Abstract
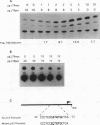
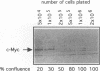
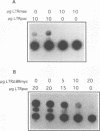
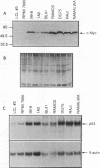
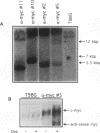
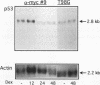
Elevated levels of mutant forms of the p53 tumor suppressor are a hallmark of many transformed cells. Multiple mechanisms such as increased stability of the protein and increased transcription of the gene can account for elevated p53 expression. Recent findings indicate that c-Myc/Max heterodimers can bind to an essential CA(C/T)GTG-containing site in the p53 promoter and elevate its expression. We have addressed the possibility that elevated mutant p53 expression is due to deregulated c-Myc expression. Here we demonstrate that the human p53 promoter is transactivated by high c-Myc expression and repressed by high Max expression. In examining the relative levels of c-Myc and p53 in human Burkitt's lymphomas and other B-lymphoid lines, we found that there is a correlation between the levels of c-Myc protein and p53 mRNA expression. In particular, cells that express very low levels of c-Myc protein also express low levels of p53 mRNA, while cells that express high levels of c-Myc tend to express high levels of p53 mRNA. To determine whether the p53 gene can be a target for c-Myc in vivo, we assayed the effects of antisense c-myc RNA on the levels of endogenous p53 mRNA. The results indicate that the presence of antisense c-myc RNA leads to a reduction in the levels of c-Myc protein, p53 mRNA, and expression from the p53 promoter. Taken together, our findings support a direct role for c-Myc in elevating expression of the mutant p53 gene in some tumors.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak Y., Juven T., Haffner R., Oren M. mdm2 expression is induced by wild type p53 activity. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):461–468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello-Fernandez C., Packham G., Cleveland J. L. The ornithine decarboxylase gene is a transcriptional target of c-Myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7804–7808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benvenisty N., Leder A., Kuo A., Leder P. An embryonically expressed gene is a target for c-Myc regulation via the c-Myc-binding sequence. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2513–2523. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich S., Hyde-DeRuyscher N., Espenshade P., Cole M. max encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein and is not regulated by serum growth factors. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):775–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia K. G., Gutiérrez M. I., Huppi K., Siwarski D., Magrath I. T. The pattern of p53 mutations in Burkitt's lymphoma differs from that of solid tumors. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 1;52(15):4273–4276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia K., Huppi K., Spangler G., Siwarski D., Iyer R., Magrath I. Point mutations in the c-Myc transactivation domain are common in Burkitt's lymphoma and mouse plasmacytomas. Nat Genet. 1993 Sep;5(1):56–61. doi: 10.1038/ng0993-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette R. P., Echeverri F., Mahboubi A., Green D. R. Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):552–554. doi: 10.1038/359552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Huang J., Ma A., Kretzner L., Alt F. W., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Binding of myc proteins to canonical and noncanonical DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5216–5224. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressac B., Kew M., Wands J., Ozturk M. Selective G to T mutations of p53 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma from southern Africa. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):429–431. doi: 10.1038/350429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Chen Y. M., Bookstein R., Lee W. H. Genetic mechanisms of tumor suppression by the human p53 gene. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1576–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.2274789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenevix-Trench G., Martin N. G., Ellem K. A. Gene expression in melanoma cell lines and cultured melanocytes: correlation between levels of c-src-1, c-myc and p53. Oncogene. 1990 Aug;5(8):1187–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho Y., Gorina S., Jeffrey P. D., Pavletich N. P. Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):346–355. doi: 10.1126/science.8023157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Buschhausen-Denker G., Patschinsky T., Steinmeyer K. Cell cycle control of p53 in normal (3T3) and chemically transformed (Meth A) mouse cells. II. Requirement for cell cycle progression. Oncogene. 1990 Nov;5(11):1701–1706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmer D., Pati S., Zambetti G., Chu S., Teresky A. K., Moore M., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Gain of function mutations in p53. Nat Genet. 1993 May;4(1):42–46. doi: 10.1038/ng0593-42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Ruppert J. M., Aster J. C., Winchester E. Inhibition of DNA replication factor RPA by p53. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):79–82. doi: 10.1038/365079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erisman M. D., Scott J. K., Watt R. A., Astrin S. M. The c-myc protein is constitutively expressed at elevated levels in colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Allan G. J., Shanahan F., Vousden K. H., Crook T. p53 is frequently mutated in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2879–2887. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A. The mdm-2 oncogene can overcome wild-type p53 suppression of transformed cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):301–306. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaidano G., Ballerini P., Gong J. Z., Inghirami G., Neri A., Newcomb E. W., Magrath I. T., Knowles D. M., Dalla-Favera R. p53 mutations in human lymphoid malignancies: association with Burkitt lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5413–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaubatz S., Meichle A., Eilers M. An E-box element localized in the first intron mediates regulation of the prothymosin alpha gene by c-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3853–3862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Mechta F., Yaniv M., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can down-modulate the activity of various promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9979–9983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grignani F., Lombardi L., Inghirami G., Sternas L., Cechova K., Dalla-Favera R. Negative autoregulation of c-myc gene expression is inactivated in transformed cells. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3913–3922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Seth A., Davis R. J. Transactivation of gene expression by Myc is inhibited by mutation at the phosphorylation sites Thr-58 and Ser-62. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3216–3220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hateboer G., Timmers H. T., Rustgi A. K., Billaud M., van 't Veer L. J., Bernards R. TATA-binding protein and the retinoblastoma gene product bind to overlapping epitopes on c-Myc and adenovirus E1A protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8489–8493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. C., Metcalf R. A., Sun T., Welsh J. A., Wang N. J., Harris C. C. Mutational hotspot in the p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):427–428. doi: 10.1038/350427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Dürr P., Meichle A., Steiner P., Pagano M., Finke K., Botz J., Wessbecher J., Draetta G., Eilers M. Differential modulation of cyclin gene expression by MYC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3685–3689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Dang C. V. An amino-terminal c-myc domain required for neoplastic transformation activates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5914–5920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Lee W. M., Chen L. L., Dang C. V. Max: functional domains and interaction with c-Myc. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max proteins possess distinct transcriptional activities. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):426–429. doi: 10.1038/359426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuerbitz S. J., Plunkett B. S., Walsh W. V., Kastan M. B. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., Maltby V., Mock D., Rossant J., Pawson T., Bernstein A. High incidence of lung, bone, and lymphoid tumors in transgenic mice overexpressing mutant alleles of the p53 oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3982–3991. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Botchan M. R. The acidic transcriptional activation domains of VP16 and p53 bind the cellular replication protein A and stimulate in vitro BPV-1 DNA replication. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1207–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90649-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Miller C. W., Koeffler P. H., Berk A. J. The p53 activation domain binds the TATA box-binding polypeptide in Holo-TFIID, and a neighboring p53 domain inhibits transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3291–3300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Lane D. P. Differential induction of transcriptionally active p53 following UV or ionizing radiation: defects in chromosome instability syndromes? Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):765–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90496-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. H., Vartikar J., Pipas J. M., Laimins L. A. Specific repression of TATA-mediated but not initiator-mediated transcription by wild-type p53. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):281–283. doi: 10.1038/363281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltzman W., Czyzyk L. UV irradiation stimulates levels of p53 cellular tumor antigen in nontransformed mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1689–1694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Shields M. T., Amin M., Sauve G. J., Appella E., Romano J. W., Ullrich S. J. Negative growth regulation in a glioblastoma tumor cell line that conditionally expresses human wild-type p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6166–6170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. p53 mutations: gains or losses? J Cell Biochem. 1991 Jan;45(1):22–29. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240450108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Unger T., Huibregtse J. M., Howley P. M. The transcriptional transactivation function of wild-type p53 is inhibited by SV40 large T-antigen and by HPV-16 E6 oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5013–5020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Gyuris J., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncoprotein MDM2 conceals the activation domain of tumour suppressor p53. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):857–860. doi: 10.1038/362857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Schmidt J. R., Yoas K., Hao M. M., Lozano G. Analysis of p53 mutants for transcriptional activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6067–6074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Alpers J. D., Nowell P. C., Hoover R. G. Sequential expression of protooncogenes during lectin-stimulated mitogenesis of normal human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):199–201. doi: 10.1038/308199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
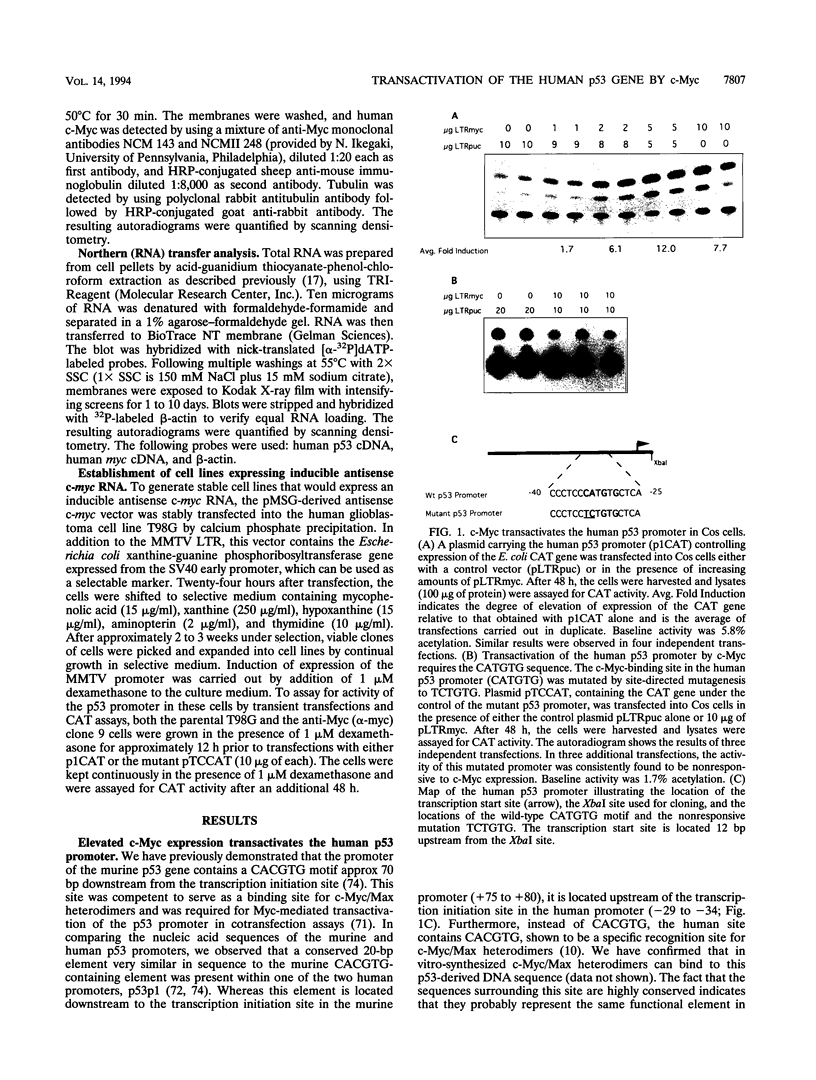
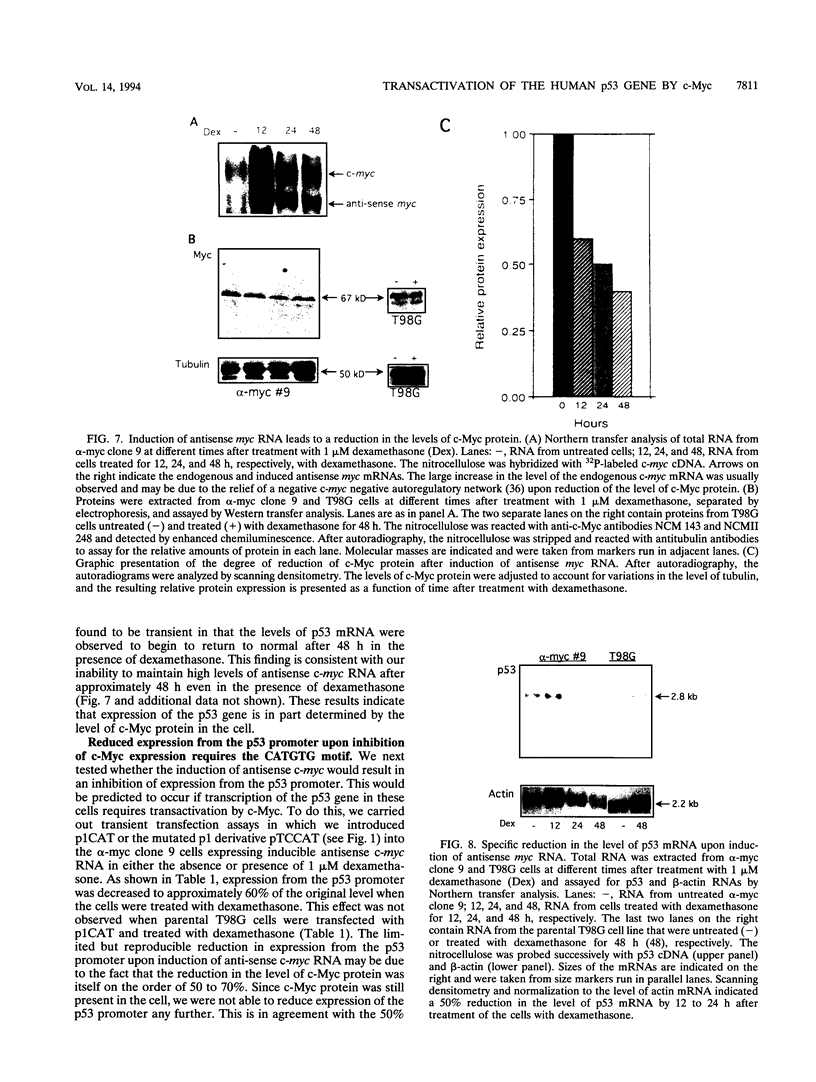
- Reisman D., Elkind N. B., Roy B., Beamon J., Rotter V. c-Myc trans-activates the p53 promoter through a required downstream CACGTG motif. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Feb;4(2):57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Greenberg M., Rotter V. Human p53 oncogene contains one promoter upstream of exon 1 and a second, stronger promoter within intron 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5146–5150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Rotter V. The helix-loop-helix containing transcription factor USF binds to and transactivates the promoter of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):345–350. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronen D., Rotter V., Reisman D. Expression from the murine p53 promoter is mediated by factor binding to a downstream helix-loop-helix recognition motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4128–4132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Carruthers C., Gutjahr T., Roeder R. G. Direct role for Myc in transcription initiation mediated by interactions with TFII-I. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):359–361. doi: 10.1038/365359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Usheva A., Zambetti G. P., Momand J., Horikoshi N., Weinmann R., Levine A. J., Shenk T. Wild-type p53 binds to the TATA-binding protein and represses transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12028–12032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulian E., Zauberman A., Ginsberg D., Oren M. Identification of a minimal transforming domain of p53: negative dominance through abrogation of sequence-specific DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5581–5592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Ben-Ze'ev A., Rotter V. Subcellular distribution of the p53 protein during the cell cycle of Balb/c 3T3 cells. Oncogene. 1990 Nov;5(11):1707–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Goldfinger N., Peled A., Rotter V. Involvement of wild-type p53 in pre-B-cell differentiation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8982–8986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Goldfinger N., Rotter V. Alterations in tumor development in vivo mediated by expression of wild type or mutant p53 proteins. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 1;51(19):5232–5237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Bovey R., Tardy S., Sahli R., Sordat B., Costa J. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Glynn J. M., Guilbert L. J., Cotter T. G., Bissonnette R. P., Green D. R. Role for c-myc in activation-induced apoptotic cell death in T cell hybridomas. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):212–214. doi: 10.1126/science.1378649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava A., Saleque S., Kalpana G. V., Artandi S., Goff S. P., Calame K. Inhibition of transcriptional regulator Yin-Yang-1 by association with c-Myc. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1889–1892. doi: 10.1126/science.8266081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Groudine M. Control of c-myc regulation in normal and neoplastic cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;56:1–48. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Brain R., Maimets T., Addison C., Rudge K., Jenkins J. R. Mouse p53 blocks SV40 DNA replication in vitro and downregulates T antigen DNA helicase activity. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):405–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuck S. P., Crawford L. Characterization of the human p53 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2163–2172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Mietz J. A., Scheffner M., Yee C. L., Howley P. M. Functional domains of wild-type and mutant p53 proteins involved in transcriptional regulation, transdominant inhibition, and transformation suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5186–5194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Nau M. M., Segal S., Minna J. D. p53: a transdominant regulator of transcription whose function is ablated by mutations occurring in human cancer. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1383–1390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner A. J., Small M. B., Hay N. Myc-mediated apoptosis is blocked by ectopic expression of Bcl-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2432–2440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Hauschka S., Tapscott S. J. The MCK enhancer contains a p53 responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4570–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Rotter V. Reconstitution of p53 expression in a nonproducer Ab-MuLV-transformed cell line by transfection of a functional p53 gene. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Bayle J. H., Olson D., Levine A. J. The p53-mdm-2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1126–1132. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew P. R., Berk A. J. Inhibition of p53 transactivation required for transformation by adenovirus early 1B protein. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):82–85. doi: 10.1038/357082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Bargonetti J., Walker K., Prives C., Levine A. J. Wild-type p53 mediates positive regulation of gene expression through a specific DNA sequence element. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1143–1152. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]