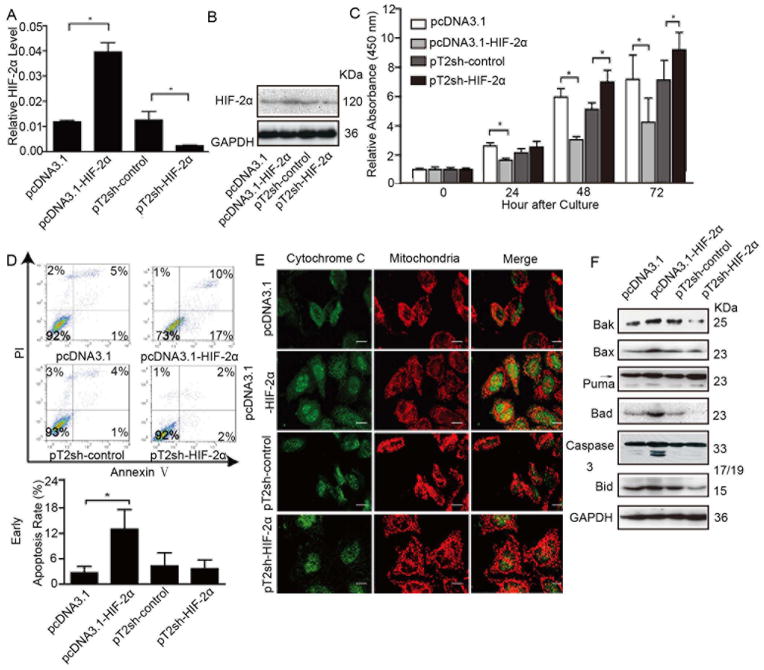
Figure 2.
HIF-2α induces HCC cell growth arrest in vitro mainly through effects on apoptosis. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-HIF-2α or pT2sh-HIF-2α recombinant plasmid or corresponding empty vector (pcDNA3.1, pT2), then monoclones were selected. (A) HIF-2α mRNA levels of each representative monoclone, in which error bars indicate standard deviation (n=3). *, p<0.01 by two-tailed test. (B) Protein levels of HIF-2α and (C) proliferative ability of representative monoclonal cells. The relative absorbance at each time point was normalized to that measured at the first time point (*, p<0.01). (D) Flow cytometry with annexin V/PI plots in different groups represented by an individual monoclone and column bar of mean apoptotic percentage; error bars indicate standard deviation (SD). *, p<0.05. (E) Cells were trypsinized and plated on coverslips. After 48 hours, cells were labeled with mito Tracker™ for 30 minutes at 37°C, subjected to indirect immunofluorescence staining for cytochrome C expression. Representative images with bars =5 μm. (F) Western blot analysis of the expression of Bak, Bax, Puma, Bad, activated caspase 3, Bid, and GAPDH in monoclonal cells.