Abstract
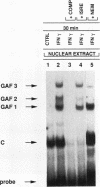
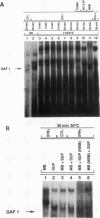
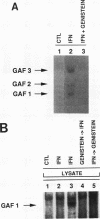
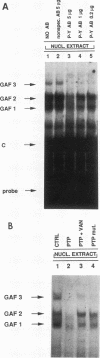
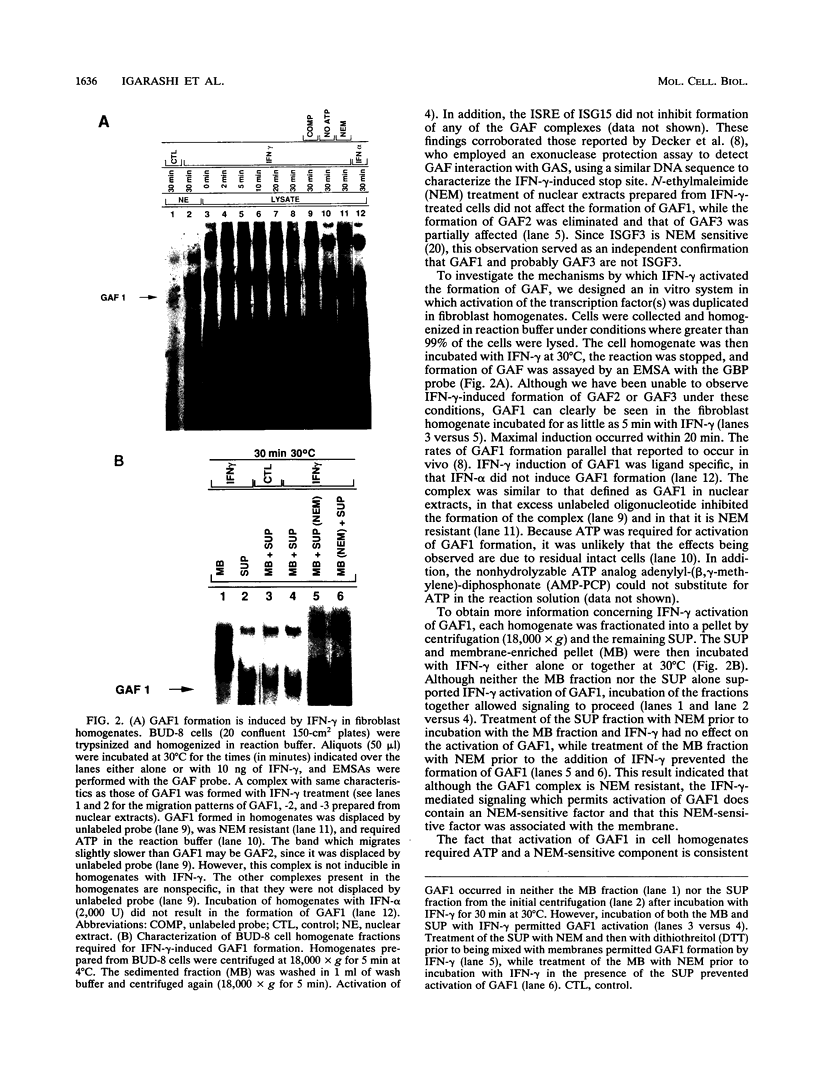
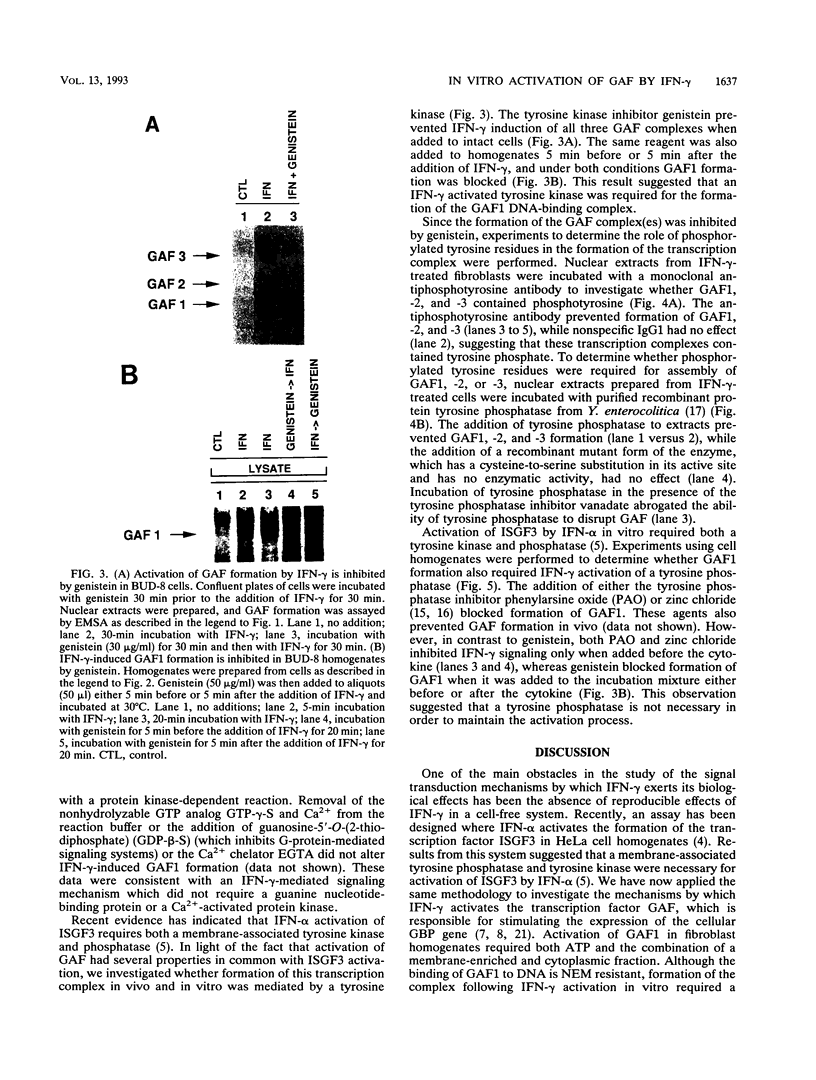
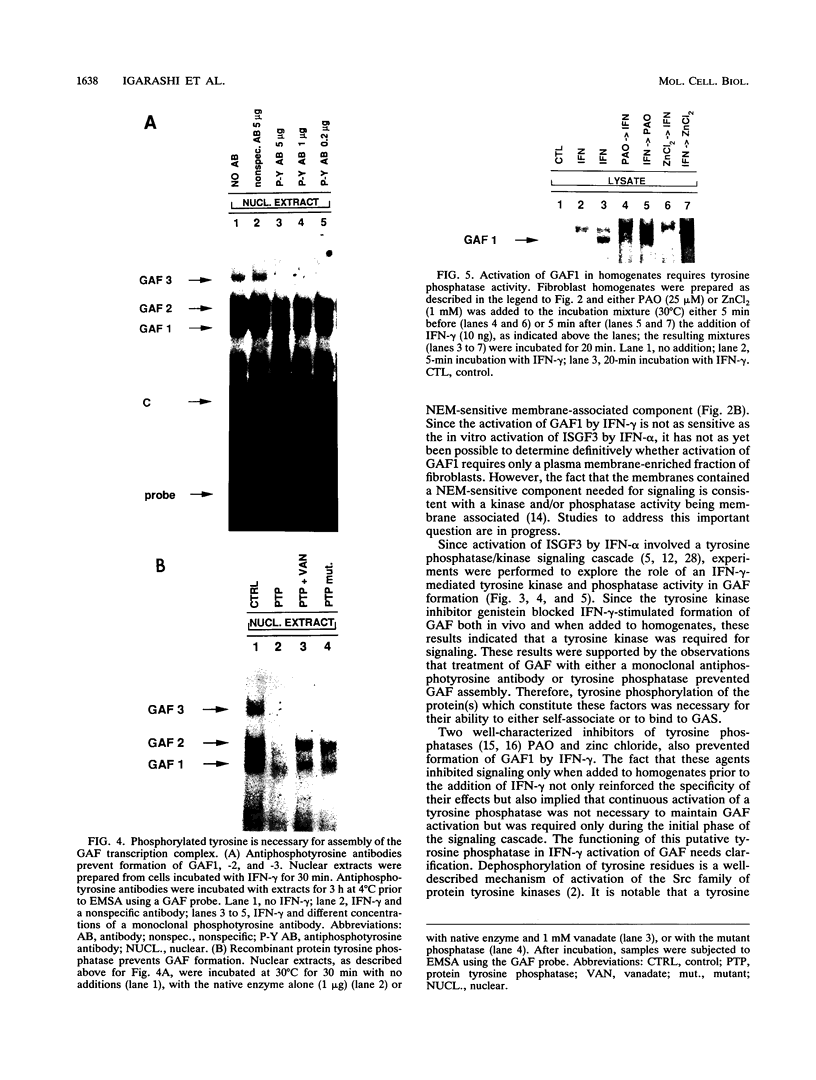
Although it has been well documented that the biological activities of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) are initiated through interaction with its cell surface receptor, the signal transduction mechanisms which mediate the effects of this cytokine have remained unclear. In order to facilitate a better understanding of IFN-gamma signaling, we have designed an assay using human fibroblast cell homogenates in which IFN-gamma activates the formation of the IFN-gamma activation factor (GAF) transcription complex. GAF mediates the rapid transcriptional activation of the guanylate-binding protein gene by IFN-gamma. Activation of GAF in homogenates required ATP, but not Ca2+ or GTP. Fractionation of homogenates indicated that both the pellet (18,000 x g) and the remaining cytoplasmic fraction were required for GAF activation by IFN-gamma. In intact cells and cell homogenates, the activation of GAF was prevented by the specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein. Treatment of GAF-containing nuclear extracts with either monoclonal antiphosphotyrosine antibody or protein tyrosine phosphatase prevented the assembly of the transcription complex, indicating that its formation required phosphorylation of tyrosine residues. Furthermore, the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors phenylarsine oxide and zinc chloride also inhibited GAF formation in vitro, but only if these agents were added to cell homogenates before IFN-gamma was added. The addition of either agent 5 min after IFN-gamma had no effect. These results provide the first evidence for an IFN-gamma-regulated tyrosine phosphatase/kinase signaling cascade that permits this cytokine to activate the transcription of an early-response gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste E. N., Vidovic M., Panek R. B., Norris J. G., Reddy A. T., Benos D. J. Interferon-gamma-induced astrocyte class II major histocompatibility complex gene expression is associated with both protein kinase C activation and Na+ entry. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18119–18126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Larner A. C. Activation of transcription factors by interferon-alpha in a cell-free system. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):813–815. doi: 10.1126/science.1496402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Cheng Y. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interactions of alpha- and gamma-interferon in the transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding a guanylate-binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2009–2014. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Darnell J. E., Jr Two distinct alpha-interferon-dependent signal transduction pathways may contribute to activation of transcription of the guanylate-binding protein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5147–5153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan X. D., Goldberg M., Bloom B. R. Interferon-gamma-induced transcriptional activation is mediated by protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5122–5125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S., Wahl L. M., Winestock K. D. The receptor for interferon-gamma on human peripheral blood monocytes consists of multiple distinct subunits. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22545–22548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y. A transcription factor with SH2 and SH3 domains is directly activated by an interferon alpha-induced cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase(s). Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90106-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8555–8559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukazawa H., Mizuno S., Uehara Y. Effects of herbimycin A and various SH-reagents on p60v-src kinase activity in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):276–282. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Morales P., Minami Y., Luong E., Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. Tyrosine phosphorylation in T cells is regulated by phosphatase activity: studies with phenylarsine oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9255–9259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. A. Use of vanadate as protein-phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:477–482. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity of an essential virulence determinant in Yersinia. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2166336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey G. K., McCourt D. W., Schreiber R. D. Ligand-induced phosphorylation of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Dependence on the presence of a functionally active receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17868–17875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent transcriptional activation: signal transduction without second messenger involvement? New Biol. 1990 Oct;2(10):923–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Strehlow I., Darnell J. E. Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh J. E., Chang C. H., Fodor W. L., Flavell R. A. Dissection of the interferon gamma-MHC class II signal transduction pathway reveals that type I and type II interferon systems share common signalling component(s). EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1351–1363. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster A. D., Ravetch J. V. Genomic characterization of a gamma-interferon-inducible gene (IP-10) and identification of an interferon-inducible hypersensitive site. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3723–3731. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C., Merlin G., Ballotti R., Metzler M., Aguet M. Rapid increase of the human IFN-gamma receptor phosphorylation in response to human IFN-gamma and phorbol myristate acetate. Involvement of different serine/threonine kinases. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4257–4264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Ravetch J. V. Characterization of the promoter of the human gene encoding the high-affinity IgG receptor: transcriptional induction by gamma-interferon is mediated through common DNA response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11305–11309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pot D. A., Woodford T. A., Remboutsika E., Haun R. S., Dixon J. E. Cloning, bacterial expression, purification, and characterization of the cytoplasmic domain of rat LAR, a receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19688–19696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez L., Fellous M., Stark G. R., Pellegrini S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. Y., Clemens J. C., Schubert H. L., Stuckey J. A., Fischer M. W., Hume D. M., Saper M. A., Dixon J. E. Expression, purification, and physicochemical characterization of a recombinant Yersinia protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23759–23766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]