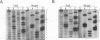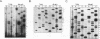Abstract
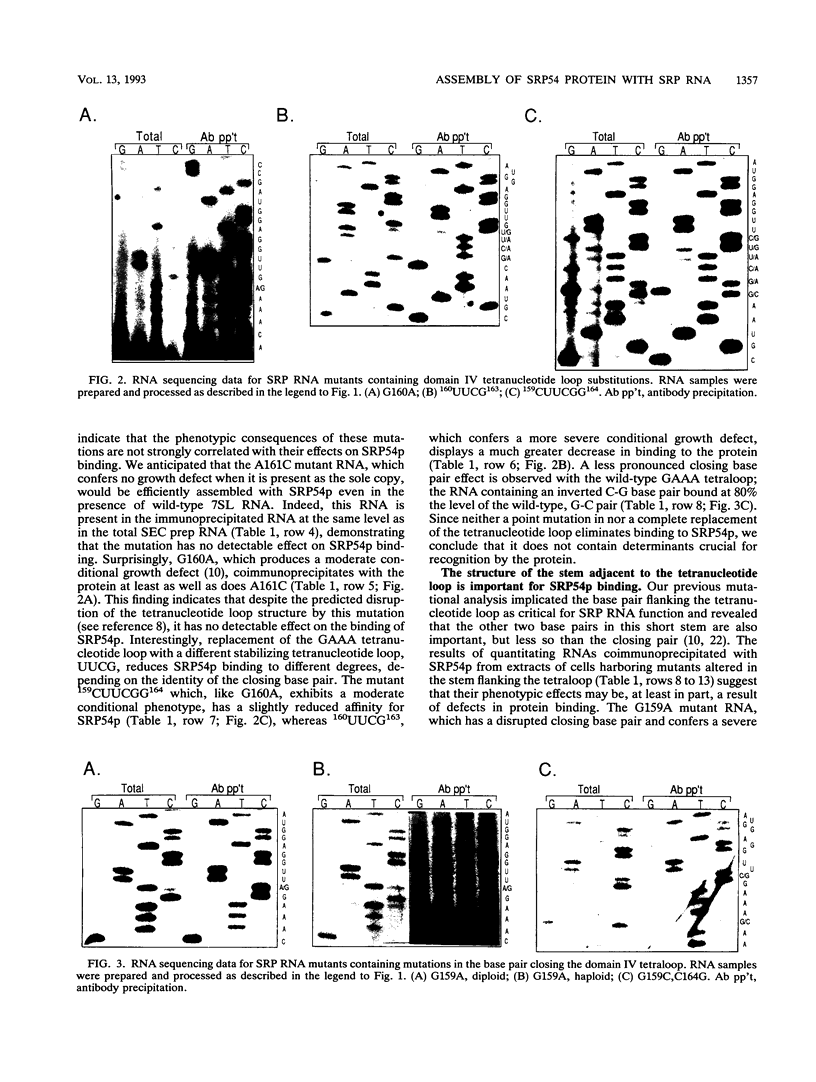
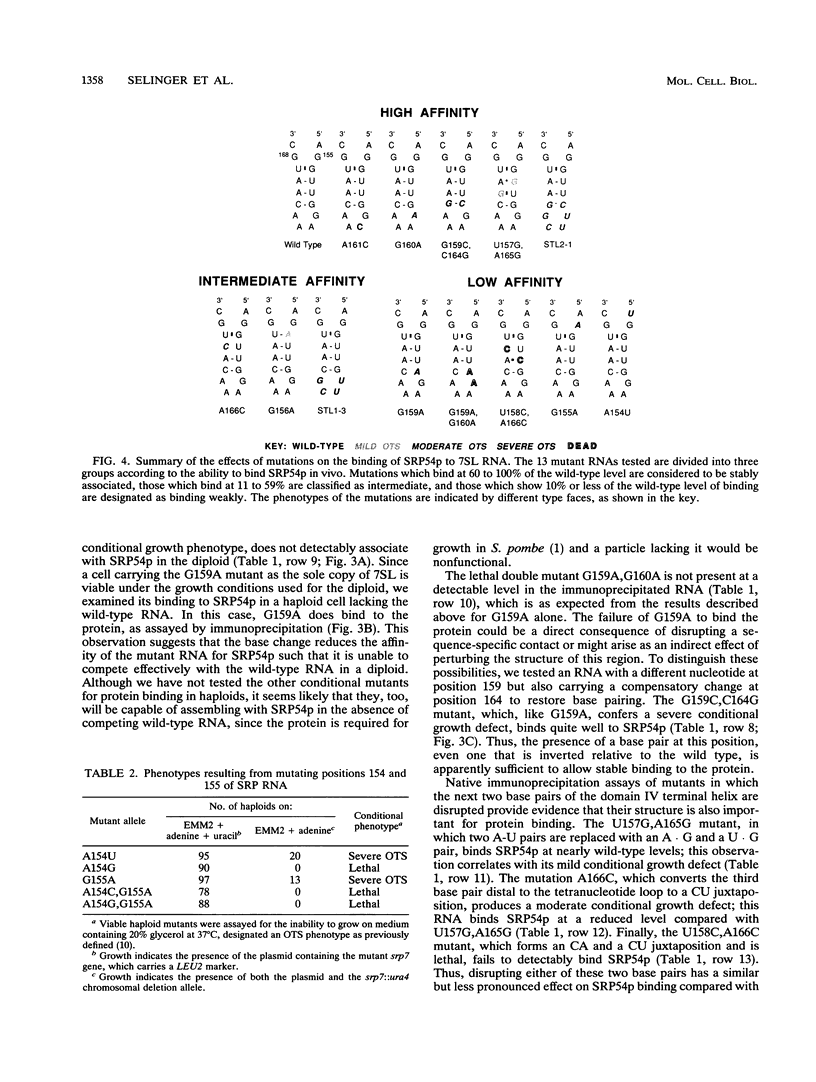
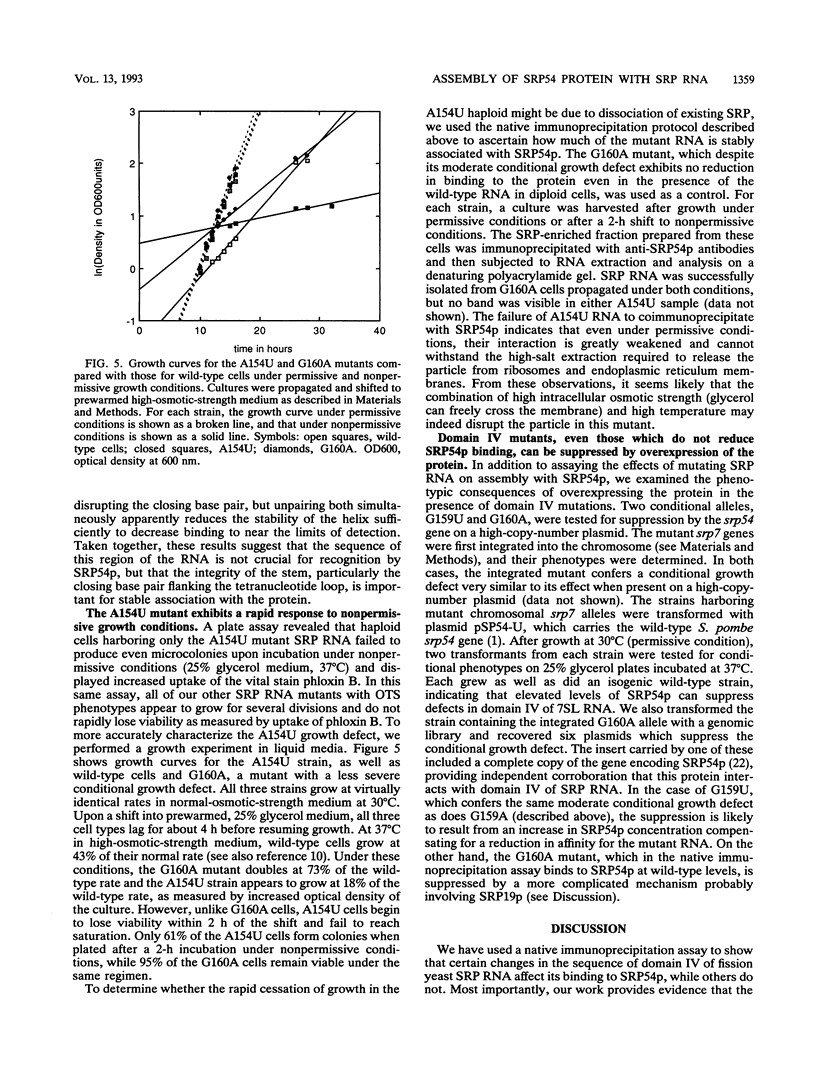
Signal recognition particle (SRP) is a ribonucleoprotein composed of six polypeptides and a single RNA molecule. SRP RNA can be divided into four structural domains, the last of which is the most highly conserved and, in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, is the primary location to which deleterious mutations map. The ability of mammalian SRP54 protein (SRP54p) to bind Escherichia coli 4.5S RNA, a homolog of SRP RNA which contains only domain IV, suggested that SRP54p might interact directly with this region. To determine whether domain IV is critical for SRP54p binding in fission yeast cells, we used a native immunoprecipitation-RNA sequencing assay to test 13 mutant SRP RNAs for the ability to associate with the protein in vivo. The G156A mutation, which alters the 5' residue of the noncanonical first base pair of the domain IV terminal helix and confers a mild conditional growth defect, reduces assembly of the RNA with SRP54p. Mutating either of the two evolutionarily invariant residues in the bulged region 5' to G156 is more deleterious to growth and virtually abolishes SRP54p binding. We conclude that the conservation of nucleotides 154 to 156 is likely to be a consequence of their role as a sequence-specific recognition element for the SRP54 protein. We also tested a series of mutants with nucleotide substitutions in the conserved tetranucleotide loop and adjoining stem of domain IV. Although tetraloop mutations are deleterious to growth, they have little effect on SRP54p binding. Mutations which disrupt the base pair flanking the tetraloop result in conditional growth defects and significantly reduce association with SRP54p. Disruption of the other two base pairs in the short stem adjacent to the tetranucleotide loop has similar but less dramatic effects on SRP54p binding. These data provide the first evidence that both sequence-specific contacts and the structural integrity of domain IV of SRP RNA are important for assembly with SRP54p.
Full text
PDF


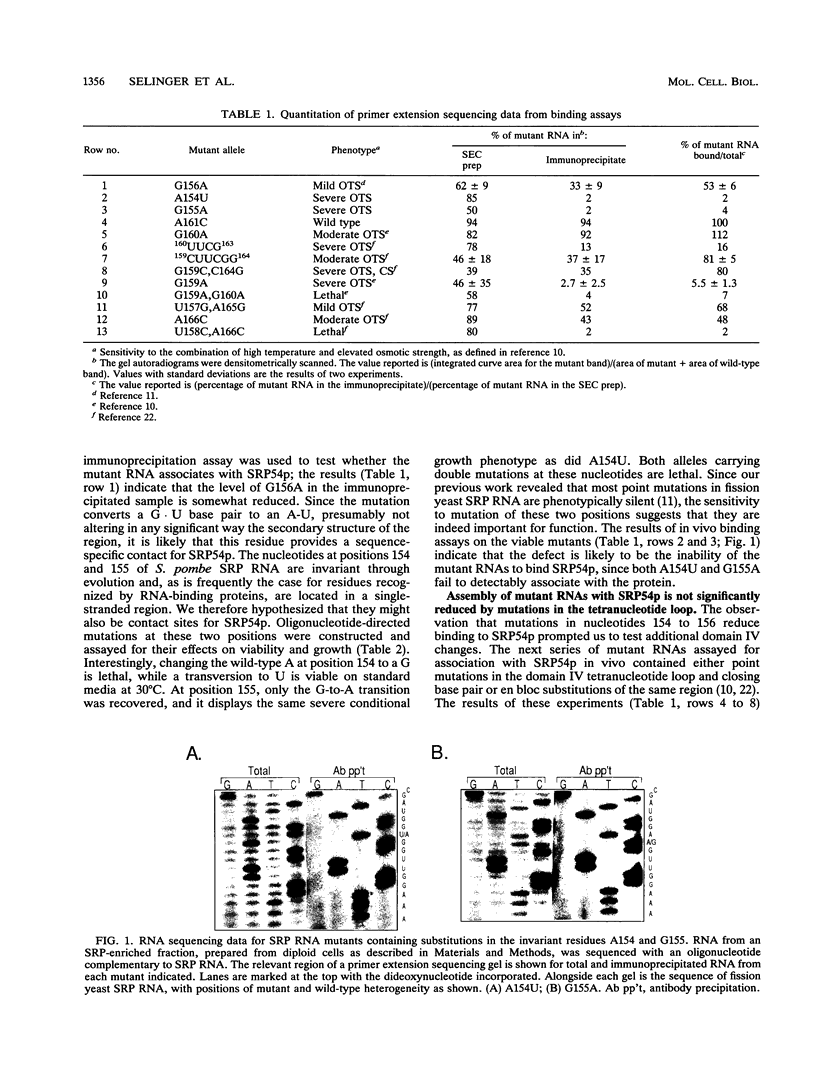



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antao V. P., Lai S. Y., Tinoco I., Jr A thermodynamic study of unusually stable RNA and DNA hairpins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5901–5905. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennwald P., Liao X., Holm K., Porter G., Wise J. A. Identification of an essential Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA homologous to the 7SL component of signal recognition particle. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1580–1590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnouf D., Koehl P., Fuchs R. P. Single adduct mutagenesis: strong effect of the position of a single acetylaminofluorene adduct within a mutation hot spot. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4147–4151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin, 5'GGAC(UUCG)GUCC. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):680–682. doi: 10.1038/346680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Poritz M. A., Walter P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe contain a homologue to the 54-kD subunit of the signal recognition particle that in S. cerevisiae is essential for growth. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3223–3230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Stirling C. J., Walter P. SEC65 gene product is a subunit of the yeast signal recognition particle required for its integrity. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):532–533. doi: 10.1038/356532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heus H. A., Pardi A. Structural features that give rise to the unusual stability of RNA hairpins containing GNRA loops. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):191–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1712983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N., Zwieb C. SRP-RNA sequence alignment and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):209–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao X., Selinger D., Althoff S., Chiang A., Hamilton D., Ma M., Wise J. A. Random mutagenesis of Schizosaccharomyces pombe SRP RNA: lethal and conditional lesions cluster in presumptive protein binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1607–1615. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Lacroute F. Plasmids carrying the yeast OMP decarboxylase structural and regulatory genes: transcription regulation in a foreign environment. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):371–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90456-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Bernstein H. D., Strub K., Zopf D., Wilhelm H., Walter P. An E. coli ribonucleoprotein containing 4.5S RNA resembles mammalian signal recognition particle. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1111–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.1701272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Siegel V., Hansen W., Walter P. Small ribonucleoproteins in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Yarrowia lipolytica homologous to signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4315–4319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Strub K., Walter P. Human SRP RNA and E. coli 4.5S RNA contain a highly homologous structural domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):4–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes V., Dehoux P., Tollervey D. 7SL RNA from Schizosaccharomyces pombe is encoded by a single copy essential gene. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):231–237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02804.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes V., Römisch K., Giner A., Dobberstein B., Tollervey D. E. coli 4.5S RNA is part of a ribonucleoprotein particle that has properties related to signal recognition particle. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90454-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Wolin S., Guthrie C. A subset of yeast snRNA's contains functional binding sites for the highly conserved Sm antigen. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):328–331. doi: 10.1126/science.2948278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Lingelbach K., Gausepohl H., Dobberstein B. The 54-kD protein of signal recognition particle contains a methionine-rich RNA binding domain. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):1793–1802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Binding sites of the 19-kDa and 68/72-kDa signal recognition particle (SRP) proteins on SRP RNA as determined in protein-RNA "footprinting". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1801–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling C. J., Hewitt E. W. The S. cerevisiae SEC65 gene encodes a component of yeast signal recognition particle with homology to human SRP19. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):534–537. doi: 10.1038/356534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gauss P., Thermes C., Groebe D. R., Gayle M., Guild N., Stormo G., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Uhlenbeck O. C., Tinoco I., Jr CUUCGG hairpins: extraordinarily stable RNA secondary structures associated with various biochemical processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1364–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Disassembly and reconstitution of signal recognition particle. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):525–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zopf D., Bernstein H. D., Johnson A. E., Walter P. The methionine-rich domain of the 54 kd protein subunit of the signal recognition particle contains an RNA binding site and can be crosslinked to a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4511–4517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C. Interaction of protein SRP19 with signal recognition particle RNA lacking individual RNA-helices. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2955–2960. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]