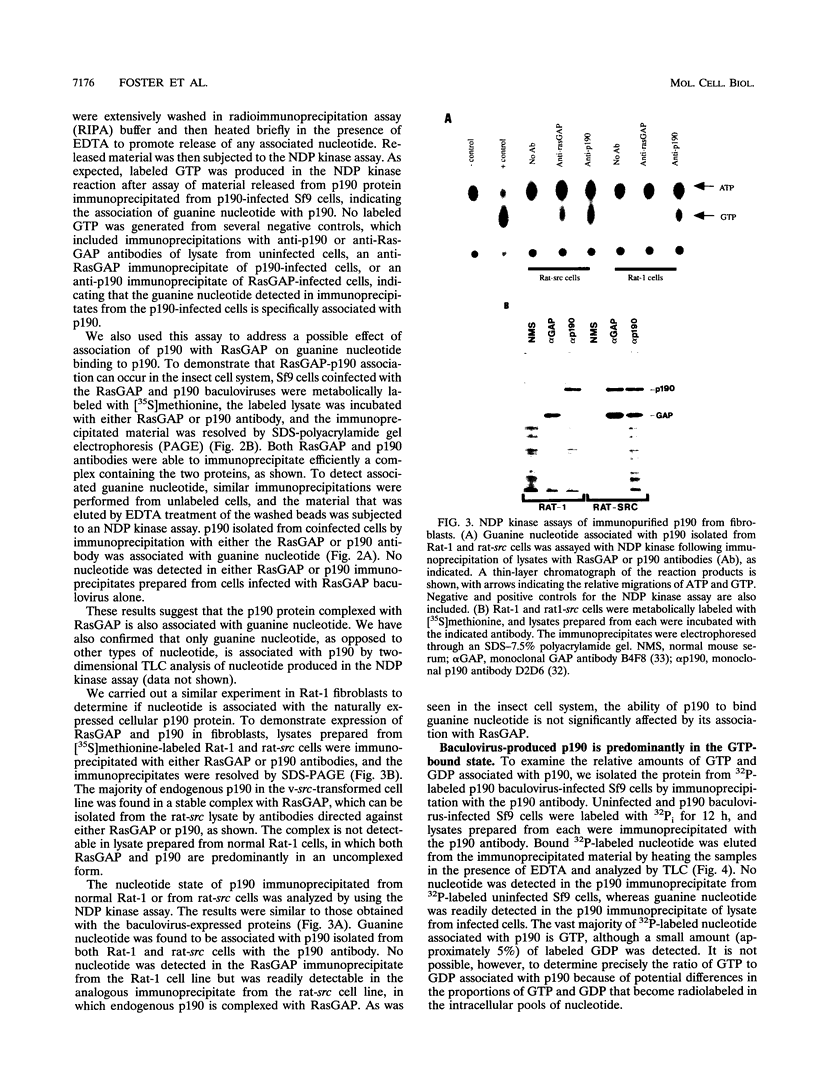
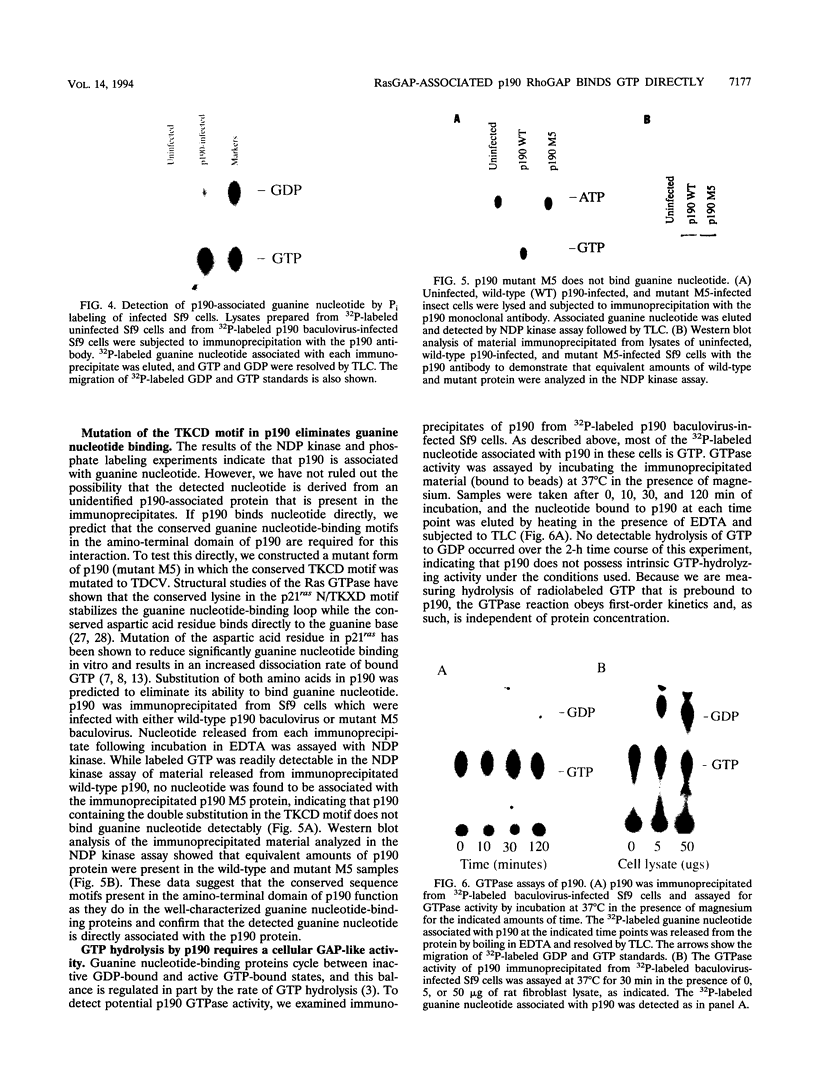
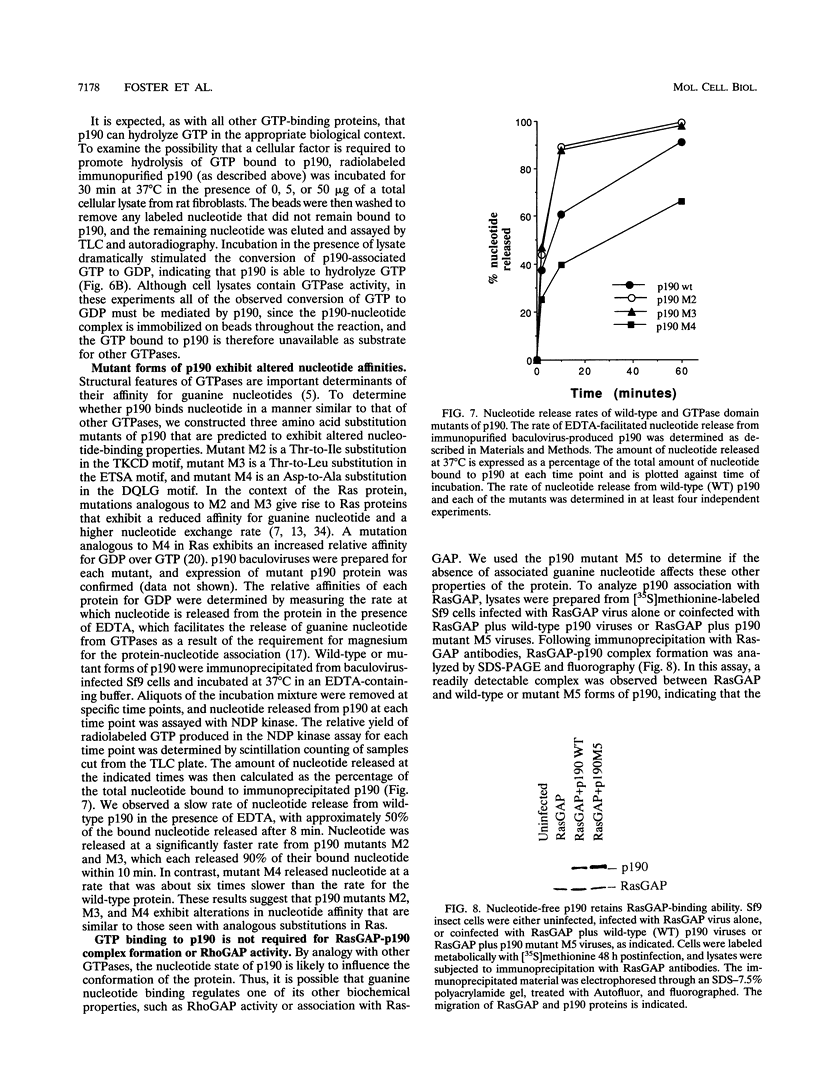
In mitogenically stimulated cells, a specific complex forms between the Ras GTPase-activating protein (RasGAP) and the cellular protein p190. We have previously reported that p190 contains a carboxy-terminal domain that functions as a GAP for the Rho family GTPases. Thus, the RasGAP-p190 complex may serve to couple Ras- and Rho-mediated signalling pathways. In addition to its RhoGAP domain, p190 contains an amino-terminal domain that contains sequence motifs found in all known GTPases. Here, we report that p190 binds GTP and GDP through this conserved domain and that the structural requirements for binding are similar to those seen with other GTPases. While the purified protein is unable to hydrolyze GTP, we detect an activity in cell lysates that can promote GTP hydrolysis by p190. A mutated form of p190 that fails to bind nucleotide retains its RasGAP binding and RhoGAP activities, indicating that GTP binding by p190 is not required for these functions. The sequence of p190 in the GTP-binding domain, which shares structural features with both the Ras-like small GTPases and the larger G proteins, suggests that this protein defines a novel class of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adari H., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M., Der C. J., McCormick F. Guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (GAP) interacts with the p21 ras effector binding domain. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2833817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal R. P., Robison B., Parks R. E., Jr Nucleoside diphosphokinase from human erythrocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1978;51:376–386. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)51051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Zhang K., Redford P., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Suppression of src transformation by overexpression of full-length GTPase-activating protein (GAP) or of the GAP C terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2819–2825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der C. J., Pan B. T., Cooper G. M. rasH mutants deficient in GTP binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3291–3294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez I., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., García de Herreros A., Cornet M. E., Graziani G., Diaz-Meco M. T., Johansen T., McCormick F., Moscat J. Role of GTPase activating protein in mitogenic signalling through phosphatidylcholine-hydrolysing phospholipase C. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3215–3220. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchesne M., Schweighoffer F., Parker F., Clerc F., Frobert Y., Thang M. N., Tocqué B. Identification of the SH3 domain of GAP as an essential sequence for Ras-GAP-mediated signaling. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):525–528. doi: 10.1126/science.7678707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano O., Crechet J. B., Parmeggiani A. Preparation of nucleotide-free elongation factor Tu and its stabilization by the antibiotic kirromycin. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 15;124(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Pan B. T., Roberts T. M., Cooper G. M. Isolation of ras GTP-binding mutants using an in situ colony-binding assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4607–4611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein J., Goody R. S., Wittinghofer A. Preparation and characterization of nucleotide-free and metal ion-free p21 "apoprotein". J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8455–8458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Schaber M. D., Schofield T. L., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Xenopus oocyte germinal-vesicle breakdown induced by [Val12]Ras is inhibited by a cytosol-localized Ras mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6630–6634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A., Self A. J. The effect of Mg2+ on the guanine nucleotide exchange rate of p21N-ras. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):10963–10965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubruck H., Engelke U., Mertins P., Gallwitz D. Structural and functional analysis of ypt2, an essential ras-related gene in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe encoding a Sec4 protein homologue. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1957–1962. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08323.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., Miller D. L. A study of the kinetic mechanism of elongation factor Ts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11498–11502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J., Rensland H., Schlichting I., Vetter I., Borasio G. D., Goody R. S., Wittinghofer A. Kinetic and structural analysis of the Mg(2+)-binding site of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein p21H-ras. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):923–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. The protein cofactor necessary for ADP-ribosylation of Gs by cholera toxin is itself a GTP binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7906–7911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markby D. W., Onrust R., Bourne H. R. Separate GTP binding and GTPase activating domains of a G alpha subunit. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1895–1901. doi: 10.1126/science.8266082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Brünger A., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Kim S. H. Molecular switch for signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):939–945. doi: 10.1126/science.2406906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Wilhelm H., Gierasch L., Gilmore R., Walter P. GTP binding and hydrolysis by the signal recognition particle during initiation of protein translocation. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):351–354. doi: 10.1038/366351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Polakis P., McCormick F., Pawson T., Ellis C. Protein-tyrosine kinases regulate the phosphorylation, protein interactions, subcellular distribution, and activity of p21ras GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1804–1812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Krengel U., Petsko G. A., Goody R. S., Kabsch W., Wittinghofer A. Refined crystal structure of the triphosphate conformation of H-ras p21 at 1.35 A resolution: implications for the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2351–2359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzbach C. J., Spremulli L. L. Bovine mitochondrial protein synthesis elongation factors. Identification and initial characterization of an elongation factor Tu-elongation factor Ts complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19125–19131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Albright C. F., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Association between GTPase activators for Rho and Ras families. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):153–154. doi: 10.1038/359153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Narasimhan V., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding the GAP-associated protein p190: implications for a signaling pathway from ras to the nucleus. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90454-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Temeles G. L., Wolanski B. S., Socher S. H., Scolnick E. M. Mutant ras-encoded proteins with altered nucleotide binding exert dominant biological effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):952–956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa G., Orci L., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Helms J. B., Rothman J. E. Hydrolysis of bound GTP by ARF protein triggers uncoating of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 1):1365–1371. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittinghofer A. The structure of transducin G alpha t: more to view than just ras. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Okabe K., Polakis P., Halenbeck R., McCormick F., Brown A. M. ras p21 and GAP inhibit coupling of muscarinic receptors to atrial K+ channels. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90187-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., DeClue J. E., Vass W. C., Papageorge A. G., McCormick F., Lowy D. R. Suppression of c-ras transformation by GTPase-activating protein. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):754–756. doi: 10.1038/346754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. F., Settleman J., Kyriakis J. M., Takeuchi-Suzuki E., Elledge S. J., Marshall M. S., Bruder J. T., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Normal and oncogenic p21ras proteins bind to the amino-terminal regulatory domain of c-Raf-1. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):308–313. doi: 10.1038/364308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]