Abstract
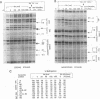
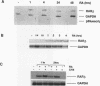
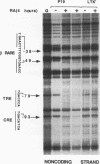
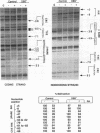
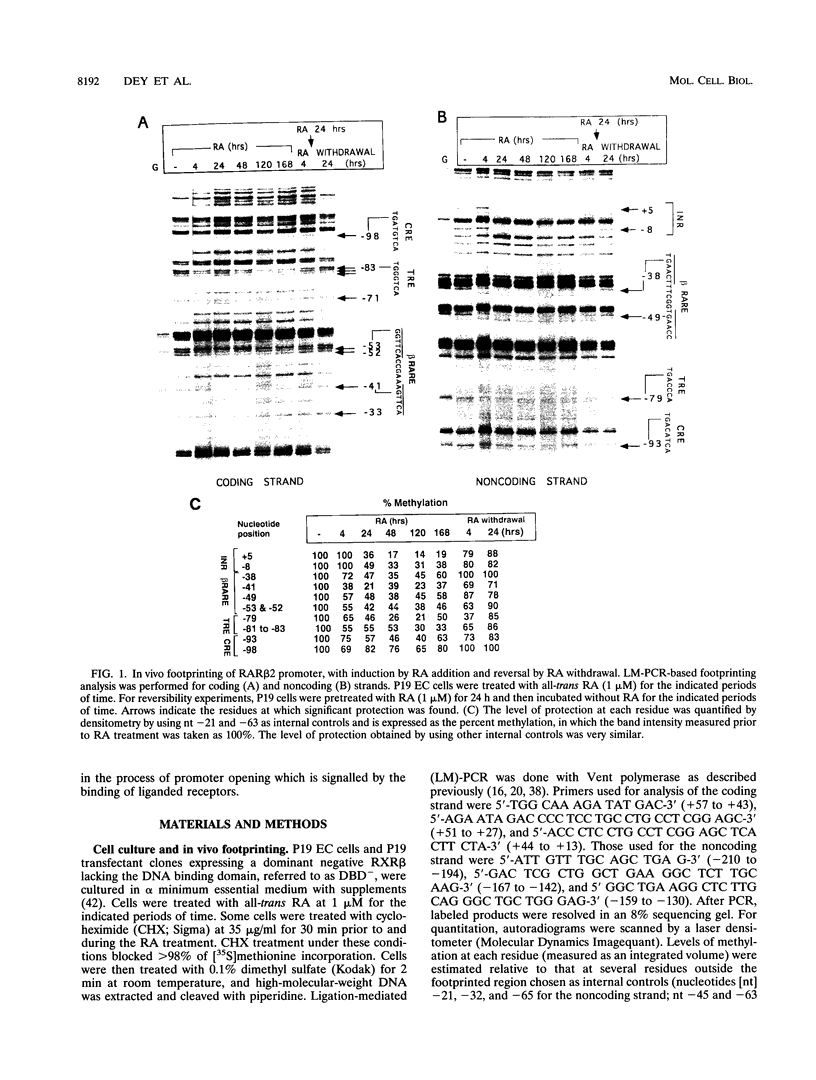
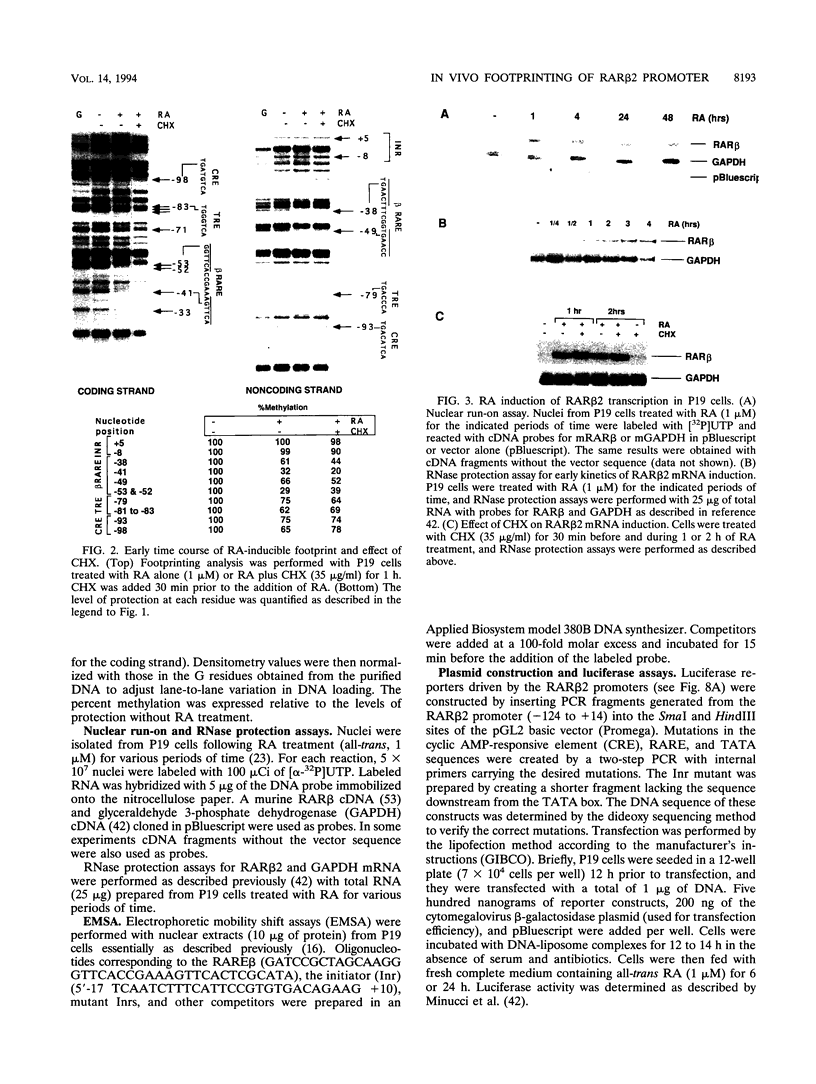
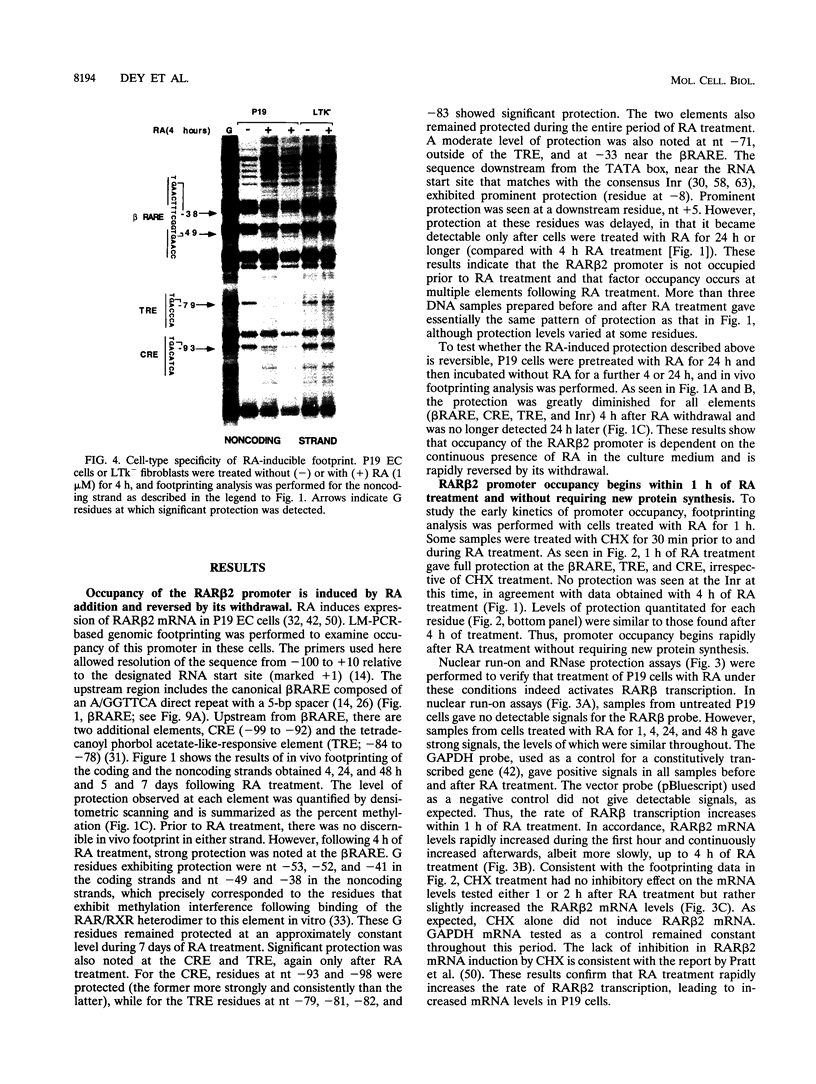
Retinoic acid (RA) activates transcription of the RA receptor beta 2 (RAR beta 2) gene in embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells. This activation involves binding of the RAR/retinoid X receptor (RAR/RXR) heterodimer to the RA-responsive element (beta RARE). Dimethyl sulfate-based genomic footprinting was performed to examine occupancy of this promoter in P19 EC cells. No footprint was detected at the beta RARE prior to RA treatment, but a footprint was detected within the first hour of RA treatment. Concomitantly, other elements in the promoter, the cyclic AMP-responsive element and tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-like-responsive element became footprinted. Footprints at these elements were induced by RA without requiring new protein synthesis and remained for the entire duration of RA treatment but rapidly reversed upon withdrawal of RA. A delayed protection observed at the initiator site was also reversed upon RA withdrawal. The RA-inducible footprint was not due to induction of factors that bind to these element, since in vitro assays showed that these factors are present in P19 cell extracts before RA treatment. Significantly, no RA-induced footprint was observed at any of these elements in P19 cells expressing a dominant negative RXR beta, in which RXR heterodimers are unable to bind to the beta RARE. Results indicate that binding of a liganded heterodimer receptor to the beta RARE is the initial event that allows other elements to gain access to the factors. In accordance, reporter analyses showed that a mutation in the beta RARE, but not those in other elements, abrogates RA activation of the promoter. It is likely that the RAR beta 2 promoter opens in a hierarchically ordered manner, signalled by the occupancy of liganded heterodimers.
Full text
PDF
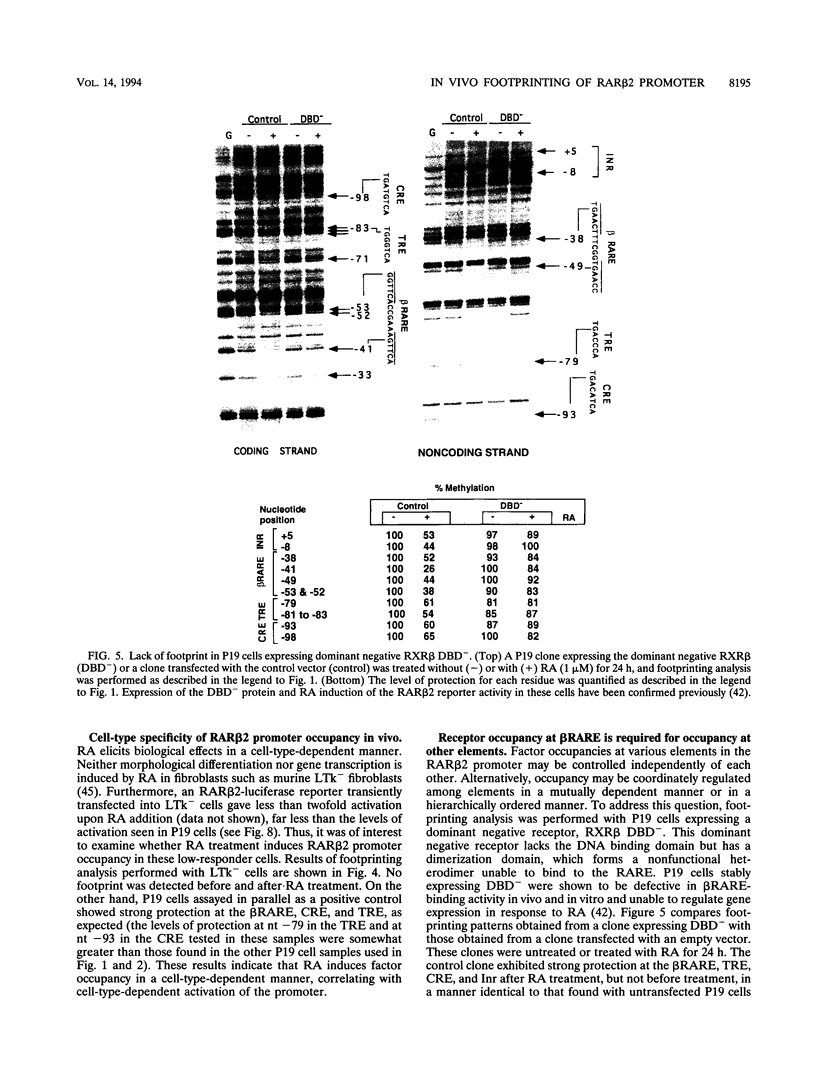
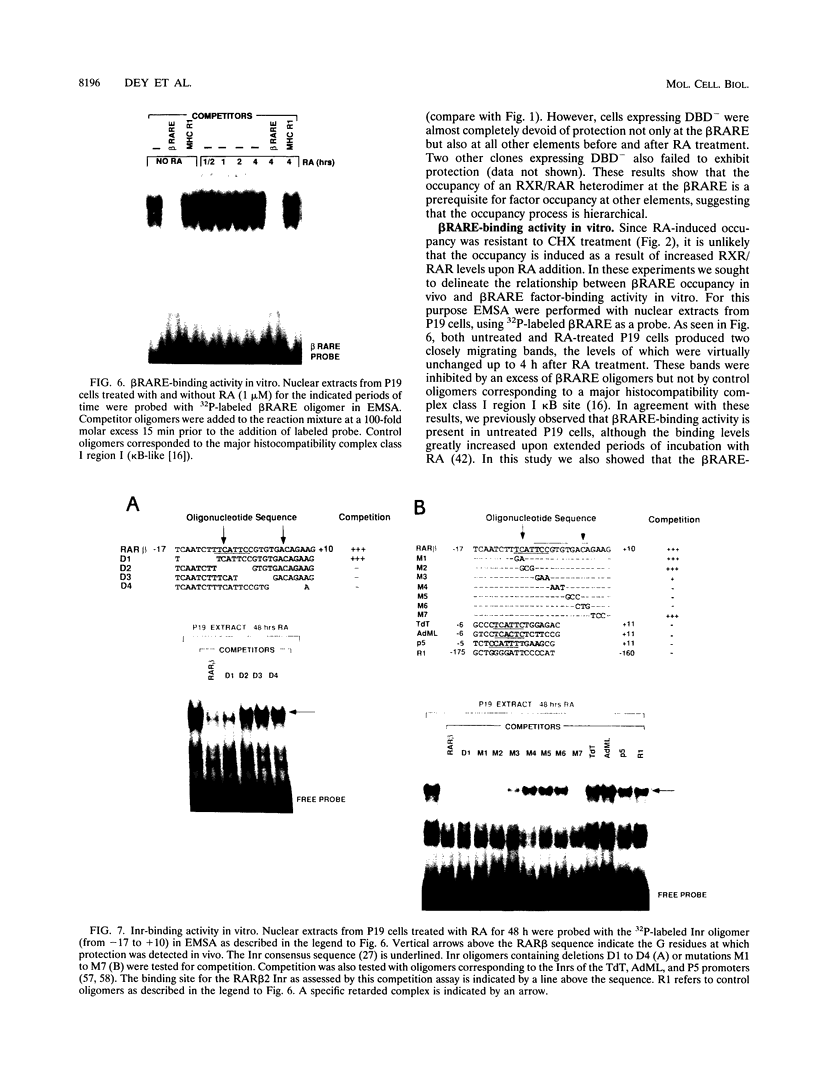
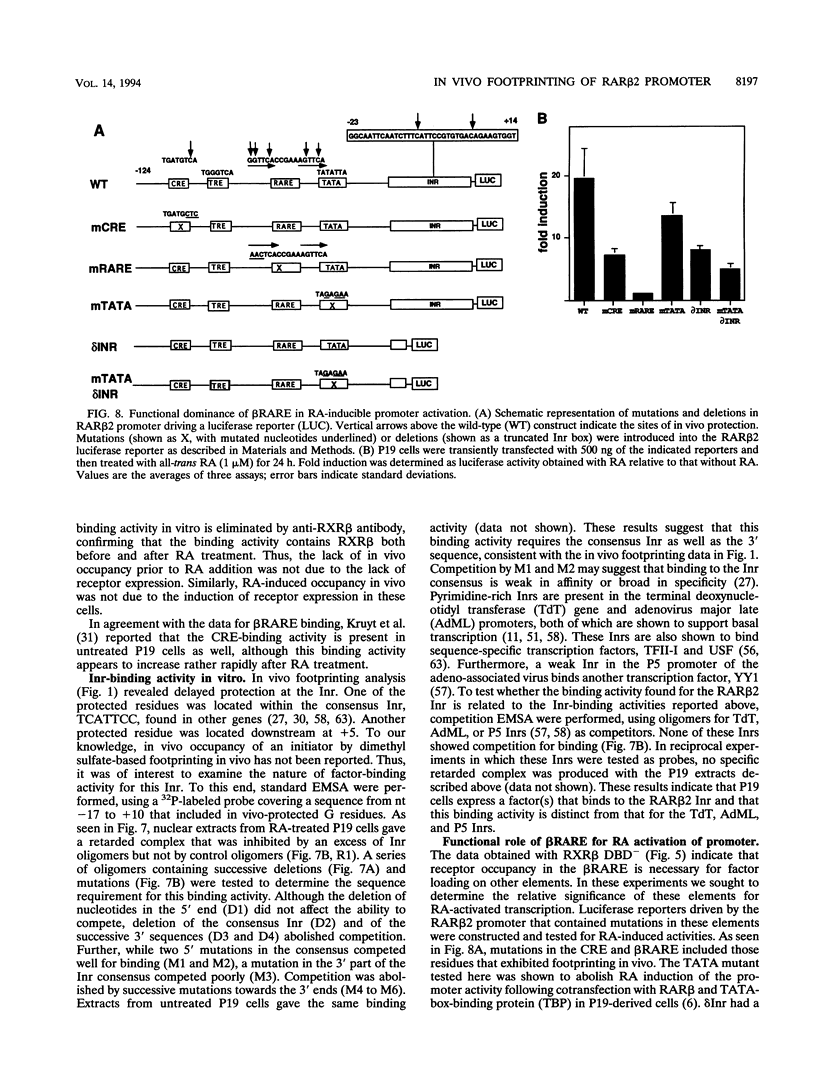
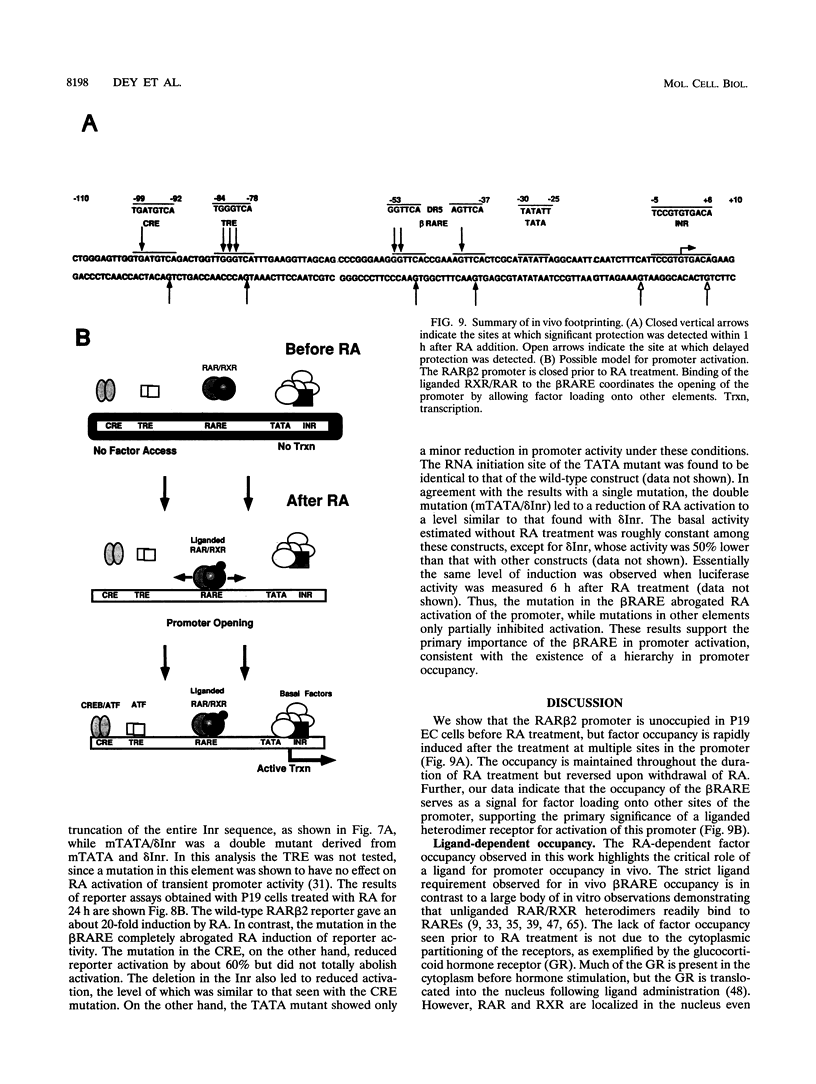



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abravaya K., Phillips B., Morimoto R. I. Heat shock-induced interactions of heat shock transcription factor and the human hsp70 promoter examined by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):586–592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan G. F., Leng X., Tsai S. Y., Weigel N. L., Edwards D. P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Hormone and antihormone induce distinct conformational changes which are central to steroid receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19513–19520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Lefebvre P., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor loading on the MMTV promoter: a bimodal mechanism for promoter activation. Science. 1992 Mar 20;255(5051):1573–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.1347958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au-Fliegner M., Helmer E., Casanova J., Raaka B. M., Samuels H. H. The conserved ninth C-terminal heptad in thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors mediates diverse responses by affecting heterodimer but not homodimer formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5725–5737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P., Renkawitz R., Schütz G. Tissue-specific DNaseI hypersensitive sites in the 5'-flanking sequences of the tryptophan oxygenase and the tyrosine aminotransferase genes. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2015–2020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02084.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenstam A., Vivanco Ruiz M. M., Barettino D., Horikoshi M., Stunnenberg H. G. Cooperativity in transactivation between retinoic acid receptor and TFIID requires an activity analogous to E1A. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90443-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan J. F., Lohnes D., Taneja R., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. Loss of retinoic acid receptor gamma function in F9 cells by gene disruption results in aberrant Hoxa-1 expression and differentiation upon retinoic acid treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9601–9605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. Developmental biology. Reading the retinoid signals. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):766–768. doi: 10.1038/345766a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns K., Duggan B., Atkinson E. A., Famulski K. S., Nemer M., Bleackley R. C., Michalak M. Modulation of gene expression by calreticulin binding to the glucocorticoid receptor. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):476–480. doi: 10.1038/367476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Buckbinder L., Reinberg D. The initiator directs the assembly of a transcription factor IID-dependent transcription complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8052–8056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr K. D., Richard-Foy H. Glucocorticoids locally disrupt an array of positioned nucleosomes on the rat tyrosine aminotransferase promoter in hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9300–9304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedhar S., Rennie P. S., Shago M., Hagesteijn C. Y., Yang H., Filmus J., Hawley R. G., Bruchovsky N., Cheng H., Matusik R. J. Inhibition of nuclear hormone receptor activity by calreticulin. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):480–483. doi: 10.1038/367480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey A., Nebert D. W., Ozato K. The AP-1 site and the cAMP- and serum response elements of the c-fos gene are constitutively occupied in vivo. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;10(7):537–544. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey A., Thornton A. M., Lonergan M., Weissman S. M., Chamberlain J. W., Ozato K. Occupancy of upstream regulatory sites in vivo coincides with major histocompatibility complex class I gene expression in mouse tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3590–3599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espeseth A. S., Murphy S. P., Linney E. Retinoic acid receptor expression vector inhibits differentiation of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1647–1656. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Force W. R., Spindler S. R. 3,5,3'-L-triiodothyronine (thyroid hormone)-induced protein-DNA interactions in the thyroid hormone response elements and cell type-specific elements of the rat growth hormone gene revealed by in vivo dimethyl sulfate footprinting. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9682–9686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrity P. A., Chen D., Rothenberg E. V., Wold B. J. Interleukin-2 transcription is regulated in vivo at the level of coordinated binding of both constitutive and regulated factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2159–2169. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrity P. A., Wold B. J. Effects of different DNA polymerases in ligation-mediated PCR: enhanced genomic sequencing and in vivo footprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1021–1025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaub M. P., Lutz Y., Ruberte E., Petkovich M., Brand N., Chambon P. Antibodies specific to the retinoic acid human nuclear receptors alpha and beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3089–3093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Roux J., Rigaud G., Pictet R. Two remote glucocorticoid responsive units interact cooperatively to promote glucocorticoid induction of rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8695–8709. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Nucleosomes: regulators of transcription. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):395–400. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90299-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R. E., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Occupation of the c-fos serum response element in vivo by a multi-protein complex is unaltered by growth factor induction. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):68–70. doi: 10.1038/340068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Hermann T., Husmann M., Graupner G., Pfahl M. A retinoic acid receptor-specific element controls the retinoic acid receptor-beta promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1727–1736. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javahery R., Khachi A., Lo K., Zenzie-Gregory B., Smale S. T. DNA sequence requirements for transcriptional initiator activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):116–127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., Rudnicki M. A., Harris J. F., McBurney M. W. Retinoic acid-induced neural differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2271–2279. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonk L. J., de Jonge M. E., Vervaart J. M., Wissink S., Kruijer W. Isolation and developmental expression of retinoic-acid-induced genes. Dev Biol. 1994 Feb;161(2):604–614. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollmar R., Farnham P. J. Site-specific initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1993 Jun;203(2):127–139. doi: 10.3181/00379727-203-43583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruyt F. A., Folkers G., van den Brink C. E., van der Saag P. T. A cyclic AMP response element is involved in retinoic acid-dependent RAR beta 2 promoter activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6393–6399. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruyt F. A., van den Brink C. E., Defize L. H., Donath M. J., Kastner P., Kruijer W., Chambon P., van der Saag P. T. Transcriptional regulation of retinoic acid receptor beta in retinoic acid-sensitive and -resistant P19 embryocarcinoma cells. Mech Dev. 1991 Mar;33(3):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa R., Yu V. C., När A., Kyakumoto S., Han Z., Silverman S., Rosenfeld M. G., Glass C. K. Differential orientations of the DNA-binding domain and carboxy-terminal dimerization interface regulate binding site selection by nuclear receptor heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1423–1435. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. L., Archer T. K. Nucleosome-mediated disruption of transcription factor-chromatin initiation complexes at the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):32–41. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E. Retinoic acid receptors: transcription factors modulating gene regulation, development, and differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1992;27:309–350. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60538-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonergan M., Dey A., Becker K. G., Drew P. D., Ozato K. A regulatory element in the beta 2-microglobulin promoter identified by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6629–6639. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson C. E., Shim E. Y., Friedman D. S., Zaret K. S. An active tissue-specific enhancer and bound transcription factors existing in a precisely positioned nucleosomal array. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80079-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minucci S., Zand D. J., Dey A., Marks M. S., Nagata T., Grippo J. F., Ozato K. Dominant negative retinoid X receptor beta inhibits retinoic acid-responsive gene regulation in embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):360–372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Decker T., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon induction of gene transcription analyzed by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Segars J. H., Levi B. Z., Ozato K. Retinoic acid-dependent transactivation of major histocompatibility complex class I promoters by the nuclear hormone receptor H-2RIIBP in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):937–941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H. Y., Davidson D., Raaka B. M., Samuels H. H. The herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene promoter contains a novel thyroid hormone response element. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Mar;7(3):319–330. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.3.8387156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Rangarajan P. N., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants for selective RAR and TR recognition of direct repeat HREs. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1411–1422. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt M. A., Kralova J., McBurney M. W. A dominant negative mutation of the alpha retinoic acid receptor gene in a retinoic acid-nonresponsive embryonal carcinoma cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6445–6453. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöpperl H., Featherstone M. S. Identification of a retinoic acid response element upstream of the murine Hox-4.2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):257–265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik A., Schütz G., Stewart A. F. Glucocorticoids are required for establishment and maintenance of an alteration in chromatin structure: induction leads to a reversible disruption of nucleosomes over an enhancer. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2569–2576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds K., Mezey E., Zimmer A. Activity of the beta-retinoic acid receptor promoter in transgenic mice. Mech Dev. 1991 Dec;36(1-2):15–29. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90068-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. In vivo footprinting of rat TAT gene: dynamic interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and a liver-specific factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90370-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Shi Y., Shenk T. YY1 is an initiator sequence-binding protein that directs and activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):241–245. doi: 10.1038/354241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G. W., Gold J. D., Petkovich M., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. A retinoic acid-responsive element is present in the 5' flanking region of the laminin B1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9099–9103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivanco Ruiz M. M., Bugge T. H., Hirschmann P., Stunnenberg H. G. Functional characterization of a natural retinoic acid responsive element. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3829–3838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis L., Reinberg D. Transcription by RNA polymerase II: initiator-directed formation of transcription-competent complexes. FASEB J. 1992 Nov;6(14):3300–3309. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.14.1426767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Transcription: in tune with the histones. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Kastner P., Krust A., Garnier J. M., Ruffenach F., Leroy P., Chambon P. Differentially expressed isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor beta generated by usage of two promoters and alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):71–81. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]