Abstract
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) is intimately involved in multiple signal-transduction pathways regulating survival, activation, proliferation, and differentiation of B-lineage lymphoid cells. Btk is overexpressed and constitutively active in several B-lineage lymphoid malignancies. Btk has emerged as a new antiapoptotic molecular target for treatment of B-lineage leukemias and lymphomas. Preclinical and early clinical results indicate that Btk inhibitors may be useful in the treatment of leukemias and lymphomas.
Keywords: tyrosine kinase, personalized therapy, kinase inhibitors, Btk, leukemia, lymphoma
Introduction
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) is intimately involved in multiple signal-transduction pathways regulating survival, activation, proliferation, and differentiation of B-lineage lymphoid cells.1,2 Btk is an upstream activator of multiple antiapoptotic signaling molecules and networks, including the signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) protein,3 phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway,4 and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) (Figure 1).5,6 Further, Btk associates with the death receptor Fas via its kinase and pleckstrin homology (PH) domains and prevents the interaction of Fas with Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD), which is essential for the recruitment and activation of caspase-8/FLICE by Fas during the apoptotic signal (Figure 1). This impairment by Btk prevents the assembly of a proapoptotic death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) after Fas ligation.7
Figure 1.
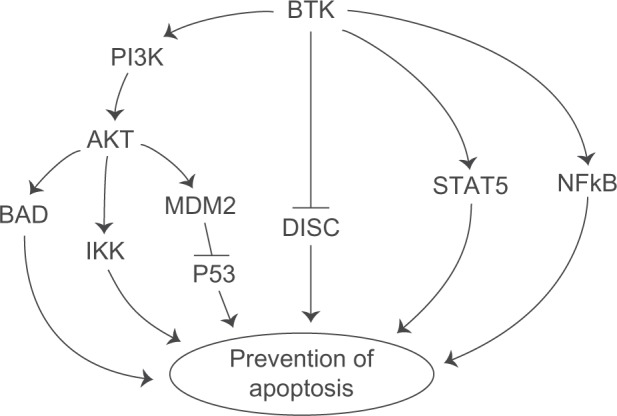
Btk activates antiapoptotic pathways. Btk is an upstream regulator of multiple antiapoptotic pathways, including the PI3K-AKT pathway, STAT5 pathway, and NFκB pathway. BTK also blocks the Fas-mediated apoptosis. See text for further discussion and references.
Abbreviations: Btk, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; BAD, B-cell lymphoma 2-associated death promoter; IKK, IκB kinase; DISC, death-inducing signaling complex; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B.
Btk is abundantly expressed in malignant cells from patients with B-cell precursor (BCP)-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL, the most common form of cancer in children and adolescents), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL).8–11 A meta-analysis of cancer-associated gene expression changes utilizing the Oncomine database revealed a marked enrichment of the most discriminating Btk-dependent antiapoptotic gene targets in 17 comparisons for diagnostic classes of human leukemias and lymphomas obtained from eight studies.11 Consequently, Btk has emerged as a new molecular target for treatment of B-lineage leukemias and lymphomas.
Btk disease targets
Lymphohematopoietic malignancies
B-lineage ALL (B-ALL) and B-cell CLL (B-CLL) are the most common childhood and adult leukemias, respectively. In both ALL and CLL, the resistance of leukemia cells to apoptosis-inducing chemotherapeutic agents hampers a more successful outcome.12–15
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
CLL is the most common leukemia in adults, accounting for 25% of all leukemias, with approximately 8000 new cases diagnosed each year.1619 CLL is characterized by the accumulation of mature, CD5+/CD23+ monoclonal B lymphocytes in the blood, secondary lymphatic tissues, and bone marrow (BM).20 It is well established that the tumor microenvironment plays a major role in the pathogenesis of CLL: various cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules provided within the lymph nodes (LNs), spleen, and BM microenvironment, as well as signaling by the B-cell receptor (BCR), play a critical role in the localization, growth, survival, and drug resistance of CLL cells.21–26 Proliferating CLL cells, which account for approximately 0.1%—1% of the CLL clone,21 are typically found within microanatomical structures called proliferation centers or pseudofollicles,22 where CLL cells interact with accessory cells (ie, stromal cells or T cells), thereby receiving survival and growth signals.23 Such external signals from the leukemia microenvironment can supplement intrinsic oncogenic lesions, thereby promoting maintenance and expansion of the CLL clone.22 Among the various external stimuli in the tissue microenvironments, BCR activation and signaling, particularly in lymphatic tissues, is a central pathologic mechanism, even though the precise mechanism of BCR stimulation and the nature of the antigen(s) that activate the BCRs remain obscure.20,24,25 The most direct evidence for the importance of BCR signaling in CLL comes from recent comparative gene-expression profiling data that revealed BCR signaling as the most prominent pathway activated in CLL cells isolated from lymphatic tissues.24 Because either tonic, chronic, or antigen-driven BCR signaling is involved in the pathogenesis of most types of B-cell malignancies, the BCR signalosome provides a rational therapeutic target, including CLL.26
Although CLL is a disease that is considered to be incurable with currently available therapy, its clinical course is heterogeneous: some patients have a more stable disease and die after many years from unrelated causes, whereas others progress very quickly and die within a few years. This variability has stimulated the search for prognostic markers with which to predict the outcome of patients and to allow treatments to be adapted to the specific risk. There is an urgent need for apoptosis-promoting new antileukemic agents against B-CLL. Several kinases are expressed at elevated levels in CLL cells, including Btk, Zeta-chain-associated protein (ZAP), and Lyn, and therefore have emerged as potential molecular targets.27
B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia
B-ALL is the most common form of cancer in children and adolescents.28 Current treatment with ALL can cure approximately 80% of children with the disease.29,30 Currently, the major challenge in the treatment of B-ALL is to cure patients who have relapsed (~20%) despite intensive multiagent chemotherapy.31,35 The standard approach to the treatment of these high-risk patients has been salvage chemotherapy to achieve a second remission and subsequent use of very intensive treatment regimens, including high-dose “supralethal” chemotherapy, often combined with total-body irradiation (TBI), followed by hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (SCT). Laboratory evidence indicates that primary clonogenic blasts from a significant portion of B-ALL patients are among those reported as the most radiation-resistant human tumor cells.36,37 Furthermore, clonogenic leukemia cells from over two-thirds of the ALL patients exhibit a substantial capacity to repair sublethal radiation damage.38 Resistance of B-leukemia cells to the proapoptotic effects of radiation-induced oxidative stress hampers the attempts to improve the survival outcome of patients with B-ALL undergoing TBI and SCT and only < 20% of high-risk B-ALL patients become long-term disease-free survivors even after TBI/SCT, with substantial short-term and long-term morbidity and mortality.38,39 These preclinical and clinical observations in B-ALL emphasize the urgent need for identification of new drug candidates capable of potentiating the antileukemic potency of pre-SCT radiochemotherapy regimens.
In contrast with the marked improvements achieved in the treatment outcome of pediatric ALL patients, adult patients with ALL continue to have a poor outcome, with long-term leukemia-free survival rates of less than 50%.39–42 This poor outcome has been attributed in part to an increased frequency of high-risk leukemia with greater drug resistance.2,40–44 A more rapid and complete reduction of the leukemia cell burden by upfront induction chemotherapy is likely to prevent drug resistance and improve the survival outcome in ALL.8,9,43 Furthermore, a more effective postinduction intensification therapy may eliminate a higher fraction of residual leukemia cells, thereby improving the duration of remission.9,13,15,43 Consequently, the development of new potent anti-ALL drugs and the design of combinative treatment protocols using these new agents have emerged as exceptional focal points for leukemia research.8,13,24
Btk is the first cytoplasmic non-Janus kinase (JAK) to be identified as a positive regulator of STAT5A in neoplastic B cells and B-cell precursors (BCPs). STAT5, a direct substrate of Btk that is activated by Btk-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of its Y694 residue,40 is an important regulator of survival17,44–46 and proliferation27,44,47–49 of BCPs at various stages of B-cell ontogeny. Recent studies have further revealed a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling system for Btk, which has implications regarding potential targets inside the nucleus and which may be critical in gene regulation during B-cell development and differentiation as well as apoptosis.50 Btk is essential for BCR-mediated activation of the NF-KB/Rel family of transcription factors, which in turn regulates genes controlling B-cell growth.51–53 STAT5 knockout mice suffer from leukopenia/lymphopenia and an accelerated rate of lymphohematopoietic cell apoptosis in the BM.17 Conversely, constitutive activation of STAT5 is capable of causing leukemic transformation of lymphohematopoietic cells19 and development of BCP leukemia in mice.45 Dominant-negative forms of STAT5 induce massive apoptosis in BCP-ALL cells.46 Btk is required for pre-BCR-dependent survival signals in BCP-ALL cells, including STAT5 activation and STAT5-mediated upregulation of BCL-xL, which rescues BCR-ABL+ BCP-ALL cells from apoptosis. The Btk-linked NF-κB and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt survival pathways are activated by chemotherapeutic agents and also contribute to drug resistance of BCP-ALL cells.54,55 Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) targeting Btk are likely to act as antileukemic agents with apoptosis-promoting and chemosensitizing properties and enhance the chemosensitivity of ALL cells.256
B-lineage non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
NHL is the third most common group of malignancies in children and adolescents in the US and accounts for approximately 7% of newly diagnosed cancers.57,58 NHL and Hodgkin’s lymphomas are represented prominently in the adolescent and young adult population. NHL constitutes 6%–10% of all pediatric malignancies in different parts of the world. NHL is the fifth most common cause of cancer deaths in young adult women aged 20–39 years. Although age-adjusted incidence rates of NHL increase with age, the more aggressive lymphomas are seen more commonly in the younger population, with a transition to low-grade, indolent subtypes as the population ages. Burkitt lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), lymphoblastic lymphoma, and anaplastic large-cell lymphoma make up the most common subtypes in the young adult population, although within the subgroup aged 30–39 years, follicular lymphoma (FL) becomes more prominent. Btk inhibitors have demonstrated clinical activity against a variety of B-cell malignancies in ongoing phase I/II trials, including mantle-cell lymphoma (MCL), CLL, FL, and DLBCL, with good tolerability.
DLBCL is one of the most common types of aggressive B-cell NHL. Pathologically, the tumor has a fast growth rate with a high Ki67 index. Without treatment, patients usually die within 6–24 months, and with current immunochemotherapeutic regimens 50%–60% of patients can be cured. However, 40%–50% of patients remain refractory to the therapy. Recently, BCR signaling has been recognized as a key pathway in the pathogenesis of DLBCL.59 Gene-expression profiling and unsupervised consensus clustering for analysis studies have identified a subset of lymphoma that demonstrates a BCR/proliferation signature (BCR-type DLBCL).60 In activated B-cell-like (ABC) DLBCL, NF-κB activity relies upon chronic active BCR signaling, which can be potentially blocked by kinase inhibitors targeting Btk. Btk inhibitors are highly active against ABC DLBCL cells in vitro, and demonstrated clinical activity in a subset of patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) ABC DLBCL.61
Follicular NHL is the most common of the indolent lymphomas, accounting for about 70% of them and about 22% of all lymphomas in North America and Europe. One of the primary concerns for any patient with follicular or other indolent lymphoma is transformation to a more aggressive lymphoma, such as DLBCL.6263 Similarly, patients with recurrent B-lineage NHL or NHL that shows progression on standard chemotherapy regimens have a dismal prognosis and are in urgent need for innovative treatments capable of overcoming the multidrug resistance of their NHL cells. In the US, approximately 70,000 people will be diagnosed with NHL and 19,000 people will die of NHL during 2013.
MCL is a malignancy of mature B cells characterized by the translocation t(11; 14) that leads to aberrant expression of cyclin D1.64 Response to first-line chemotherapy is good, but most patients relapse, resulting in a median survival of 5–7 years. Clinical studies with Btk inhibitors suggest that BCR signaling could play a role.65
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a clonal malignancy of plasma cells accumulating in the BM. Myeloma cells have a high capacity to induce osteolytic bone lesions in patients, especially in the advanced stages.66 One key clinical feature of this cancer is the hyperactive bone resorption and minimal bone regeneration, partly due to overactive osteoclasts and inactive osteoblasts via unbalanced regulation of cytokines and chemokines in the BM microenvironment.67 MM cells are highly dependent on the BM microenvironment for growth and survival through interactions, particularly with BM stromal cells, osteoclasts, and osteoblasts, all of which secrete important MM growth factors and cytokines.
Btk protein is expressed in plasma cell cancers, including MM and Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM), with baseline activation correlating with levels of protein expression. Btk plays a crucial role in myeloma-associated osteolysis via regulating a broad panel of cytokines and chemokines both at transcriptional and protein levels in osteoclast lineage cells and BMSCs, which are in close contact with MM cells within the BM microenvironment. These Btk-targeted cytokines and chemokines include macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1α,68 MIP-1β,69 stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-l,69 transforming growth factor (TGF)-βl,70 activin A,71 acidic protein rich in leucines (APRIL),72 B-cell-activating factor (BAFF),73 and interleukin (IL)-8,74 which have been shown to contribute to MM-related bone lesions and disease progression. Btk activation in the BM milieu promotes MM cell growth, survival, and interaction with other BM stromal components, in addition to triggering MM-induced bone lysis. In a genome-wide screening of mRNA for nonreceptor TKs expressed during osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation in mice, high expression of Lyn and Syk, which are upstream of Btk, as well as Src, were identified in osteoclasts. In addition, Btk was shown to regulate osteoclast maturation by modulating the activity of NFATcl, the major osteoclast transcriptional factor activated following receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) stimulation.75 These findings suggest a potential role of Btk in mediating osteolytic bone disease in MM and a framework for the clinical development of Btk inhibitors as a novel therapeutic strategy in MM.76
Solid tumors
Recently, it was discovered that Btk is expressed not only in malignant lymphohematopoietic cells but in solid tumor cells as well.77–79 Eifert used an RNA interference (RNAi) screen to perform a large-scale loss-of-function analysis to facilitate the identification of individual factors necessary for the survival of an ErbB2/human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)-2-positive breast cancer cell line.77,78 Notably, Btk short interfering RNA (siRNA) caused apoptosis in breast cancer cells.77,78 An aberrantly spliced 80 kDa Btk product with an amino-terminal extension was abundantly expressed in breast cancer cells as a potential molecular target.77,78 Likewise, Lavitrano et al79 discovered a functional isoform of Btk in colorectal cancer cells and showed that its inhibition enhances cancer cell chemosensitivity.
Btk inhibitor pipeline
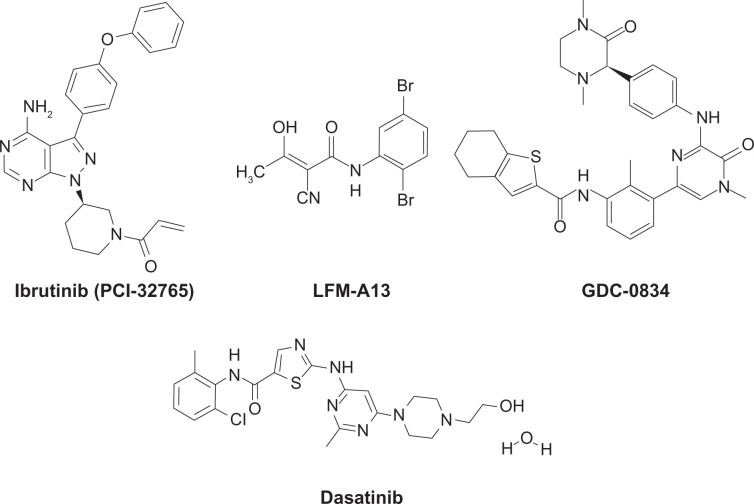
Several Btk inhibitors have been reported by us and others, and are being developed as therapeutic agents for various indications (Figure 2).80–104 Among these, the covalent inhibitor ibrutinib/PCI-32765 (Pharmacyclics) was developed as a selective and irreversible inhibitor of Btk, targeting the cysteine-481 residue in the active site.100 PCI-32765 is a potent nanomolar inhibitor of Btk, and exhibited promising activity in preclinical models of BCR-driven B-lineage lymphoma101 and clinical testing in lymphoma patients.102 Likewise, dianilinopyrimidine-based irreversible Btk inhibitors with micromolar activity were developed, and two lead compounds, AVL-101 and AVL-291 (Avila Therapeutics) showed promising in vitro activity against lymphoma cells.103 Dasatinib/Sprycel, a breakpoint cluster region-Abelson (BCR-Abl) kinase inhibitor that is FDA-approved for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), is a potent inhibitor of Btk.104,105 The availability of the coordinates of the Btk kinase domain X-ray crystal structures will continue to support further development of rationally designed Btk inhibitors.104,106
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ibrutinib (PCI-32765) is a covalent inhibitor currently under phase II and III clinical development for B-cell malignancies.
Note: LFM-AI3, GDC-0834, and dasatinib are noncovalent adenosine triphosphate-competitive Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Covalent Btk inhibitors
Conventional small-molecule inhibitors interact with high affinity in the binding site of a protein target, and the drug-target complex is favored when plasma drug concentration is high. Covalent inhibitors also form high-affinity interactions with the binding site of the protein target and bring a low-reactivity warhead in close proximity to a structurally unique amino acid. Through covalent bonding, the compound is locked to its target, thereby silencing the target’s activity. As a result, the pharmacodynamic behavior of a compound is coupled to protein half-life and turnover rather than pharmacokinetic properties. The covalent kinase inhibitors include ibrutinib/PCI-32765 (Figure 2), AVL-101, and AVL-291/292.
Ibrutinib/PCI-32765
Ibrutinib/PCI-32765 (l-[(3R)-3-[4-amino-3-(4-phenoxyphenyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]piperidin-1-yl]prop-2-en-1-one) is an orally active, small-molecule inhibitor that forms an irreversible bond with cysteine-481 in the active site of Btk and inhibits Btk phosphorylation on Tyr223, resulting in Btk inhibition (half maximal inhibitory concentration [IC50] = 0.5 nM).100,101 However, the cysteine residue is also present in a small subset of kinases with the potential for irreversible binding by PCI-32765. In vitro preclinical studies demonstrated that PCI-32765 blocks BCR-stimulated activation of ERK1/2, PI3K, and NF-κB, inhibits growth, and induces apoptosis in B-cell lymphoma cell lines.107 PCI-32765 inhibits activation-induced proliferation of CLL cells and effectively blocks survival signals provided externally to CLL cells from the microenvironment (CD40L, BAFF, IL-6, IL-4, and tumor necrosis factor [TNF]-a), fibronectin engagement, and stromal cell contact, as well as migration in response to tissue-homing chemokines (CXCL12, CXCL13).108,109 PCI-32765 targets not only B lymphocytes but also monocytes, macrophages, and mast cells, which are important Btk-expressing effector cells in arthritis.110 PCI-32765 inhibited TNF-α, IL-lβ, and IL-6 production in primary monocytes.110
PCI-32765 is active in multiple in vivo models: (1) transgenic murine model of BCR-driven lymphoma, (2) spontaneous B-cell lymphoma in canines, and (3) mouse models of autoimmune disease. Once-daily dosing resulted in 24-hour sustained target inhibition. PCI-32765 affected disease progression in an adoptive transfer T-cell leukemia/lymphoma 1 (TCL1) mouse model of CLL.108 The TCL1 transgenic mouse model of CLL has been validated as a model similar to human CLL, providing an avenue to extend study of BCR signaling in the in vivo setting.111,112 These mice spontaneously develop a CD5+ B-cell leukemia with unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable-region (IgVH) resembling unmutated CLL.113 PCI-32765 affected leukemia cell homing and disease progression. In this model, PCI-32765 caused a transient early lymphocytosis and profoundly inhibited CLL progression, as assessed by weight, development of hepatosplenomegaly, and survival.108 PCI-32765 induced objective clinical responses in dogs with spontaneous B-cell NHL.101 Active site occupancy of Btk was tightly correlated with the blockade of BCR signaling and in vivo efficacy.
Clinical studies
Ibrutinib/PCI-32765 is being investigated in patients with B-cell malignancies that include CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), MCL, DLBCL, FL, and MM (Tables 1 and 2). In phase I/II studies, PCI-32765 showed encouraging clinical activity in patients with several types of B-cell lymphoma.114
Table 1.
Small-molecule Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors in development
| Company | Compound | Indications | Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmacyclics, Janssen | Ibrutinib/PCL-32765 | R/R CLL/SLL, MCL, FL, DLBCL, MM, indolent NHL, MALT/MZL | Phase lb/II(break/)Phase III (CLL/NHL) |
| Pharmacyclics, Janssen | PCL-32765 + rituximab | R/R CLL/SLL | Phase II |
| PCL-32765 + ofatumumab(break/)PCL-32765 + bendamustine and rituximab | High-risk CLL | Phase III | |
| Avila Therapeutics, Celgene | AVL-292 | CLL, B-cell NHL, WM | Phase lb |
| Bristol-Myers Squibb | Dasatinib + fludarabine | R/R CLL/SLL | Phase II |
| University of Southern California | LFM-AI3 | B-cell malignancies | Preclinical |
| Ono Pharmaceutical | ONO-WG-307 | B-cell malignancies | Preclinical |
| Genentech, Gilead | GDC-0834 | B-cell malignancies | Preclinical |
Abbreviations: DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; R/R CLL/SLL, relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma; MCL, mantle-cell lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; MM, multiple myeloma; NHL, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; MALT/MZL, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue/marginal zone lymphoma; WM, Waldenström macroglobulinemia.
Table 2.
Summary of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor candidates and their stage of clinical development
| Compound | Indication | Trial identifier | Phase I | Phase II | Phase III |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibrutinib/PCI-32765 | B-cell lymphoma | NCT00849654 | × | ||
| B-cell lymphoma and CLL | NCT01109069 | × | |||
| Newly diagnosed B-cell NHL | NCT01569750 | × | |||
| CLL/SLL | NCT01292135 | × | |||
| CLL/SLL | NCT01105247 | × | × | ||
| CLL/SLL and prolymphocytic leukemia | NCT01217749 | × | × | ||
| CLL/SLL | NCT01744691 | × | |||
| MCL | NCT01236391 | × | |||
| DLBCL | NCT01325701 | × | |||
| R/R MM | NCT01478581 | × | |||
| MCL | NCT01599949 | × | |||
| R or R MCL | NCT01646021 | × | |||
| R or R CLL or SLL | NCT01611090 | × | |||
| R or R CLL or SLL | NCT01578707 | × | |||
| Treatment-naive CLL or SLL | NCT01722487 | × | |||
| AVL-292Dasatinib/Sprycel | R or R B-cell NHL, CLL, WM | NCT01351935 | × | ||
| R or R CLL/SLL | NCT00438854 | × |
Abbreviations: DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; R/R CLL/SLL, relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma; MCL, mantle-cell lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; MM, multiple myeloma; NHL, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; WM, Waldenström macroglobulinemia.
Relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies
Advani et al115–117 reported a dose-escalating phase I study of PCI-32765 (1.25 mg/kg/day to 12.5 mg/kg in a 28-day cycle) in 56 patients with multiple histologic subtypes of B-cell NHL (NCT00849654). The overall response rate was achieved in 30 (62%) of 50 evaluable patients, including seven complete responses (CRs) and 23 partial responses (PRs). Responses were achieved in eleven (79%) patients with CLL/SLL, seven (78%) with MCL, six (46%) with FL, three (75%) with WM (Waldenström macroglobulinemia), two (29%) with DLBCL, and one (33%) with Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL). Median progression-free survival in all patients was 13.6 months. Therapy was well tolerated, and grade 3 or higher adverse events (AEs) observed were neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia (<20%). In a second phase I study by Fowler et al118,119 in 47 patients with various relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies, a dose of 420 mg daily was established based on >90% occupancy of Btk. In this study, PCI-32765 induced a durable objective response (CR + PR) in various relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies.
Relapsed/refractory MCL
An interim analysis of a phase II study in patients with relapsed or refractory MCL, Staudt et al,120 showed that PCI-32765 (560 mg daily in 28-day cycles) produced an objective response of 67%; in patients pretreated with bortezomib (Velcade) the overall response rate was 75%, compared with 58%) in bortezomib-naive patients.121 PCI-32765 was generally well tolerated, with hematologic grade 3/4 AEs occurring in <5%o of patients. A unique observation of marked lymphocytosis, termed a “compartment shift,” was observed where the lymphocyte count doubled from about day 8 to 28 of cycle 1, and then slowly declined to about 40% above baseline with subsequent cycles. These lymphocytes were identified as being CD5+ and CD45+, consistent with circulating, mobilized lymphoma cells. The mechanism may be related to inhibition of tissue-homing cytokines CXCL12 and CXCL13, and inhibition of adhesion molecule functioning. Wang et al122 reported the results of a phase II study of PCI-32765 in relapsed or refractory MCL patients. In this study, 111 patients (bortezomib-naive and bortezomib-exposed) received oral PCI-32765 (560 mg daily). The primary end point of the study was overall response rate. Duration of response and safety evaluation were secondary end points. The median follow-up time was 9.2 months, with a range of time to response to treatment of 1.4 to 16.4 months. The study showed an overall response rate of 68% (22%o CR and 46% PR), with a median progression-free survival estimated at 13.9 months. Results were similar between the bortezomib-naive and bortezomib-exposed patients. Long-term follow-up of the initial 51 patients showed an incremental improvement in the response rate over time. The overall response rate increased for this patient subset to 75%. PCI-32765 resulted in high and durable responses and was generally well tolerated. Pneumonia was the only grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent AE occurring in ≥5% of patients. Recently, Janssen has initated a randomized, multicenter phase III trial comparing PCI-32765 versus temsirolimus as a monotherapy in relapsed or refractory MCL patients who had a prior rituximab-containing chemotherapy regimen (NCT01646021). The primary end point of the study is progression-free survival when compared to temsirolimus. The plan is to enroll 280 patients outside the US.
MCL cells express surface IgM and Btk and exhibit constitutive Btk autophosphorylation, which is inhibited by PCI-32765. Ponader et al123 tested the comparative sensitivity of PCI-32765 to inhibit BCR-signaling pathways in nine MCL cell lines, including phosphorylation of phospholipase C (PLC)-γ that leads to calcium flux. In resistant cells, IgM stimulation induces p-Btk but not pPLC-γ2 or calcium flux. PCI-32765-sensitive cell lines were shown to display constitutive p-ERK activity, which was increased on IgM stimulation and completely abrogated by PCI-32765. The more resistant cell lines had low endogenous levels of p-ERK, which was induced strongly by IgM and only partially blocked by PCI-32765. Sensitive cell lines showed a dose-dependent inhibition of IgM-induced p-ERK. These data suggested the existence of additional Btk-dependent pathways (perhaps leading to p-ERK) in MCL that regulate their growth and phosphorylation of downstream kinase, supporting ERK as a marker of sensitivity to PCI-32765.
Relapsed/refractory DLBCL
Wilson et al124 reported the results of a phase II study of PCI-32765 in 70 patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL in two genetically distinct subtypes of DLBCL: the ABC subtype and the germinal center (GC) subtype. The ABC subtype appears to be more driven by BCR signaling. The overall response rate in the heavily pretreated population was 23% (16 of 70 patients). Responses were primarily in the ABC subtype, with twelve of 29 patients (41%) responding (five CR and seven PR). In the 20 GC patients, only one patient (5%) had a PR. This study supports the use of ABC DLBCL molecular subtype as a biomarker for enrichment of patients for future PCI-32765 studies. Grade 3 or higher AEs were 5%–10% of the patients.
Relapsed/refractory CLL or SLL
Daily oral administration of PCI-32765 has been evaluated in patients with R/R CLL or SLL that had been treated with at least two prior therapies, including fludarabine.125 In an ongoing phase Ib/II study by O’Brien et al,126,127 61 patients with R/R CLL enrolled at two dose levels: 420 mg (n = 27) or 840 mg (n = 34). Serious grade 3 or 4 infections were noted in 25% of patients in the 420 mg cohort and 29% patients in the 840 mg cohort. Treatment was associated with an early increase in lymphocytosis that began around 1 week and persisted for several months in the majority of patients. With a median follow-up of 12.6 months in the 420 mg cohort and 9.3 months in the 840 mg cohort, the overall response rate for the 420 mg dose level was 67%, and for the 840 mg dose 68%. In addition, six (22%) and eight (24%) of patients in the 420 mg and 840 mg cohorts had a nodal response with persistent lymphocytosis. The 1-year estimated progression-free survival for the patients enrolled on this study is 86%.125 These data indicate that PCI-32765 is highly active and well tolerated in CLL/SLL patients, irrespective of high-risk genomic abnormalities, and suggest that this drug may be an important new targeted treatment approach for CLL, particularly in combination with other agents.
Recently, O’Brien et al128 reported the updated results of a phase Ib/II trial (NCT01105247) in R/R CLL (n = 61) and TN CLL (n = 31) patients enrolled at two fixed continuous-dose levels of PCI-32765 (420 mg and 840 mg). In addition to the data reported by Byrd et al,129,130 on the treatment-naive patients, this report provided updated progression-free survival data in the R/R patient population. With a median follow-up of 17.5-months, progression-free survival in the 420 mg cohort was 87.7%. High risk R/R patients with 17p deletion (n = 20) and IgVH unmutated status (n = 42) had estimated 18-month progression-free survival of >70% and >80%, respectively. In the treatment-naive 420 mg dose cohort patients (≥65 years old) the overall response rate was 81%), which included a 12% complete response rate. Fifty percent of patients with pretreatment of cytopenias experienced sustained improvement in hemoglobin and/or platelet levels. The estimated progression-free survival in the treatment naive patients at 15 months was 96% in the 420 mg cohort. Recently, Byrd et al129,130 reported the results of a phase Ib/II study of PCI-32765 in subjects with CLL/SLL either R/R (n = 85) or treatment-naive (n = 31) patients (≥65 years) designed to assess safety, tolerability, and efficacy at two dose levels (420 mg or 840 mg daily). Among 116 patients, the overall response rate was 68% in treatment-naive patients, with an estimated 96% progression-free survival rate at 26 months (NCT01105247). In patients with R/R CLL/SLL, the overall response rate was 71%, with an estimated progression-free survival at 26 months of 75%. Responses were independent of high-risk clinical or genetic features, such as a deletion of part of chromosome 17 (dell7p). Grade 3–4 toxicities (10%–13%) included diarrhea, infection, and hematologic toxicity (anemia and thrombocytopenia). There was no evidence of cumulative toxicity or long-term safety concerns. With a maximum follow up of 26 months, it was estimated that 96% of the treatment-naive and 75% of the R/R high-risk patients were without progression.
Combination clinical trials of PCI-32765
Currently, PCI-32765 is being tested in phase Ib/II combination with ofatumumab (NCT01217749), fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab or bendamustine and rituximab (NCT01292135) in CLL patients in the relapsed setting. Data from phase I/II trials demonstrated that high-risk CLL patients respond equally as well as low-risk patients to PCI-32765-treated CLL patients with characteristically delayed responses or stable disease due to persistent lymphocytosis, caused by redistribution of tissue-resident CLL cells into the peripheral blood. To accelerate and improve responses and to expand upon the PCI-32765 experience in high-risk CLL patients, Burger et al131 reported results of an ongoing phase II study of PCI-32765 plus rituximab in 40 patients (median age 65 years). The high-risk patients had one of the following characteristics, all predictive of poor outcome to standard chemotherapy: deletion in chromosome 17p, mutation in the tumor-suppressor gene TP53, deletion in chromosome llq or relapse < 36 months after chemoimmunotherapy. Patients were treated with PCI-32765 420 mg daily in combination with weekly rituximab (375 mg/m2) for weeks 1–4 (cycle 1), then daily PCI-32765 plus monthly rituximab until cycle 6, followed by daily single-agent PCI-32765. After a follow-up of 6 months, the overall response rate was 83%, and 38 of 40 patients continued on therapy without disease progression with 95% of all patients and 90% of patients with del17p not progressing. There was a large and rapid reduction in lymph-node and spleen sizes, with 84% of patients (26/31) experiencing more than a 50% decrease in lymph-node size. Treatment was well tolerated overall, with grade 3 or grade 4 toxicities infrequent and transient in nature, including febrile neutropenia, anemia, mucositis, and pneumonia, in this clinical study.
Brown et al132 and O’Brien et al133 reported the interim phase Ib/II study data on the combination of PCI-32765 with bendamustine/rituximab (BR) in patients with R/R CLL (median age 65 years). BR produced an overall response rate of 59% in R/R CLL. This combination trial (NCT01292135) enrolled a total of 30 patients in the BR cohort; 37% were refractory to a purine analogue-containing regimen and 13% refractory to bendamustine. Twenty-three percent of the patients had deletion 17p, and 43% had deletion 11q. R/R CLL patients received 420 mg of PCI-32765 daily for 28-day cycles until disease progression. Bendamustine 70 mg/m2 was administered on days 1 and 2 combined with rituximab 375 mg/m2 on day 0 for cycle 1, escalating to rituximab 500 mg/m2 for cycles 2–6. Response was evaluated according to the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia criteria. Grade 3/4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia were noted in 47% and 10% of patients, respectively. At 8.5 months of median follow-up, the overall response rate with BR was 93%, with 13%) of patients achieving a complete response with no morphologic evidence of CLL. Responses appeared independent of high-risk clinical or genomic features. No new safety signals with the combination of PCI-32765 and BR were identified. The estimated 11-month progression-free survival was 90%. The high overall response rate, rapid onset of response, low rate of progressive disease, and good tolerability compared favorably with historical controls and prompted a randomized phase III study of PCI-32765 in combination with BR (Table 2).
Jaglowski et al134 reported the results of a phase Ib/II study of a combination of PCI-32765 with ofatumumab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. Patients with R/R CLL/SLL following two or more therapies were treated with PCI-32765 first given as a single agent, 420 mg/day, 4 weeks prior to the addition of ofatumumab on day 1 of cycle 2 (initial dose 300 mg; 2000 mg on days 8, 15, and 22 of cycle 2, weekly in cycle 3, and day 1 of cycles 5–8). Interim data from 27 patients (median age 65 years) with either CLL/SLL (n = 24) or Richter’s transformation (RT = 3) underwent at least six cycles of treatment. All 24/24 CLL/SLL/PLL patients achieved PR (100%) overall response rate) within six cycles; two of three RT patients had a PR. The majority of AEs were grade 1/2. Grade 3/4 AEs included anemia, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, and hyponatremia (7%–l 1%). PCI-32765 combined with ofatumumab was well tolerated and highly active in patients with heavily pretreated R/R CLL/SLL. Rapid onset of response, low relapse rate, and a favorable safety profile make this combination worthy of further study.
Pharmacyclics has initiated randomized phase III clinical trials (NCT01646021, NCT01611090) of PCI-32765 in combination with bendamustine and rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory R/R CLL/SLL (Table 2). Another trial is designed to demonstrate superiority of PCI-32765 versus ofatumumab (NCT01578707). The primary end point of the latter study is to demonstrate a clinically significant improvement in progression-free survival in relapsed or refractory CLL/SLL patients. This global study is open, and Pharmacyclics plans to enroll 350 patients worldwide. Pharmacyclics has also initiated the Resonate-17p study (NCT01744691), a randomized, phase II trial using PCI-32765 as a monotherapy in patients who have deletion 17p and who did not respond to or relapsed after at least one prior treatment with chemoimmunotherapy. The primary outcome of the study is overall response rate. The key secondary end points are duration of response and other measures of clinical benefit. This study plans to enroll 111 patients worldwide. In addition, Pharmacyclics and Janssen have initiated a pivotal phase III trial of PCI-32765 in combination with bendamustine and rituximab in R/R CLL/SLL patients who received at least one line of prior systemic therapy. The primary end point of the study is to demonstrate a clinically significant improvement in progression-free survival versus bendamustine and rituximab therapy alone. The key secondary end points include overall response rates, overall survival, and other measures of clinical benefit. This global study is expected to enroll 580 patients worldwide.
Ibrutinib/PCI-32765 inhibits 22 tyrosine kinases other than Btk at nanomolar concentrations.101 Furthermore, it exhibited antileukemic activity only at micromolar concentrations (EC50 10 μM, EC90 100 μM), at which it has been shown to inhibit almost every tyrosine kinase it was tested against. Several kinases with homology to Btk in the Tec kinase family, including Bmx and Itk, have similar cysteine residues that might also be reversibly or irreversibly inhibited by PCI-32765. The fact that ibrutinib/PCI-32765 inhibits many other protein tyrosine kinases also at nanomolar concentrations demonstrates that its proposed mechanism of action is not sufficient to explain its experimentally documented promiscuity towards virtually all tyrosine kinases. Its interaction with multiple protein tyrosine kinases would be expected to result in poor intracellular pharmacokinetics, due to undesired binding to a large pool of “competing” kinases leading to reduced occupancy of the Btk-active site. That is likely the cause for the mg/kg dose levels and >100 nM plasma concentrations of ibrutinib/PCI-32765 required for Btk active-site occupancy in clinical settings.115,117 Furthermore, many of the protein tyrosine kinases it inhibits at nanomolar concentrations, including Lyn and C-terminal Src kinase (Csk)101 are inhibitory protein tyrosine kinases that counterbalance Btk action. Therefore, its promiscuity would be expected to significantly compromise its net impact on leukemia/lymphoma cell survival. These predictions were confirmed in recently published preclinical and clinical data on ibrutinib/PCI-32765.65,101,135 In the only animal model in which its antineoplastic activity was evaluated, ibrutinib/PCI-32765 showed activity at mg/kg dose levels that yield concentrations far above those inhibitory to multiple protein tyrosine kinases.101 Therefore, neither the in vitro antileukemic activity nor the promising clinical activity of PCI-32765 can be attributed to its Btk-inhibitory activity alone.
AVL-101, AVL-291, and AVL-292
AVL-101, AVL-291, and AVL-292 (Avila Therapeutics/Celgene Corporation) are orally active dianilinopyrimidine-based irreversible Btk inhibitors with micromolar activity against lymphoma cells.136 AVL-101/291/292 covalently modify their targets, leading to nonspecific and durable silencing of the targeted proteins, including PDGFR, c-Kit, EGFR, and Btk, in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo. At low micromolar concentrations, AVL-101 inhibited the Tec (tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma) family of kinases (Bmx, Btk, Itk) as well as JAK 2, Aurora A, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR)-l, Flt4, Ret, and TrkA. AVL-291/292 also inhibited the Tec family of kinases (Bmx, Btk, Tec) as well as JAK2, JAK3, Txk, Flt4.136 AVL-101 disrupts the BCR-signaling pathway, as measured by the inhibition of both Btk Y223 autophosphorylation and Btk substrate PLC-γ2 phosphorylation.137,138 AVL-101 inhibited the proliferation of the B-cell lymphoma cell lines DOHH2, DHLA4, and WSU-DLCL2 in vitro. Moreover, AVL-101 inhibited Btk-dependent B-cell function in vivo. These properties support the potential of AVL-101/291/292 in B-cell malignancies.
In preclinical studies, AVL-291 selectively and potently inhibited Btk and BCR signaling in vitro and was efficacious in a variety of animal disease models. Moreover, AVL-292 inhibited osteoclast function and reduced osteoclast-stimulated proliferation of MM cells.139 AVL-291 modified the course of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in animal models, with 75% inhibition of the clinical score at an oral dose of 3 mg/kg that correlated directly with 75% Btk target occupancy.140 AVL-291 reduced clinical arthritis scores, as well as inflammation, joint damage, cartilage damage, and bone erosion in the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) models of RA. Complete inhibition of the disease correlated with complete target occupancy at 10 mg/kg. Thus, AVL-291 is potentially useful for patients with lymphoid malignancies and RA and possibly in other autoimmune diseases characterized by aberrant B-cell activation. AVL-292 is currently being investigated in autoimmune diseases as well as in B-cell malignancies.141 AVL-292 has demonstrated biological activity in patients suffering from CLL as well as preclinical data on its therapeutic potential in the prevention of bone destruction by abrogating osteoclast sealing zone formation caused by MM and MM-related bone disease.
Clinical studies
AVL-292 has successfully completed two phase Ia clinical studies to date. Westlin et al143 assessed the safety and pharmacokinetics of AVL-292 in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-ascending-dose study in healthy adult subjects. Single oral doses of 0.5–7.0 mg/kg AVL-292 were safe and well tolerated. Subjects that received 1–2 mg/kg of AVL-292 achieved > 80% Btk occupancy, which was sustained through 24 hours even after plasma levels of AVL-292 had declined.143 The minimum dose that achieved complete target occupancy in this study (125 mg) was carried forward as the starting dose in a phase Ib study of hematological malignancies of B-cell origin. Subjects diagnosed with B-cell malignancies received single daily oral doses of AVL-292 in continuous 28-day cycles. Btk occupancy in this phase Ib clinical study confirmed observations in healthy volunteer subjects. The ongoing phase Ib clinical trial of AVL-292 is being conducted in patients with B-cell malignancies, including B-cell NHL, CLL, and WM. An escalating-dose study (125–625 mg) in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell NHL, CLL, and WM is ongoing (NCT01351935).
Noncovalent Btk inhibitors
Dasatinib (Sprycel)
Dasatinib (Sprycel/BMS-354825, Bristol-Myers Squibb) [N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-(6-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl) piperazin-1-yl)-2-methylpyrimidin-4-ylamino)thiazole-5-carboxamide], is a potent, orally active, multikinase BCR/Abl and Src family TKI that is FDA-approved for treatment of CML and is a potent inhibitor of Btk.105,144 A chemical proteomics-profiling approach identified the Tec kinases Btk and Tec to be very prominent targets of dasatinib.105,145 Structure-based mutagenesis experiments by Hantschel et al105 identified the gatekeeper residue as a critical determinant for dasatinib sensitivity. Mutation of Thr-474 in Btk to Ile conferred resistance to dasatinib. Small gatekeeper residues like Thr in Btk allow for dasatinib binding, whereas bulky gatekeeper residues block dasatinib binding.
Inhibition of Btk by dasatinib might be of clinical benefit in pre-B lymphoblastic leukemia. In the LN microenvironment, CLL cells are protected from apoptosis by upregulation of antiapoptotic proteins. The situation in CLL LN could be mimicked by prolonged in vitro CD40 stimulation of CLL cells, which results in upregulation of antiapoptotic Bcl-xL, Al/Bfl-1, and Mcl-1 proteins, and affords resistance to various chemotherapeutics (fludarabine, bortezomib, roscovitine). The antiapoptotic profile of CD40-triggered CLL resembles BCR-Abl-dependent changes seen in CML. Dasatinib prevented CD40-mediated antiapoptotic changes in CLL with Abl and Btk as dominant targets.145 Functional analysis revealed that CD40-mediated antiapoptotic signals and drug resistance could be overcome both by dasatinib and the Abl inhibitor imatinib, but not by the Btk inhibitor ibrutinib/PCI-32765. BCR- and chemokine-controlled adhesion can be abolished by dasatinib and ibrutinib, but not by imatinib.146 Thus, dasatinib combines two key aspects that are clinically relevant: inhibition of Abl overrides chemoprotective survival signals, whereas inhibition of Btk impairs integrin-mediated adhesion of CLL cells in the microenvironmental niche.
A phase II trial evaluated the combined inhibition of Abl and Btk by dasatinib and fludarabine in 20 refractory CLL patients.147 In agreement with the in vitro data, reductions in LN size (≥20%) were observed in most patients that provided a significant improved progression-free survival (256 days) and overall survival (510 days), as compared to nonresponders (80 days and 158 days, respectively). Thus, in agreement with in vitro molecular studies, dasatinib seems to have clinical efficacy in heavily pretreated refractory CLL patients. These data encourage further studies on the use of dasatinib in combination with other classes of drugs in R/R CLL.
LFM-A13
LFM-A13 (alpha-cyano-beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl-N-(2,5-ibromophenyl) propenamide) is a rationally designed selective Tec family kinase inhibitor.148,149 The selectivity of LFM-A13 against Tec family kinases has been extensively tested in diverse preclinical models by several research groups. LFM-A13 binds to the catalytic pocket of the kinase domain. In vitro, LFM-A13 inhibited recombinant Btk with an IC50 value of 2.5 μM, but it did not affect the enzymatic activity of other protein tyrosine kinases, including JAK1 and JAK2, Src family kinase Hck, and receptor family tyrosine kinases, EGF-receptor kinase and insulin-receptor kinase (Irk), at concentrations as high as 278 μm.148 Kim et al150 and Heinonen et al151 further demonstrated that its effects are virtually identical to those of Btk-specific siRNA duplexes that target human Btk mRNA. Among serine/threonine kinases, LFM-A13 inhibited only polo-like kinase (Plk), but none of the remaining twelve kinases.152 Both targets of LFM-A13 (viz Btk and Plk) are expressed in B-lineage lymphoid malignancies, including DLBCL and B-ALL.152,153 In vivo, LFM-A13 at nontoxic dose levels exhibited antineoplastic, antithrombotic, and immunosuppressive activity in various mouse models.151–156 Unlike the covalent inhibitors, LFM-A13 exhibits proapoptotic activity against mature B cells with an intact BCR signaling apparatus as well as BCR-negative leukemic B-cell precursors, and it is the only Btk inhibitor with experimentally documented in vitro and in vivo antineoplastic activity against human B-ALL cells.154
Good manufacturing practice-grade LFM-A13 exhibited potent single-agent activity in a nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse model of chemotherapy-resistant B-ALL that employs a highly aggressive and chemotherapy-resistant ALL cell line (viz NALM-6). When used for only 4 consecutive treatment days at 1 mg/kg/day, a dose level that corresponds to 1% of single-dose no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) and 0.09% of multiple-dose cumulative NOAEL; this therapeutic margin and potency against B-ALL is unprecedented among other drug candidates in development.11,155 LFM-A13 plus vincristine (VCR) combinations also were significantly more effective than vehicle or VCR alone, as evidenced by the significantly lower human leukemia burden in LFM-A13 plus VCR vs vehicle/VCR-treated control mice.156 Thus, the chemoresistance of relapsed B-cell precursor ALL can be overcome by using LFM-A13 in combination with chemotherapy. LFM-A13 also inhibited MM cells in vitro and prevented in a SCID mouse xenograft model of MM, the formation of osteolytic lesions in implanted bones.156
ONO-WG-307
ONO-WG-307 (Ono Pharmaceutical) is a multikinase inhibitor with greater selectivity for Btk (IC50 = 2 nM) than Lyk, Fyn, or Lyn A in the in vitro kinase assay. In vitro, ONO-WG-307 exhibited differential antiproliferative effects in the nanomicromolar range against multiple NHL/CLL cell lines.158 Quantitative phosphoproteome studies with both sensitive and nonsensitive cells revealed selective ONO-WG-307 suppression of Akt-mediated signaling and cellular protein kinase D activity in sensitive compared to nonsensitive cells.159 These findings suggest a critical role of Btk-mediated signaling through Akt and protein kinase D. Orally administered ONO-WG-307 (50 mg/kg) induced a dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth in an ABC-DLBCL xenograft (TMD-8) model and moderate antitumor activity in an FL xenograft model.158 Based on these preliminary preclinical results, ONO-WG-307 is being developed for the treatment of B-cell lymphoproliferative diseases.
GDC-0834
GDC-0834 (Genentech, Gilead): 2.2 GDC-0834 GDC-0834 [R-N-(3-(6-(4-(l,4-dimethyl-3-oxopiperazin-2-yl) phenylamino)-4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydropyrazin-2-yl)-2-methylphenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b] thiophene-2-carboxamide], is a reversible, adenosine triphosphate-competitive small-molecule inhibitor of Btk potentially useful in the treatment of RA and lymphoid malignancies.160,161 GDC-0834 inhibited Btk phosphorylation (p-Btk) in in vitro assays and in vivo in rodents. GDC-0834 inhibited p-Btk-Y223 with an in vitro IC50 of 5.9 nM and 6.4 nM in biochemical and cellular assays, respectively, and in vivo IC50 of 1.1 and 5.6 μM in mouse and rat, respectively. GDC-0834 prevented murine and human B-cell proliferation in response to BCR or CD40 stimulation. GDC-0834 suppressed arthritis in the prophylactic rat CIA model in a dose-dependent manner. Administration of GDC-0834 (30–100 mg/kg) in the rat CIA model resulted in a dose-dependent decrease of ankle swelling and reduction of morphologic pathology. In addition, GDC-0834 significantly inhibited joint inflammation, cartilage damage, and bone resorption. However, GDC-0834 has been discontinued due to poor pharmacokinetics in humans.161
Conclusion
Inhibition of Btk is emerging as a promising mechanism for targeting B-cell malignancies. Ibrutinib/PCI-32765, a covalent multikinase inhibitor, is undergoing late-stage efficacy studies in patients with various B-cell malignancies. PCI-32765 induced a durable objective response in various relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies. PCI-32765 is highly active and well tolerated in CLL/SLL patients, irrespective of high-risk genomic abnormalities, which suggests that this drug candidate may be an important new targeted treatment approach for CLL, particularly in combination with other agents. Data from several phase I/II trials demonstrated that high-risk CLL patients respond equally as well as low-risk patients to PCI-32765. This compound has shown an interesting pattern of response, in which very rapid nodal shrinkage occurs at the same time as the lymphocyte count rises, suggesting redistribution of CLL cells from the LNs and BM to the peripheral blood. Ibrutinib in combination with bendamustine/rituximab or ofatumumab had high overall response rates, rapid onset of response, low rate of progressive disease, and good tolerability in patients with heavily pretreated R/R CLL/SLL.
A major drawback of the long-term covalent inhibition of Btk function is the potential to inhibit a number of kinases in addition to crucial functions of the nonlymphoid lineages, especially the normal functioning of platelets. The most prominent dose-limiting toxicity observed with covalent Btk inhibitors was thrombocytopenia. It remains to be seen whether long-term Btk suppression by covalent Btk inhibitors is a viable therapeutic strategy in indolent diseases like CLL/SLL, which could result in hematological toxicity as well as infectious complications. In contrast, rationally designed novel noncovalent Btk inhibitors show potential as antileukemia/antilymphoma drug candidates with apoptosis-promoting and chemosensitizing properties. The incorporation of the apoptosis-promoting Btk inhibitors into the treatment regimens of patients with recurrent or high-risk B-lineage lymphoid malignancies may help overcome the chemotherapy resistance of their neoplastic B cells/B-cell precursors and thereby improve their treatment response and survival outcome.
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Kurosaki T, Tsukada S. BLNK: connecting Syk and Btk to calcium signals. Immunity. 2000;12:1–5. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schwartzberg PL, Finkelstein LD, Readinger JA. TEC-family kinases: regulators of T-helper-cell differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:284–295. doi: 10.1038/nri1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mahajan S, Vassilev A, Sun N, Ozer Z, Mao C, Uckun FM. Transcription factor STAT5A is a substrate of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:31216–31228. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104874200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Glassford J, Soeiro I, Skarell SM, et al. BCR targets cyclin D2 via Btk and the p85alpha subunit of PI3-K to induce cell cycle progression in primary mouse B cells. Oncogene. 2003;22:2248–2259. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bajpai UD, Zhang K, Teutsch M, Sen R, Wortis HH. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase links the B cell receptor to nuclear factor kappaB activation. J Exp Med. 2000;191:1735–1744. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.10.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Petro JB, Khan WN. Phospholipase C-gamma 2 couples Bruton’s tyrosine kinase to the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:1715–1719. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009137200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vassilev A, Ozer Z, Navara C, Mahajan S, Uckun FM. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase as an inhibitor of the Fas/CD95 death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:1646–1656. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.3.1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Verschuren MC, Kraakman ME, Mensink RG, Schuurman RK, van Dongen JJ, Hendriks RW. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase gene is expressed throughout B cell differentiation, from early precursor B cell stages preceding immunoglobulin gene rearrangement up to mature B cell stages. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23:3109–3114. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Martinez N, Camacho FI, Ruíz-Ballesteros E, et al. Variability in the degree of expression of phosphorylated IkappaBalpha in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cases with nodal involvement. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:6796–6806. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ortolano S, Hwang IY, Han SB, Kehrl JH. Roles for phosphoinositide 3-kinases, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and Jun kinases in B lymphocyte Chemotaxis and homing. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36:1285–1295. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Uckun F, Dibirdik I, Sarkissian A, Qazi S. In vitro and in vivo chemosensitizing activity of LFM-A13, a dual-function inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase and polo-like kinases, against human leukemic B-cell precursors. Arzneimittelforschung. 2011;61:252–259. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1296196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.American Cancer Society What are the key statistics for chronic lymphocytic leukemia? 2013Available from: http://www.cancer.org/cancer/leukemia-chroniclymphocyticcll/detailedguide/leukemia-chronic-lymphocytic-key-statisticsAccessed February 5, 2013
- 13.Gaynon PS. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and relapse. Br J Haematol. 2005;131:579–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gaynon PS, Trigg M, Uckun FM. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. In: Holland J, Frei E, Bast R, editors. Cancer Medicine. 5th ed. Hamilton (ON): BC Decker; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pui CH, Evans WE. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:166–178. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra052603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Leukemia facts and statistics 2012Available from: http://www.lls.Org/#/diseaseinformation/getinformationsupport/factsstatistics/leukemiaAccessed February 5, 2013
- 17.Abbott BL. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: recent advances in diagnosis and treatment. Oncologist. 2006;11:21–30. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.11-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Byrd JC, Lin TS, Grever MR. Treatment of relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia: old and new therapies. Semin Oncol. 2006;33:210–219. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wierda WG, O’Brien SM. Initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin Oncol. 2006;33:202–209. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:804–815. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra041720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pleyer L, Egle A, Hartmann TN, Greil R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of CLL: novel therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:405–418. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zenz T, Mertens D, Kuppers R, Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S. From pathogenesis to treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:37–50. doi: 10.1038/nrc2764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Burger JA, Ghia P, Rosenwald A, Caligaris-Cappio F. The microenvironment in mature B-cell malignancies: a target for new treatment strategies. Blood. 2009;114:3367–3375. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-225326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Smit LA, Hallaert DY, Spijker R, et al. Differential Noxa/Mcl-1 balance in peripheral versus lymph node chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells correlates with survival capacity. Blood. 2007;109:1660–1668. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-021683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Herishanu Y, Perez-Galan P, Liu D, et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-kappaB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2011;117:563–574. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-284984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Stevenson FK, Krysov S, Davies AJ, Steele AJ, Packham G. B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2011;118:4313–4320. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-06-338855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lin K, Glenn MA, Harris RJ, et al. c-Abl expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: clinical and therapeutic implications. Cancer Res. 2006;66:7801–7809. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Trigg ME, Gaynon P, Uckun FM. In: Cancer Medicine. 4th ed. Holland JF, Bast RC Jr, Morton DL, Fry E 3rd, Kufe DW, Weichselbaum RL, editors. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Moricke A, Zimmermann M, Reiter A, et al. Long-term results of five consecutive trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia performed by the ALL-BFM study group from 1981 to 2000. Leukemia. 2010;24:265–284. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Salzer WL, Devidas M, Carroll WL, et al. Long-term results of the Pediatric Oncology Group studies for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia 1984–2001: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Leukemia. 2010;24:355–370. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gaynon PS, Harris RE, Altman AJ, et al. Bone marrow transplantation versus prolonged intensive chemotherapy for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and an initial bone marrow relapse within 12 months of the completion of primary therapy: Children’s Oncology Group Study CCG-1941. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3150–3156. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.5856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Eapen M, Raetz E, Zhang MJ, et al. Outcomes after HLA-matched sibling transplantation or chemotherapy in children with B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in second remission: a collaborative study of the Children’s Oncology Group and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. Blood. 2006;107:4961–4967. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-12-4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Roy A, Cargill A, Love S, et al. Outcome after first relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia – lessons from the United Kingdom R2 trial. Br J Hematol. 2005;130:67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Uckun FM, Morar S, Qazi S. Vinorelbine-based salvage chemotherapy for therapy-refractory aggressive leukemias. Br J Haematol. 2006;135:500–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Malempati S, Gaynon PS, Sather H, La MK, Stork LC, Children’s Oncology Group Outcome after relapse among children with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Children’s Oncology Group study CCG-1952. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5800–5807. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.10.7508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Uckun FM, Jaszcz W, Chandan-Langlie M, Waddick KG, Gajl-Peczalska K, Song CW. Intrinsic radiation resistance of primary clonogenic blasts from children with newly diagnosed B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1993;91:1044–1051. doi: 10.1172/JCI116261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Uckun F M, Song CW. Lack of CD24 antigen expression in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia is associated with intrinsic radiation resistance of primary clonogenic blasts. Blood. 1993;81:1323–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Uckun FM, Chandan-Langlie M, Jaszcz W, Obuz V, Waddick K, Song CW. Radiation damage repair capacity of primary clonogenic blasts in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res. 1993;53:1431–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Larson RA. The US trials in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2004;83(Suppl 1):S127–S128. doi: 10.1007/s00277-004-0850-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Annino L, Vegna ML, Camera A, et al. Treatment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): long-term follow-up of the GIMEMA ALL 0288 randomized study. Blood. 2002;99:863–871. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.3.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Goekbuget N, Arnold R, Buechner T, Ganser A. Intensification of induction and consolidation improves only subgroups of adult ALL: analysis of 1200 patients in GMALL study 05/93. Blood. 2001;98:802a. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Thomas X, Boiron JM, Huguet F, et al. Outcome of treatment in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: analysis of the LALA-94 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:4075–4086. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.10.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nachman JB, Sather HN, Sensel MG, et al. Augmented post-induction therapy for children with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia and a slow response to initial therapy. NEnglJMed. 1998;338:1663–1671. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199806043382304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Uckun FM. Treating chronic leukemias. Minnesota Physician. 2002;16:14. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Evrard S, Gaussem P, Helley D, Darnige L. Prognostic factors in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: contribution of recent biological markers. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 2005;63:589–597. French. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Korte W, Cogliatti S. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – the old and the new. Ther Umsch. 2004;61:151–156. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930.61.2.151. German. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pangalis GA, Vassilakopoulos TP, Dimopoulou MN, Siakantaris MP, Kontopidou FN, Angelopoulou MK. B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia: practical aspects. Hematol Oncol. 2002;20:103–146. doi: 10.1002/hon.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Faria de, Jr, de Oliveira JS, Delbone de Faria RM, et al. Prognosis related to staging systems for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Sao Paulo Med J. 2000;118:83–88. doi: 10.1590/S1516-31802000000400002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Moreno C, Villamor N, Colomer D, et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation may overcome the adverse prognosis of unmutated VH gene in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3433–3438. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kaku H, Horikawa K, Obata Y, et al. NF-kappaB is required for CD38-mediated induction of C(gamma) 1 germline transcripts inmurine B lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 2002;14:1055–1064. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxf072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Uckun FM, Waddick KG, Mahajan S, et al. BTK as a mediator of radiation-induced apoptosis in DT-40 lymphoma B cells. Science. 1996;273:1096–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5278.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Takatsu K. Role of interleukin-5 in immune regulation and inflammation. Nippon Rinsho. 2004;62:1941–1951. Japanese. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ruiz-Ballesteros E, Mollejo M, Rodriguez A, et al. Splenic marginal zone lymphoma: proposal of new diagnostic and prognostic markers identified after tissue and cDNA microarray analysis. Blood. 2006;106:1831–1838. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-3898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tibes R, Trent J, Kurzrock R. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors and the dawn of molecular cancer therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;45:357–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.45.120403.100124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Chalandon Y, Schwaller J. Targeting mutated protein tyrosine kinases and their signaling pathways in hematologic malignancies. Haematologica. 2005;90:949–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Krause DS, Etten RA. Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:172–187. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra044389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Stiller CA. International patterns of cancer incidence in adolescents. Cancer Treat Rev. 2007;33:631–645. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2007.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gross TG, Termuhlen AM. Pediatric non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Curr Oncol Rep. 2007;9:459–465. doi: 10.1007/s11912-007-0064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lenz G, Staudt LM. Aggressive lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1417–1429. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0807082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Monti S, Savage KJ, Kutok JL, et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood. 2005;105:1851–1861. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lenz G, et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature. 2010;463:88–92. doi: 10.1038/nature08638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Davies AJ, Rosenwald A, Wright G, et al. Transformation of follicular lymphoma to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma proceeds by distinct oncogenic mechanisms. Br J Haematol. 2007;136:286–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Montoto S, Fitzgibbon J. Transformation of indolent B-cell lymphomas. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1827–1834. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.7577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Weniger MA, Wiestner A. Molecular targeted approaches in mantle cell lymphoma. Semin Hematol. 2011;3:214–226. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2011.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Herman SE, Gordon AL, Hertlein E, et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase represents a promising therapeutic target for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is effectively targeted by PCI-32765. Blood. 2011;23:6287–6296. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-328484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Minter AR, Simpson H, Weiss BM, Landgren O. Bone disease from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance to multiple myeloma: pathogenesis, interventions, and future opportunities. Semin Hematol. 2011;1:55–65. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2010.11.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Raje N, Roodman GD. Advances in the biology and treatment of bone disease in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;6:1278–1286. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Abe M, Hiura K, Ozaki S, Kido S, Matsumoto T. Vicious cycle between myeloma cell binding to bone marrow stromal cells via VLA-4-VCAM-1 adhesion and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha and MIP-lbeta production. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;1:16–23. doi: 10.1007/s00774-008-0012-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zannettino AC, Farrugia AN, Kortesidis A, et al. Elevated serum levels of stromal-derived factor-1 alpha are associated with increased osteoclast activity and osteolytic bone disease in multiple myeloma patients. Cancer Res. 2005;5:1700–1709. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Takeuchi K, Abe M, Hiasa M, et al. TGF-beta inhibition restores terminal osteoblast differentiation to suppress myeloma growth. PLoS One. 2010;3:e9870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Vallet S, Mukherjee S, Vaghela N, et al. Activin A promotes multiple myeloma-induced osteolysis and is a promising target for myeloma bone disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;11:5124–5129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911929107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Moreaux J, Veyrune JL, De Vos J, Klein B. APRIL is overexpressed in cancer: link with tumor progression. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:83. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Tai YT, Li XF, Breitkreutz I, et al. Role of B-cell-activating factor in adhesion and growth of human multiple myeloma cells in the bone marrow microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2006;13:6675–6682. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kline M, Donovan K, Wellik L, et al. Cytokine and chemokine profiles in multiple myeloma; significance of stromal interaction and correlation of IL-8 production with disease progression. Leuk Res. 2007;5:591–598. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2006.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Lee SH, Kim T, Jeong D, Kim N, Choi Y. The tec family tyrosine kinase Btk regulates RANKL-induced osteoclast maturation. J Biol Chem. 2008;17:11526–11534. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708935200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Tai YT, Chang BY, Kong SY, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibition is a novel therapeutic strategy targeting tumor in the bone marrow microenvironment in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2012;120:1877–1887. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-396853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Eifert C. An RNAi Screen Targeting the Protein Tyrosine Kinases Identifies Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) as a Breast Cancer Cell Survival Factor [dissertation] Albany: State University of New York; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Conklin DS, Eifert C, Kourtidis A. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase as anti-cancer drug target. US patent application 20120165395. Jun 28, 2012.
- 79.Lavitrano M, Grassilli E, Helin K. Isoform of bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) protein. US patent 8,232,085. Jul 31, 2012.
- 80.Uckun FM, Zheng Y, Ghosh S. BTK inhibitors and methods for their identification and use. US patent 6,160,010. Dec 12, 2000.
- 81.Uckun FM, Zheng Y, Ghosh S. BTK inhibitors and methods for their identification and use. US patent 6,221,900. Apr 24, 2001.
- 82.Uckun FM, Zheng Y, Ghosh S. BTK inhibitors and methods for their identification and use. US patent 6,294,575. Sep 25, 2001.
- 83.Uckun FM, Zheng Y, Ghosh S. BTK inhibitors and methods for their identification and use. US patent 6,303,652. Oct 16, 2001.
- 84.Uckun FM, Zheng Y, Ghosh S. BTK inhibitors and methods for their identification and use. US patent 6,365,626. Apr 2, 2002.
- 85.Uckun FM, Malaviya R. BTK inhibitors and methods for their identification and use. US patent 6,753,348. Jun 22, 2004.
- 86.Uckun FM, Zheng Y, Ghosh S. BTK Inhibitors and methods for their identification and use European patent 1 071 658 B1. Jun 16, 2004.
- 87.Zhu Z. Intrabodies. US patent application 20100143371. Jun 10, 2010.
- 88.Honigberg L. Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. US patent application 20100041677. Feb 18, 2010.
- 89.Honigberg L, Verner E, Pan Z. Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. US patent application 20100022561. Jan 28, 2010.
- 90.Honigberg L, Verner E, Pan Z. Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. US patent application 20100004270. 2010 Jan 7; [Google Scholar]
- 91.Honigberg L, Verner E, Pan Z. Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. US patent application 20080139582. Jun 12, 2008.
- 92.Tripp M, Babish J, Bland J, et al. Substituted 1,3-cyclopentadione multi-target protein kinase modulators of cancer, angiogenesis and the inflammatory pathways associated therewith. US patent application 20100137449. Jun 10, 2010.
- 93.Kennedy-Smith J, Kondru RK, Loe BE, et al. Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. US patent application 20100099659. Apr 22, 2010.
- 94.Jankowski OD, Palmer JT, Honigberg L. Inhibitors of tyrosine kinases and uses thereof. US patent application 20100035841. Feb 11, 2010.
- 95.Johns RA, Su Q, Champion HC. HIMF and BTK in pulmonary, cardiac, and inflammation disorders. US patent application 20100028355. Feb 4, 2010.
- 96.Dewdney NJ, Lou Y, Sjogren E, Soth M, Sweeney ZK. Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. US patent application 20100004231. Jan 7, 2010.
- 97.Dewdney NJ, Kondru RK, Loe BE, et al. Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. US patent application 20090318448. Dec 24, 2009.
- 98.Dewdney NJ, Kennedy-Smith J, Kondru RK, et al. Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. US patent application 20090306041. Dec 10, 2009.
- 99.Dewdney NJ, Lou Y, Sjogren E, Soth M. Inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. US patent application 20100016301. 2010 Jan 21; [Google Scholar]
- 100.Pan Z, Scheerens H, Li SJ, et al. Discovery of selective irreversible inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Chem Med Chem. 2007;2:58–61. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200600221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Honigberg LA, Smith AM, Sirisawad M, et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 blocks B-cell activation and is efficacious in models of autoimmune disease and B-cell malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:13075–13080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004594107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Singh J, Petter RC, Kluge AF. Targeted covalent drugs of the kinase family. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.06.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Evans E, Tester R, Aslanian S, et al. A novel platform-based approach to silence oncoproteins using small molecule therapeutics – application to Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; Paper presented at the 100th AACR Annual Meeting; April 18–22, 2009; Denver, CO, USA. [Google Scholar]
- 104.Marcotte DJ, Liu YT, Arduini RM, et al. Structures of human Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in active and inactive conformations suggest a mechanism of activation for TEC family kinases. Protein Sci. 2010;19:429–439. doi: 10.1002/pro.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Hantschel O, Rix U, Schmidt U, et al. The Btk tyrosine kinase is a major target of the Bcr-Abl inhibitor dasatinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:13283–13288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702654104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Mao C, Zhou M, Uckun FM. Crystal structure of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase domain suggests a novel pathway for activation and provides insights into the molecular basis of X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41435–41443. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104828200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Herman SE, Gordon AL, Hertlein E, et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase represents a promising therapeutic target for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is effectively targeted by PCI-32765. Blood. 2011;23:6287–6296. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-328484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Ponader S, Chen SS, Buggy JJ, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 thwarts chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival and tissue homing in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 2012;119:1182–1189. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-386417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.de Rooij MF, Kuil A, Geest CR, et al. The clinically active BTK inhibitor PCI-32765 targets B-cell receptor- and chemokine-controlled adhesion and migration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2012;119:2590–2594. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-390989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Chang BY, Huang MM, Francesco M, et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 ameliorates autoimmune arthritis by inhibition of multiple effector cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;4:R115. doi: 10.1186/ar3400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Holler C, Pinon JD, Denk U, et al. PKCbeta is essential for the development of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the TCL1 transgenic mouse model: validation of PKCbeta as a therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2009;113:2791–2794. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-06-160713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Gorgun G, Ramsay AG, Holderried TA, et al. E(μ)-TCL1 mice represent a model for immunotherapeutic reversal of chronic lymphocytic leukemia-induced T-cell dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sei USA. 2009;106:6250–6255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901166106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Johnson AJ, Lucas DM, Muthusamy N, et al. Characterization of the TCL-1 transgenic mouse as a preclinical drug development tool for human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2006;108:1334–1338. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-12-011213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Burger JA, O’Brien S, Fowler N, et al. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, PCI-32765, is well tolerated and demonstrates promising clinical activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL): an update on ongoing phase 1 studies. Blood. 2010;116:32a. [Google Scholar]
- 115.Advani R, Sharman JP, Smith SM, et al. Effect of Btk inhibitor PCI-32765 monotherapy on responses in patients with relapsed aggressive NHL: evidence of antitumor activity from a phase I study [abstract] J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:15s. [Google Scholar]
- 116.Advani R, Sharman J, Smith ST, et al. The Btk inhibitor PCI-32765 is highly active and well tolerated in patients with relapsed/refractory B cell malignancies: final results from a phase I study. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(Suppl 4):ivl35–ivl37. [Google Scholar]
- 117.Advani RH, Buggy JJ, Sharman JP, et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor Ibrutinib (PCI-32765) has significant activity in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:88–94. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.7906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Fowler N, Sharman JP, Smith SM, et al. The Btk inhibitor, PCI-32765, induces durable responses with minimal toxicity in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies: results from a phase I study. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts. Blood. 2010;116:964A. [Google Scholar]
- 119.Fowler NH, Advani RH, Sharman JP, et al. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) is active and tolerated in relapsed follicular lymphoma; Paper presented at the 2012 ASH Annual Meeting; December 8–11, 2012; Atlanta, GA, USA. p. Abstract 156. [Google Scholar]
- 120.Staudt LM, Dunleavy K, Buggy JJ, et al. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor PCI-32765 modulates chronic active BCR signaling and induces tumor regression in relapsed/refractory ABC DLBCL. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstract) 2011;118:abstract 2716. [Google Scholar]
- 121.Harrison C. Trial watch: BTK inhibitor shows positive results in B cell malignancies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11:96. doi: 10.1038/nrd3656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Wang M, Rule SA, Martin P, et al. Interim results of an international, multicenter, phase 2 study of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, Ibrutinib (PCI-32765), in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL): durable efficacy and tolerability with longer follow-up; 2012 ASH Annual Meeting; December 8–11, 2012; Atlanta, GA, USA. p. Abstract 904. [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ponader P, Balasubramanian S, Pham LV, et al. Activity of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor PCI-32765 in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) identified BTK as a novel therapeutic target; 53rd ASH Annual Meeting; December 10–13, 2011; San Diego, CA, USA. p. Abstract 3688. [Google Scholar]
- 124.Wilson WH, Gerecitano JF, Goy A, et al. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, ibrutinib, has preferential activity in the ABC subtype of relapsed/refractory de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): interim results of a multicenter, open-label, phase 2 study; 2012 ASH Annual Meeting; December 8–11, 2012; Atlanta, GA, USA. p. Abstract 686. [Google Scholar]
- 125.O’Brien S, Burger JA, Blum KA, et al. The Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor PCI-32765 Induces Durable Responses in Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL/SLL): Follow-up of a Phase Ib/II Study; 53rd ASH Annual Meeting; December 10–13, 2011; San Diego, CA, USA. p. Abstract 983. [Google Scholar]
- 126.O’Brien S, Burger JA, Coutre SE, et al. The Btk Inhibitor PCI-32765 is highly active and tolerable in patients with poor-risk CLL: interim results from a phase Ib/II study. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(Suppl 4):ivl23–ivl24. [Google Scholar]
- 127.O’Brien S, Burger JA, Blum KA, et al. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor PCI-32765 induces durable responses in relapsed or refractory (R/R) chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL): follow-up of a phase Ib/II study. Blood. 2011;118:449. [Google Scholar]
- 128.O’Brien S, Furman RF, Coutre SE, et al. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) is highly active and tolerable in relapsed or refractory and treatment naive chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients, updated results of a phase Ib/II study; 17th Congress of European Hematology Association; June 14–17, 2012; Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 2012. p. Abstract 1970. [Google Scholar]
- 129.Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor PCI-32765 (P) in treatment-naive (TN) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients (pts): interim results of a phase Ib/II study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;(Suppl 30):6507. [Google Scholar]
- 130.Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre S, Flinn IW, Burger JA, Blum KA. The Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib promotes high response rate, durable remissions, and is tolerable in treatment naïve (TN) and relapsed or refractory (RR) CLL or SLL patients including patients with high-risk (HR) disease: new and updated results of 116 patients in a phase Ib/II Study; 2012 ASH Annual Meeting; December 8–11, 2012; Atlanta, GA, USA. p. Abstract 189. [Google Scholar]
- 131.Burger JA, Keating MJ, Wierda WG, et al. The Btk inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) in combination with rituximab is well tolerated and displays profound activity in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients; 2012 ASH Annual Meeting; December 8–11, 2012; Atlanta, GA, USA. p. Abstract 187. [Google Scholar]
- 132.Brown JR, Barrientos J, Flinn IW, et al. Combination of the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 with bendamustine/rituximab (BR) in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: interim results of a phase Ib/II study; 17th Congress of European Hematology Association; Amsterdam, The Netherlands. June 14–17, 2012; p. Abstract 1590. [Google Scholar]
- 133.O’Brien SM, Barrientos JC, Flinn IW, et al. Combination of the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor PCI-32765 with bendamustine (B)/rituximab (R) (BR) in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): interim results of a phase Ib/II study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;(Suppl 30):6515. [Google Scholar]
- 134.Jaglowski SM, Jones JA, Flynn JM, et al. A phase Ib/II study evaluating activity and tolerability of BTK inhibitor PCI-32765 and ofatumumab in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and related diseases. 2012 J Clin Oncol;(Suppl 30):6508. [Google Scholar]
- 135.Advani R, Sharman JP, Smith SM, et al. Effect of BTK inhibitor PCI-32765 monotherapy on responses in patients with relapsed aggressive NHL: evidence of anti-tumor activity from a phase I study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;(Suppl 28):8012. [Google Scholar]
- 136.Singh J, Russell P, Deqiang N, et al. Protein kinase conjugates and inhibitors. US patent application 20110117073. May 19, 2011.
- 137.Evans E, Tester R, Aslanian S, et al. A novel platform-based approach to silence oncoproteins using small molecule therapeutics–application to Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; Proceedings of the 103rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research; April 18–22, 2009; Denver, CO, USA. p. Abstract 3739. [Google Scholar]
- 138.Evans E, Sheets M, Bernar H, et al. Prolonged inhibition of BCR signaling and suppression of B cell lymphoma through irreversible inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase [abstract] Blood. 2008;112:904. [Google Scholar]
- 139.Evans E, Ponader S, Karp R, et al. Covalent inhibition of Btk with clinical development compound AVL-292 disrupts signaling that maintains the microenvironment necessary for chronic lymphocytic leukemia growth [abstract] Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011;11(Suppl2):S173–S174. [Google Scholar]
- 140.Eda H, Santo L, Cirstea DD, et al. Targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase as a novel approach to inhibit osteoclast function in multiple myeloma [abstract] Blood. 2011;118:1243. [Google Scholar]
- 141.Evans E, Tester R, Sharon A, et al. Translational medicine of a selective inhibitor of Btk in rheumatic diseases: pharmacology and early clinical development [abstract] Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(Suppl 10):1757. [Google Scholar]
- 142.Evans E, Teste R, Aslanian S, et al. Clinical development of AVL-292; a potent, selective covalent Btk inhibitor for the treatment of B cell malignancies [abstract] Blood. 2011;118:1487. [Google Scholar]
- 143.Westlin WF, Stiede K, Lounsbury H, et al. Translational medicine enables rapid early clinical development of AVL-292, a highly selective, orally available inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, in a phase lb clinical trial. Cancer Res. 2012;72(Suppl 8):1745. [Google Scholar]
- 144.Hantschel O, Rix U, Superti-Furga G. Target spectrum of the BCR-ABL inhibitors imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49:615–619. doi: 10.1080/10428190801896103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Hallaert DY, Jaspers A, van Noesel CJ, van Oers MH, Kater AP, Eidering E. Abl kinase inhibitors overcome CD40-mediated drug resistance in CLL: implications for therapeutic targeting of chemoresistant niches. Blood. 2008;112:5141–5149. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-146704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Eldering E, Geest CR, de Rooij MFM, et al. Mapping the targets of dasatinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia reveals distinct roles for Abl and Btk in drug resistance and adhesion, and explains clinical effects on lymph node reduction; Proceedings: 2012 ASH Annual Meeting; December 8–11, 2012; Atlanta, GA, USA. p. Abstract 3900. [Google Scholar]
- 147.Amrein PC, Attar EC, Takvorian T, et al. Phase II study of dasatinib in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:2977–2986. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Mahajan S, Ghosh S, Sudbeck EA, et al. Rational design and synthesis of a novel anti-leukemic agent targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), LFM-A13 [alpha-cyano-beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl-N-(2,5-dibromophenyl) propenamide] J Biol Chem. 1999;274:9587–9599. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.14.9587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Ghosh S, Jennissen JD, Zheng Y, Uckun FM. Three leflunomide metabolite analogs. Acta Crystallogr C. 2000;56:1254–1257. doi: 10.1107/s0108270100009768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Kim YJ, Sekiya F, Poulin B, Bae YS, Rhee SG. Mechanism of B-cell receptor-induced phosphorylation and activation of phospholipase C-gamma2. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:9986–9999. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.9986-9999.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Heinonen JE, Smith CI, Nore BE. Silencing of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) using short interfering RNA duplexes (siRNA) FEBS Lett. 2002;527:274–278. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Uckun FM, Ozer Z, Qazi S, Tuel-Ahlgren L, Mao C. Polo-like-kinase 1 (PLK1) as a molecular target to overcome SYK-mediated resistance of B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells to oxidative stress. Br J Haematol. 2010;148:714–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.07983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Uckun FM, Dibirdik I, Qazi S, et al. Anti-breast cancer activity of LFM-A13, a potent inhibitor of polo-like kinase (PLK) Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15:800–814. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2006.10.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Uckun FM. Chemosensitizing anti-cancer activity of LFM-A13, a leflunomide metabolite analog targeting polo-like kinases. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:3021–3026. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.24.5096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Uckun FM. Rationally designed anti-mitotic agents with pro-apoptotic activity. Curr Pharm Des. 2001;7:1627–39. doi: 10.2174/1381612013397177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Uckun FM, Zheng Y, Cetkovic-Cvrlje M, et al. In vivo pharmacokinetic features, toxicity profile, and chemosensitizing activity of alpha-cyano-beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl-N-(2,5-dibromophenyl) propenamide (LFM-A13), a novel antileukemic agent targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:1224–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Cetkovic-Cvrlje M, Uckun FM. Dual targeting of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase and Janus kinase 3 with rationally designed inhibitors prevents graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) in a murine allogeneic bone marrow transplantation model. Br J Hematol. 2004;126:821–827. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Kozaki R, Yoshizawa T, Yasuhiro T, et al. Development of a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor–ONO-WG-307, a potential treatment for B-cell malignancies. Cancer Res. 2012;72(Suppl B):857. [Google Scholar]
- 159.Yasuhiro T, Yoshizawa T, Daub H, Weber C, Narita M, Kawabata K. ONO-WG-307, a novel, potent and selective inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk), results in sustained inhibition of the ERK, AKT and PKD signaling pathways. Cancer Res. 2012;72(Suppl B):2021. [Google Scholar]
- 160.Liu L, Di Paolo J, Barbosa J, Rong H, Reif K, Wong H. Antiarthritis effect of a novel Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor in rat collagen-induced arthritis and mechanism-based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling: relationships between inhibition of BTK phosphorylation and efficacy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;338:154–163. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.181545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Liu L, Halladay JS, Shin Y, et al. Significant species difference in amide hydrolysis of GDC-0834, a novel potent and selective Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39:1840–1849. doi: 10.1124/dmd.111.040840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]