Abstract
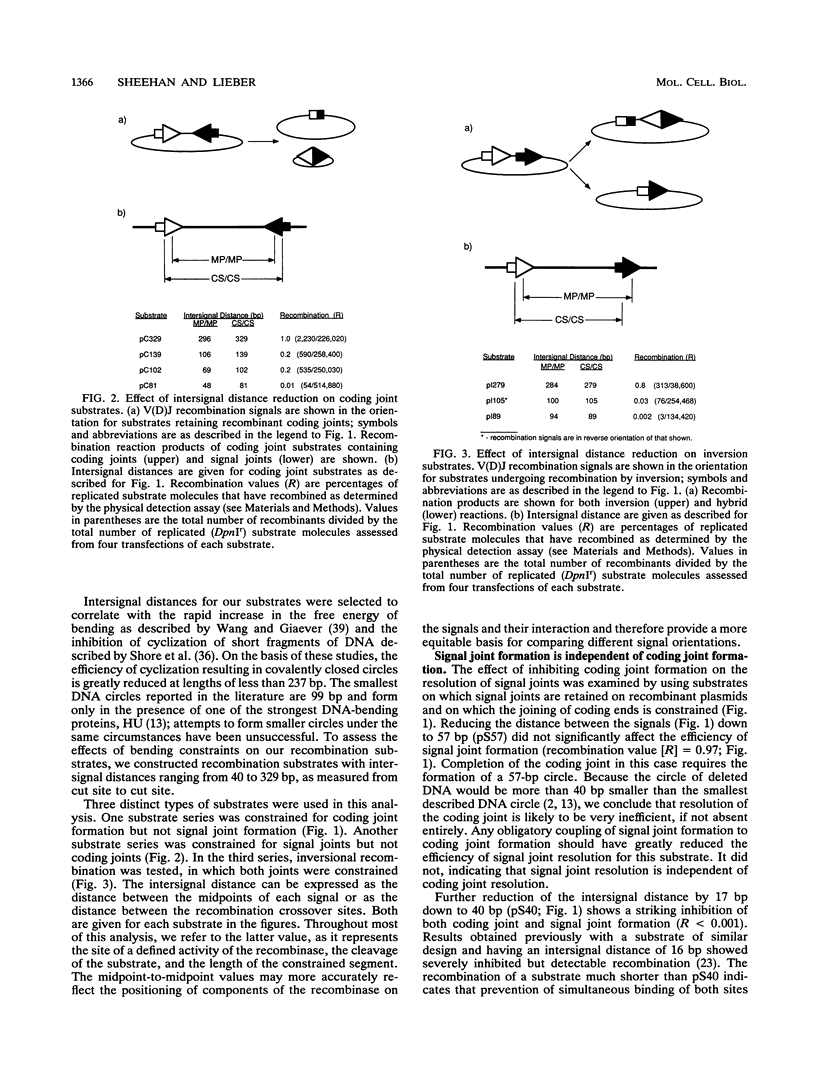
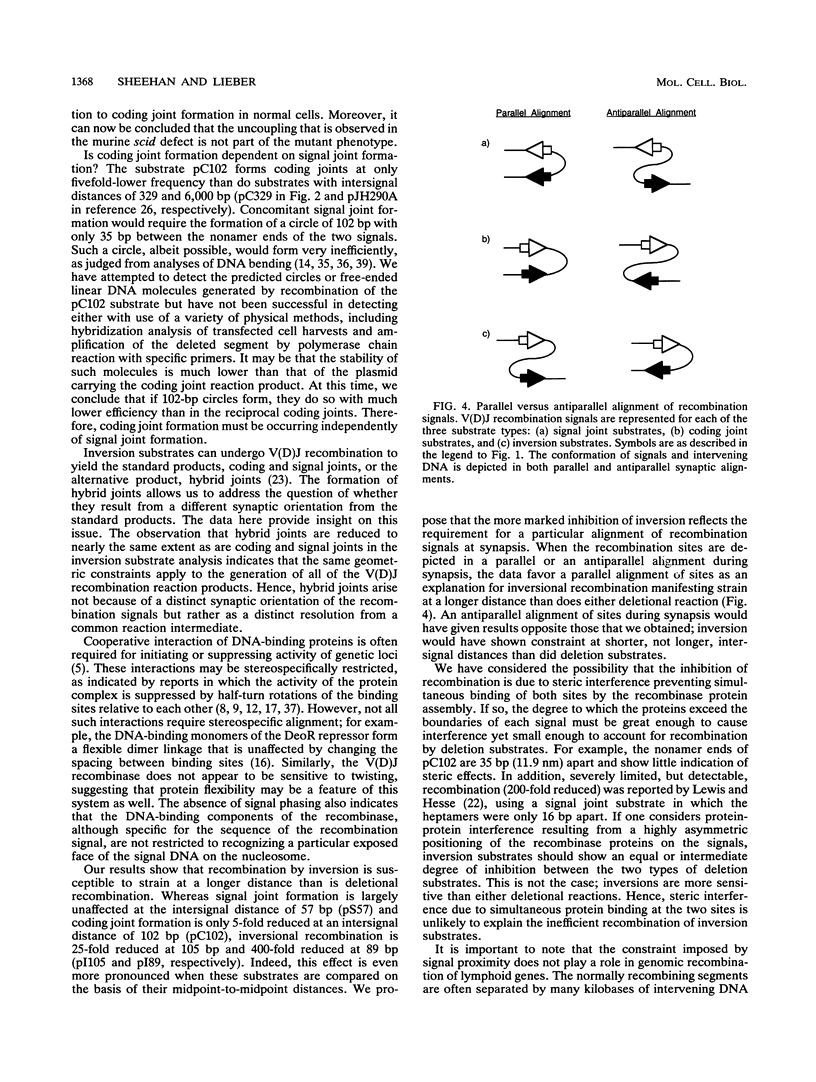
V(D)J recombination in lymphoid cells is a site-specific process in which the activity of the recombinase enzyme is targeted to signal sequences flanking the coding elements of antigen receptor genes. The order of the steps in this reaction and their mechanistic interdependence are important to the understanding of how the reaction fails and thereby contributes to genomic instability in lymphoid cells. The products of the normal reaction are recombinant joints linking the coding sequences of the receptor genes and, reciprocally, the signal ends. Extrachromosomal substrate molecules were modified to inhibit the physical synapsis of the recombination signals. In this way, it has been possible to assess how inhibiting the formation of one joint affects the resolution efficiency of the other. Our results indicate that signal joint and coding joint formation are resolved independently in that they can be uncoupled from each other. We also find that signal synapsis is critical for the generation of recombinant products, which greatly restricts the degree of potential single-site cutting that might otherwise occur in the genome. Finally, inversion substrates manifest synaptic inhibition at much longer distances than do deletion substrates, suggesting that a parallel rather than an antiparallel alignment of the signals is required during synapsis. These observations are important for understanding the interaction of V(D)J signals with the recombinase. Moreover, the role of signal synapsis in regulating recombinase activity has significant implications for genome stability regarding the frequency of recombinase-mediated chromosomal translocations.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aster J. C., Kobayashi Y., Shiota M., Mori S., Sklar J. Detection of the t(14;18) at similar frequencies in hyperplastic lymphoid tissues from American and Japanese patients. Am J Pathol. 1992 Aug;141(2):291–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates A. D., Maxwell A. DNA gyrase can supercoil DNA circles as small as 174 base pairs. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1861–1866. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Malynn B. A., Pollock R. R., Ferrier P., Covey L. R., Fulop G. M., Phillips R. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Isolation of scid pre-B cells that rearrange kappa light chain genes: formation of normal signal and abnormal coding joins. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):735–742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03433.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. Role of DNA topology in Mu transposition: mechanism of sensing the relative orientation of two DNA segments. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90554-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M. J., Hall Z. W. How many agrins does it take to make a synapse? Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90525-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Bell A., Kolb A., Buc H., Busby S. Stringent spacing requirements for transcription activation by CRP. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson E. A., Liu V. F., Weaver D. T. Strand breaks without DNA rearrangement in V (D)J recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3155–3162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Lieber M. R., Gellert M., Mizuuchi K. Extrachromosomal DNA substrates in pre-B cells undergo inversion or deletion at immunoglobulin V-(D)-J joining signals. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90615-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges-Garcia Y., Hagerman P. J., Pettijohn D. E. DNA ring closure mediated by protein HU. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14621–14623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Wang J. C. Torsional rigidity of DNA and length dependence of the free energy of DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):75–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. L., Lieber M. R. CpG methylated minichromosomes become inaccessible for V(D)J recombination after undergoing replication. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):315–325. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05054.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. J., Bracco L. P., Eisenbeis S. J., Gayle R. B., Beaton G., Caruthers M. H. Role of the Cro repressor carboxy-terminal domain and flexible dimer linkage in operator and nonspecific DNA binding. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9241–9249. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Amouyal M., Nordheim A., Müller-Hill B. DNA supercoiling changes the spacing requirement of two lac operators for DNA loop formation with lac repressor. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):547–556. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafaille J. J., DeCloux A., Bonneville M., Takagaki Y., Tonegawa S. Junctional sequences of T cell receptor gamma delta genes: implications for gamma delta T cell lineages and for a novel intermediate of V-(D)-J joining. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):859–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90609-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Schatz D. G., Rosa M., Baltimore D. Increased frequency of N-region insertion in a murine pre-B-cell line infected with a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase retroviral expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3237–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Hesse J. E. Cutting and closing without recombination in V(D)J joining. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3631–3639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Hesse J. E., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. Novel strand exchanges in V(D)J recombination. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1099–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90254-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Gellert M. The mechanism of antigen receptor gene assembly. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):585–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Gifford A., Baltimore D. DNA elements are asymmetrically joined during the site-specific recombination of kappa immunoglobulin genes. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):677–685. doi: 10.1126/science.3158075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R., Hesse J. E., Lewis S., Bosma G. C., Rosenberg N., Mizuuchi K., Bosma M. J., Gellert M. The defect in murine severe combined immune deficiency: joining of signal sequences but not coding segments in V(D)J recombination. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R., Hesse J. E., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. Lymphoid V(D)J recombination: nucleotide insertion at signal joints as well as coding joints. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8588–8592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R. Site-specific recombination in the immune system. FASEB J. 1991 Nov;5(14):2934–2944. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.14.1752360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limpens J., de Jong D., van Krieken J. H., Price C. G., Young B. D., van Ommen G. J., Kluin P. M. Bcl-2/JH rearrangements in benign lymphoid tissues with follicular hyperplasia. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2271–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Tjoelker L. W., Carlson L. M., Petryniak B., Barth C. F., Humphries E. H., Thompson C. B. Chicken IgL gene rearrangement involves deletion of a circular episome and addition of single nonrandom nucleotides to both coding segments. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):785–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90683-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKearn J. P., Rosenberg N. Mapping cell surface antigens on mouse pre-B cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Mar;15(3):295–298. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Davis D. D., Sakano H. T cell receptor beta gene sequences in the circular DNA of thymocyte nuclei: direct evidence for intramolecular DNA deletion in V-D-J joining. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90450-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Nakajima P. B., Menetski J. P., Bosma M. J., Gellert M. V(D)J recombination in mouse thymocytes: double-strand breaks near T cell receptor delta rearrangement signals. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90117-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Schlissel M. S. V(D)J recombination: molecular biology and regulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:359–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Baldwin R. L. Energetics of DNA twisting. I. Relation between twist and cyclization probability. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):957–981. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Langowski J., Baldwin R. L. DNA flexibility studied by covalent closure of short fragments into circles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L., Bodner M., Trifonov E. N., Choder M. Curved DNA: design, synthesis, and circularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):862–866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Giaever G. N. Action at a distance along a DNA. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):300–304. doi: 10.1126/science.3281259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Aubenton Carafa Y., Brody E., Thermes C. Prediction of rho-independent Escherichia coli transcription terminators. A statistical analysis of their RNA stem-loop structures. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 20;216(4):835–858. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(99)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


