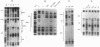Abstract
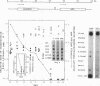
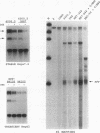
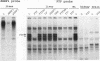
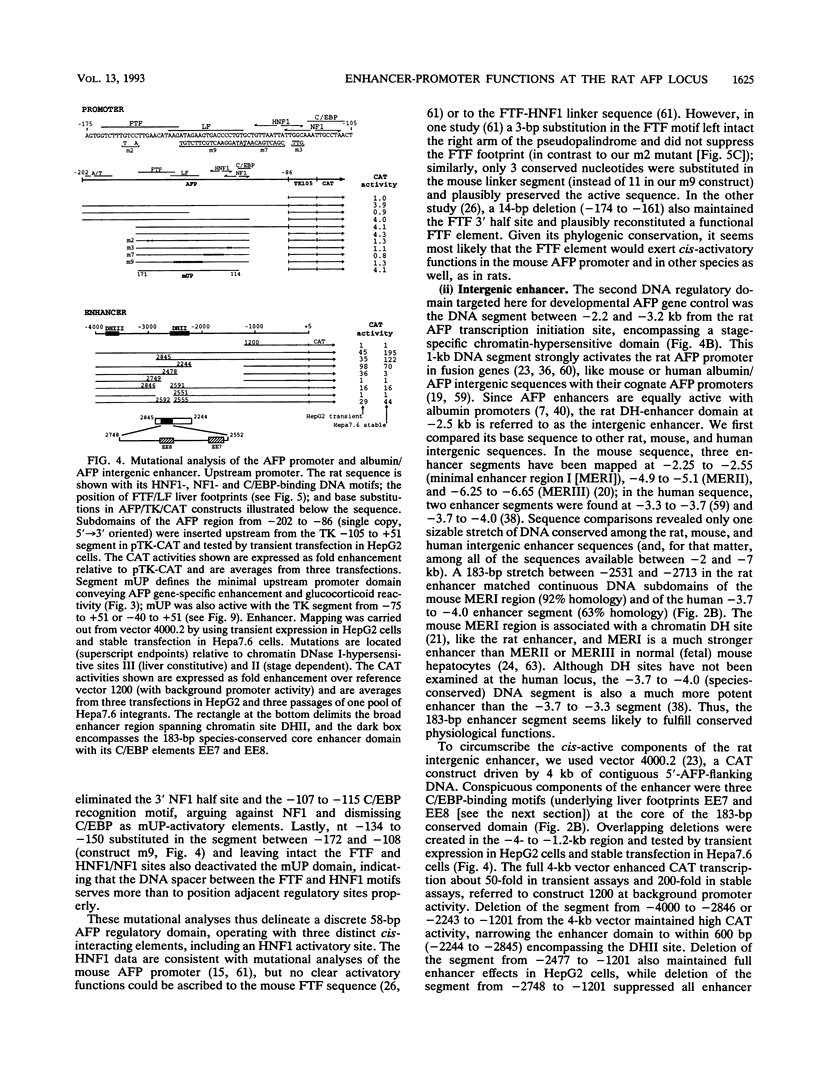
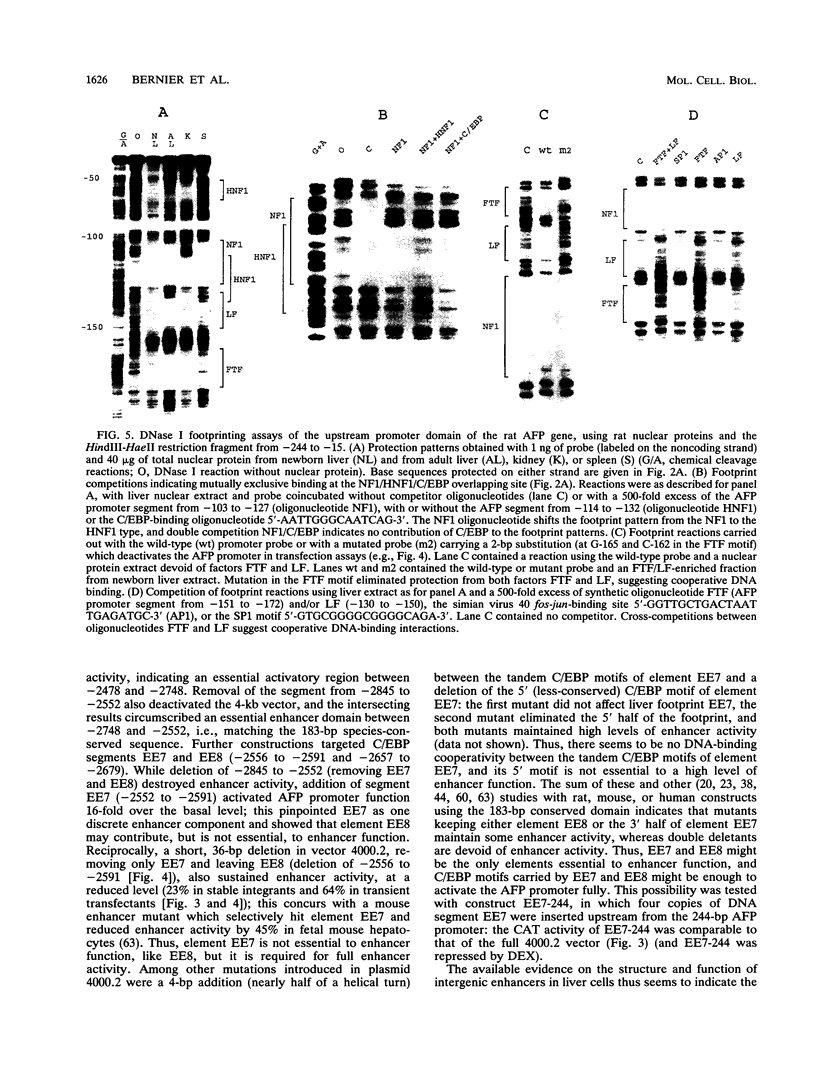
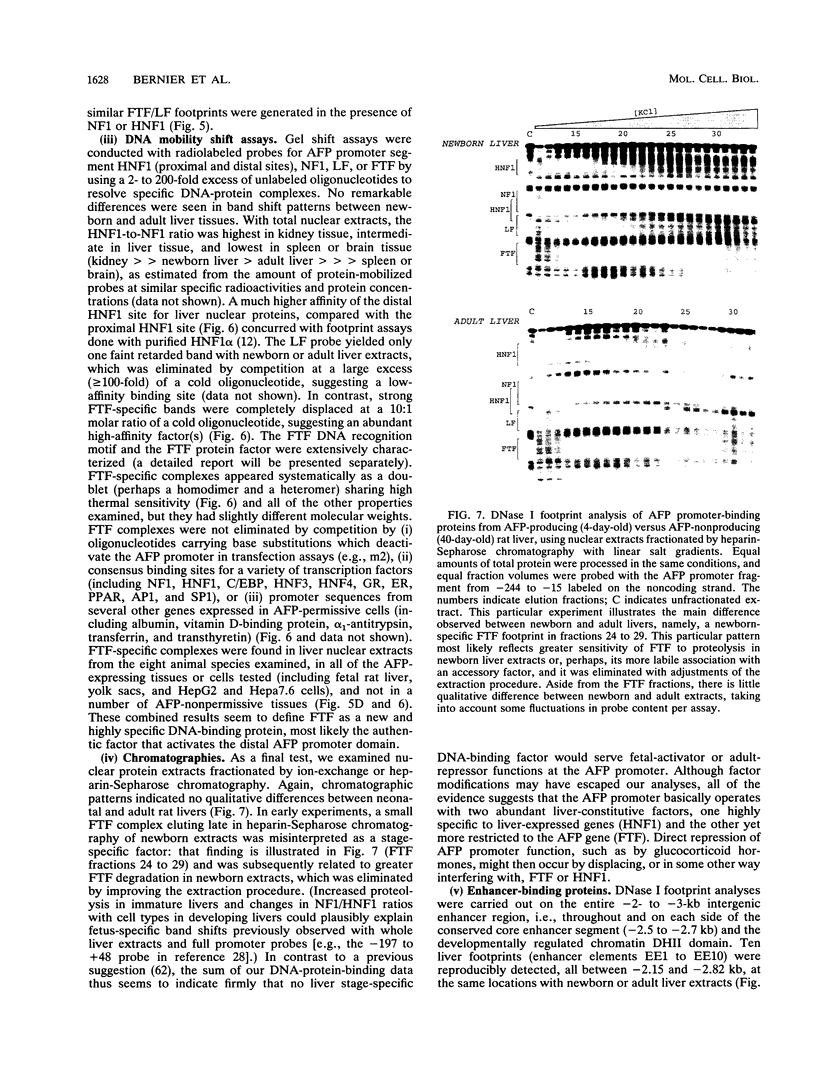
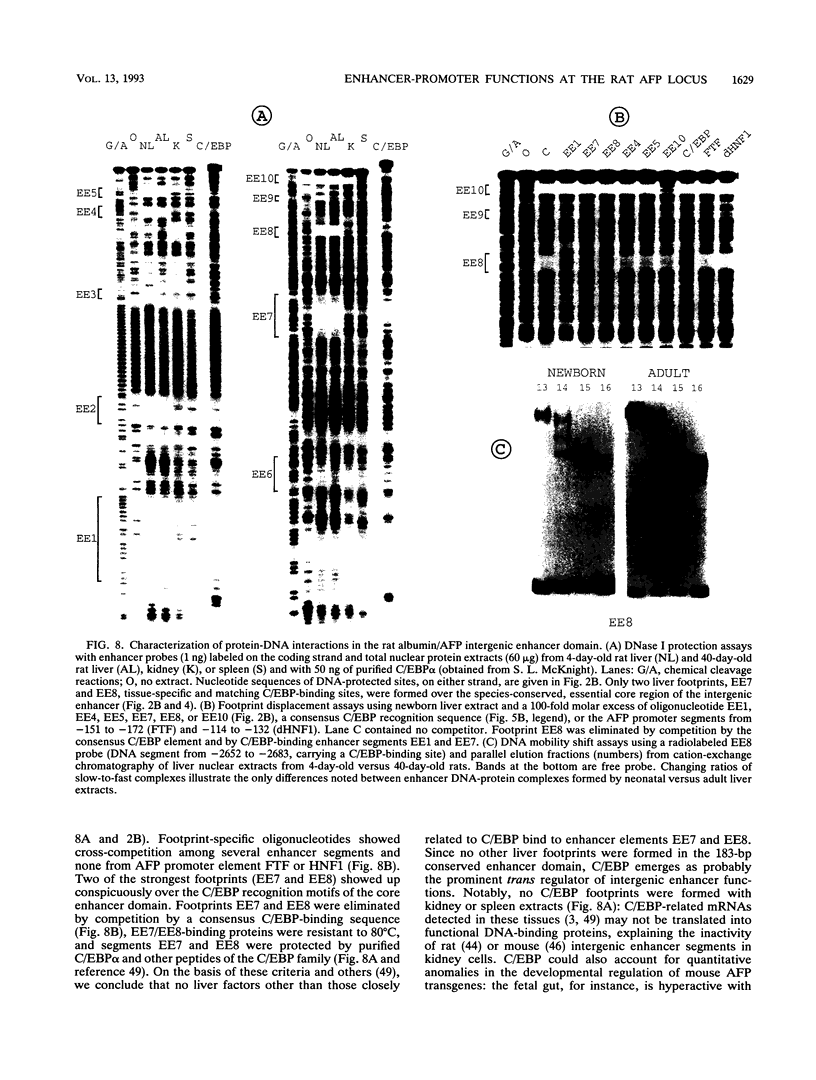
During liver development, the tandem alpha 1-fetoprotein (AFP)/albumin locus is triggered at the AFP end and then asymmetrically enhanced; this is followed by autonomous repression of the AFP-encoding gene. To understand this regulation better, we characterized the two early developmental stage-specific DNase I-hypersensitive (DH) sites so far identified in rat liver AFP/albumin chromatin: an intergenic DH-enhancer site and the AFP DH-promoter site. Mutation-transfection analyses circumscribed the DH-enhancer domain to a 200-bp DNA segment stringently conserved among species. Targeted mutations, DNA-protein-binding assays, and coexpression experiments pinpointed C/EBP as the major activatory component of the intergenic enhancer. Structure-function relationships at the AFP DH-promoter site defined a discrete glucocorticoid-regulated domain activated cooperatively by HNF1 and a highly specific AFP transcription factor, FTF, which binds to a steroid receptor recognition motif. The HNF1/FTF/DNA complex is deactivated by glucocorticoid receptors or by the ubiquitous factor NF1, which eliminates HNF1 by competition at an overlapping, high-affinity binding site. We propose that the HNF1-NF1 site might serve as a developmental switch to direct autonomous AFP gene repression in late liver development. We also conclude that the intergenic enhancer is driven by C/EBP alpha primarily to fulfill albumin gene activation functions at early developmental stages. Factor FTF seems to be the key regulator of AFP gene-specific functions in carcinoembryonic states.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABELEV G. I., PEROVA S. D., KHRAMKOVA N. I., POSTNIKOVA Z. A., IRLIN I. S. Production of embryonal alpha-globulin by transplantable mouse hepatomas. Transplantation. 1963 Apr;1:174–180. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196301020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belanger L., Baril P., Guertin M., Gingras M. C., Gourdeau H., Anderson A., Hamel D., Boucher J. M. Oncodevelopmental and hormonal regulation of alpha 1-fetoprotein gene expression. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1983;21:73–99. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(83)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld M., Maury M., Chouard T., Yaniv M., Condamine H. Hepatic nuclear factor 1 (HNF1) shows a wider distribution than products of its known target genes in developing mouse. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):589–599. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Beato M. Nuclear factor I acts as a transcription factor on the MMTV promoter but competes with steroid hormone receptors for DNA binding. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2233–2239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzard G., Locker J. The transcription control region of the rat alpha-fetoprotein gene. DNA sequence and homology studies. DNA Seq. 1990;1(1):33–48. doi: 10.3109/10425179009041345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper S. A., Tilghman S. M. Postnatal repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene is enhancer independent. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):537–546. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevrette M., Guertin M., Turcotte B., Bélanger L. The rat alpha 1-fetoprotein gene: characterization of the 5'-flanking region and tandem organization with the albumin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1338–1339. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. Developmental regulation of beta-globin gene switching. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziadek M. A., Andrews G. K. Tissue specificity of alpha-fetoprotein messenger RNA expression during mouse embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):549–554. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerman M. H., Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Tissue-specific transcription of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene promoter is dependent on HNF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4204–4212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D. Sites of alpha-fetoprotein synthesis. N Engl J Med. 1971 Dec 16;285(25):1436–1437. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197112162852517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Fine-structure mapping of the three mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R., Tilghman S. M. Multiple regulatory elements in the intergenic region between the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):477–487. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Tilghman S. M. Configuration of the alpha-fetoprotein regulatory domain during development. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):949–956. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
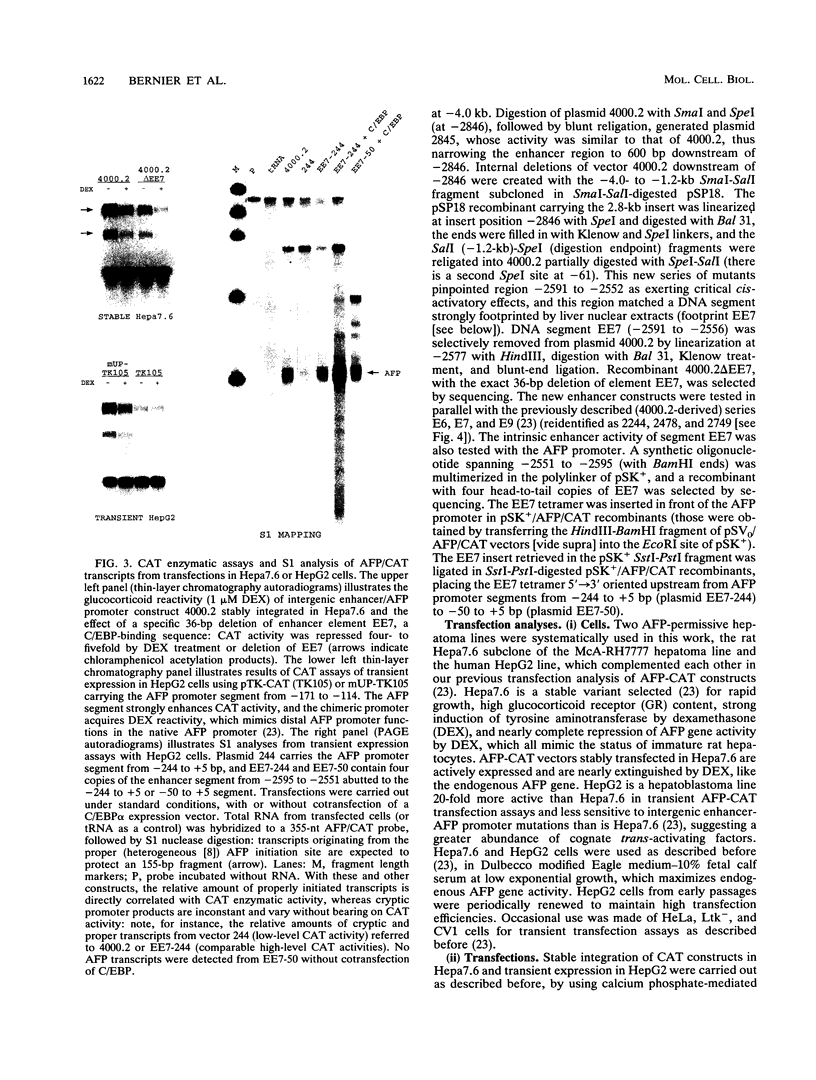
- Guertin M., LaRue H., Bernier D., Wrange O., Chevrette M., Gingras M. C., Bélanger L. Enhancer and promoter elements directing activation and glucocorticoid repression of the alpha 1-fetoprotein gene in hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1398–1407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haefliger D. N., Moskaitis J. E., Schoenberg D. R., Wahli W. Amphibian albumins as members of the albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, vitamin D-binding protein multigene family. J Mol Evol. 1989 Oct;29(4):344–354. doi: 10.1007/BF02103621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Krumlauf R., Camper S. A., Brinster R. L., Tilghman S. M. Diversity of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in mice is generated by a combination of separate enhancer elements. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2432657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Friedman N., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. Positive and negative regulatory elements in the mouse albumin enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houart C., Szpirer J., Szpirer C. The alpha-foetoprotein proximal enhancer: localization, cell specificity and modulation by dexamethasone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6277–6282. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jose-Estanyol M., Danan J. L. A liver-specific factor and nuclear factor I bind to the rat alpha-fetoprotein promoter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10865–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. H., Darlington G. J. Modulation of the liver specific phenotype in the human hepatoblastoma line Hep G2. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;25(2):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF02626182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laborda J., Naval J., Calvo M., Lampreave F., Uriel J. Alpha-fetoprotein and albumin uptake by mouse tissues during development. Biol Neonate. 1989;56(6):332–341. doi: 10.1159/000243142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladias J. A., Karathanasis S. K. Regulation of the apolipoprotein AI gene by ARP-1, a novel member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Science. 1991 Feb 1;251(4993):561–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1899293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The role of cis-acting promoter elements in tissue-specific albumin gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2711183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Hansen L. P., Graves M. K., Conley P. B., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 alpha and HNF-1 beta (vHNF-1) share dimerization and homeo domains, but not activation domains, and form heterodimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1042–1056. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muglia L., Rothman-Denes L. B. Cell type-specific negative regulatory element in the control region of the rat alpha-fetoprotein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7653–7657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahon J. L., Venetianer A., Sala-Trepat J. M. Specific sets of DNase I-hypersensitive sites are associated with the potential and overt expression of the rat albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2135–2139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Hashimoto T., Miyao Y., Tjong K. K., Chan J., Tamaoki T. A position-dependent silencer plays a major role in repressing alpha-fetoprotein expression in human hepatoma. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5885–5893. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Lawless D., Ohe Y., Miyao Y., Nakabayashi H., Kamiya H., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Tamaoki T. c-Ha-ras down regulates the alpha-fetoprotein gene but not the albumin gene in human hepatoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1461–1469. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata K., Motomura M., Nakabayashi H., Ido A., Tamaoki T. A possible mechanism of inverse developmental regulation of alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Studies with epidermal growth factor and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1331–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsa I., Flancbaum L. Long term organ culture of rat liver rudiment in a synthetic medium: morphological and biochemical development. Dev Biol. 1975 Sep;46(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. An albumin enhancer located 10 kb upstream functions along with its promoter to direct efficient, liver-specific expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):268–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poliard A. M., Bernuau D., Tournier I., Legrès L. G., Schoevaert D., Feldmann G., Sala-Trepat J. M. Cellular analysis by in situ hybridization and immunoperoxidase of alpha-fetoprotein and albumin gene expression in rat liver during the perinatal period. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):777–786. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poliard A., Bakkali L., Poiret M., Foiret D., Danan J. L. Regulation of the rat alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in liver. Both the promoter region and an enhancer element are liver-specific and negatively modulated by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2137–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabek J. P., Hsie D. Y., Papaconstantinou J. Alpha-fetoprotein expression in fetal kidney cells does not require enhancers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 6;1130(3):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S. C., Zielinski R., Dugaiczyk A. Structure of the gorilla alpha-fetoprotein gene and the divergence of primates. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):60–72. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90221-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiojiri N., Lemire J. M., Fausto N. Cell lineages and oval cell progenitors in rat liver development. Cancer Res. 1991 May 15;51(10):2611–2620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassin H., Hamel D., Bernier D., Guertin M., Belanger L. Molecular cloning of two C/EBP-related proteins that bind to the promoter and the enhancer of the alpha 1-fetoprotein gene. Further analysis of C/EBP beta and C/EBP gamma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3091–3098. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Belayew A. Transcriptional control of the murine albumin/alpha-fetoprotein locus during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5254–5257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratner I., Nahon J. L., Sala-Trepat J. M., Venetianer A. Albumin and alpha-fetoprotein gene transcription in rat hepatoma cell lines is correlated with specific DNA hypomethylation and altered chromatin structure in the 5' region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1856–1864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronche F., Rollier A., Herbomel P., Bach I., Cereghini S., Weiss M., Yaniv M. Anatomy of the rat albumin promoter. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Apr;7(2):173–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugwood J. D., Issemann I., Anderson R. G., Bundell K. R., McPheat W. L., Green S. The mouse peroxisome proliferator activated receptor recognizes a response element in the 5' flanking sequence of the rat acyl CoA oxidase gene. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):433–439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte B., Guertin M., Chevrette M., Bélanger L. Rat alpha 1-fetoprotein messenger RNA: 5'-end sequence and glucocorticoid-suppressed liver transcription in an improved nuclear run-off assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte B., Guertin M., Chevrette M., LaRue H., Bélanger L. DNase I hypersensitivity and methylation of the 5'-flanking region of the alpha 1-fetoprotein gene during developmental and glucocorticoid-induced repression of its activity in rat liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9827–9841. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacher J., Tilghman S. M. Dominant negative regulation of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene in adult liver. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1732–1735. doi: 10.1126/science.1702902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt T. F., Compton R. S., Scott R. W., Tilghman S. M. Differential requirements for cellular enhancers in stem and differentiated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):487–500. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Martinez E. Superfamily of steroid nuclear receptors: positive and negative regulators of gene expression. FASEB J. 1991 Jun;5(9):2243–2249. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.9.1860615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Saito A., Tamaoki T. Cell-specific enhancer activity in a far upstream region of the human alpha-fetoprotein gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4812–4818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen P., Groupp E. R., Buzard G., Crawford N., Locker J. Enhancer, repressor, and promoter specificities combine to regulate the rat alpha-fetoprotein gene. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;10(7):525–536. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D. E., Ge X., Rabek J. P., Papaconstantinou J. Functional analysis of the trans-acting factor binding sites of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein proximal promoter by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21179–21185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D. E., Hoyt P. R., Papaconstantinou J. Localization of DNA protein-binding sites in the proximal and distal promoter regions of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3382–3391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D. E., Rabek J. P., Hsieh C. C., Torres-Ramos C., Papaconstantinou J. Functional analysis of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein enhancers and their subfragments in primary mouse hepatocyte cultures. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10676–10682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Dong J. M., Chiu J. F. Regulation of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression by antagonism between AP-1 and the glucocorticoid receptor at their overlapping binding site. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8248–8254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]