Abstract
The present work highlights recent advances in elucidating the methane oxidation mechanism of inorganic Cu-ZSM-5 biomimic and in identifying the reactive intermediates that are involved. Such molecular understanding is important in view of upgrading abundantly available methane, but also to comprehend the working mechanism of genuine Cu-containing oxidation enzymes.
Keywords: Zeolite, Cu-ZSM-5, Dioxygen activation, Dicopper(II) oxo, Model complex, Selective methane oxidation, C-H activation
1. Introduction
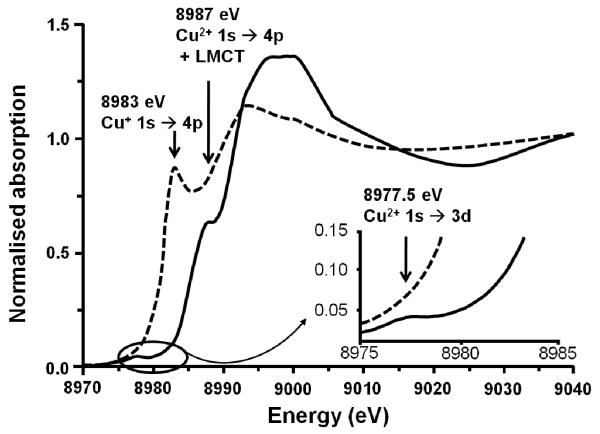
In 1986, Iwamoto and his group [1] discovered that over-exchanged Cu-ZSM-5 was an excellent catalyst for the decomposition of nitric oxides. Those findings have been reported and reviewed [2-11] and motivated further research on Cu-ZSM-5 and its (re)activity [12-14]. A unique property of Cu+2 and other TMI-zeolites is the so-called “auto-reduction” phenomenon: the exchanged metal ion partially reduces at high temperature in inert atmosphere. Partial reduction has been confirmed by several spectroscopic techniques such as XAFS, luminescence spectroscopy and probe IR spectroscopy [15-17]. As an example, XAFS demonstrates a reduced number of O atoms in the first coordination shell; also, a feature at 8983 eV, assigned to 1s → 4p transition in Cu+, appears in XANES during He treatment at 500 °C at the expense of Cu2+ transitions, typically present in O2-treated samples (Fig. 1). [3, 18]
Figure 1.
(- - -) Cu-ZSM-5 treated in He at 773 K, ( — ) Cu-ZSM-5 after contact with O2 at 623K. Adapted from ref. [19].
In 2005, Groothaert et al. [20] were the first to report the selective oxidation of methane into methanol using Cu-ZSM-5. Due to the low temperature of the reaction (<200 °C), methanol remained adsorbed on the catalyst, presumably as a methoxide, but it can be recovered by extraction with a suitable solvent or solvent mixture. Thus, the reaction is stoichiometric. Such a stoichiometric oxidation of methane was also reported for Fe-ZSM-5 by Panov’s group [21-25], and thoroughly reviewed by Zecchina et al. [26]. Both catalysts, Cu-ZSM-5 and Fe-ZSM-5, have very similar activation procedures and reaction conditions (Table 1). The most notable difference is that the active site in Fe-ZSM-5 is only formed from N2O, while Cu-ZSM-5 is also capable of being activated by O2, which is an advantage from an economical standpoint.
Table 1.
Comparison of activation procedures, reaction conditions and methanol yield of Cu-ZSM-5 and Fe-ZSM-5 [25, 27].
| Cu-ZSM-5 | Fe-ZSM-5 | |
|---|---|---|
| Activation with oxidant | Autoreduction at 500°C | Autoreduction at 900°C |
| Contact with O2 (less than 200°C) or N2O (already at room temperature) |
N2O at about 200°C | |
| Reaction with CH4 | Temperature range 100 – 200°C |
Room temperature |
| Maximum methanol yield: 10 μmol/g |
Maximum methanol yield: 40 μmol/g |
Cu- and Fe-enzymes also have the ability to selectively convert methane into methanol at ambient temperatures. These are the enzymes soluble methane mono-oxygenase (sMMO) and particulate methane mono-oxygenase (pMMO). While sMMO uses Fe to carry out this difficult reaction, pMMO employs Cu. In both enzymes, methane oxidation occurs at a binuclear active site.
Nature has always been rich in inspiration for developing new catalysts. Indeed, biomimetic catalysis is a very mature research field today showing many fascinating examples of model systems. Such synthetic catalysts typically contain ligated metal active sites (e.g., Fe, Cu, Mo, W, and Ru) and are soluble in the reaction environment [28-34]. The ideal catalyst in an industrial operating system, however, is preferably a solid material for reasons of ease of handling and recovery. Immobilization of such homogeneous catalysts is an elegant option [35-43], but the design of a completely inorganic model is even better from the perspective of stability and catalyst service lifetime. An appealing approach, applied for instance in Cu-ZSM-5 and Fe-ZSM-5, is the substitution of ligands around the active sites by the rigid zeolite lattice.
It is thus interesting to determine whether similarities exist between the heterogeneous Cu-ZSM-5 and the active sites designed by nature, e.g., in pMMO. We therefore pursued a systematic study of the Cu-ZSM-5 system.
The spectroscopic features of Cu ions, coordinated to the zeolite lattice, are best resolved at low Cu loadings. EPR and UV-vis-NIR measurements show a fourfold coordination of Cu2+ located in six-membered rings (MRs). Cu2+ is not symmetrically coordinated in the center of the 6MRs, but preferentially coordinates with O atoms of the Al tetrahedra [12, 44, 45]. Similar spectroscopic and theoretical information on the coordination chemistry of Cu+ in zeolites have been reported as well [15-17, 46-53]. Isolated, monovalent Cu+ sites in ZSM-5 show two luminescence bands; they have been assigned to Cu+ coordinated to 3 or 4 oxygen atoms of the 6MR inside the zeolite channel (at 480 nm) and to 2 oxygen atoms at the channel intersections (at 540 nm) [16, 17, 47-49]. It is not yet clear if Cu+ and Cu2+ occupy the same sites or whether Cu ions migrate from one site to another upon reduction.
A high Cu loading is very important in the methane oxidation. Unfortunately, the spectroscopic information of Cu2+ sites at the higher Cu loadings is less clear due to co-existence of various Cu species. Binuclear, oligonuclear and even chains of CuOx have been described [54]. The amount of Cu in a zeolite is typically expressed as the Cu/Al ratio. Ideally, this ratio is between 0 and 0.5, with the two limits representing, respectively, no exchange of Cu2+ and 100% exchange (i.e., all Na+ is replaced by Cu2+). An over-exchanged Cu-ZSM-5 has a Cu/Al ratio above 0.5. The total amount of Cu2+ in the zeolite is typically measured by Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Absorption (ICP-AA) after dissolution of the catalyst in HF.
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) is an important tool to determine the content of non-magnetically interacting Cu2+ ions on zeolites (Fig. 2) [55, 56]. Up to Cu/Al = 0.2, both ICP and EPR give the same result, meaning that all Cu2+ is present as isolated ions. Above Cu/Al = 0.2, the intensity of the EPR signal reaches a maximum, while the total amount of Cu continues to increase. This indicates that a large fraction of the Cu2+ is EPR-silent at Cu/Al loadings larger than 0.2 due to the close proximity of magnetically interacting Cu2+ ions. The presence of (Cu2+)x clusters in the sample is unlikely due to strong electrostatic repulsion. Formation of (CuO)x clusters is only expected for over-exchanged samples (i.e., Cu/Al > 0.5).
Figure 2.
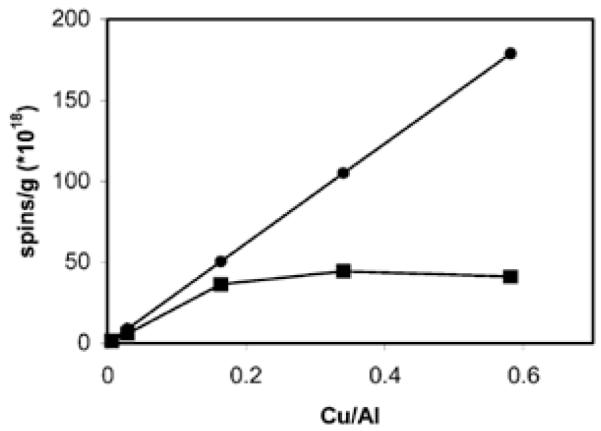
(■) Amount of spins/g catalyst detected with EPR as a function of the Cu/Al obtained with ICP, (●) highest possible spin concentrations (i.e. ICP copper concentrations) [44]. Reproduced by permission of the PCCP Owner Societies.
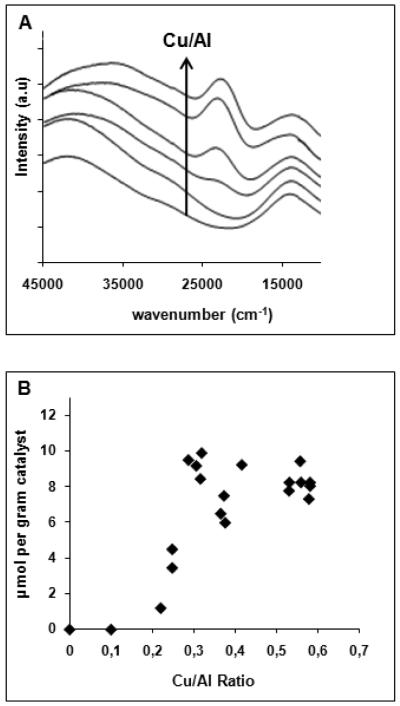
Upon contacting the highly loaded Cu-exchanged ZSM-5 with dioxygen at elevated temperature, its color changes from blue to yellow-green. Fig. 3A shows the UV-vis absorption spectra of the activated catalysts. At low copper loadings (<Cu/Al = 0.2), there are no observable absorption features except for a weak absorption at ~13,300 cm−1 due to d-d transitions of Cu2+, and at higher wavenumbers, an intense band around 40,000 cm−1, due to charge transfer transitions from the oxygens of the zeolite lattice to Cu2+. As soon as the Cu/Al ratio exceeds 0.2, a new absorption band appears in the visible region at 22,700 cm−1. The band intensity increases with the Cu/Al ratio (Fig. 3A). Those absorption features are only present for Cu-ZSM-5 samples with a Si/Al ratio between 12 and 30.
Figure 3.
(A) UV-vis-NIR absorption spectra of the of Cu-ZSM-5 samples (Si/Al=12) activated in O2 at 450°C, (B) amount of methanol extracted per gram of Cu-ZSM-5 sample, as a function of the Cu/Al ratio [20]). Reprinted with permission from ref.[20], © 2005 American Chemical Society.
Fig. 3B shows the amount of methanol extracted from the corresponding catalysts after reaction with methane at 175 °C. Methanol can only be extracted from samples which contain the 22,700 cm−1 band, i.e., for O2-treated Cu-ZSM-5 with Cu/Al > 0.2. The amount extracted increases with the Cu/Al ratio until a maximum of 10 μmol/g (Cu/Al = 0.3) is obtained. The extraction is a measure of the methanol produced, but is not quantitative. The maximum is most likely an underestimate of the total amount of methanol formed due to inefficiency of the extraction, pore blocking or side reactions [20, 27, 57].
2. Spectroscopic and computational characterization of the methane-oxidizing active site
Methane oxidation is thus directly linked to the presence of the 22,700 cm−1 absorption band [58]. A comparison of previous results from a combined UV-vis, EPR, and EXAFS study with those accumulated for structurally and spectroscopically characterized Cu/O2 complexes indicates that the absorption spectrum of Cu-ZSM-5 best corresponds to an O2-derived binuclear Cu species [59-70]. There are three common O2-bridged Cu pairs, viz bis(μ-oxo)dicopper, trans-(μ-1,2-peroxo)dicopper and (μ-η2:η2-peroxo)dicopper. All of these are observed in synthetic models, whereas only the latter is also observed in the active sites of the proteins hemocyanin, tyrosinase, and catechol oxidase in their oxy form. The structural and spectroscopic characteristics are summarized in Table 2 [67, 71-77].
Table 2.
Spectroscopically characterized mononuclear and binuclear Cu/O2 complexes
| Cu/O2 species | λmax[cm−1] (ε[M−1 cm−1]) |
Cu…..Cu distance[Å] |
rR vibrations (Δ18O2) [cm−1] |
reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2 activated Cu-ZSM-5 |
22700 30000 |
2.87 | 456 (8) 870 (40) |
||
| bis(μ-oxo) dicopper(III) |
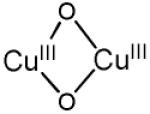
|
22300-25000 (13000- 28000) 30800-32700 (11000- 21000) |
2.74 - 2.91 | νCu-O=606 (23) | [71-73, 78, 79] |
| μ-(η2:η2) peroxo dicopper(II) (planar) |
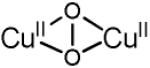
|
17000-19800 (1000) 27300-29600 (20000) |
3.5 - 3.8 | νCu-Cu=284 (0) νO-O=763 (40) |
[73-76, 80] |
| μ-(η2:η2) peroxo dicopper(II) (bent) |
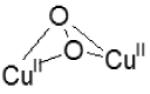
|
18200 (1000) 20400-23800 ( 5000) 27800 (20000) |
3.2 - 3.4 | [77] | |
| η1-superoxo copper(II) |
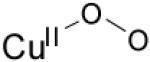
|
23923(4300) 16260(1100) 13037(840) |
νCu-O=472 (20) νO-O=1121 (63) |
[81] | |
| η2-superoxo copper(II) |
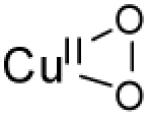
|
10200 (<400) 14300 (<400) 22100 (<400) 26100 (<400) |
νCu-O=554 (20) νO-O=1043 (59) |
[82] | |
| η1-hydroperoxo copper(II) |
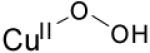
|
16730 (1540) 12 000 (300) |
νCu-O=624 (17) νO-O=843 (44) |
[83] | |
| trans-μ-1,2-peroxo dicopper(II) |
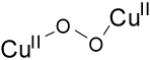
|
22989 (1700) 19083 (11300 16260 (5800) |
4.36 | νCu-O=561 (26) νO-O=832 (44) |
[67, 83] |
| μ-1,1-hydroperoxo dicopper(II) |
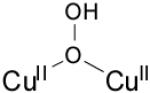
|
25 200 (6700) 21 000 15 500 (660) |
2.95 - 3.04 | νCu-O=322 (10) νO-O=892 (52) |
[84] |
The active core was first assigned to a bis(μ-oxo)dicopper core based on the spectroscopic similarities with these copper complexes [3] despite the formal ‘+3’ oxidation state of Cu, which was not detected by EXAFS [85]. A peroxo Cu site was excluded because the Cu-Cu distance obtained by EXAFS (2.8 Å) was too short, and the energy of the characteristic absorption band is inconsistent with a peroxo Cu site [3, 12, 67]. However, only a minor fraction (~5%) of copper species is involved in the formation of the active core, as estimated from the amount of methanol produced in a single turnover experiment. Therefore, a selective spectroscopic probe that exclusively focuses on the catalytically relevant site is mandatory. Direct evidence for assigning the active site was established by resonance Raman (rR) spectroscopy. The rR spectra of 16O2- and 18O2-treated Cu-ZSM-5 samples are shown in Fig. 4 (λex = 457.9 nm) [58].
Figure 4.
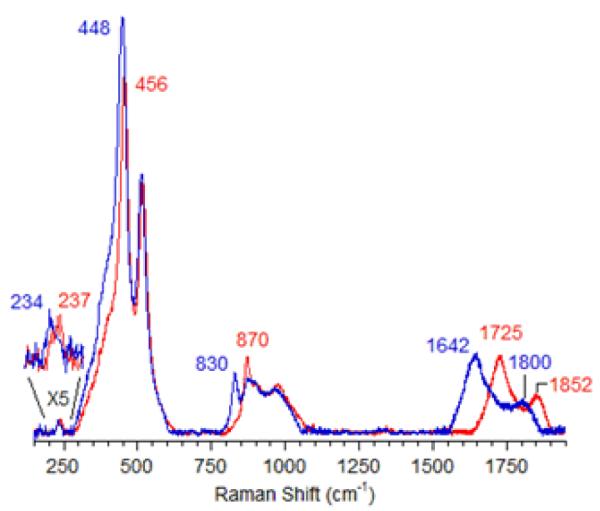
rR spectra (λex=457,9nm) of Cu-ZSM-5 after calcination in 16O2 (red) and 18O2 (blue) [58]. Reproduced with permission from ref.[58], © 2009 the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
These resonance-enhanced vibrations profile the 22,700 cm−1 absorption band and disappear upon reaction with CH4 as well as autoreduction in He at temperatures higher than 350 °C. The isotope-sensitive vibrations reflect the active O moiety since CH318OH was obtained from the CH4 reaction on the 18O2-activated Cu-ZSM-5. Isotope insensitive resonance-enhanced lattice modes are also observed, viz at 514 and 540 cm−1. The previously suggested bis-μ-oxo Cu(III)2 species was definitively excluded due to the lack of an intense isotope sensitive vibration at 600 cm−1 (Table 2) [78, 79] in the O2-treated Cu-ZSM-5.
The energies and isotope shifts of the active-site vibrations are inconsistent with all Cu-complexes found in the literature (table 2), i.e. μ-(η2:η2) peroxo (νCu-Cu ~270 cm−1, νO-O ~750 cm−1) or a superoxo (νO-O ~1100 cm−1) species [80-82]. Also an end-on bridged peroxo (832 cm−1) and hydroperoxide (843–892 cm−1) complex [83] are excluded since no intermediate vibration at ~850 cm−1 is observed in mixed dioxygen isotope-activated samples. This observation shows that the 870 cm−1 vibration is not due to an O-O stretch. Thus, all known Cu/O2 complexes are excluded based on the absorption and rR data. The active site is therefore assigned to a new Cu-oxo species, not yet described in inorganic chemistry literature [58, 86]. Correlating the observed vibrations to a normal coordinate analysis (NCA), the rR vibrations at 237 cm−1, 456 cm−1 and 870 cm−1 are assigned to the bending mode, the symmetric Cu-oxo stretch (νs) and anti-symmetric Cu-oxo stretch (νas) of a mono-μ-oxo bridged dicopper core, respectively. This assignment is required by the high intensity of the first overtone (at 1725 cm−1) of the formally forbidden anti-symmetric Cu-oxo stretch, as the second quantum (2νas) is symmetric and rR allowed [58]. A similar intensity pattern has also been found in oxo-diferric complexes [87]. NCA of the symmetric/anti-symmetric splitting and their isotope perturbation data give a Cu-O-Cu angle of 140° [58].
A model of the new Cu-O-Cu species in ZSM-5 was developed with the aid of DFT calculations. The experimentally obtained copper core is stabilized in the 10-membered ring (MR) of ZSM-5 with the two coppers binding bidentate to oxygens of Al T sites, which are separated by two Si T sites (Fig. 5) [58]. The rigid lattice structure induces a slight asymmetry in the core, resulting from differences in the Olattice-Cu bond strengths. The copper core likely contains CuII ions since calculations starting from CuIII result in the relaxation of the two holes into oxygen T atoms of the lattice [58]. Moreover, the 10 MR is the only channel large enough for CH4 migration. The proposed structure in Fig. 5 corroborates two important structural criteria, namely the Cu/Al ratio and the lattice Si/Al ratio. The dimeric nature of the active sites agrees well with the high Cu/Al ratio required to form the active site, while the active site resides in ZSM-5 only when the Si/Al ratio of the lattice is smaller than 30 [27]. The latter is in accordance with the stabilizing and charge compensating role of the two Al sites.
Figure 5.
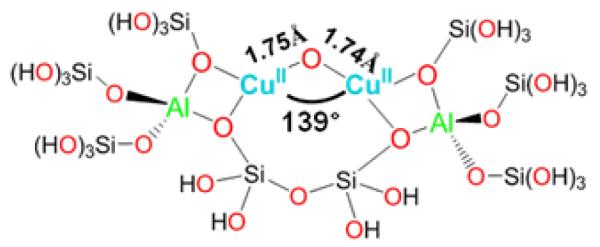
Large structural model constructed from part of the 10 MR of Cu-ZSM-5 used for DFT calculations of the Cu2O intermediate [58]. Reproduced with permission from ref. [58], © 2009 the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
It should be emphasized that this is the first time a Cu-oxo complex with oxidative reactivity toward methane has been unequivocally characterized. Thus far, there were a few bent Cu-O-Cu cores suggested [88-92], but they were not characterized in terms of structure or reactivity with methane. It is also the first time that an active TMI site of a heterogeneous catalyst has been unambiguously identified spectroscopically [85]. This assignment is made possible by the characteristic 22,700 cm−1 absorption feature, which was used to selectively probe the active site with rR and to study the catalyst in situ, during the catalytic reaction, with fiber optical technology.
3. Formation of the active site: the O2 activation pathway
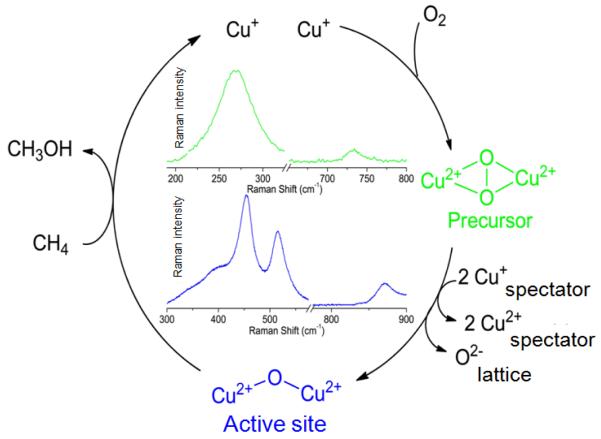
An appealing part of the reaction scheme for Cu-ZSM-5 is the formation of the methane oxidizing species (a mono-oxo species) from dioxygen. Further study of the O2 activation process in Cu-ZSM-5 will lead to a better overall understanding of the implementation of O2, an abundant and environmentally benign molecule, in selective oxidation reactions. Formation of the [Cu2O]2+ core formally requires the cleavage of the O-O bond, and thus, two extra electrons (i.e. two Cu+ react with O2, reducing it by two electrons to the peroxo level and a second two electrons are required for complete reduction to the oxo level).
A precursor complex to the active site was recently discovered by activating Cu-ZSM-5 with O2 at ambient temperatures [93]. A characteristic absorption band in the UV-vis spectrum at 29,000 cm−1 was observed, which transforms into the 22,700 cm−1 band upon heating (Fig. 6). The 29,000 cm−1 feature is formed in Cu-ZSM-5 samples with Cu/Al ratios higher than 0.2, much like the 22,700 cm−1 band.
Figure 6.
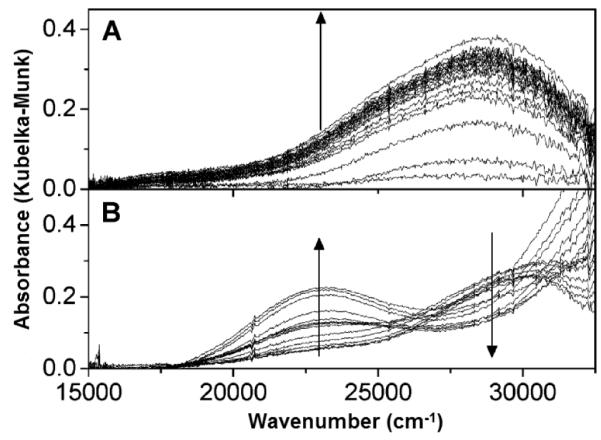
UV-vis absorption spectra of a prereduced Cu-ZSM-5 (in He at 450 °C) during (A) O2 treatment at RT (10 s time interval between spectra in the first 2 min, then every 50 s for 10 min) and (B) subsequent heating from 25 to 375 °C in He atmosphere (heating rate 2°C min−1; temperature interval between spectra is 25 °C) [93]. Reprinted with permission from ref [93], © 2011 American Chemical Society.
Laser excitation into the 29,000 cm−1 absorption feature yields a rR spectrum characterized by 18O2 isotope sensitive and insensitive vibrations at 736 (Δ18O2: 41 cm−1) and 269 cm−1, respectively (Fig. 7) [93].
Figure 7.
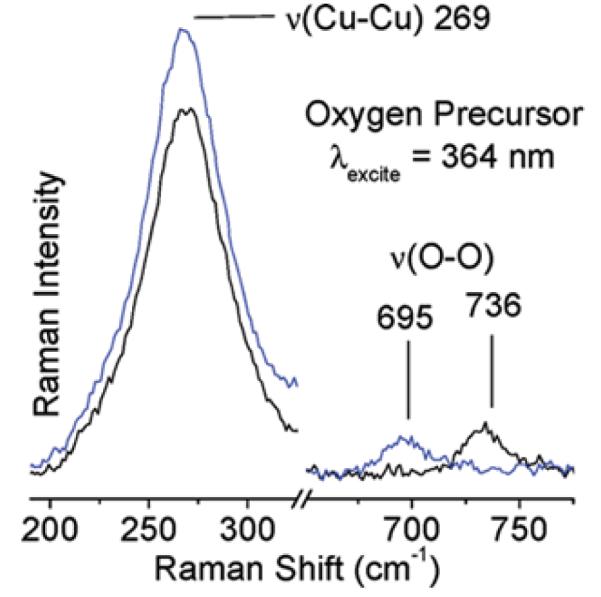
rR spectra (363.8 nm) of 16O2 (black) and 18O2 (blue) precursor formed at RT [93]. Reprinted with permission from ref [93], © 2011 American Chemical Society.
The vibrational frequencies and isotope perturbation pattern in Fig. 7 are characteristic of a μ-(η2:η2) peroxo dicopper(II) species, [Cu2(O2)]2+ [80]. Thus, the 736 and 269 cm−1 features are assigned to the O-O stretch (νO-O) and the Cu-Cu stretch (νCu-Cu) of a μ-(η2:η2) peroxo dicopper(II) moiety, respectively. The 29,000 cm−1 absorption band is assigned to a peroxo π*σ to Cu(II) charge-transfer (CT) transition [70]. The interconversion of the two absorption bands, viz. 29,000-22,700 cm−1, indicates that the side-on bridged peroxo dicopper(II) precursor converts directly into the bent [Cu2O]2+ species, which is reactive in the selective oxidation of methane into methanol. O2-TPD experiments with 18O2 show the incorporation of the second 18O atom into the zeolite lattice during the transformation of [Cu2(O2)]2+ into [Cu2O]2+, since no 18O2 desorbs during the temperature increase. The formation of the active core from [Cu2(O2)]2+ requires two additional electrons. It is possible that these electrons are provided by spectator Cu+ ions in neighboring ion-exchange sites; electron donor and acceptor capacities of the zeolite lattice have been established experimentally [93-96]. Analogously, there also exist non-coupled binuclear Cu enzymes, i.e. peptidylglycine-α-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) and dopamine α-monooxygenase (DβM), with one copper site merely serving as an electron transfer function. In these enzymes, the two coppers are separated by 11 Å. [70] The O2 activation process in Cu-ZSM-5 is summarized in Fig. 8.
Figure 8.
O2 activation pathway in Cu-ZSM-5. Reprinted with permission from ref [93], © 2011 American Chemical Society.
Side-on peroxo dicopper moieties are known for their reactivity in the hydroxylation of aromatic compounds through an electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism, e.g., in tyrosinase [70, 97, 98]. Reaction of benzene with this peroxo species in Cu-ZSM-5 would therefore further elucidate the potential chemistry of this new Cu/O2 species in Cu-ZSM-5.
4. Evaluation of the methane to methanol reaction mechanism
A complete understanding of the active site requires the evaluation of its reactivity. This should elucidate the activity of the Cu-ZSM-5 site and its propensity for oxidizing strong C-H bonds.
An experimental activation energy, Ea, of 15.7 ± 0.5 kcal/mol was determined using Arrhenius plots of the 22,700 cm−1 absorption band. In addition, an increase in the activation energy of 3.1 ± 0.5 kcal/mol at 175 °C was determined from an Arrhenius plot of the reaction of C2H4. This clearly indicates that C-H bond breaking is involved in the rate-limiting step of the oxidation of CH4. [20, 58].
Once activated, the Cu-ZSM-5 site is capable of reacting with methane already at 100 °C. A DFT study suggests that the high reactivity toward H-atom abstraction could likely be attributed to two contributions. The reaction is driven by the high O-H bond strength (90 kcal/mol) in the [Cu-(OH)-Cu]2+ complex formed during H atom abstraction (Fig. 9A). Furthermore, an analysis of the frontier molecular orbitals (FMOs) of the active species indicates that upon CH4 approach, a low-lying SOMO (oriented toward the zeolite channel and the H-CH3 bond) polarizes so as to gain oxygen p-character. This transfers the originally Cu-based hole to the oxo group, and thus creates a CuI-oxyl-CuII at the transition state (Fig. 9A and B) [58]. The rigid structure of the zeolite lattice, resulting in an asymmetric [Cu2O]2+ core, is crucial in the formation of the Cu2+-O•−-Cu+ radical (Fig. 10). Such a cupric-oxyl core has been presented as a very reactive species in the literature, but had never been observed before in an enzymatic or model complex [99, 100]. The Ea and KIE obtained from calculations are in reasonable agreement with the experimental values; however, further experimental evaluation of the reaction mechanism is mandatory.
Figure 9.
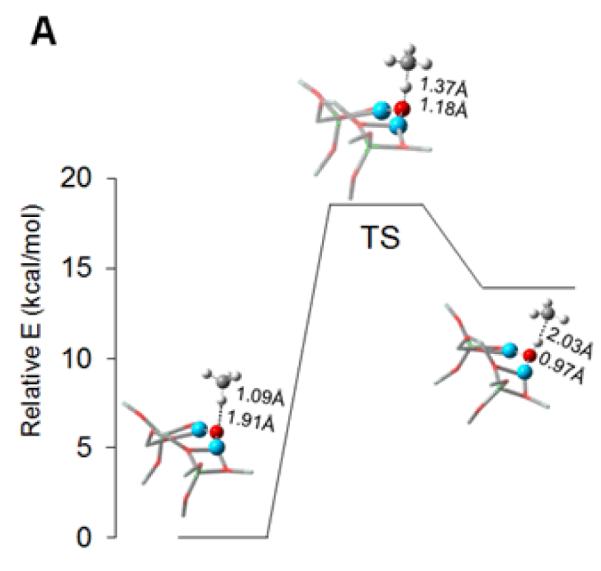
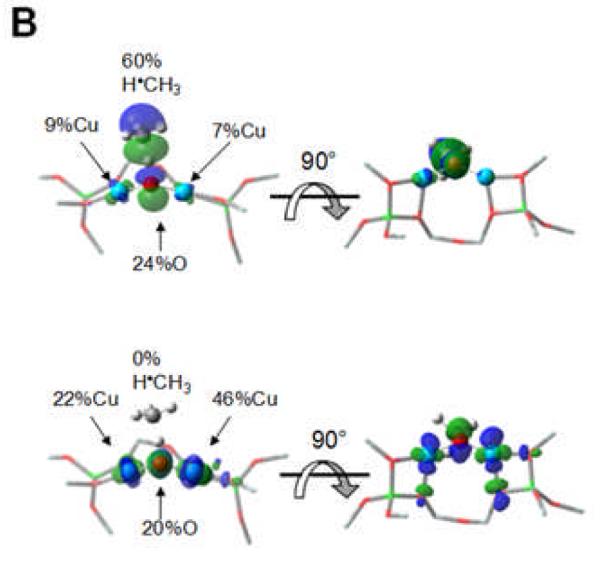
A) Reaction coordinate of H-atom abstraction from CH4 by L-CuII2O. B) SOMO’s at the H-atom abstraction TS shown with the line of CH4 approach in the plane (left) and below the plane of the figure (right). Reproduced with permission from ref. [58], © 2009 the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
Figure 10.
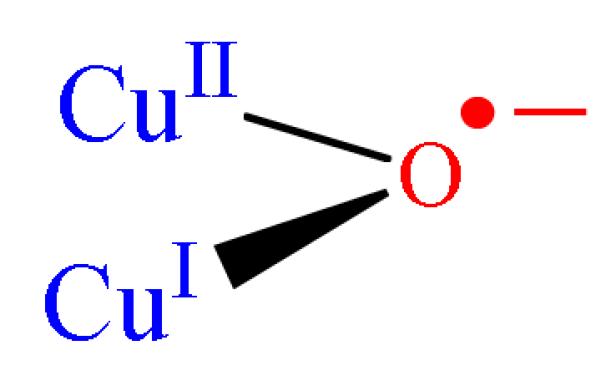
Schematic presentation of CuII-oxyl.
5. Outlook and significance
A complete understanding of the methanol producing core described here will provide major contributions to a variety of scientific disciplines. Cu-ZSM-5 could potentially serve as a model for the design of catalytic and/or highly reactive active sites while also serving as a tool to better understand the working mechanisms of enzymes. Ultimately, the insight gained from studying the elementary steps in the reaction of Cu-ZSM-5 with CH4 will hopefully pave the way for the development of a methane to methanol process.
Cu-ZSM-5 may, in further research, provide a system to experimentally probe and ultimately more fully understand the H-atom abstraction mechanism. Trapping the putative Cu(I)-OH-Cu(II) intermediate before rebound to the •CH3 radical could provide significant insight into understanding the mechanism. However, as H bond breaking is involved in the rate-limiting step, as indicated by the KIE, this will likely be challenging.
Presently, the stoichiometric reaction is not suitable for an industrial process, unless perhaps a high density of Cu active sites could be acquired, making methanol extraction, for instance in subsequent steaming cycles, economically feasible. Understanding the cause of the hampered methanol desorption is therefore of utmost importance. Methanol is often considered to adsorb as a methoxy species on the catalyst surface. It is not clear whether that is due to direct inhibition of the active site by the methoxy species or due to the strong readsorption of the methanol product. A manner to spectroscopically probe the methoxy species would provide the knowledge to define strategies to accomplish facile methanol desorption. Eventually such knowledge may lead to a catalytic cycle where activation with O2 or N2O, reaction with CH4, desorption of methanol and regeneration of the active site would all occur within the same mild temperature range.
A mono-oxygen bridged Cu-dimer with methane-oxidizing properties has previously not been observed in inorganic chemistry. It is astonishing that such an active copper complex has been identified in Cu-ZSM-5, whereas the copper core and its O2 reaction mechanism in the pMMO enzyme is still unidentified. Its identification opens a new and significant perspective on the model role of Cu-ZSM-5. Recently, it has been demonstrated that the pMMO active site consists of a binuclear copper core [101-104]. In earlier computational studies on pMMO, a bis(μ-oxo)dicopper(III) was proposed [105], but its potential to selectively oxidize methane was questioned. A mixed-valent CuII–(O)2–CuIII species was predicted to be more reactive toward C-H bond activation, but no experimental evidence has been found for such a Cu moiety [106]. The discovery of the bent Cu(II)-O-Cu(II) core in Cu-ZSM-5 may shed new light on the fascinating world of pMMO research. The bent [Cu2O]2+ at least fits the X-ray structure of pMMO, which consists of three histidines and an N-terminal amino nitrogen (4N-type ligation) and a short Cu-Cu interaction (Fig. 11) [86, 101-103, 107].
Figure 11.
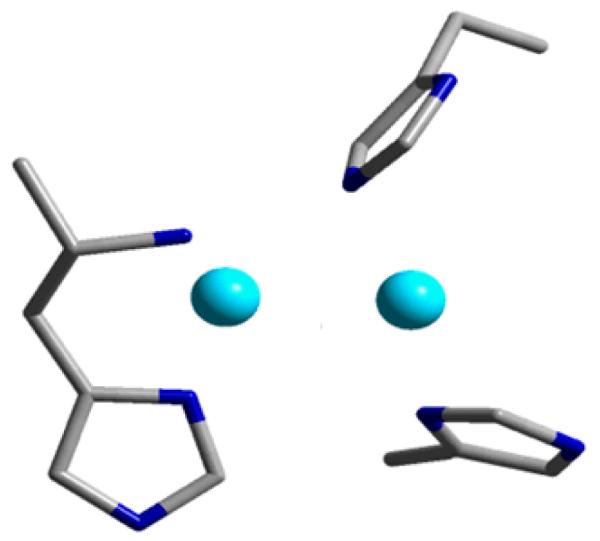
The dicopper active site of pMMO. Adapted from ref. [107].
Recently, Solomon et al. modeled the active [Cu2O]2+ core in the active site of pMMO, and found the same polarization mechanism toward a reactive CuII-oxyl radical along the reaction coordinate. Therefore, a similar reactivity for C-H atom abstraction from methane is possible [107, 108]. Experimental evidence evaluating this possibility still has to be obtained. The importance of the zeolite constraints to stabilize the active bent [Cu2O]2+ core and its correlation with the ligand environment in the protein pocket are important issues. For the zeolite system, a variety of parameters are likely crucial to stabilize the active [Cu2O]2+ site and to induce its high reactivity, e.g., channel sizes, channel intersections, dimensionality of the zeolite pore architecture, Si/Al ratio, Al distribution in the lattice. In this context, it has been observed that Cu-MOR also allows the formation of a methane-oxidizing active site [20, 27]. Thus far, it is unclear if the active core in MOR is related to the Cu-ZSM-5 active site. The larger pore size in MOR might favor desorption and transportation of the reaction product.
In summary, zeolites provide a manifold to create metal active sites and channels to deliver substrates that very much parallel metalloenzymes and have the advantages associated with heterogeneous systems and large-scale synthesis. The parallels (and differences) between these very complementary areas of catalysis are now an area of active research effort.
Acknowledgments
This work was performed within the framework of FWO (G.0596.11), IAP (Belspo), ERIC and Methusalem (long-term structural funding by the Flemish Government) projects. E.I.S acknowledges the NIH (Grant DK-31450) and R.G.H. acknowledges a Gerhard Casper Stanford Graduate Fellowship.
References
- 1.Iwamoto M, Furukawa H, Mine Y, Uemura F, Mikuriya SI, Kagawa S. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1986:1272. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Centi G, Perathoner S. Appl. Catal., A. 1995;132:179. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Groothaert MH, van Bokhoven JA, Battiston AA, Weckhuysen BM, Schoonheydt RA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:7629. doi: 10.1021/ja029684w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gilot P, Guyon M, Stanmore BR. Fuel. 1997;76:507. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Groothaert MH, Lievens K, Leeman H, Weckhuysen BM, Schoonheydt RA. J. Catal. 2003;220:500. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Iwamoto M, Hamada H. Catal. Today. 1991;10:57. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shelef M. Chem. Rev. 1995;95:209. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Smeets PJ, Groothaert MH, van Teeffelen RM, Leeman H, Hensen EJM, Schoonheydt RA. J. Catal. 2007;245:358. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Smeets PJ, Sels BF, van Teeffelen RM, Leeman H, Hensen EJM, Schoonheydt RA. J. Catal. 2008;256:183. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kapteijn F, Marban G, RodriguezMirasol J, Moulijn JA. J. Catal. 1997;167:256. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Giamello E, Murphy D, Magnacca G, Morterra C, Shioya Y, Nomura T, Anpo M. J. Catal. 1992;136:510. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Smeets PJ, Woertink JS, Sels BF, Solomon EI, Schoonheydt RA. Inorg. Chem. 2010;49:3573. doi: 10.1021/ic901814f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zecchina A, Bordiga S, Palomino GT, Scarano D, Lamberti C, Salvalaggio M. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1999;103:3833. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lamberti C, Palomino GT, Bordiga S, Berlier G, D’Acapito F, Zecchina A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2000;39:2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kumashiro P, Kuroda Y, Nagao M. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1999;103:89. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wichterlova B, Dedecek J, Vondrova A. J. Phys. Chem. 1995;99:1065. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dedecek J, Sobalik Z, Tvaruzkova Z, Kaucky D, Wichterlova B. J. Phys. Chem. 1995;99:16327. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kau LS, Spirasolomon DJ, Pennerhahn JE, Hodgson KO, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987;109:6433. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Groothaert MH, Lievens K, van Bokhoven JA, Battiston AA, Weckhuysen BM, Pierloot K, Schoonheydt RA. ChemPhyschem. 2003;4:626. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200300746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Groothaert MH, Smeets PJ, Sels BF, Jacobs PA, Schoonheydt RA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:1394. doi: 10.1021/ja047158u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sobolev VI, Dubkov KA, Panna OV, Panov GI. Catal. Today. 1995;24:251. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dubkov KA, Sobolev VI, Talsi EP, Rodkin MA, Watkins NH, Shteinman AA, Panov GI. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 1997;123:155. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ovanesyan NS, Shteinman AA, Dubkov KA, Sobolev VI, Panov GI. Kinet. Catal. 1998;39:792. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dubkov KA, Paukshtis EA, Panov GI. Kinet. Catal. 2001;42:205. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Starokon EV, Parfenov MV, Pirutko LV, Abornev SI, Panov GI. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2011;115:2155. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zecchina A, Rivallan M, Berlier G, Lamberti C, Ricchiardi G. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007;9:3483. doi: 10.1039/b703445h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Smeets PJ, Groothaert MH, Schoonheydt RA. Catal. Today. 2005;110:303. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lewis EA, Tolman WB. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:1047. doi: 10.1021/cr020633r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mirica LM, Vance M, Rudd DJ, Hedman B, Hodgson KO, Solomon EI, Stack TDP. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:9332. doi: 10.1021/ja026905p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Riley DP, Henke SL, Lennon PJ, Weiss RH, Neumann WL, Rivers WJ, Aston KW, Sample KR, Rahman H, Ling CS, Shieh JJ, Busch DH, Szulbinski W. Inorg. Chem. 1996;35:5213. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Butler A, Clague MJ, Meister GE. Chem. Rev. 1994;94:625. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Meister GE, Butler A. Inorg. Chem. 1994;33:3269. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Butler A, Baldwin AH. Struct. Bond. 1997;89:109. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Enemark JH, Cooney JJA. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:1175. doi: 10.1021/cr020609d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.De Vos DE, Dams M, Sels BF, Jacobs PA. Chem. Rev. 2002;102:3615. doi: 10.1021/cr010368u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sels B, De Vos D, Buntinx M, Pierard F, Kirsch-De Mesmaeker A, Jacobs P. Nature. 1999;400:855. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sels BF, De Vos DE, Jacobs PA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:8350. doi: 10.1021/ja015930c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sels BF, De Vos DE, Buntinx M, Jacobs PA. J. Catal. 2003;216:288. [Google Scholar]
- 39.De Vos DE, Sels BF, Jacobs PA. Cattech. 2002;6:14. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Parton RF, Vankelecom IFJ, Casselman MJA, Bezoukhanova CP, Uytterhoeven JB, Jacobs PA. Nature. 1994;370:541. doi: 10.1038/370541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Baute D, Arieli D, Neese F, Zimmermann H, Weckhuysen BM, Goldfarb D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:11733. doi: 10.1021/ja047761c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fu L, Weckhuysen BM, Verberckmoes AA, Schoonheydt RA. Clay Miner. 1996;31:491. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Weckhuysen BM, Verberckmoes AA, Vannijvel IP, Pelgrims JA, Buskens PL, Jacobs PA, Schoonheydt RA. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1995;34:2652. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Groothaert MH, Pierloot K, Delabie A, Schoonheydt RA. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003;5:2135. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pierloot K, Delabie A, Groothaert MH, Schoonheydt RA. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001;3:2174. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rodriguez-Santiago L, Sierka M, Branchadell V, Sodupe M, Sauer J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998;120:1545. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Nachtigallova D, Nachtigall P, Sierka M, Sauer J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999;1:2019. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Nachtigall P, Nachtigallova D, Sauer J. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2000;104:1738. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nachtigallova D, Nachtigall P, Sauer J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001;3:1552. doi: 10.1039/c2cp23237e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Davidova M, Nachtigallova D, Bulanek R, Nachtigall P. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2003;107:2327. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bludsky O, Silhan M, Nachtigallova D, Nachtigall P. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2003;107:10381. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Davidova M, Nachtigallova D, Nachtigall P, Sauer J. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004;108:13674. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lamberti C, Bordiga S, Salvalaggio M, Spoto G, Zecchina A, Geobaldo F, Vlaic G, Bellatreccia M. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1997;101:344. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kuroda Y, Kotani A, Maeda H, Moriwaki H, Morimato T, Nagao M. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1992;88:1583. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Palomino GT, Fisicaro P, Bordiga S, Zecchina A, Giamello E, Lamberti C. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2000;104:4064. doi: 10.1021/jp993893u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Xamena F, Fisicaro P, Berlier G, Zecchina A, Palomino GT, Prestipino C, Bordiga S, Giamello E, Lamberti C. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2003;107:7036. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Beznis NV, Weckhuysen BM, Bitter JH. Catal. Lett. 2010;138:14. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Woertink JS, Smeets PJ, Groothaert MH, Vance MA, Sels BF, Schoonheydt RA, Solomon EI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009;106:18908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910461106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Fujisawa K, Tanaka M, Morooka Y, Kitajima N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994;116:12079. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wada A, Harata M, Hasegawa K, Jitsukawa K, Masuda H, Mukai M, Kitagawa T, Einaga H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1998;37:798. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980403)37:6<798::AID-ANIE798>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kitajima N, Morooka Y. Chem. Rev. 1994;94:737. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Wei N, Murthy NN, Chen Q, Zubieta J, Karlin KD. Inorg. Chem. 1994;33:1953. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Spencer DJE, Aboelella NW, Reynolds AM, Holland PL, Tolman WB. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:2108. doi: 10.1021/ja017820b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Schatz M, Becker M, Thaler F, Hampel F, Schindler S, Jacobson RR, Tyeklar Z, Murthy NN, Ghosh P, Chen Q, Zubieta J, Karlin KD. Inorg. Chem. 2001;40:2312. doi: 10.1021/ic000924n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Que L, Tolman WB. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002;41:1114. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020402)41:7<1114::aid-anie1114>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Jacobson RR, Tyeklar Z, Farooq A, Karlin KD, Liu S, Zubieta J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988;110:3690. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Tyeklar Z, Jacobson RR, Wei N, Murthy NN, Zubieta J, Karlin KD. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993;115:2677. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cole AP, Root DE, Mukherjee P, Solomon EI, Stack TDP. Science. 1996;273:1848. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5283.1848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Reim J, Werner R, Haase W, Krebs B. Chem.- Eur. J. 1998;4:289. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Solomon EI, Sarangi R, Woertink JS, Augustine AJ, Yoon J, Ghosh S. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007;40:581. doi: 10.1021/ar600060t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Halfen JA, Mahapatra S, Wilkinson EC, Kaderli S, Young VG, Que L, Zuberbuhler AD, Tolman WB. Science. 1996;271:1397. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5254.1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Tolman WB. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997;30:227. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Holland PL, Tolman WB. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999;192:855. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Solomon EI, Sundaram UM, Machonkin TE. Chem. Rev. 1996;96:2563. doi: 10.1021/cr950046o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Eicken C, Zippel F, Buldt-Karentzopoulos K, Krebs B. FEBS Lett. 1998;436:293. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kitajima N, Fujisawa K, Fujimoto C, Morooka Y, Hashimoto S, Kitagawa T, Toriumi K, Tatsumi K, Nakamura A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992;114:1277. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Pidcock E, Obias HV, Abe M, Liang HC, Karlin KD, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:1299. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Henson MJ, Mukherjee P, Root DE, Stack TDP, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:10332. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Mahapatra S, Halfen JA, Wilkinson EC, Pan GF, Cramer CJ, Que L, Tolman WB. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995;117:8865. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Baldwin MJ, Root DE, Pate JE, Fujisawa K, Kitajima N, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992;114:10421. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Maiti D, Fry HC, Woertink JS, Vance MA, Solomon EI, Karlin KD. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:264. doi: 10.1021/ja067411l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Chen P, Root DE, Campochiaro C, Fujisawa K, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:466. doi: 10.1021/ja020969i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Baldwin MJ, Ross PK, Pate JE, Tyeklar Z, Karlin KD, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991;113:8671. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Root DE, Mahroof-Tahir M, Karlin KD, Solomon EI. Inorg. Chem. 1998;37:4838. doi: 10.1021/ic980606c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Schoonheydt RA. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010;39:5051. doi: 10.1039/c0cs00080a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Himes RA, Karlin KD. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009;106:18877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911413106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Czernuszewicz RS, Sheats JE, Spiro TG. Inorg. Chem. 1987;26:2063. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Kitajima N, Koda T, Hashimoto S, Kitagawa T, Morooka Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991;113:5664. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Karlin KD, Gultneh Y, Hayes JC, Zubieta J. Inorg. Chem. 1984;23:519. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Rice MJ, Chakraborty AK, Bell AT. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2000;104:9987. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Iwamoto M, Yahiro H, Tanda K, Mizuno N, Mine Y, Kagawa S. J. Phys. Chem. 1991;95:3727. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Haddad MS, Wilson SR, Hodgson DJ, Hendrickson DN. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981;103:384. [Google Scholar]
- 93.Smeets PJ, Hadt RG, Woertink JS, Vanelderen P, Schoonheydt RA, Sels BF, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:14736. doi: 10.1021/ja106283u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Yoon KB. Chem. Rev. 1993;93:321. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Garcia H, Roth HD. Chem. Rev. 2002;102:3947. doi: 10.1021/cr980026x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Corma A, Garcia H. Chem. Rev. 2002;102:3837. doi: 10.1021/cr010333u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Mirica LM, Vance M, Rudd DJ, Hedman B, Hodgson KO, Solomon EI, Stack TDP. Science. 2005;308:1890. doi: 10.1126/science.1112081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Pidcock E, Obias HV, Zhang CX, Karlin KD, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998;120:7841. [Google Scholar]
- 99.Decker A, Solomon EI. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005;9:152. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Himes RA, Karlin KD. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2009;13:119. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.02.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Balasubramanian R, Smith SM, Rawat S, Yatsunyk LA, Stemmler TL, Rosenzweig AC. Nature. 2010;465:115. doi: 10.1038/nature08992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Lieberman RL, Rosenzweig AC. Nature. 2005;434:177. doi: 10.1038/nature03311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Richard KBD, Himes A, Karlin Kenneth D. Prof. Dr., Angew. Chem. Int. 2010;49:2. [Google Scholar]
- 104.Bollinger JM. Natur. 2010;465:40. doi: 10.1038/465040a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Balasubramanian R, Rosenzweig AC. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007;40:573. doi: 10.1021/ar700004s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Shiota Y, Yoshizawa K. Inorg. Chem. 2009;48:838. doi: 10.1021/ic8003933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Solomon EI, Ginsbach JW, Heppner DE, Kieber-Emmons MT, Kjaergaard CH, Smeets PJ, Tian L, Woertink JS. Faraday Discuss. 2011;148:11. doi: 10.1039/c005500j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Hadt RG, Woertink JS, Smeets PJ, Solomon EI. in preparation.