Abstract
Amino acid radical generation and transport are fundamentally important to numerous essential biological processes to which small molecule models lend valuable mechanistic insights. Pyridyl-amino acid-methyl esters are appended to a rhenium(I) tricarbonyl 1,10-phenanthroline core to yield rhenium–amino acid complexes with tyrosine ([Re]–Y–OH) and phenylalanine ([Re]–F). The emission from the [Re] center is more significantly quenched for [Re]–Y–OH upon addition of base. Time-resolved studies establish that excited-state quenching occurs by a combination of static and dynamic mechanisms. The degree of quenching depends on the strength of the base, consistent with a proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) quenching mechanism. Comparative studies of [Re]–Y–OH and [Re]–F enable a detailed mechanistic analysis of a bidirectional PCET process.
Introduction
Tyrosyl radicals are key intermediates in a wide variety of energy conversion processes.1 Tyrosine oxidation has been a subject of significant focus in the literature. Specifically, the proton transfer (PT) component of tyrosine oxidation has been of particular interest both in natural2 and model systems.3,4 Tyrosyl radicals are particularly essential to a biology as diverse as that derived from photosystem II,5,6 cytochrome c oxidase7 and ribonucleotide reductase (RNR).8 We have developed biophysical tools that permit tyrosine radicals (Y•) to be photogenerated in biological systems with emphasis on RNR.9 These photoRNRs have been invaluable for deciphering the PCET mechanism by which radicals are generated and transported in this enzyme.10–13 The value of Y• photogeneration in the development of new biophysical tools for radical enzymology14 provides an imperative for a mechanistic understanding of tyrosine photooxidation.
Formation of tyrosyl radical from tyrosine requires both deprotonation and one-electron oxidation of the native amino acid. Stepwise mechanisms are thermodynamically demanding and result in high-energy intermediates, implicating a PCET mechanism for this reaction. In natural systems, PCET processes occur with exquisite sensitivity and remarkable selectivity by separating the PT coordinate form the ET coordinate, i.e. by installing a bidirectional PCET pathway. This requirement is due to the relatively large mass of a proton in comparison to an electron. Hence, whereas the electron can tunnel over long distances, the proton cannot;15,16 the control of the PT coordinate over a different length scale to that of the electron is essential for the kinetic feasibility of a PCET reaction and the attendant opportunity to exercise kinetic control over the reaction.
To this end, well-defined, pre-organized PT pathways are essential for the generation of Y•, and the incorporation of a well-defined proton acceptor is essential for the generation of Y•. A variety of studies have demonstrated the importance of hydrogen bonding on the kinetics of phenol oxidation by PCET.17–22 Herein, we report the use of a bidirectional scaffold for the study of tyrosine oxidation that enables the independent variation of the driving force for both proton transfer (PT) and electron transfer (ET), which are critical determinants of the PCET governing tyrosine photooxidation.23 A pyridyl-amino acid-methyl ester (Py–AA) has been appended to a rhenium(I) tricarbonyl 1,10-phenanthroline core [Re] to yield rhenium–amino acid complexes with tyrosine ([Re]–Y–OH) and phenylalanine ([Re]–F). A PCET network is self assembled by association of [Re]–Y–OH to a base, which is both well-defined and easily varied to permit the PT to be examined in concert with ET to the photoexcited [Re] core. We find that the efficacy of radical generation depends intimately on the strength of the associated base.
Experimental
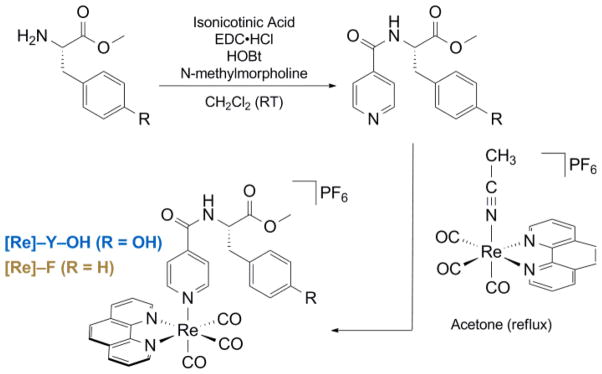
The [Re]–AA compounds are synthesized via the route shown in Scheme 1. Syntheses were accomplished by methodologies described in the ESI and products were spectroscopically and analytically characterized in detail to ensure compound identification and purity; these data are also given in the ESI.
Scheme 1.
Steady-state spectroscopy was performed using dilute solutions of [Re]–AA (AA = Y or F) complexes. Emission titrations were performed by adding sequential volumes of pyridine (neat) or imidazole (1.0 M in dichloromethane) to a sample of [Re]–Y–OH (50 μM in dichloromethane). Equilibrium constants were determined for the association of [Re]–Y–OH and pyridine or imidazole by monitoring emission quenching as a function of base added. Fitting to determine the equilibrium association constants for [Re]–Y–OH binding to bases was performed according to published methods.24
Time-resolved absorption and emission experiments were completed by nanosecond flash photolysis, which were performed using a system which was significantly modified from one previously described.25,26 Emission lifetimes were measured for both [Re]–Y–OH and [Re]–F as a function of pyridine and imidazole concentrations. Full experimental procedures, detailed description of experimental apparatus, a complete explanation of data analysis, and a derivation of the rate law for excited-state quenching are provided in ESI. Errors reported for rate constants and equilibrium constants measured are two standard deviations, as calculated from the standard error of the corresponding fit.
Results and Discussion
The [Re]–AA compounds shown in Scheme 1 were developed as a modular platform where relevant driving forces could be varied for the study of PCET. A similar method of their synthesis has recently been reported.27 The PCET network is self assembled by addition of base (pyridine or imidazole) to a solution of [Re]–Y–OH in dichloromethane. as shown in Fig. 1. This approach for forming the bidirectional PCET network provides a modular and versatile platform for studying tyrosine oxidation. The absence of a hydrogen bond in the [Re]–F system prevents assembly of the PCET network, and hence this system provides a control for kinetic measurements associated with the photogeneration of Y•. Moreover, because F is redox inactive, any disparity in excited-state lifetimes between [Re]–F and [Re]–Y–OH is directly attributable to reactivity at the tyrosine phenol.
Fig. 1.
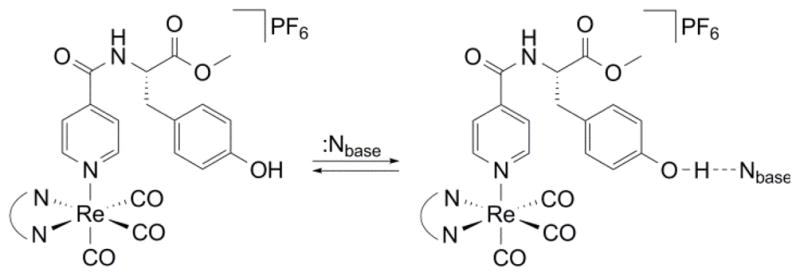
Self-assembly of a bidirectional network for the photo-oxidation of tyrosine by PCET.
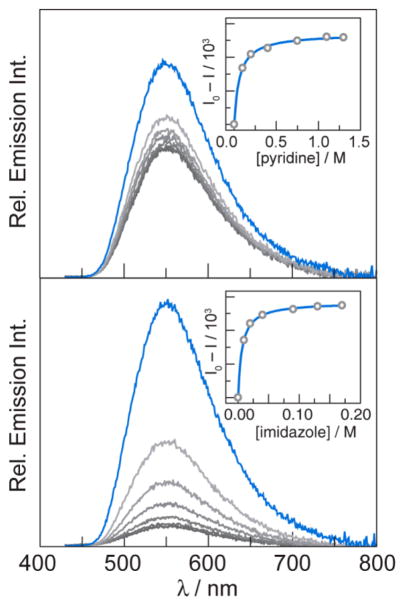
Ground state absorption and steady state emission spectra of [Re]–Y–OH and [Re]–F (Fig. 2) are nearly identical to one another and dominated by the electronic properties of the [Re] centre. Hydrogen-bonded association between the tyrosine phenol proton of [Re]–Y–OH and base is evident from emission spectra. In dichloromethane solution, [Re]–Y–OH is highly emissive from a 3MLCT excited state (3[ReI]*). As shown in Fig. 3, emission from [Re]–Y–OH is quenched significantly upon addition of base (pyridine or imidazole). The equilibrium constants, Kassoc, for association between [Re]–Y–OH and the added base may be measured from the concentration dependence of this quenching. Equilibrium constants were measured for both pyridine (Kassoc = 16 ± 2 M−1) and imidazole (Kassoc = 157 ± 13 M−1) by fitting the concentration dependence of emission intensity as previously reported.24 The stronger binding to imidazole than to pyridine is in accordance with the relative aqueous pKa values. These equilibrium rate constants correspond to reaction free energies of ΔGo = −6.9 kJ mol−1 and ΔGo = −12.5 kJ mol−1.
Fig. 2.
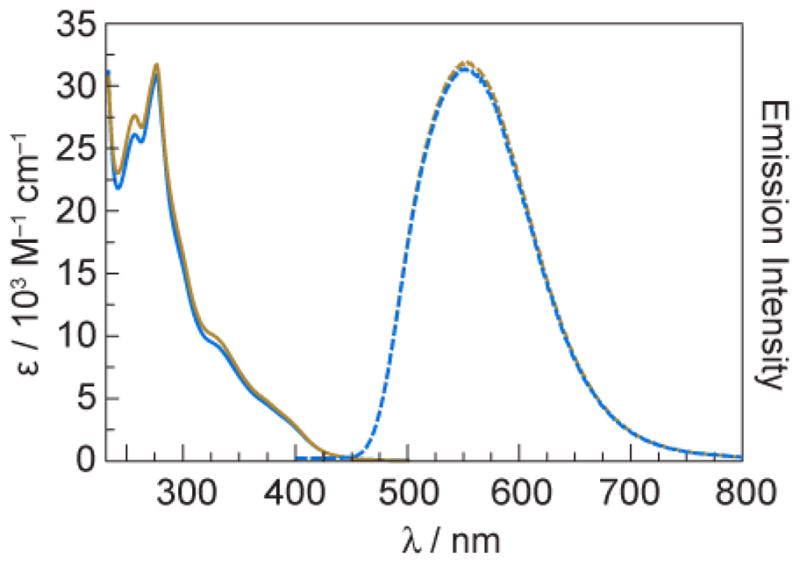
Electronic absorption (solid lines) and emission(λexc = 355 nm) (dashed lines) spectra of [Re]–Y–OH (
 ) and [Re]–F (
) and [Re]–F (
 ) at 50 μM concentration in dichloromethane.
) at 50 μM concentration in dichloromethane.
Fig. 3.
Excited-state quenching titrations monitored by steady-state emission of [Re]–Y–OH. Addition of pyridine (top) or imidazole (bottom) to solutions of [Re]–Y–OH (50 μM in dichloromethane) results in significant quenching of steady-state emission (λexc = 400 nm). Spectra are shown in the absence of base (
 , blue) and the presence of increasing concentrations of base (
, blue) and the presence of increasing concentrations of base (
 , grey). Association constants are calculated using integrated emission intensity as previously reported (insets).24
, grey). Association constants are calculated using integrated emission intensity as previously reported (insets).24
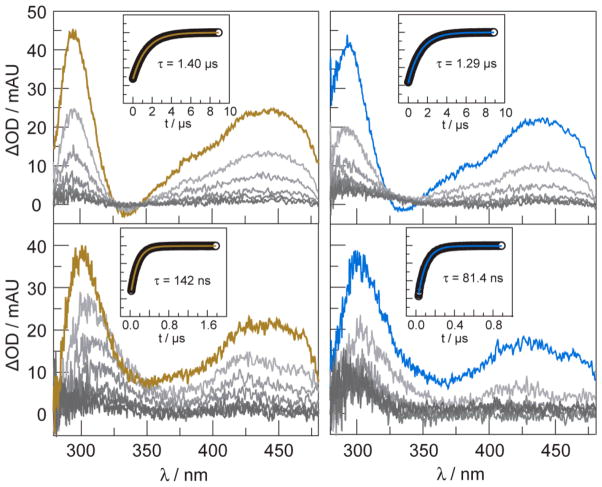
Transient absorption spectra indicate that the 3[ReI]* excited state reacts with base by electron transfer. The transient absorption spectra and single-wavelength kinetic data for solutions of [Re]–Y–OH and [Re]–F in dichloromethane are shown in Fig. 4 (top) in the absence of base. Transient spectra exhibit absorption features as expected for compounds of this type.28 Significant growth features are observed at 300 and 450 nm. The transient signals decay monoexponentially; 3[ReI]* excited state in [Re]–Y–OH is slightly shorter than [Re]–F. This is consistent with oxidation of tyrosine by the [Re]–Y–OH. The 3[ReI]* excited state is highly oxidizing and is of sufficient potential to oxidize base (Eo(ReI*/0) = 1.7 V vs. NHE)29. The given value was measured in acetonitrile and provides only an estimate for the present report where experiments are conducted in dichloromethane. Furthermore, previously reported electrochemical experiments show the onset of pyridine and imidazole oxidation at potentials of ~1.6 V30 and ~1.4 V31 vs. NHE, respectively. These values are consistent with oxidation by the 3[ReI]* excited state as well as the relative rates of oxidation for imidazole and pyridine.
Fig. 4.
Transient absorption spectra (λexc = 355 nm) of [Re]–F (
 , gold) and [Re]–Y–OH (
, gold) and [Re]–Y–OH (
 , blue) (50 μM in dichloromethane) in the absence of base (top), and in the presence of 0.20 M imidazole (bottom). Spectra are collected immediately after the laser pulse and every 1000 ns (in the absence of base) or 150 ns (in the presence of base) thereafter. Single-wavelength emission decay kinetics monitored at 550 nm are shown in the insets. Decays are monoexponential. The lifetimes derived from the monexponetial fit, shown by the solid line, are given.
, blue) (50 μM in dichloromethane) in the absence of base (top), and in the presence of 0.20 M imidazole (bottom). Spectra are collected immediately after the laser pulse and every 1000 ns (in the absence of base) or 150 ns (in the presence of base) thereafter. Single-wavelength emission decay kinetics monitored at 550 nm are shown in the insets. Decays are monoexponential. The lifetimes derived from the monexponetial fit, shown by the solid line, are given.
When pyridine or imidazole is added to solutions of [Re]–F and [Re]–Y–OH, the TA signal of the 3[ReI]* excited state is considerably shortened, more so for imidazole than pyridine (Fig. 4, bottom). Concentrations of base were chosen to ensure that at least 95% of [Re]–Y–OH was bound. We note that a transient signal for photo-oxidized tyrosine is not observed, indicating that the intermediate does not accumulate owing to back electron transfer rate that is faster than the forward PCET rate constant for quenching.
In the absence of direct observation of a transient signal for base owing to fast back reaction, the excited state kinetics were further examined by transient emission spectroscopy. The quenching paths of 3[ReI]* for [Re]–F and [Re]–Y–OH are shown in Figure 5. In this model, we assume that the intrinsic decay processes of and bimolecular processes of [Re]–Y–OH and [Re]–Y–OH---Nbase cannot be distinguished in excited state decay profiles.
Fig. 5.
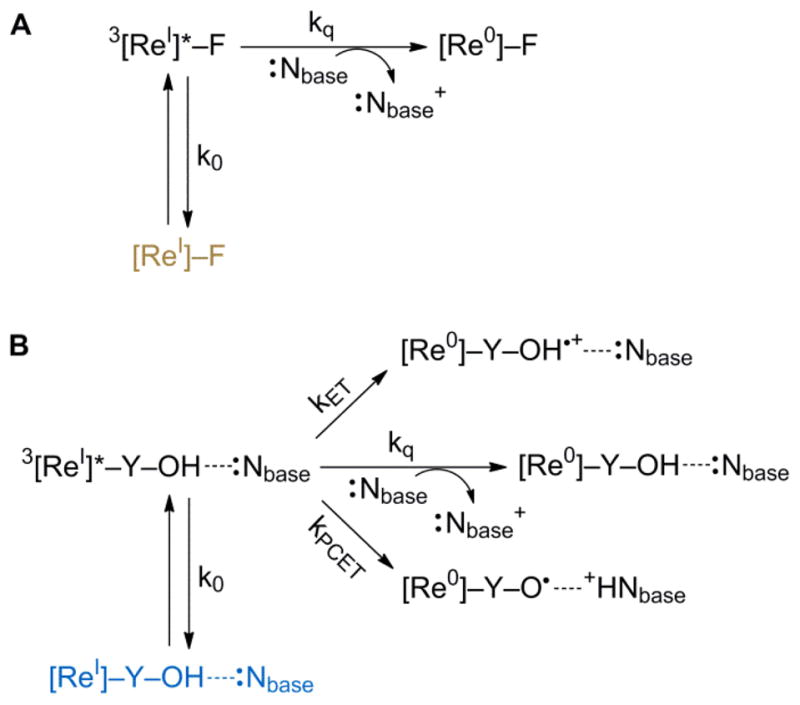
Excited-state quenching pathways for (A) [Re]–F and (B) [Re]–Y–OH---Nbase. The rate contants k0 and kq are assumed to be the same for both paths (A) and (B), and are defined by the natural lifetime of [Re]–F and the quenching of [Re]–F by base, respectively.
The excited-state reactivity of [Re]–F with base is straightforward; the emission will decay with intrinsic radiative and nonradiative process defined by k0 (= 1/τ0) or react with base by electron transfer, defined by the bimolecular quenching rate constant kq. In a Stern-Volmer process, the overall observed emission rate constant for reaction (= 1/τF) should follow the kinetics,
| (1) |
As predicted by eq. 1, Stern-Volmer plots are linear with increasing concentration of base. From the natural lifetime of in Fig. 4, bimolecular quenching rate constants kq = 3.2(6) × 105 M−1 s−1 and 3.1(6) × 107 M−1 s−1 for pyridine and imidazole, respectively. These data are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Values for rate constants shown in Fig. 5 for excited state dynamics of [Re]–F and [Re]–Y–OH associated to base.
| Base Independent Parameters
| ||
|---|---|---|
| [Re]–F | [Re]–Y–OH | |
| k0/s−1 a | 7.1 × 105 | 7.1 × 105 |
| kET/s−1 b | – | 6.1 × 104 |
|
| ||
| Base Association and Related Kinetic Parameters | ||
|
| ||
| pyridine | imidazole | |
|
| ||
| kq/M−1 s−1 c | 3.2(6) × 105 | 3.1(6) × 107 |
| Kassoc/M−1 | 16(2) | 157(13) |
| kPCET/s−1 | 4.1(6) × 105 | 4.8(8) × 106 |
Determined from natural lifetime of [Re]–F in dichloromethane at room temperature.
Calculated from eq (2).
Determined from Stern-Volmer analysis of [Re]–F with base in dichloromethane at room temperature.
The excited state decay processes of 3[ReI]* in the [Re]–Y–OH---Nbase assembly are richer. In addition to the natural decay of the 3[ReI*] excited state and its bimolecular quenching by base, two unique unimocular processes arise from electron transfer from Y–OH to 3[ReI]* and PCET. The excited state dynamics of the rhenium center should not be affected by the remote amino acid inasmuch as the it is not conjugated to the ligands of the the rhenium center. Hence k0 and kq, to a first approximation, should be the same for both systems. One possible exception to this approximation may be the difference in reduction potential of the bound base relative to base in solution; however, the large excess of free base is expected to dominate the kinetics of base oxidation by 3[ReI]*. Moreover, lacking the tyrosine phenol, Re–F cannot be oxidized by 3[ReI]*; oxidation of toluene (a suitable approximation to the phenylalanine sidechain) occurs at a potential greater than that of 3[ReI]* (1.8 V32 vs. NHE),. Accordingly, the Re–F center provides a reference for the ET process between the unassociated tyrosine and the excited rhenium center.
The kET rate constant is given by,
| (2) |
From the data in Fig. 4 and rate constants summarized in Table 1, a kET = 6.1 × 104 s−1 is determined. Whereas the kinetics associated with ET are straighforward, the PCET process is more complicated. The emission decay dynamics are modulated by the equilibrium between [Re]–Y–OH and Nbase. For this reason, a linear Stern-Volmer relation is not expected. Indeed, the base concentration dependence of the emission lifetime exhibits significant curvature as shown in Figure S1. The rate of excited-state decay for [Re]–Y–OH varies as a function of base concentration according to the following equation,
| (3) |
Detailed derivations of these rate laws (eqs. 1 and 2) are available in the ESI. The last term of the above equation accounts for the equilibrium between [Re]–Y–OH and base, and the PCET process enabled by that equilibrium. Although variations in the observed rate constants (k0, kET, kq) may occur as a result of hydrogen bonding to the tyrosine phenol, in the context of the final analysis, where the PCET rates exceed kET by a factor of 10 or 100, variation in kET is unlikely to cause significant interference with the calculation of kPCET. The only unkown variable in the above equation is kPCET. Fitting the observed rate constant for excited-state deactivation, kobs (as calculated from the emission lifetime), to the concentration of base furnishes kPCET = 4.1(6) × 105 s−1 and kPCET = 4.8(8) × 106 s−1 and for pyridine and imidazole respectively.
These PCET rates are comparable to those previously observed in unimolecular systems incorporating hydrogen bonding to phenols within bimolecular17 and unimolecular (tethered)18 frameworks. In these cases, the photoacceptor is ruthenium(II) tris(bipyridine), which is less oxidizing Re(I) polypyridyl excited states. Hydrogen bonding facilitates PCET by substantially decreasing the inner-sphere contribution to reorganization energy from the phenol and by introducing ‘promoting’ vibrational modes; the thermodynamic strength of the hydrogen bond has been observed to have a lesser impact on PCET rate enhancement.19 This is not the case here. The rateenhancement for phenol oxidation in [Re]–Y–OH---Nbase varies with the strength of the hydrogen bond as has also recently been observed in protein maquettes.33 The correlation may be more apparent for [Re]–Y–OH---Nbase owing to the imilarity of the hydrogen bond type formed by imidazole and pyridine. Previous studies on phenol photooxidations have emphasized hydrogen bonding networks that are formed from carboxylates where differences in the hydrogen-bonded adduct (e.g., six- or seven-membered rings formed in the two cases) likely introduces importatnt vibrational effects and the greater sensitivity to the vibrational modes of the hydrogen bonding network. When this complexity is removed, it appears that the PCET rate for photooxidation follows a more straightforward thermodynamic trend with the strength of the hydrogen bonds within the PCET network.
With respect to the observed variation of kPCET with respect to the proton acceptor pKa, previous work in a bimolecular system has shown that the as the strength base (proton acceptor) increases, faster rates of PCET are observed for phenol oxidation.34,35 In recent related work, the importance of hydrogen bond distance (rather than strength) on the rate of PCET reactions has been investigated.36,37 Although the present scaffold does not offer a way to directly control the proton transfer distance, the facile variation of hydrogen-bond strength that can be achieved with this scaffold may yield valuable insights of interest to this discussion.
Conclusions
The supramolecular assembly formed between a rhenium–tyrosine complex associated to base estableshes a network for the photogeneration of tyrosyl radical by a PCET mechanism. An equilibrium interaction between the tyrosine phenol proton and bases in solution provides a well-defined proton acceptor, simplifying analysis of PCET kinetics. The observed rates of tyrosine oxidation associated to base are consistent with those reported in the literature for intramolecular model systems. The approach affords for the self-assembly of a modular scaffold for the study of bidirectional PCET by simply varying the nature of the base. To this end, the approach reduces the complexity associated ith the synthesis of tethered networks.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Dr. Emily J. McLaurin for assistance with preliminary laser flash photolysis experiments. This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health (GM47274).
Footnotes
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) available: Synthetic procedures, detailed experimental methods, kinetic analysis, fitting details, base concentration-dependent emission quenching data. See DOI: 10.1039/b000000x/
Notes and References
- 1.Hammarström L, Styring S. Energy Environ Sci. 2011;4:2379. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jenson DL, Barry BA. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:10567. doi: 10.1021/ja902896e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ishikita H, Soudackov AV, Hammes-Schiffer S. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:11146. doi: 10.1021/ja072708k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Irebo T, Reece SY, Sjödin M, Nocera DG, Hammarström J. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:15462. doi: 10.1021/ja073012u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Keough JM, Jenson DL, Zuniga AN, Barry BA. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:11084. doi: 10.1021/ja2041139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Barry BA. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2011;104:60. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2011.01.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kaila RI, Verkhovsky MI, Wikström M. Chem Rev. 2010;110:7062. doi: 10.1021/cr1002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stubbe J, Nocera DG, Yee CS, Chang MCY. Chem Rev. 2003;103:2167. doi: 10.1021/cr020421u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Reece SY, Hodgkiss JM, Stubbe J, Nocera DG. Philos Trans R Soc London, B. 2006;361:1351. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2006.1874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chang MCY, Yee CS, Stubbe J, Nocera DG. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:6882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401718101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reece SY, Seyedsayamdost MR, Stubbe J, Nocera DG. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:13828. doi: 10.1021/ja074452o. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Holder PG, Pizano AA, Anderson BL, Stubbe J, Nocera DG. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:1172. doi: 10.1021/ja209016j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pizano AA, Lutterman DA, Holder PG, Teets TS, Stubbe J, Nocera DG. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:39. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115778108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Reece SY, Nocera DG. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:673. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.080207.092132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cukier RI, Nocera DG. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1998;49:337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physchem.49.1.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hammes-Schiffer S. Acc Chem Res. 2009;42:1881. doi: 10.1021/ar9001284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sjödin M, Irebo T, Utas JE, Lind J, Merényi G, Åkermark B, Hammarström L. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:13076. doi: 10.1021/ja063264f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Irebo T, Johansson O, Hammarström L. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:9194. doi: 10.1021/ja802076v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Johannissen LO, Irebo T, Sjödin M, Johansson O, Hammarström L. J Phys Chem B. 2009;113:16214. doi: 10.1021/jp9048633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rhile IJ, Mayer JM. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:12718. doi: 10.1021/ja031583q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rhile IJ, Markle TF, Nagao H, DiPasquale AG, Lam OP, Lockwood MA, Rotter K, Mayer JM. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:6075. doi: 10.1021/ja054167+. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Markle TF, Mayer JM. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47:738. doi: 10.1002/anie.200702486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bonin J, Constentin C, Louault C, Robert M, Routier M, Savéant JM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914693107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Concepcion JJ, Brennaman MK, Deyton JR, Lebedeva NV, Forbes MDE, Papanikolas JM, Meyer TJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:6968. doi: 10.1021/ja069049g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Loh ZH, Miller SE, Chang CJ, Carpenter SD, Nocera DG. J Phys Chem A. 2002;106:11700. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Reece SY, Seyedsayamdost MR, Stubbe J, Nocera DG. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:13828. doi: 10.1021/ja074452o. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Blanco-Rodríguez AM, Towrie M, Sýkora J, Záliš S, Vlček A., Jr Inorg Chem. 2011;50:6122. doi: 10.1021/ic200252z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kalyanasurndaram K. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans. 1986;82:2401. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dattelbaum DM, Omberg KM, Schoonover JR, Martin RL, Meyer TJ. Inorg Chem. 2002;41:6071. doi: 10.1021/ic020400i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Aurbach D, Gofer Y. In: Nonaqueous Electrochemistry. Aurbach D, editor. CRC Press; 1999. pp. 137–212. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang HL, O’Malley RM, Fernandez JE. Macromolecules. 1994;27:893. [Google Scholar]
- 32.D’Elia LF, Ortiz RL. J Electrochem Soc. 2006;153:187. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Martinez-Rivera MC, Berry BW, Valentine KG, Westerlund K, Hay S, Tommos C. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:17786. doi: 10.1021/ja206876h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fecenko CJ, Meyer TJ, Thorp H. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:11020. doi: 10.1021/ja061931z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fecenko CJ, Thorp H, Meyer TJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:15098. doi: 10.1021/ja072558d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Markle TF, Rhile IJ, Mayer JM. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:17341. doi: 10.1021/ja2056853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhang MT, Irebo T, Johansson O, Hammarström L. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:13224. doi: 10.1021/ja203483j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.