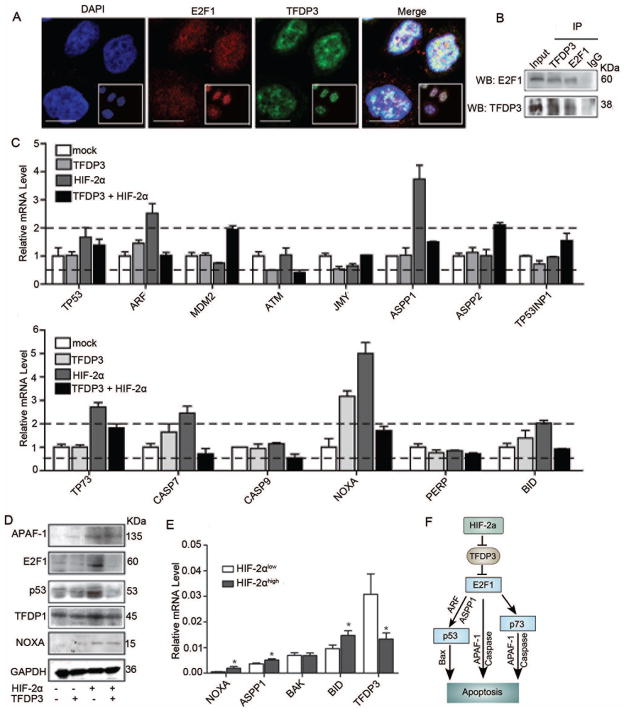
Figure 5.
HIF-2α-TFDP3 controls apoptosis through multiple E2F1 pathways. (A) MHCC97H cells were seeded on coverslips. Representative images of E2F1 and TFDP3 nuclear co-localization were obtained by confocal microscopy. Bar, 10μm. (B) MHCC97H cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-TFDP3 or anti-IgG antibody, followed by western blot assay with anti-E2F1 antibody (upper panels). Reciprocal IP was done with anti-E2F1 or anti-IgG antibody, followed by western blot assay with anti-TFDP3 antibody (lower panels). (C) The changes in mRNA expression level of genes involved in the p53-dependent and -independent pathways in cells that were transiently transfected with HIF-2α or TFDP3 expression plasmids. (D) Western blot analysis of proteins involved in the E2F1 pathway in cells with different HIF-2α and TFDP3 expression levels. (E) The expression levels of TFDP3 and select apoptotic genes in sixty human HCC specimens with different HIF-2α levels identified by immunohistochemical staining. (F) Proposed pathway of HIF-2α-induced apoptosis.