Abstract
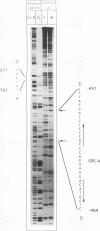
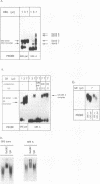
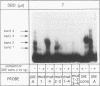
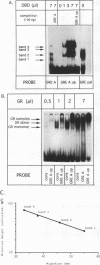
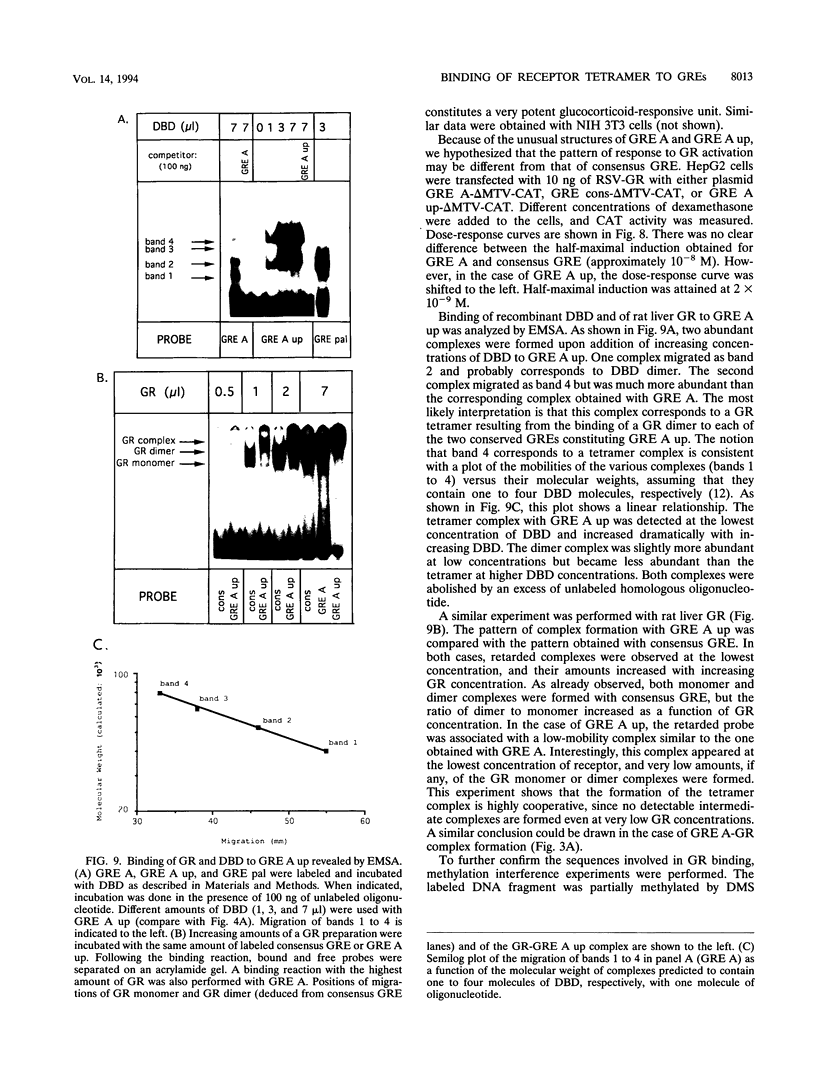
An unusual glucocorticoid-responsive element (called GRE A) was found to mediate the induction of the cytosolic aspartate aminotransferase gene by glucocorticoids and was bound by the glucocorticoid receptor in a DNase I footprinting assay. GRE A consists of two overlapping GREs, each comprising a conserved half-site and an imperfect half-site. The complete unit was able to confer glucocorticoid inducibility to a heterologous promoter (delta MTV-CAT). Mutation of any of the half-sites, including the imperfect ones, abolished inducibility by the hormone, demonstrating that each of the isolated GREs was inactive. In electrophoretic mobility shift assays, purified rat liver glucocorticoid receptor (GR) formed a low-mobility complex with GRE A, presumably containing a GR tetramer. When purified bacterially expressed DBD was used, low-mobility complexes as well as dimer and monomer complexes were formed. In inactive mutated oligonucleotides, no GR tetramer formation was detected. Modification of the imperfect half-sites in order to increase their affinity for GR gave a DNA sequence that bound a GR tetramer in a highly cooperative manner. This activated unit consisting of two overlapping consensus GREs mediated glucocorticoid induction with a higher efficiency than consensus GRE.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggerbeck M., Garlatti M., Feilleux-Duché S., Veyssier C., Daheshia M., Hanoune J., Barouki R. Regulation of the cytosolic aspartate aminotransferase housekeeping gene promoter by glucocorticoids, cAMP, and insulin. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 7;32(35):9065–9072. doi: 10.1021/bi00086a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns W., Cairns C., Pongratz I., Poellinger L., Okret S. Assembly of a glucocorticoid receptor complex prior to DNA binding enhances its specific interaction with a glucocorticoid response element. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11221–11226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X., Preiss T., Slater E. P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Expression and functional analysis of steroid receptor fragments secreted from Staphylococcus aureus. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;44(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(93)90145-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson-Jurica M. A., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Steroid receptor family: structure and functions. Endocr Rev. 1990 May;11(2):201–220. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Schauer M., Cao X. A., Beato M. Efficient binding of glucocorticoid receptor to its responsive element requires a dimer and DNA flanking sequences. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;9(5):355–368. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin J., Sun Y. L., Chamberland M., Gauthier Y., De Léan A., Nemer M., Schmidt T. J. Novel glucocorticoid receptor complex with DNA element of the hormone-repressed POMC gene. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):145–156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05640.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin J., Trifiro M. A., Plante R. K., Nemer M., Eriksson P., Wrange O. Glucocorticoid receptor binding to a specific DNA sequence is required for hormone-dependent repression of pro-opiomelanocortin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5305–5314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlatti M., Tchesnokov V., Daheshia M., Feilleux-Duché S., Hanoune J., Aggerbeck M., Barouki R. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-related proteins bind to the unusual promoter of the aspartate aminotransferase housekeeping gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6567–6574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisse S., Scheidereit C., Westphal H. M., Hynes N. E., Groner B., Beato M. Glucocorticoid receptors recognize DNA sequences in and around murine mammary tumour virus DNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1613–1619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer S. R., Marschke K. B., Wilson E. M., French F. S. Receptor accessory factor enhances specific DNA binding of androgen and glucocorticoid receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17519–17527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa R., Yu V. C., När A., Kyakumoto S., Han Z., Silverman S., Rosenfeld M. G., Glass C. K. Differential orientations of the DNA-binding domain and carboxy-terminal dimerization interface regulate binding site selection by nuclear receptor heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1423–1435. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Chen J. Y., Chen Z., White J., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. The patterns of binding of RAR, RXR and TR homo- and heterodimers to direct repeats are dictated by the binding specificites of the DNA binding domains. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5029–5041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Wahli W. Cooperative binding of estrogen receptor to imperfect estrogen-responsive DNA elements correlates with their synergistic hormone-dependent enhancer activity. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3781–3791. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K., Suh B. J., Kühnel B., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Structural determinants of a glucocorticoid receptor recognition element. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1866–1873. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavé-Preux M., Aggerbeck M., Veyssier C., Bousquet-Lemercier B., Hanoune J., Barouki R. Hormonal discrimination among transcription start sites of aspartate aminotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4444–4448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Rangarajan P. N., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants for selective RAR and TR recognition of direct repeat HREs. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1411–1422. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Göttlicher M., Gustafsson J. A. The dioxin and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear receptors in search of endogenous ligands. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jun;13(6):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90076-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponglikitmongkol M., White J. H., Chambon P. Synergistic activation of transcription by the human estrogen receptor bound to tandem responsive elements. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2221–2231. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht R., Arriza J. L., Spengler D., Reul J. M., Evans R. M., Holsboer F., Damm K. Transactivation and synergistic properties of the mineralocorticoid receptor: relationship to the glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Apr;7(4):597–603. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.4.8388999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid W., Strähle U., Schütz G., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H. Glucocorticoid receptor binds cooperatively to adjacent recognition sites. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2257–2263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. P., Redeuilh G., Beato M. Hormonal regulation of vitellogenin genes: an estrogen-responsive element in the Xenopus A2 gene and a multihormonal regulatory region in the chicken II gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Mar;5(3):386–396. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-3-386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan G., Thompson E. B. Overexpression of full-length human glucocorticoid receptor in Spodoptera frugiperda cells using the baculovirus expression vector system. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):209–216. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truss M., Beato M. Steroid hormone receptors: interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid and transcription factors. Endocr Rev. 1993 Aug;14(4):459–479. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truss M., Chalepakis G., Slater E. P., Mader S., Beato M. Functional interaction of hybrid response elements with wild-type and mutant steroid hormone receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3247–3258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Cooperative binding of steroid hormone receptors contributes to transcriptional synergism at target enhancer elements. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90919-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants of target gene specificity for steroid/thyroid hormone receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1139–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]