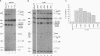
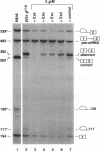
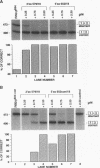
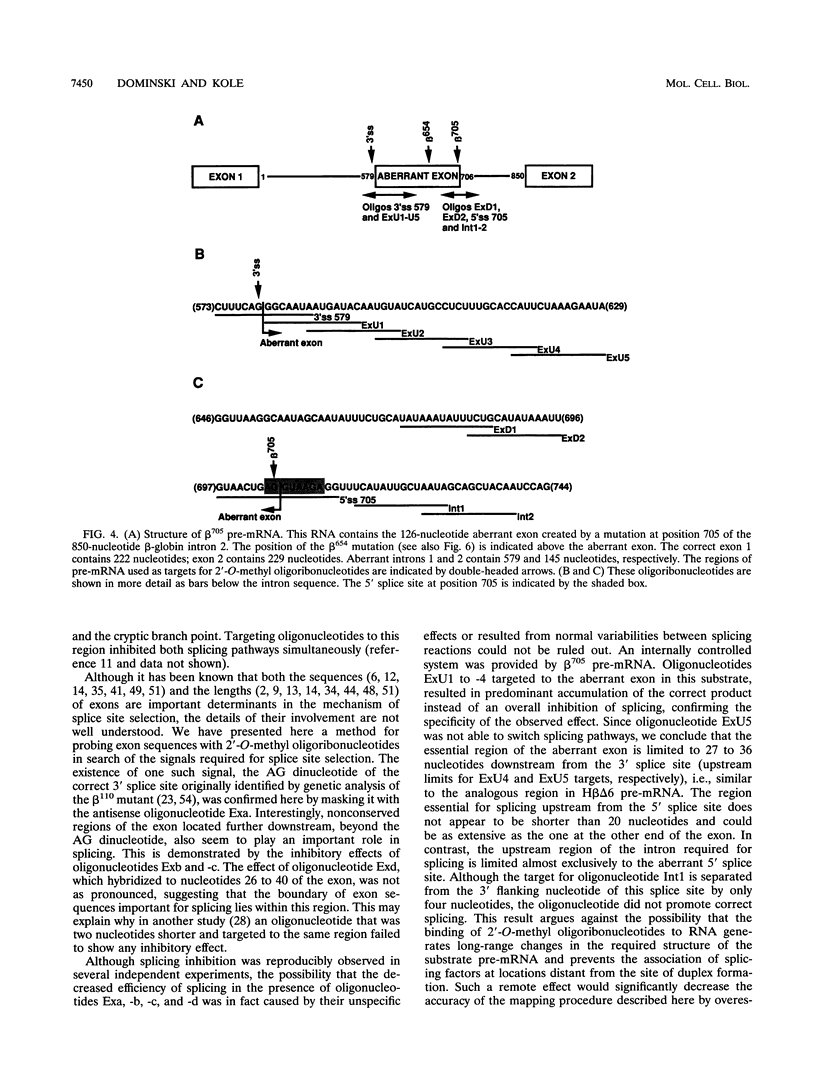
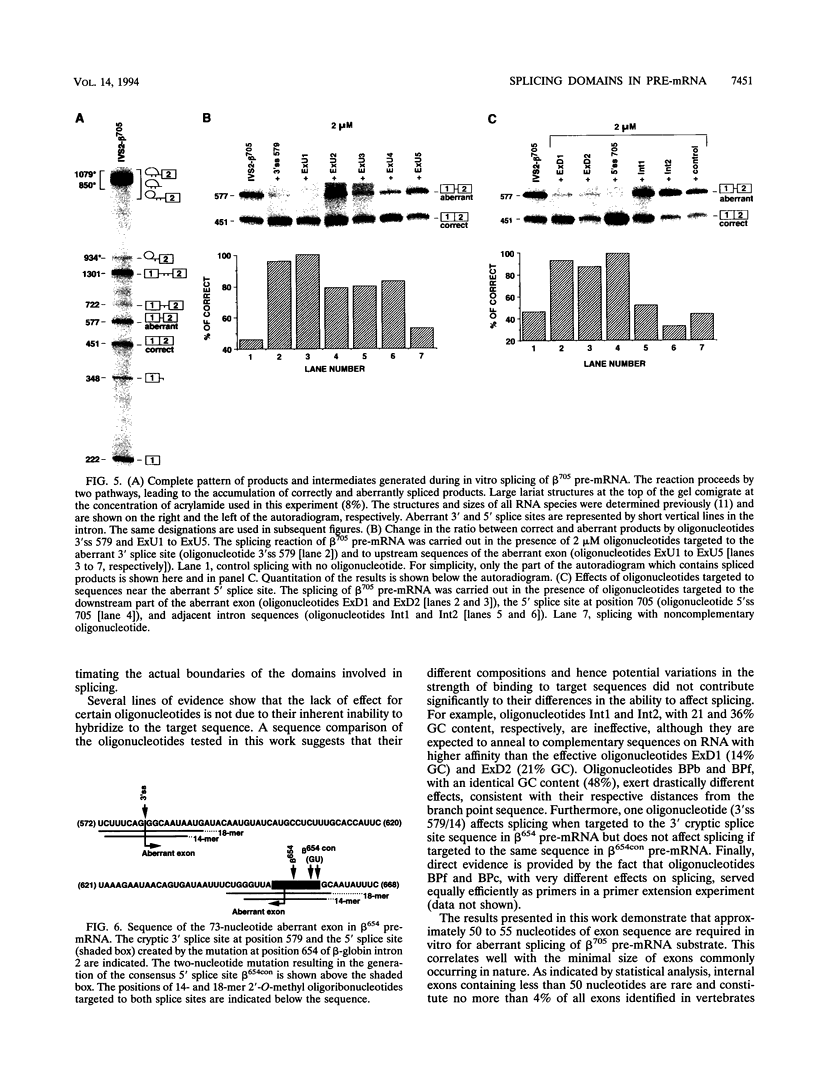
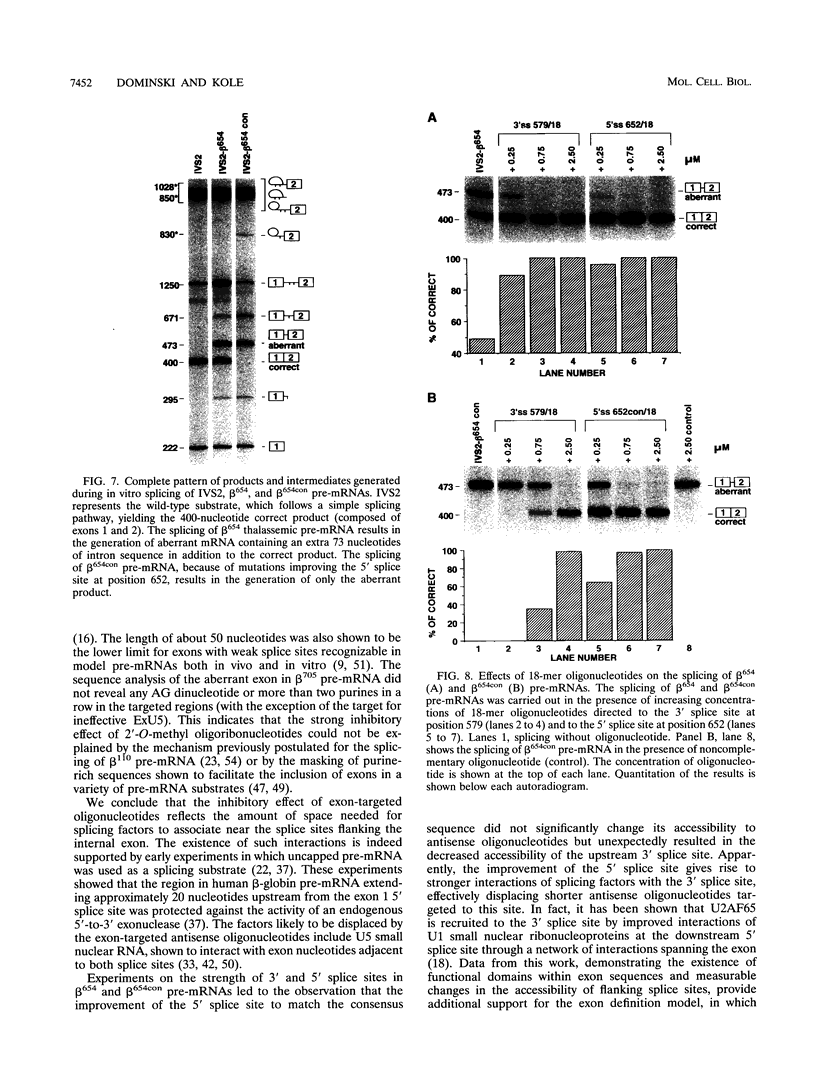
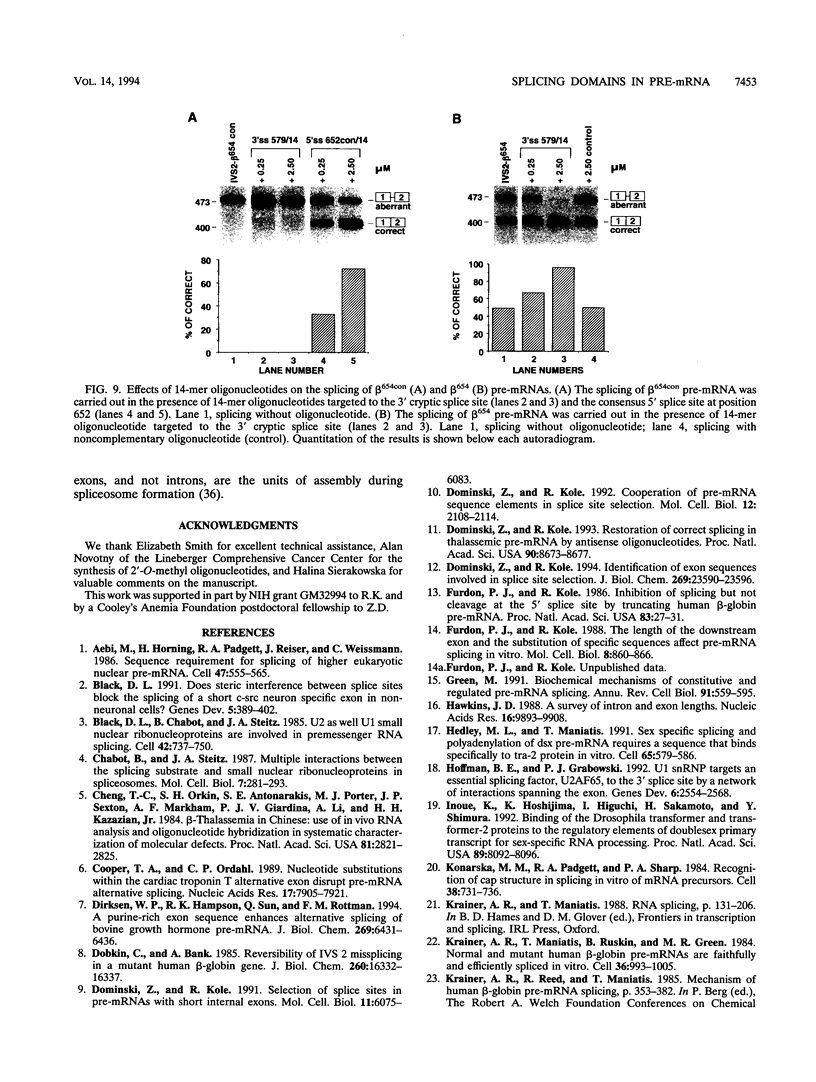
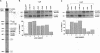Abstract
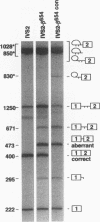
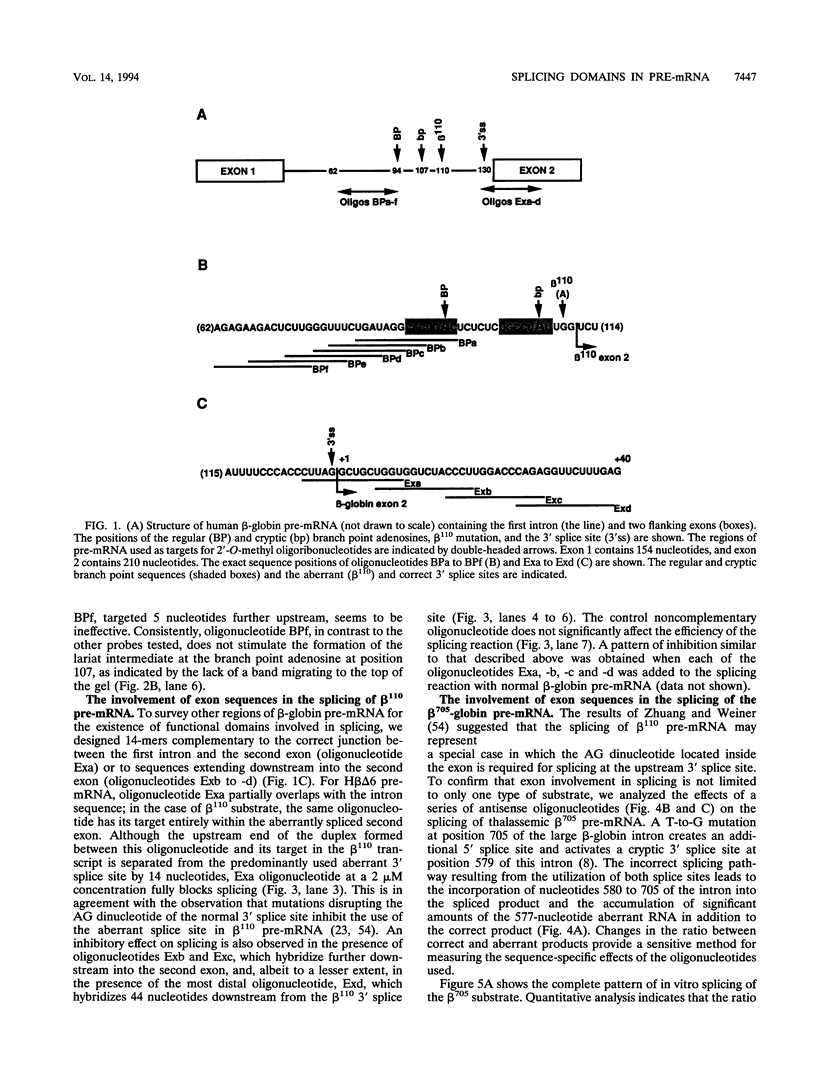
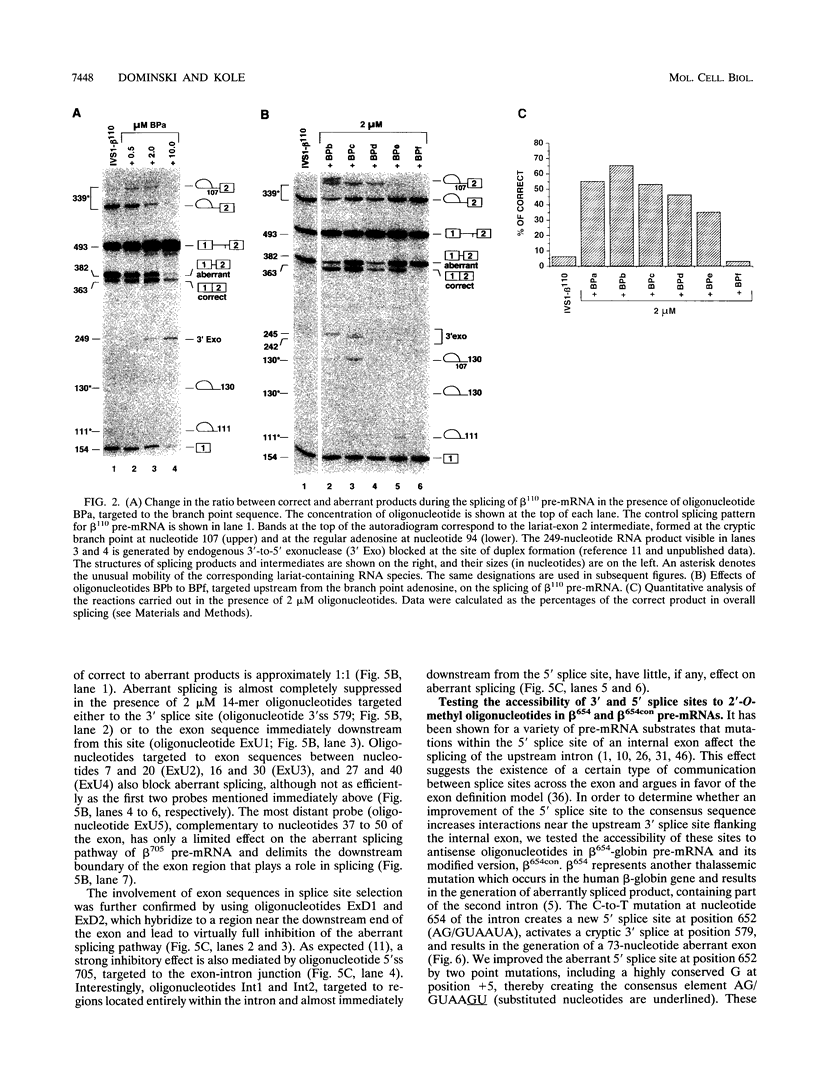
Certain thalassemic human beta-globin pre-mRNAs carry mutations that generate aberrant splice sites and/or activate cryptic splice sites, providing a convenient and clinically relevant system to study splice site selection. Antisense 2'-O-methyl oligoribonucleotides were used to block a number of sequences in these pre-mRNAs and were tested for their ability to inhibit splicing in vitro or to affect the ratio between aberrantly and correctly spliced products. By this approach, it was found that (i) up to 19 nucleotides upstream from the branch point adenosine are involved in proper recognition and functioning of the branch point sequence; (ii) whereas at least 25 nucleotides of exon sequences at both 3' and 5' ends are required for splicing, this requirement does not extend past the 5' splice site sequence of the intron; and (iii) improving the 5' splice site of the internal exon to match the consensus sequence strongly decreases the accessibility of the upstream 3' splice site to antisense 2'-O-methyl oligoribonucleotides. This result most likely reflects changes in the strength of interactions near the 3' splice site in response to improvement of the 5' splice site and further supports the existence of communication between these sites across the exon.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L. Does steric interference between splice sites block the splicing of a short c-src neuron-specific exon in non-neuronal cells? Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):389–402. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Steitz J. A. Multiple interactions between the splicing substrate and small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in spliceosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):281–293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T. C., Orkin S. H., Antonarakis S. E., Potter M. J., Sexton J. P., Markham A. F., Giardina P. J., Li A., Kazazian H. H., Jr beta-Thalassemia in Chinese: use of in vivo RNA analysis and oligonucleotide hybridization in systematic characterization of molecular defects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2821–2825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. A., Ordahl C. P. Nucleotide substitutions within the cardiac troponin T alternative exon disrupt pre-mRNA alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7905–7921. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen W. P., Hampson R. K., Sun Q., Rottman F. M. A purine-rich exon sequence enhances alternative splicing of bovine growth hormone pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6431–6436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobkin C., Bank A. Reversibility of IVS 2 missplicing in a mutant human beta-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16332–16337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominski Z., Kole R. Cooperation of pre-mRNA sequence elements in splice site selection. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2108–2114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominski Z., Kole R. Identification of exon sequences involved in splice site selection. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23590–23596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominski Z., Kole R. Restoration of correct splicing in thalassemic pre-mRNA by antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8673–8677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominski Z., Kole R. Selection of splice sites in pre-mRNAs with short internal exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6075–6083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furdon P. J., Kole R. The length of the downstream exon and the substitution of specific sequences affect pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):860–866. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins J. D. A survey on intron and exon lengths. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9893–9908. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley M. L., Maniatis T. Sex-specific splicing and polyadenylation of dsx pre-mRNA requires a sequence that binds specifically to tra-2 protein in vitro. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):579–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90090-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. E., Grabowski P. J. U1 snRNP targets an essential splicing factor, U2AF65, to the 3' splice site by a network of interactions spanning the exon. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2554–2568. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Hoshijima K., Higuchi I., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Binding of the Drosophila transformer and transformer-2 proteins to the regulatory elements of doublesex primary transcript for sex-specific RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8092–8096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A. Analysis of RNase-A-resistant regions of adenovirus 2 major late precursor-mRNA in splicing extracts reveals an ordered interaction of nuclear components with the substrate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):559–573. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo H. C., Nasim F. H., Grabowski P. J. Control of alternative splicing by the differential binding of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle. Science. 1991 Mar 1;251(4997):1045–1050. doi: 10.1126/science.1825520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., La Branche H., Kornblihtt A. R., Chabot B. A splicing enhancer in the human fibronectin alternate ED1 exon interacts with SR proteins and stimulates U2 snRNP binding. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2405–2417. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Hayase Y., Inoue H., Ohtsuka E., Ohshima Y. Surveying cis-acting sequences of pre-mRNA by adding antisense 2'-O-methyl oligoribonucleotides to a splicing reaction. J Biochem. 1990 Sep;108(3):399–405. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagoshi R. N., Baker B. S. Regulation of sex-specific RNA splicing at the Drosophila doublesex gene: cis-acting mutations in exon sequences alter sex-specific RNA splicing patterns. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):89–97. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasim F. H., Spears P. A., Hoffmann H. M., Kuo H. C., Grabowski P. J. A Sequential splicing mechanism promotes selection of an optimal exon by repositioning a downstream 5' splice site in preprotachykinin pre-mRNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1172–1184. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Green M. R. Mechanism for cryptic splice site activation during pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6253–6257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Norman C. U5 snRNA interacts with exon sequences at 5' and 3' splice sites. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):743–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A., Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. Minimal exon sequence requirements for efficient in vitro splicing of mono-intronic nuclear pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11284–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson B. L., Cote G. J., Berget S. M. Exon definition may facilitate splice site selection in RNAs with multiple exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):84–94. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Specific and stable intron-factor interactions are established early during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Greene J. M., Green M. R. Cryptic branch point activation allows accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin intron mutants. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):833–844. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawa H., Shimura Y. Alterations of RNase H sensitivity of the 3' splice site region during the in vitro splicing reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3953–3958. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somasekhar M. B., Mertz J. E. Exon mutations that affect the choice of splice sites used in processing the SV40 late transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5591–5609. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer E. J., Steitz J. A. The U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs as active site components of the spliceosome. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):1989–1996. doi: 10.1126/science.8266094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterner D. A., Berget S. M. In vivo recognition of a vertebrate mini-exon as an exon-intron-exon unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2677–2687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Q., Mayeda A., Hampson R. K., Krainer A. R., Rottman F. M. General splicing factor SF2/ASF promotes alternative splicing by binding to an exonic splicing enhancer. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2598–2608. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talerico M., Berget S. M. Effect of 5' splice site mutations on splicing of the preceding intron. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6299–6305. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Watakabe A., Shimura Y. Polypurine sequences within a downstream exon function as a splicing enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1347–1354. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull-Ross A. D., Else A. J., Eperon I. C. The dependence of splicing efficiency on the length of 3' exon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):395–411. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watakabe A., Tanaka K., Shimura Y. The role of exon sequences in splice site selection. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):407–418. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Sontheimer E. J., Steitz J. A. Site-specific cross-linking of mammalian U5 snRNP to the 5' splice site before the first step of pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2542–2553. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R., Teng J., Cooper T. A. The cardiac troponin T alternative exon contains a novel purine-rich positive splicing element. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3660–3674. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Leung H., Weiner A. M. The natural 5' splice site of simian virus 40 large T antigen can be improved by increasing the base complementarity to U1 RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):3018–3020. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.3018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. The conserved dinucleotide AG of the 3' splice site may be recognized twice during in vitro splicing of mammalian mRNA precursors. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]