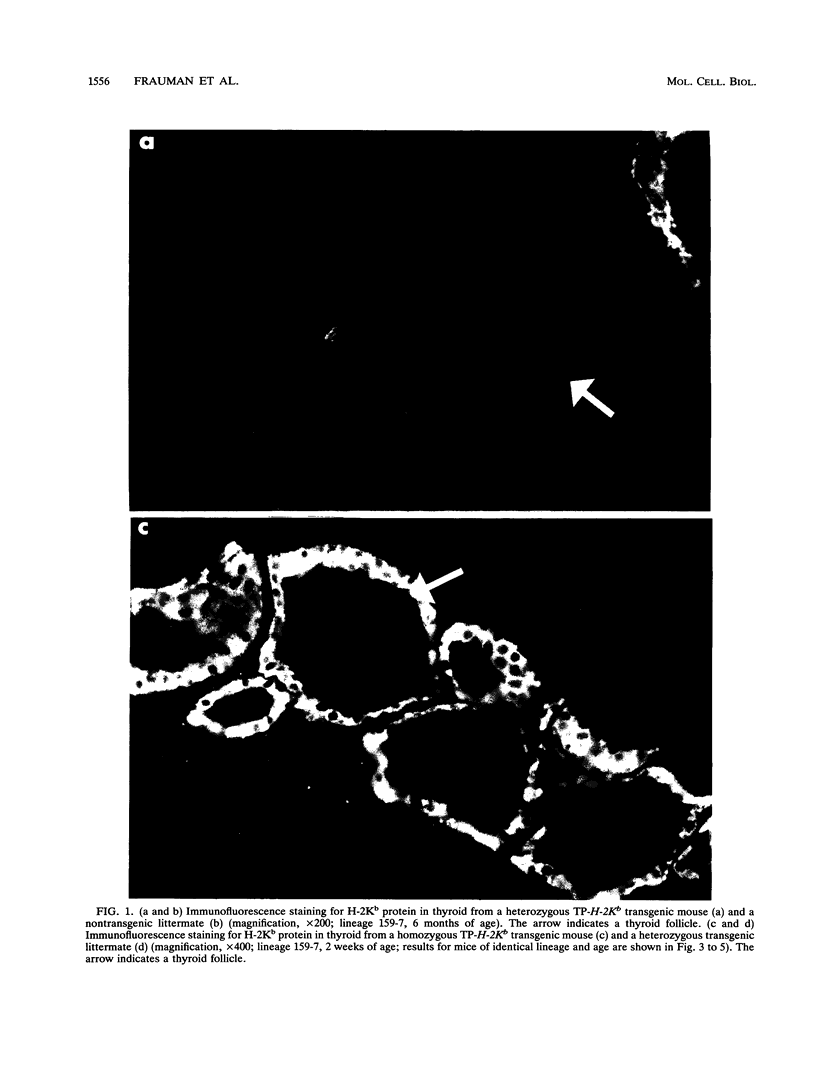
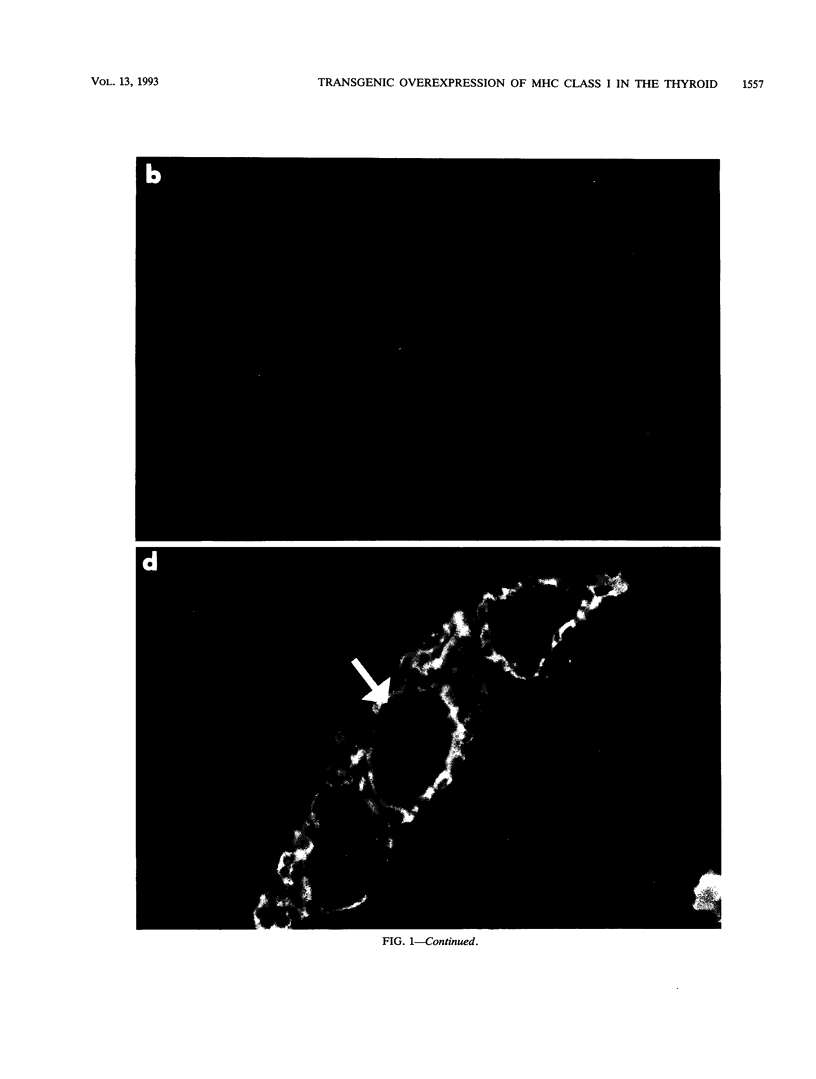
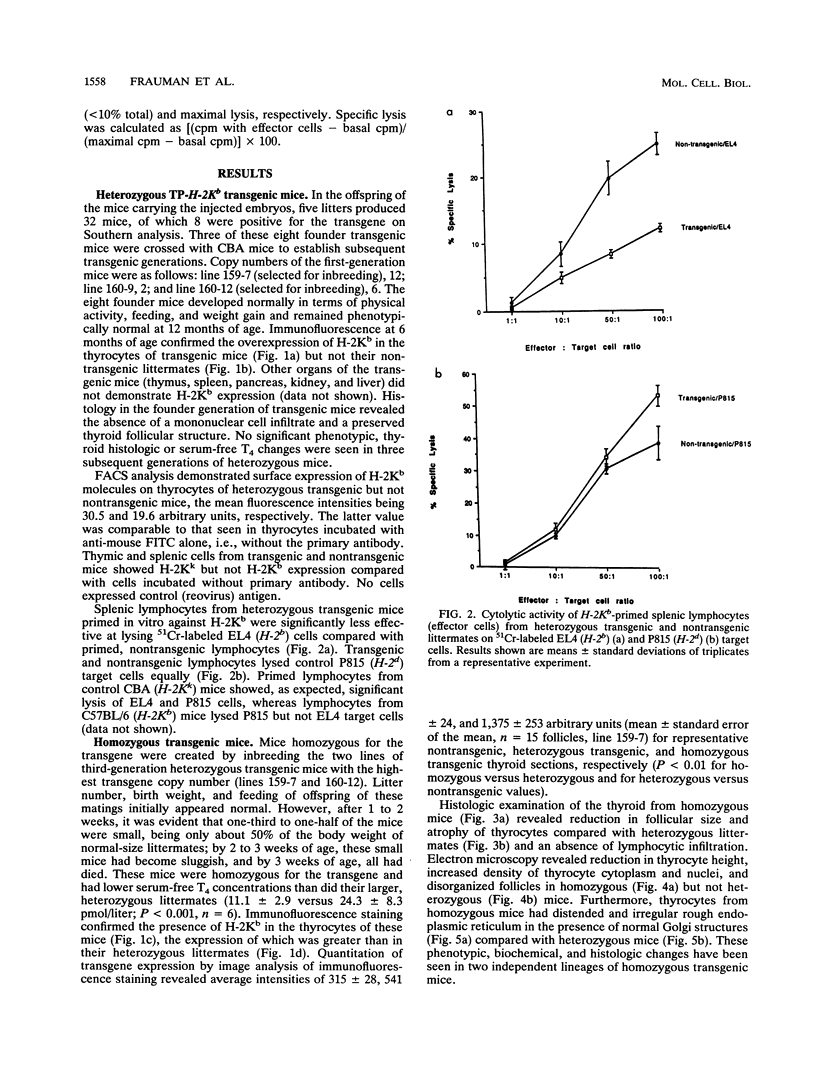
Abstract
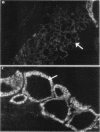
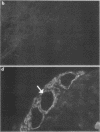
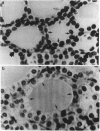
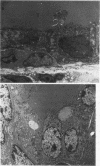
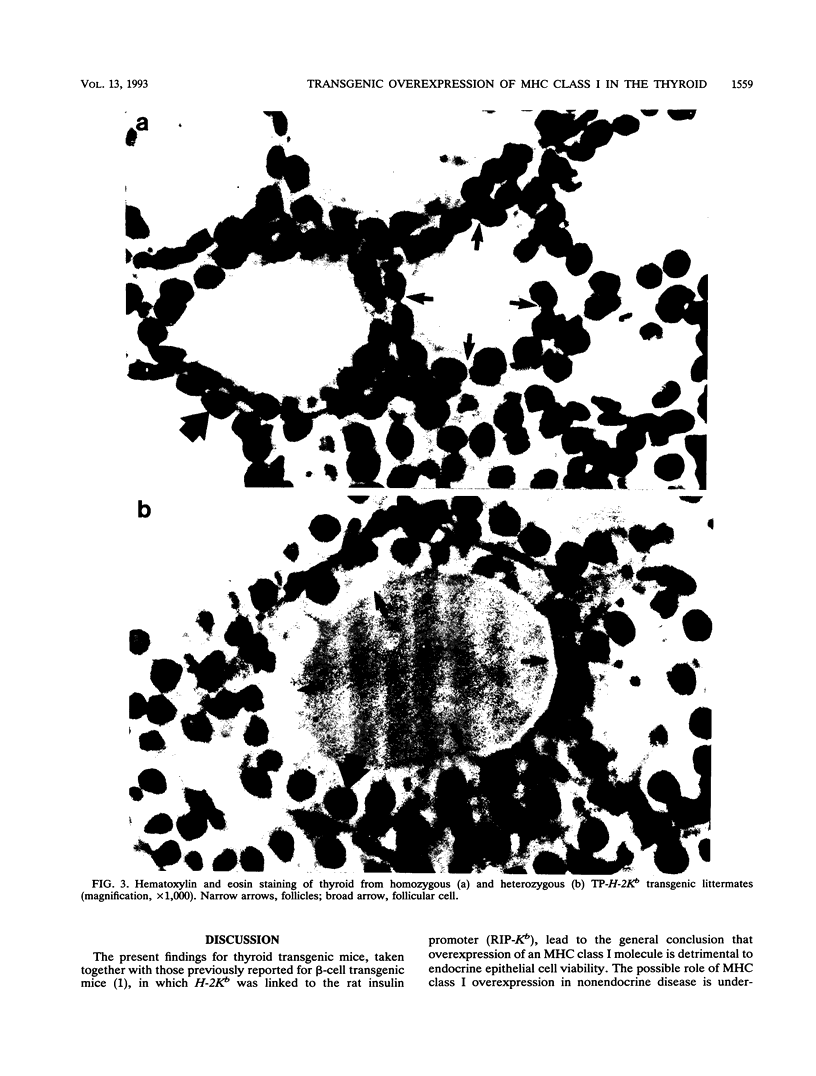
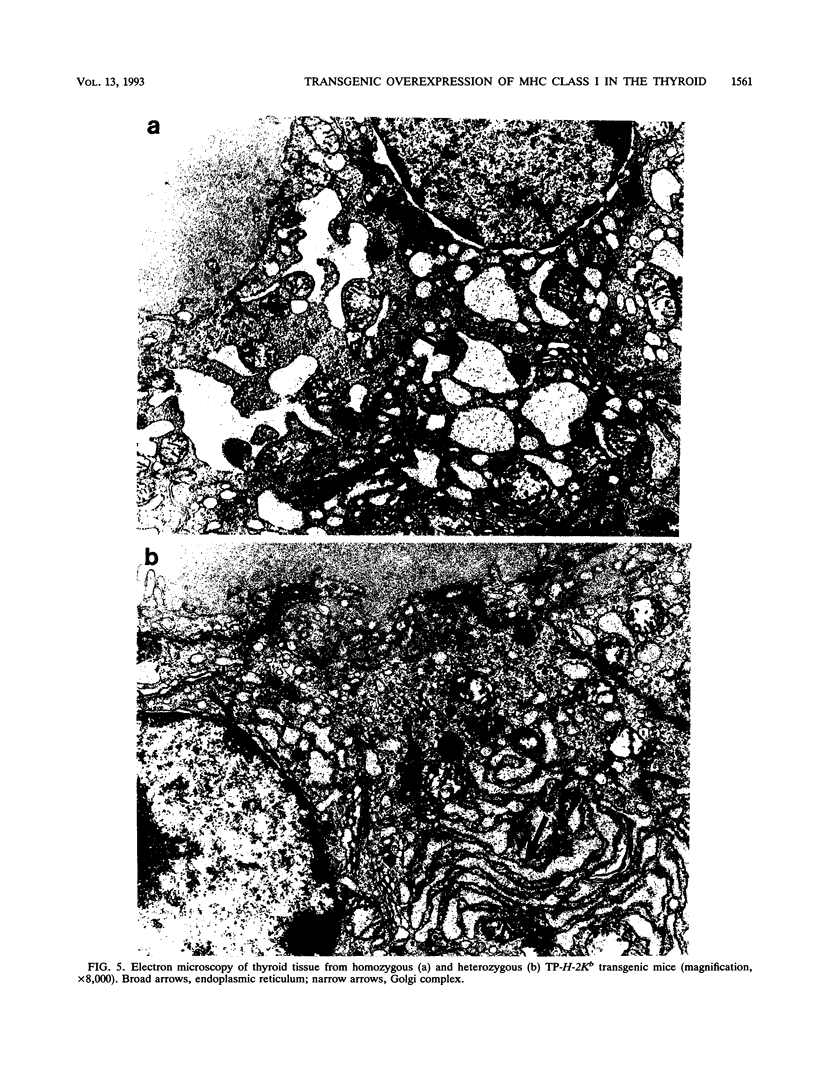
The overexpression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules in endocrine epithelial cells is an early feature of autoimmune thyroid disease and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, which may reflect a cellular response, e.g., to viruses or toxins. Evidence from a transgenic model in pancreatic beta cells suggests that MHC class I overexpression could play an independent role in endocrine cell destruction. We demonstrate in this study that the transgenic overexpression of an allogeneic MHC class I protein (H-2Kb) linked to the rat thyroglobulin promoter, in H-2Kk mice homozygous for the transgene, leads to thyrocyte atrophy, hypothyroidism, growth retardation, and death. Thyrocyte atrophy occurred in the absence of lymphocytic infiltration. Tolerance to allogeneic class I was revealed by the reduced ability of primed lymphocytes from transgenic mice to lyse H-2Kb target cells in vitro. This nonimmune form of thyrocyte destruction and hypothyroidism recapitulates the beta-cell destruction and diabetes that results from transgenic overexpression of MHC class I molecules in pancreatic beta cells. Thus, we conclude that overexpression of MHC class I molecules may be a general mechanism that directly impairs endocrine epithelial cell viability.
Full text
PDF
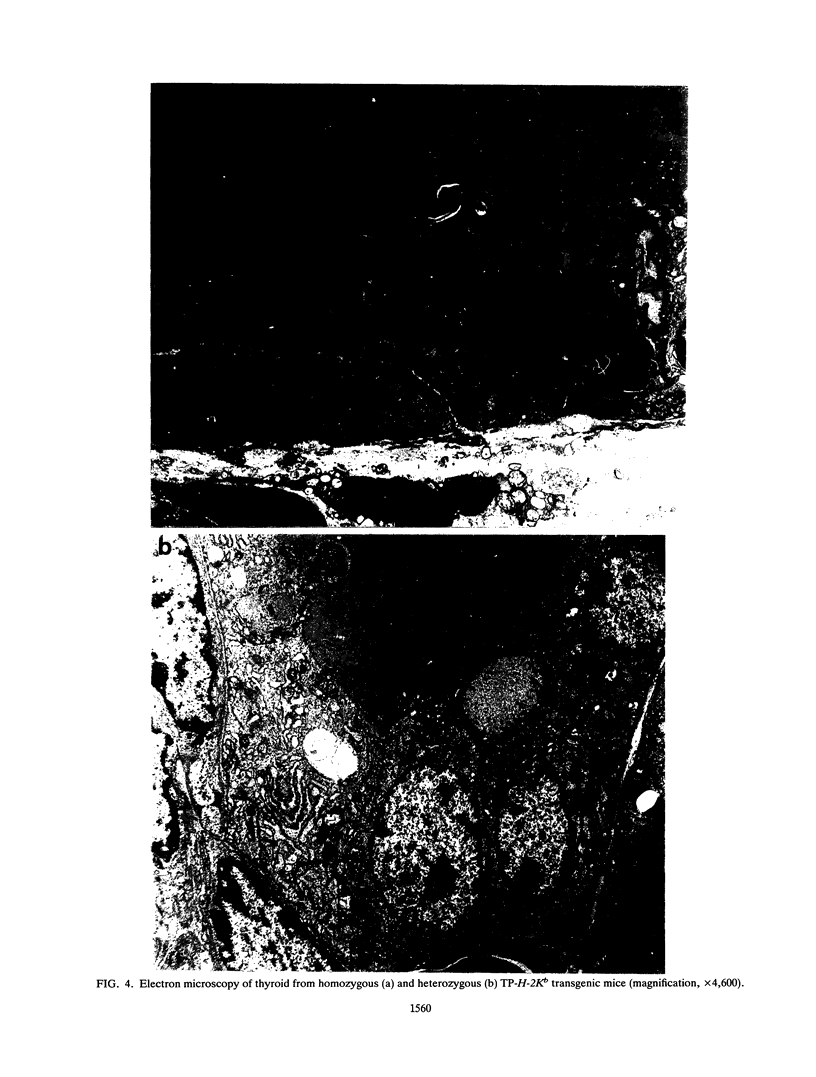





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J., Campbell I. L., Morahan G., Mandel T. E., Harrison L. C., Miller J. F. Diabetes in transgenic mice resulting from over-expression of class I histocompatibility molecules in pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):529–533. doi: 10.1038/333529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison J., Malcolm L., Culvenor J., Bartholomeusz R. K., Holmberg K., Miller J. F. Overexpression of beta 2-microglobulin in transgenic mouse islet beta cells results in defective insulin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2070–2074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfiore A., Mauerhoff T., Pujol-Borrell R., Badenhoop K., Buscema M., Mirakian R., Bottazzo G. F. De novo HLA class II and enhanced HLA class I molecule expression in SV40 transfected human thyroid epithelial cells. J Autoimmun. 1991 Jun;4(3):397–414. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Dean B. M., McNally J. M., MacKay E. H., Swift P. G., Gamble D. R. In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 8;313(6):353–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508083130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Guagliardi L. E. The cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:707–744. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Bizilj K., Colman P. G., Tuch B. E., Harrison L. C. Interferon-gamma induces the expression of HLA-A,B,C but not HLA-DR on human pancreatic beta-cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jun;62(6):1101–1109. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-6-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Cutri A., Wilkinson D., Boyd A. W., Harrison L. C. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 is induced on isolated endocrine islet cells by cytokines but not by reovirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4282–4286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Harrison L. C., Ashcroft R. G., Jack I. Reovirus infection enhances expression of class I MHC proteins on human beta-cell and rat RINm5F cell. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):362–365. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Harrison L. C. Molecular pathology of type 1 diabetes. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Aug;7(4):299–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Iscaro A., Harrison L. C. IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cytotoxicity to murine islets of Langerhans. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2325–2329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Oxbrow L., West J., Harrison L. C. Regulation of MHC protein expression in pancreatic beta-cells by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Feb;2(2):101–107. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-2-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Wong G. H., Schrader J. W., Harrison L. C. Interferon-gamma enhances the expression of the major histocompatibility class I antigens on mouse pancreatic beta cells. Diabetes. 1985 Nov;34(11):1205–1209. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.11.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P., Ruel J., Dussault J. H. Analysis of nuclear 5,5,3'-triiodothyronine-binding capacity and tissue response in the liver of the neonatal rat. Endocrinology. 1979 Oct;105(4):952–959. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-4-952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen E., Cohen-Doyle M. F., Williams D. B. Efficient dissociation of the p88 chaperone from major histocompatibility complex class I molecules requires both beta 2-microglobulin and peptide. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1653–1661. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen E., Williams D. B. Participation of a novel 88-kD protein in the biogenesis of murine class I histocompatibility molecules. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1099–1115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faustman D., Li X. P., Lin H. Y., Fu Y. E., Eisenbarth G., Avruch J., Guo J. Linkage of faulty major histocompatibility complex class I to autoimmune diabetes. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1756–1761. doi: 10.1126/science.1763324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K., Farquharson M. A., Hardman R. Aberrant expression of class II major histocompatibility complex molecules by B cells and hyperexpression of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules by insulin containing islets in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1987 May;30(5):333–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00299027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K., Farquharson M. A., Meager A. Immunoreactive alpha-interferon in insulin-secreting beta cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1987 Dec 19;2(8573):1423–1427. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Pujol-Borrell R., Chiovato L., Russell R. C., Doniach D., Bottazzo G. F. Aberrant expression of HLA-DR antigen on thyrocytes in Graves' disease: relevance for autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1111–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90628-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Campbell I. L., Allison J., Miller J. F. MHC molecules and beta-cell destruction. Immune and nonimmune mechanisms. Diabetes. 1989 Jul;38(7):815–818. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.7.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath W. R., Allison J., Hoffmann M. W., Schönrich G., Hämmerling G., Arnold B., Miller J. F. Autoimmune diabetes as a consequence of locally produced interleukin-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):547–549. doi: 10.1038/359547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga Y., Matsubayashi S., Akasu F., Miller N., Jamieson C., Volpé R. Effects of recombinant human interleukin-2 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with or without interferon-gamma on human thyroid tissues from patients with Graves' disease and from normal subjects xenografted into nude mice. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jun;72(6):1296–1301. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-6-1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo D., Burkly L. C., Widera G., Cowing C., Flavell R. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Diabetes and tolerance in transgenic mice expressing class II MHC molecules in pancreatic beta cells. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migita K., Eguchi K., Otsubo T., Kawakami A., Nakao H., Ueki Y., Shimomura C., Kurata A., Fukuda T., Matsunaga M. Cytokine regulation of HLA on thyroid epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Dec;82(3):548–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Morahan G., Allison J. Extrathymic acquisition of tolerance by T lymphocytes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54(Pt 2):807–813. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1989.054.01.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J. A molecular model of MHC class-I-restricted antigen processing. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90122-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan G., Allison J., Miller J. F. Tolerance of class I histocompatibility antigens expressed extrathymically. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):622–624. doi: 10.1038/339622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld D. S., Davies T. F. Strain-specific determination of the degree of thyroid cell MHC class II antigen expression: evaluation of established Wistar and Fisher rat thyroid cell lines. Endocrinology. 1990 Sep;127(3):1254–1259. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi P. S., Oehen S., Buerki K., Pircher H., Ohashi C. T., Odermatt B., Malissen B., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. Ablation of "tolerance" and induction of diabetes by virus infection in viral antigen transgenic mice. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90164-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P. Intolerable secretion in tolerant transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):500–503. doi: 10.1038/333500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P. Multiple sclerosis. The case of the wonky mouse. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):503–505. doi: 10.1038/353503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platzer M., Neufeld D. S., piccinini L. A., Davies T. F. Induction of rat thyroid cell MHC class II antigen by thyrotropin and gamma-interferon. Endocrinology. 1987 Dec;121(6):2087–2092. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-6-2087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pujol-Borrell R., Todd I., Doshi M., Bottazzo G. F., Sutton R., Gray D., Adolf G. R., Feldmann M. HLA class II induction in human islet cells by interferon-gamma plus tumour necrosis factor or lymphotoxin. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):304–306. doi: 10.1038/326304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvetnick N., Liggitt D., Pitts S. L., Hansen S. E., Stewart T. A. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced in transgenic mice by ectopic expression of class II MHC and interferon-gamma. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90414-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. E., Matthews P. Thyroid hormone metabolism and the source of plasma triiodothyronine in 2-week-old rats: effects of thyroid status. Endocrinology. 1984 Jun;114(6):2394–2405. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-6-2394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnley A. M., Morahan G., Okano H., Bernard O., Mikoshiba K., Allison J., Bartlett P. F., Miller J. F. Dysmyelination in transgenic mice resulting from expression of class I histocompatibility molecules in oligodendrocytes. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):566–569. doi: 10.1038/353566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei M. L., Cresswell P. HLA-A2 molecules in an antigen-processing mutant cell contain signal sequence-derived peptides. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):443–446. doi: 10.1038/356443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Golden L., Zakut R., Mellor A., Fahrner K., Kvist S., Flavell R. A. The DNA sequence of the H-2kb gene: evidence for gene conversion as a mechanism for the generation of polymorphism in histocompatibilty antigens. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):453–462. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]