Abstract
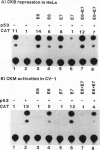
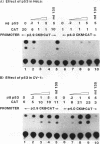
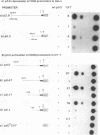
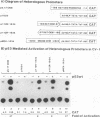
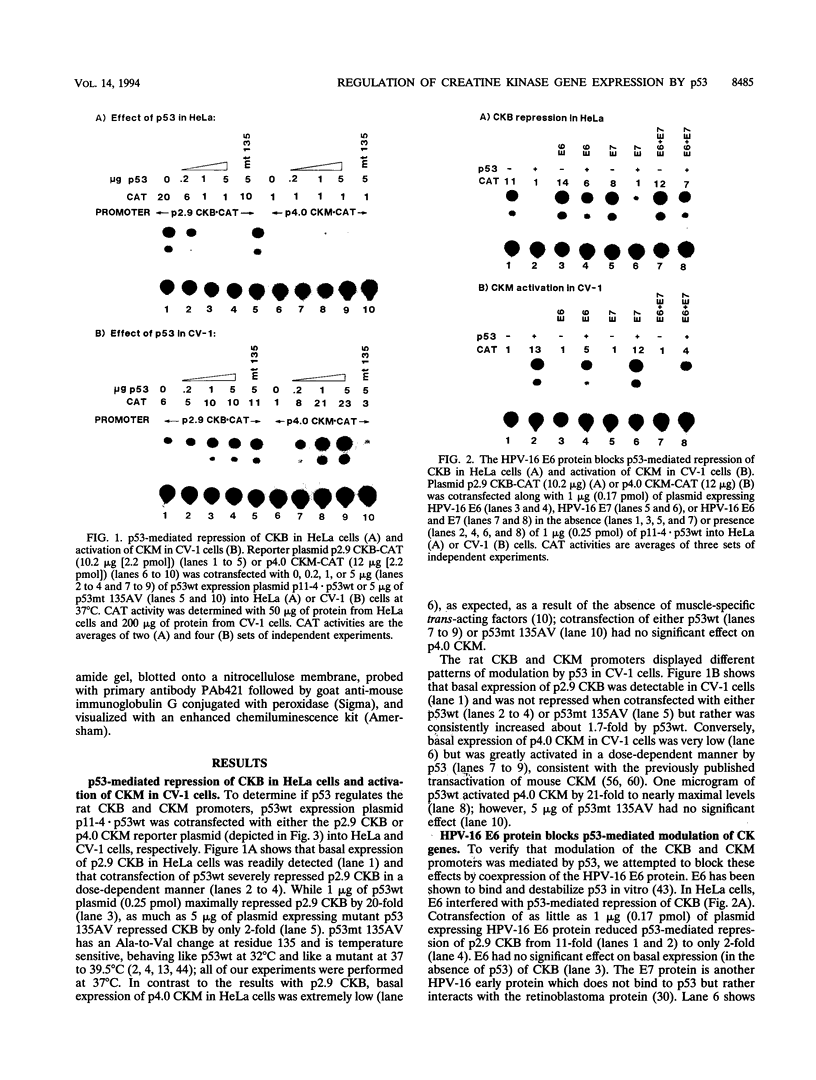
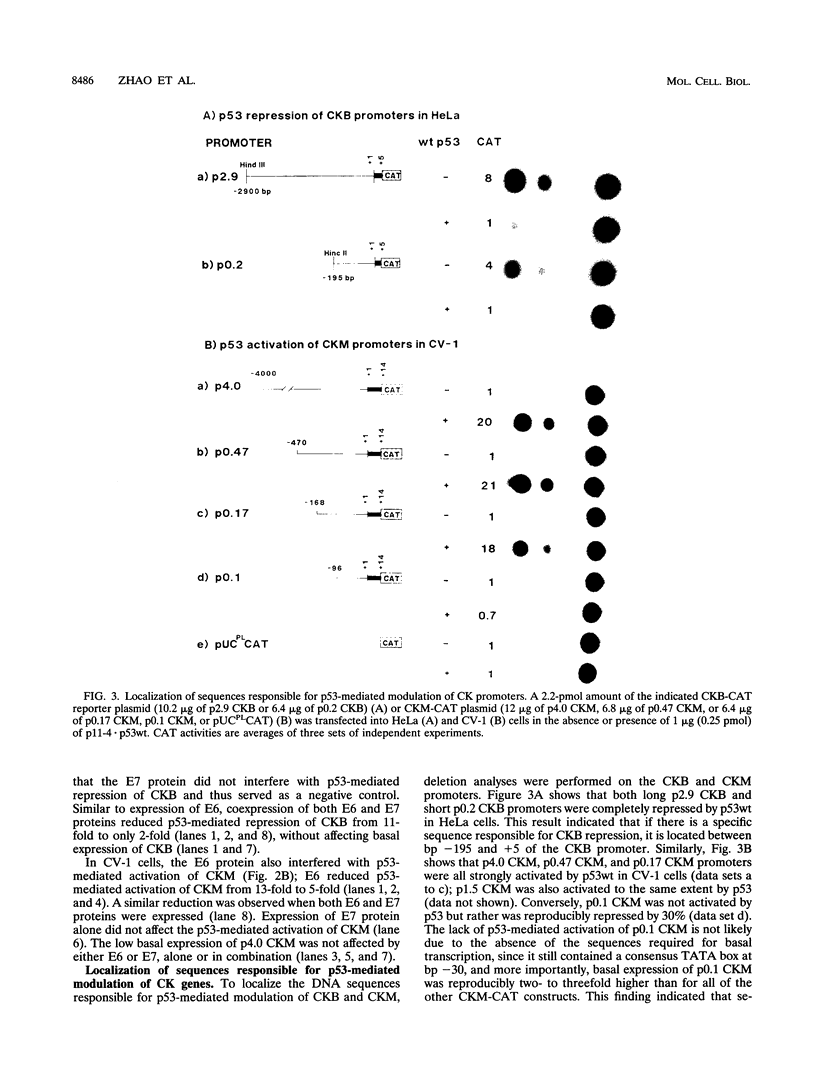
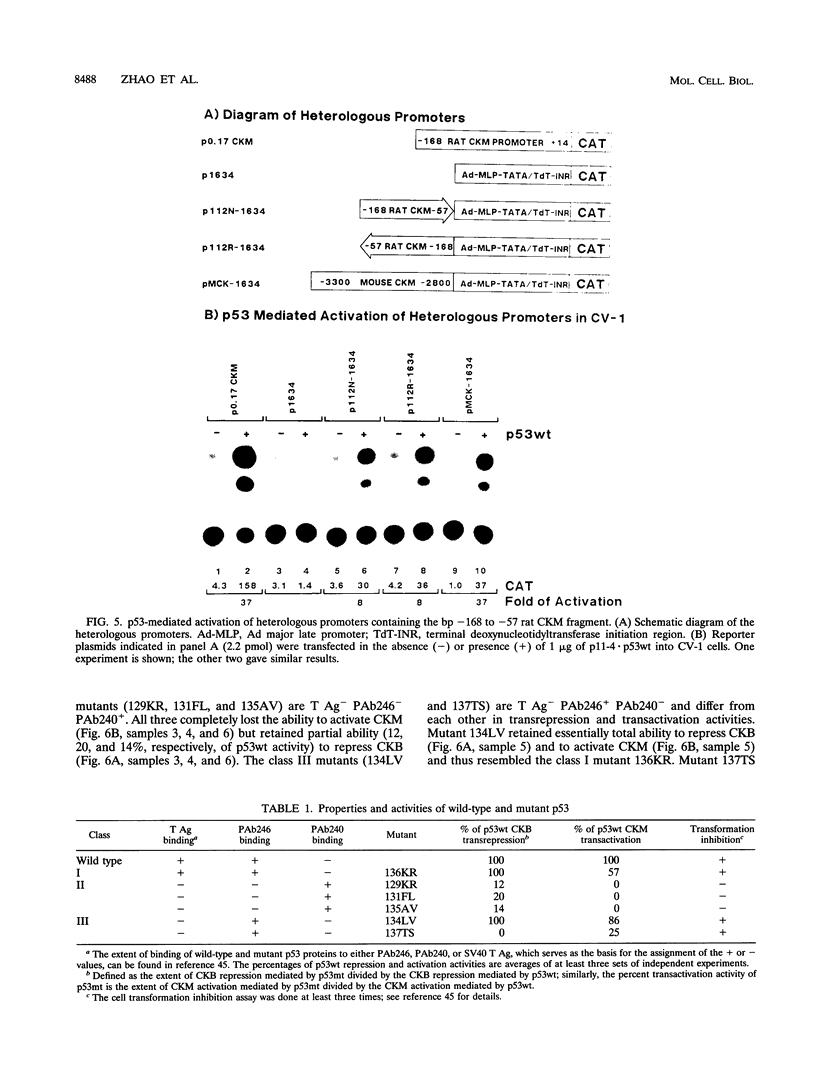
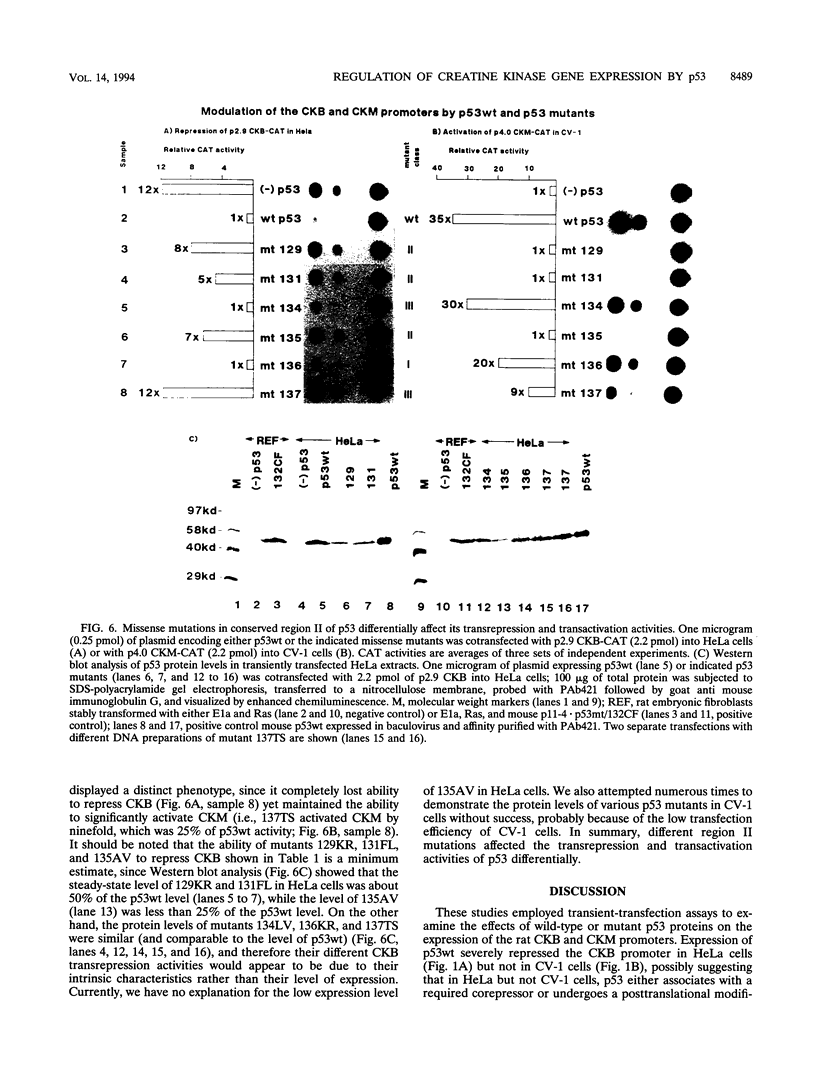
The creatine kinases (CK) regenerate ATP for cellular reactions with a high energy expenditure. While muscle CK (CKM) is expressed almost exclusively in adult skeletal and cardiac muscle, brain CK (CKB) expression is more widespread and is highest in brain glial cells. CKB expression is also high in human lung tumor cells, many of which contain mutations in p53 alleles. We have recently detected high levels of CKB mRNA in HeLa cells and, in this study, have tested whether this may be due to the extremely low amounts of p53 protein present in HeLa cells. Transient transfection experiments showed that wild-type mouse p53 severely repressed the rat CKB promoter in HeLa but not CV-1 monkey kidney cells, suggesting that, in HeLa but not CV-1 cells, p53 either associates with a required corepressor or undergoes a posttranslational modification necessary for CKB repression. Conversely, mouse wild-type p53 strongly activated the rat CKM promoter in CV-1 cells but not in HeLa cells, suggesting that, in CV-1 cells, p53 may associate with a required coactivator or is modified in a manner necessary for CKM activation. The DNA sequences required for p53-mediated modulations were found to be within bp -195 to +5 of the CKB promoter and within bp -168 to -97 of the CKM promoter. Moreover, a 112-bp fragment from the proximal rat CKM promoter (bp -168 to -57), which contained five degenerate p53-binding elements, was capable of conferring p53-mediated activation on a heterologous promoter in CV-1 cells. Also, this novel p53 sequence, when situated in the native 168-bp rat CKM promoter, conferred p53-mediated activation equal to or greater than that of the originally characterized far-upstream (bp -3160) mouse CKM p53 element. Therefore, CKB and CKM may be among the few cellular genes which could be targets of p53 in vivo. In addition, we analyzed a series of missense mutants with alterations in conserved region II of p53. Mutations affected p53 transrepression and transactivation activities differently, indicating that these activities in p53 are separable. The ability of p53 mutants to transactivate correlated well with their ability to inhibit transformation of rat embryonic fibroblasts by adenovirus E1a and activated Ras.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama N., Nagase T., Sawazaki T., Mizuguchi G., Nakagoshi H., Fujisawa J. I., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Overlap of the p53-responsive element and cAMP-responsive element in the enhancer of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5403–5407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai N., Nomura D., Yokota K., Wolf D., Brill E., Shohat O., Rotter V. Immunologically distinct p53 molecules generated by alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3232–3239. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz B., Zakut-Houri R., Givol D., Oren M. Analysis of the gene coding for the murine cellular tumour antigen p53. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2179–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond-Matthews B., Davidson N. Transcription from each of the Drosophila act5C leader exons is driven by a separate functional promoter. Gene. 1988;62(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deffie A., Wu H., Reinke V., Lozano G. The tumor suppressor p53 regulates its own transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3415–3423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Harvey M., Slagle B. L., McArthur M. J., Montgomery C. A., Jr, Butel J. S., Bradley A. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):215–221. doi: 10.1038/356215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. Helix-loop-helix proteins as regulators of muscle-specific transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):755–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foord O., Navot N., Rotter V. Isolation and characterization of DNA sequences that are specifically bound by wild-type p53 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1378–1384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., Pak D. T., Karas R. H., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. A transcriptionally active DNA-binding site for human p53 protein complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2866–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Zweig M. H., Carney D. N., Van Steirteghen A. C., Baylin S. B., Minna J. D. Levels of creatine kinase and its BB isoenzyme in lung cancer specimens and cultures. Cancer Res. 1981 Jul;41(7):2773–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Mechta F., Yaniv M., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can down-modulate the activity of various promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9979–9983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson G. M., Mitchell M. T., Molloy G. R., Pearson M. L., Benfield P. A. Identification of a novel TA-rich DNA binding protein that recognizes a TATA sequence within the brain creatine kinase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8925–8944. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson G. M., Molloy G. R., Benfield P. A. Identification of cis-acting regulatory elements in the promoter region of the rat brain creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6533–6543. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juven T., Barak Y., Zauberman A., George D. L., Oren M. Wild type p53 can mediate sequence-specific transactivation of an internal promoter within the mdm2 gene. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3411–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzhikandathil E. V., Molloy G. R. Transcription of the brain creatine kinase gene in glial cells is modulated by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Neurosci Res. 1994 Sep 1;39(1):70–82. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490390110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski R. W., Ehrismann R., Schweinfest C. W., Dottin R. P. Accumulation of creatine kinase mRNA during myogenesis: molecular cloning of a B-creatine kinase cDNA. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J. Tumor suppressor genes: the p53 and retinoblastoma sensitivity genes and gene products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 1;1032(1):119–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(90)90015-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Shields M. T., Lin D., Appella E., Ullrich S. J. Growth suppression induced by wild-type p53 protein is accompanied by selective down-regulation of proliferating-cell nuclear antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1958–1962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Unger T., Huibregtse J. M., Howley P. M. The transcriptional transactivation function of wild-type p53 is inhibited by SV40 large T-antigen and by HPV-16 E6 oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5013–5020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. T., Benfield P. A. Two different RNA polymerase II initiation complexes can assemble on the rat brain creatine kinase promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8259–8267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy G. R., Wilson C. D., Benfield P., de Vellis J., Kumar S. Rat brain creatine kinase messenger RNA levels are high in primary cultures of brain astrocytes and oligodendrocytes and low in neurons. J Neurochem. 1992 Nov;59(5):1925–1932. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie M. E., Trask R. V., Fontanet H. L., Billadello J. J. Multiple positive and negative elements regulate human brain creatine kinase gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6231–6240. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santhanam U., Ray A., Sehgal P. B. Repression of the interleukin 6 gene promoter by p53 and the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7605–7609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Münger K., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. The state of the p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5523–5527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieg F. I., Simmons D. T. Characterization of the in vitro interaction between SV40 T antigen and p53: mapping the p53 binding site. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):132–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90628-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieg F. I., Simmons D. T. p53 mutants with changes in conserved region II: three classes with differing antibody reactivity, SV40 T antigen binding and ability to inhibit transformation of rat cells. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2043–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Usheva A., Zambetti G. P., Momand J., Horikoshi N., Weinmann R., Levine A. J., Shenk T. Wild-type p53 binds to the TATA-binding protein and represses transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12028–12032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiio Y., Yamamoto T., Yamaguchi N. Negative regulation of Rb expression by the p53 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5206–5210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Loeber G., Tegtmeyer P. Four major sequence elements of simian virus 40 large T antigen coordinate its specific and nonspecific DNA binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1973–1983. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1973-1983.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Wun-Kim K., Young W. Identification of simian virus 40 T-antigen residues important for specific and nonspecific binding to DNA and for helicase activity. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4858–4865. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4858-4865.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., Méchali M., May P., Kress M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA from Xenopus laevis coding for a protein homologous to human and murine p53. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):71–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Chiba I., Birrer M. J., Rosenberg R. K., Vinocour M., Levitt M., Pass H., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.2554494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Wallis J., Levine A. J. Identification of the p53 protein domain involved in formation of the simian virus 40 large T-antigen-p53 protein complex. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):574–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.574-583.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truant R., Xiao H., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct interaction between the transcriptional activation domain of human p53 and the TATA box-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2284–2287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdal P., Urdal K., Strømme J. H. Cytoplasmic creatine kinase isoenzymes quantitated in tissue specimens obtained at surgery. Clin Chem. 1983 Feb;29(2):310–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallimann T., Wyss M., Brdiczka D., Nicolay K., Eppenberger H. M. Intracellular compartmentation, structure and function of creatine kinase isoenzymes in tissues with high and fluctuating energy demands: the 'phosphocreatine circuit' for cellular energy homeostasis. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 1;281(Pt 1):21–40. doi: 10.1042/bj2810021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Hauschka S., Tapscott S. J. The MCK enhancer contains a p53 responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4570–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. D., Parameswaran B., Molloy G. R. Expression of the rat brain creatine kinase gene in C6 glioma cells. J Neurosci Res. 1993 May 1;35(1):92–102. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490350111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew P. R., Berk A. J. Inhibition of p53 transactivation required for transformation by adenovirus early 1B protein. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):82–85. doi: 10.1038/357082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Bargonetti J., Walker K., Prives C., Levine A. J. Wild-type p53 mediates positive regulation of gene expression through a specific DNA sequence element. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1143–1152. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Kim C. G., Bartelmez S., Cheng P., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Helix-loop-helix transcription factors E12 and E47 are not essential for skeletal or cardiac myogenesis, erythropoiesis, chondrogenesis, or neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12132–12136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]