Abstract
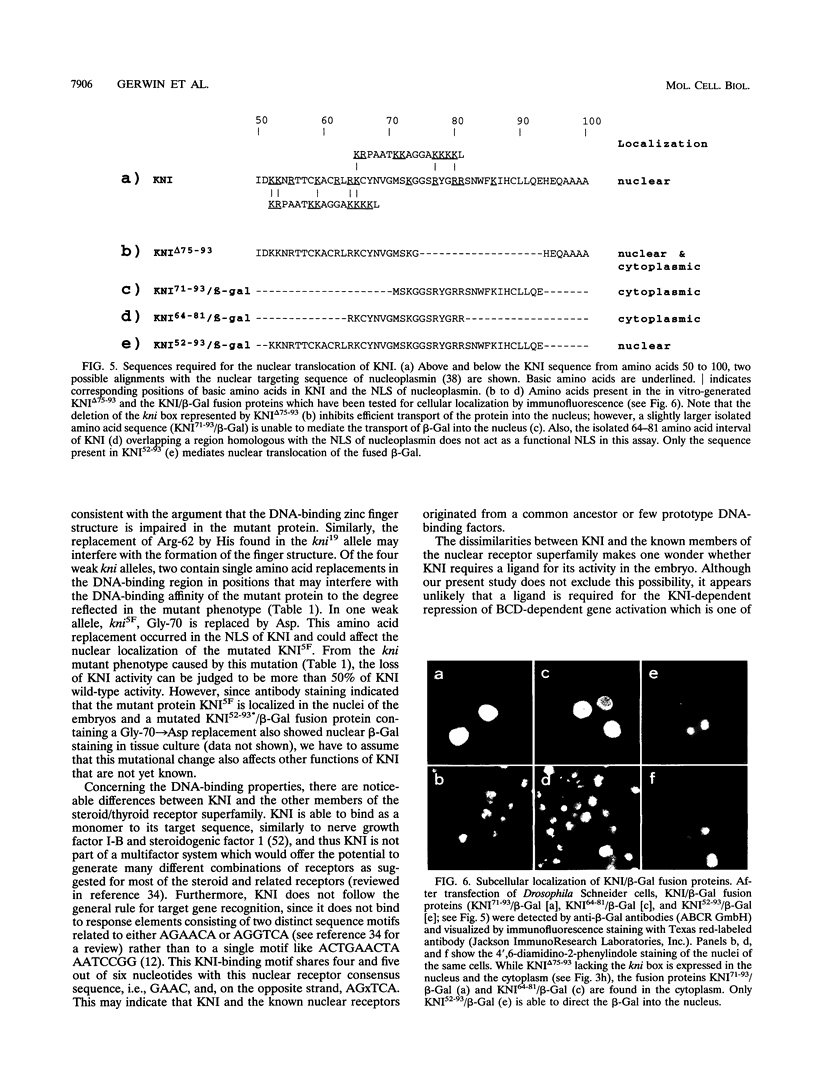
The Drosophila gap gene knirps (kni) is required for abdominal segmentation. It encodes a steroid/thyroid orphan receptor-type transcription factor which is distributed in a broad band of nuclei in the posterior region of the blastoderm. To identify essential domains of the kni protein (KNI), we cloned and sequenced the DNA encompassing the coding region of nine kni mutant alleles of different strength and kni-homologous genes of related insect species. We also examined in vitro-modified versions of KNI in various assay systems both in vitro and in tissue culture. The results show that KNI contains several functional domains which are arranged in a modular fashion. The N-terminal 185-amino-acid region which includes the DNA-binding domain and a functional nuclear location signal fails to provide kni activity to the embryo. However, a truncated KNI protein that contains additional 47 amino acids exerts rather strong kni activity which is functionally defined by a weak kni mutant phenotype of the embryo. The additional 47-amino-acid stretch includes a transcriptional repressor domain which acts in the context of a heterologous DNA-binding domain of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. The different domains of KNI as defined by functional studies are conserved during insect evolution.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akam M. The molecular basis for metameric pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunch T. A., Grinblat Y., Goldstein L. S. Characterization and use of the Drosophila metallothionein promoter in cultured Drosophila melanogaster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1043–1061. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapkin R., Merino A., Reinberg D. Regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90013-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The bicoid protein is a positive regulator of hunchback transcription in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):138–143. doi: 10.1038/337138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul U., Jäckle H. Pole region-dependent repression of the Drosophila gap gene Krüppel by maternal gene products. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):549–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul U., Jäckle H. Role of gap genes in early Drosophila development. Adv Genet. 1990;27:239–275. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression by the Drosophila even-skipped protein: definition of a minimal repression domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):491–503. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann C., Taubert H., Jäckle H., Pankratz M. J. A two-step mode of stripe formation in the Drosophila blastoderm requires interactions among primary pair rule genes. Mech Dev. 1994 Jan;45(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch M., Gerwin N., Taubert H., Jäckle H. Competition for overlapping sites in the regulatory region of the Drosophila gene Krüppel. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):94–97. doi: 10.1126/science.1348871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. The molecular genetics of embryonic pattern formation in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):25–34. doi: 10.1038/335025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingler M., Erdélyi M., Szabad J., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Function of torso in determining the terminal anlagen of the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):275–277. doi: 10.1038/335275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Saffman E. E., Kornfeld K., Hogness D. S. Transcriptional activation and repression by Ultrabithorax proteins in cultured Drosophila cells. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):1031–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Grossel M. J., Figge J., Hansen U. M. Drosophila Krüppel protein is a transcriptional repressor. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):76–79. doi: 10.1038/346076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. A new class of yeast transcriptional activators. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauber U., Pankratz M. J., Kienlin A., Seifert E., Klemm U., Jäckle H. Abdominal segmentation of the Drosophila embryo requires a hormone receptor-like protein encoded by the gap gene knirps. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):489–492. doi: 10.1038/336489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C. Determination of the embryonic axes of Drosophila. Dev Suppl. 1991;1:1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., Ong E. S., Margolis J. S., Posakony J. W., McKeown M., Evans R. M. The Drosophila gene knirps-related is a member of the steroid-receptor gene superfamily. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):493–496. doi: 10.1038/336493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankratz M. J., Seifert E., Gerwin N., Billi B., Nauber U., Jäckle H. Gradients of Krüppel and knirps gene products direct pair-rule gene stripe patterning in the posterior region of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90811-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. G. Steroid and related receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90016-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Kumar V., Chambon P., Yamamoto K. R. Signal transduction by steroid hormones: nuclear localization is differentially regulated in estrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. Cell Regul. 1990 Feb;1(3):291–299. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.3.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Nauber U., Jäckle H. Three hormone receptor-like Drosophila genes encode an identical DNA-binding finger. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3087–3094. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Pehl M., Taubert H., Jäckle H. Loss of gene function through rapid mitotic cycles in the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):156–159. doi: 10.1038/359156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Jäckle H. Dimerization and the control of transcription by Krüppel. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):454–457. doi: 10.1038/364454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer R., Tautz D. Segmentation gene expression in the housefly Musca domestica. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):419–430. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3035–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Opsomer C., McKeown Y. M., Kramer W., Zabeau M., Fritz H. J. Efficient oligonucleotide-directed construction of mutations in expression vectors by the gapped duplex DNA method using alternating selectable markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4441–4454. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieschaus E., Nusslein-Volhard C., Kluding H. Krüppel, a gene whose activity is required early in the zygotic genome for normal embryonic segmentation. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):172–186. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Fahrner T. J., Milbrandt J. The orphan receptors NGFI-B and steroidogenic factor 1 establish monomer binding as a third paradigm of nuclear receptor-DNA interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5794–5804. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]