Abstract
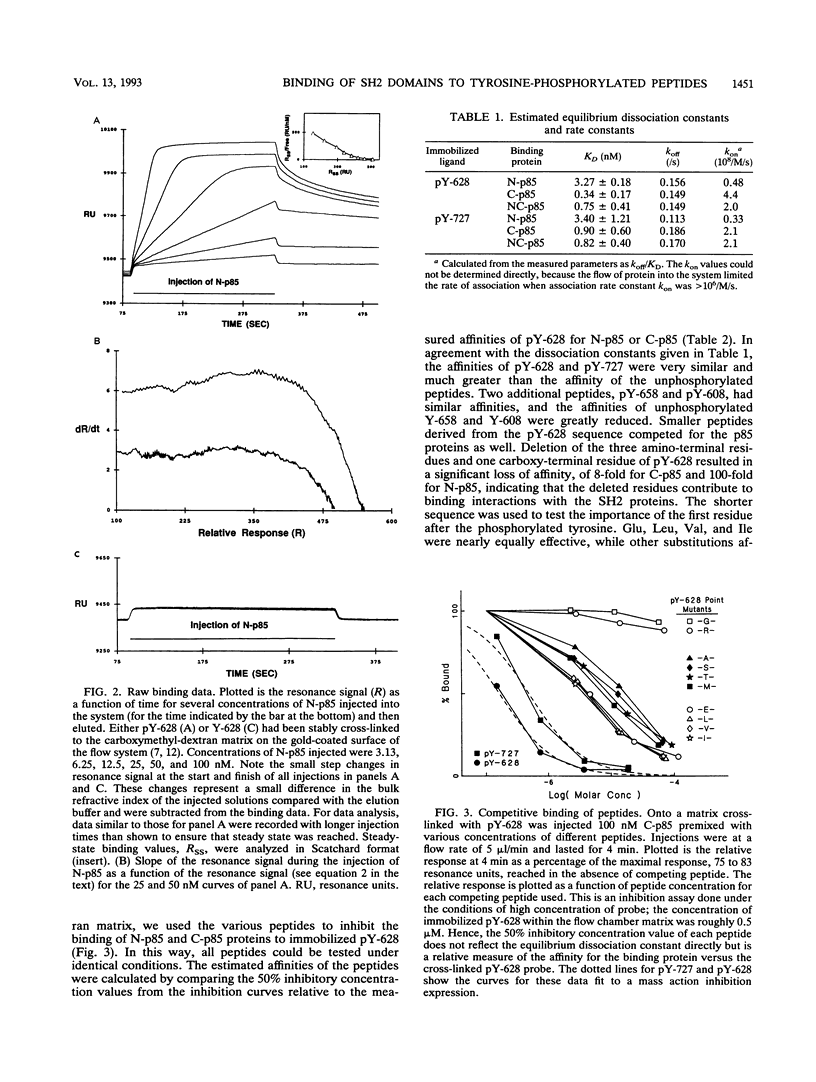
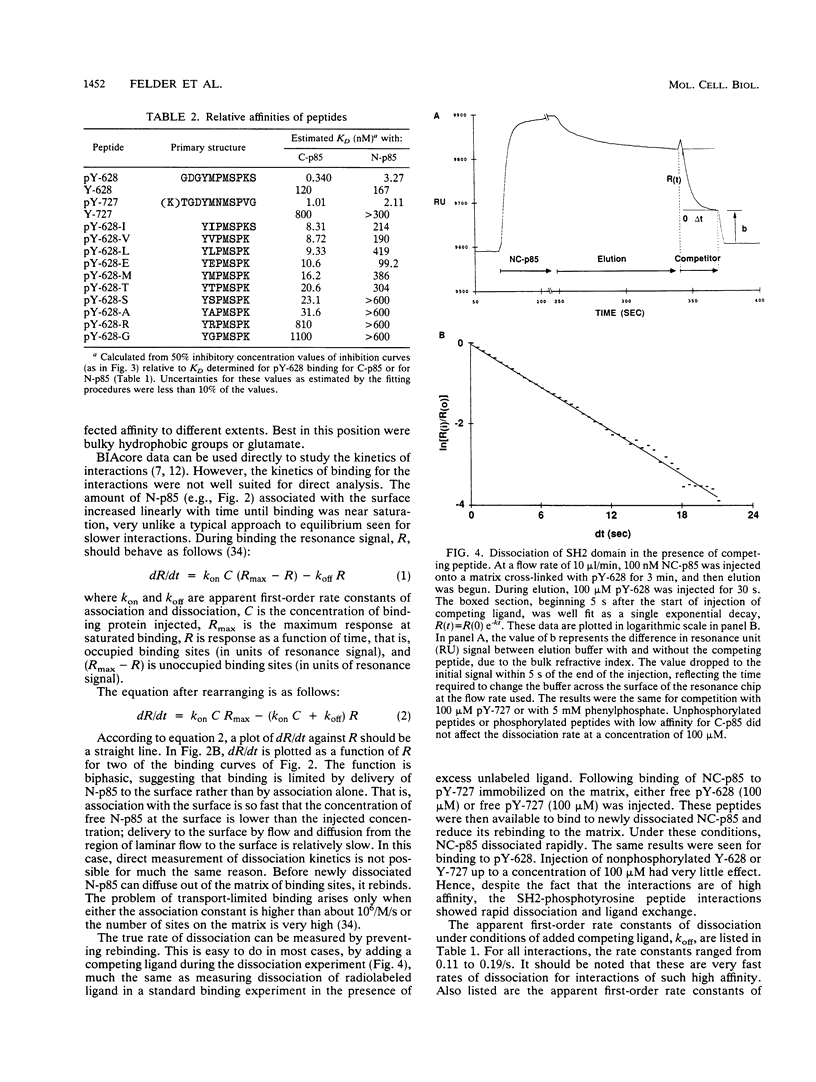
src homology 2 (SH2) domains of intracellular signaling molecules such as phospholipase C-gamma and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase-associated protein p85 represent recognition motifs for specific phosphotyrosine-containing regions on activated growth factor receptors. The binding of SH2 domains to activated growth factor receptors controls the interaction with signaling molecules and the regulation of their activities. In this report, we describe the kinetic parameters and binding affinities of SH2 domains of p85 toward short phosphotyrosine-containing peptides with the amino acid sequence motif YMXM, derived from a major insulin receptor substrate, IRS-1, by using real time biospecific interaction analysis (BIAcore). Associations were specific and of very high affinity, with dissociation constants of 0.3 to 3 nM, between phosphopeptides and the two separate SH2 domains contained within p85. Nonphosphorylated peptides showed no measurable binding, and the interactions were specific for the primary sequence very close to the phosphotyrosine residue. Moreover, the interactions between phosphopeptides and SH2 domains of other signaling molecules were of much lower affinity. Interestingly, the binding of the SH2 domains to the tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides was of high affinity as a result of a very high on rate, of 3 x 10(7) to 40 x 10(7)/M/s; at the same time, the rate of dissociation, of 0.11 to 0.19/s, was rapid, allowing for rapid exchange of associating proteins with the tyrosine phosphorylation sites.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Sadowski I., Martin G. S., Pawson T. A conserved domain regulates interactions of the v-fps protein-tyrosine kinase with the host cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9064–9068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Kaplan D. R., Kavanaugh W. M., Turck C. W., Williams L. T. A phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase binds to platelet-derived growth factor receptors through a specific receptor sequence containing phosphotyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay S. P., Posner R. G., Swann W. N., Sklar L. A. Real-time analysis of the assembly of ligand, receptor, and G protein by quantitative fluorescence flow cytometry. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):5066–5075. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H. SH2 domains: elements that control protein interactions during signal transduction. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):450–452. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90175-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Mutations in src homology regions 2 and 3 of activated chicken c-src that result in preferential transformation of mouse or chicken cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8592–8596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Interaction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-associated p85 with epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):981–990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson B., Löfås S., Lindquist G. Immobilization of proteins to a carboxymethyldextran-modified gold surface for biospecific interaction analysis in surface plasmon resonance sensors. Anal Biochem. 1991 Nov 1;198(2):268–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90424-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashishian A., Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Phosphorylation sites in the PDGF receptor with different specificities for binding GAP and PI3 kinase in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1373–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor beta subunit creates a tight binding site for phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3279–3286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Kim J. W., Zilberstein A., Margolis B., Kim J. G., Schlessinger J., Rhee S. G. PDGF stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis requires PLC-gamma 1 phosphorylation on tyrosine residues 783 and 1254. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):435–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Fantl W. J., Williams L. T. The C-terminal SH2 domain of p85 accounts for the high affinity and specificity of the binding of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1451–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Moran M., Sadowski I., Pawson T. The common src homology region 2 domain of cytoplasmic signaling proteins is a positive effector of v-fps tyrosine kinase function. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4131–4140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein E. J., Daly R. J., Batzer A. G., Li W., Margolis B., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Skolnik E. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Schlessinger J. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90167-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B. Proteins with SH2 domains: transducers in the tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Jan;3(1):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade C. J., Ellis C., Reedijk M., Anderson D., Mbamalu G., Reith A. D., Panayotou G., End P., Bernstein A., Kazlauskas A. SH2 domains of the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulate binding to growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):991–997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi M., Dionne C. A., Li W., Li N., Spivak T., Honegger A. M., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Point mutation in FGF receptor eliminates phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis without affecting mitogenesis. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):681–684. doi: 10.1038/358681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi M., Honegger A. M., Rotin D., Fischer R., Bellot F., Li W., Dionne C. A., Jaye M., Rubinstein M., Schlessinger J. A tyrosine-phosphorylated carboxy-terminal peptide of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (Flg) is a binding site for the SH2 domain of phospholipase C-gamma 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5068–5078. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. C., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Activation of the proto-oncogene p60c-src by point mutations in the SH2 domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2855–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K. G., Marie J., Wilson E., Ives H. E., Escobedo J., Del Rosario M., Mirda D., Williams L. T. Point mutation of an FGF receptor abolishes phosphatidylinositol turnover and Ca2+ flux but not mitogenesis. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):678–681. doi: 10.1038/358678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P. L., Lane W. S., Karasik A., Backer J., White M., Kahn C. R. Purification and partial sequence analysis of pp185, the major cellular substrate of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8302–8311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Honegger A. M., Margolis B. L., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Presence of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1 enhances substrate phosphorylation by increasing the affinity toward the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9678–9683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Daly R. J., Daum G., Li N., Fischer E. H., Burgess W. H., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of Tyr992 as the high-affinity binding site for SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):559–567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S. E., Chatterjee S., Chaudhuri M., White M. F. YMXM motifs of IRS-1 define substrate specificity of the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2027–2031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. M., Smith K. A. The interleukin 2 receptor. Functional consequences of its bimolecular structure. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1055–1069. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



