Abstract
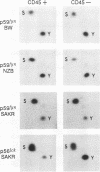
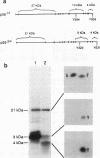
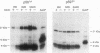
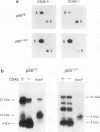
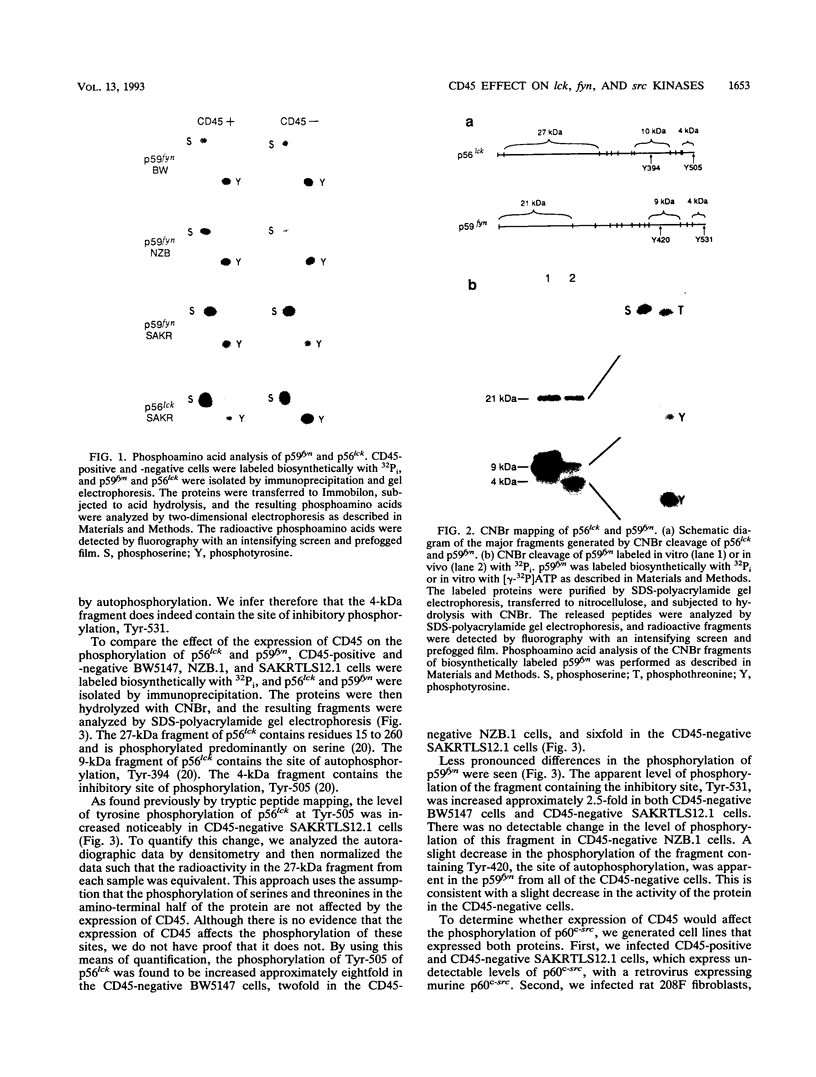
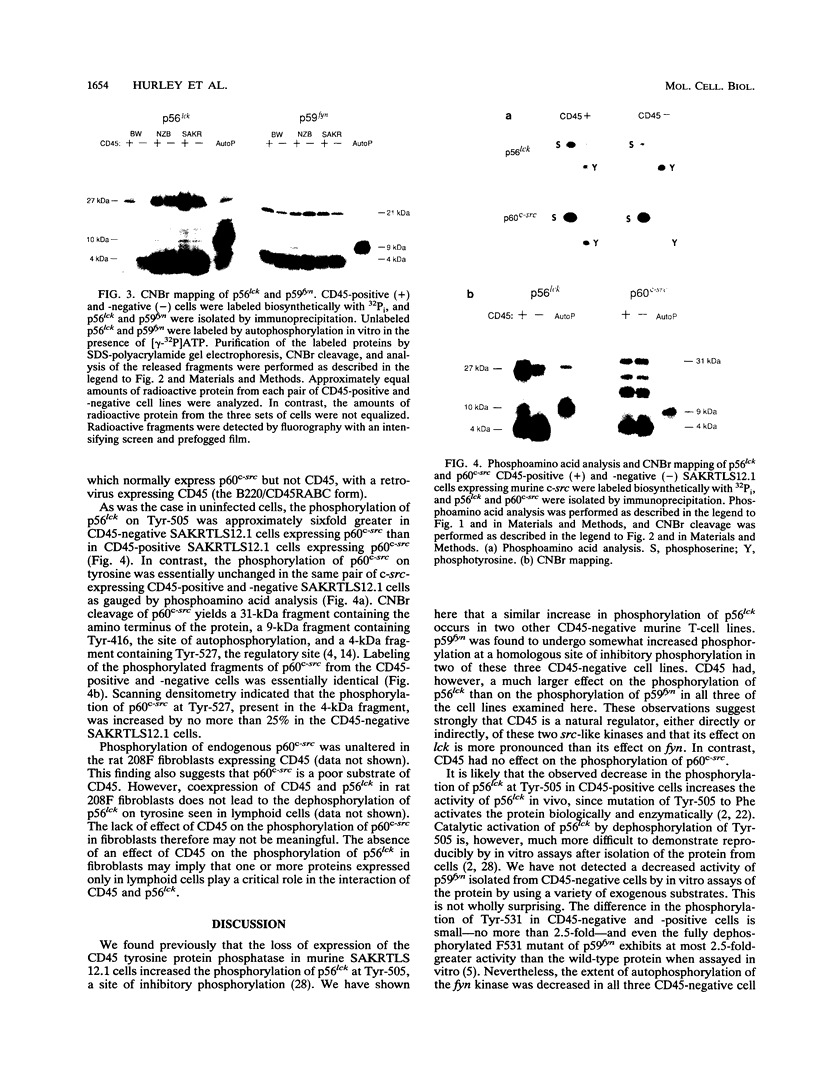
Expression of the CD45 tyrosine protein phosphatase is required for the response of functional lymphocytes to stimulation through the antigen receptor. One or more of its substrates may therefore be essential for signal transduction during lymphocyte activation. We have studied the phosphorylation of the closely related lck, fyn, and c-src tyrosine protein kinases in leukemic murine T-cell lines that have lost the expression of CD45. The phosphorylation of the lck kinase at an inhibitory site of tyrosine phosphorylation, Tyr-505, was increased by two-, six-, and eightfold in three different cell lines. Phosphorylation of the fyn kinase at the homologous site, Tyr-531, was unaltered in one of these cell lines, but increased by 2.5-fold in the two others. The phosphorylation of p60c-src at the homologous tyrosine was essentially unchanged in the one CD45-negative cell line in which it was examined. The expression of CD45 therefore regulates the phosphorylation and potentially the activity of the lck and fyn tyrosine protein kinases, but the effect on the lck kinase is much greater than on the fyn kinase. This finding and the observation that CD45 had no effect on the phosphorylation of p60c-src suggest that CD45 exhibits polypeptide substrate specificity in vivo. Additionally, these findings are consistent with the hypothesis that the unresponsiveness of CD45-negative lymphoid cells to antigenic stimulation is due largely to hyperphosphorylation of the lck kinase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham N., Miceli M. C., Parnes J. R., Veillette A. Enhancement of T-cell responsiveness by the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):62–66. doi: 10.1038/350062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrein K. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of a site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase, p56lck, reveals its oncogenic potential in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4247–4251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleby M. W., Gross J. A., Cooke M. P., Levin S. D., Qian X., Perlmutter R. M. Defective T cell receptor signaling in mice lacking the thymic isoform of p59fyn. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):751–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90309-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Veillette A., Schwartz A. M., Deseau V., Rosen N. Analysis of pp60c-src in human colon carcinoma and normal human colon mucosal cells. Oncogene Res. 1987 Jul;1(2):149–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Espino P. C., Marshall J., Harvey R., Merrill J., Smith A. E. Structural elements that regulate pp59c-fyn catalytic activity, transforming potential, and ability to associate with polyomavirus middle-T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):170–179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.170-179.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Abraham K. M., Forbush K. A., Perlmutter R. M. Regulation of T cell receptor signaling by a src family protein-tyrosine kinase (p59fyn). Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90162-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaichenhaus N., Shastri N., Littman D. R., Turner J. M. Requirement for association of p56lck with CD4 in antigen-specific signal transduction in T cells. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):511–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90235-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsi E. D., Siegel J. N., Minami Y., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell activation induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of a limited number of cellular substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10836–10842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. R., Amrein K. E., Sefton B. M. Creation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of the lck tyrosine protein kinase. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7406–7413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7406-7413.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Analysis of the activity and phosphorylation of the lck protein in lymphoid cells. Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R., Trowbridge I. Two complementation classes of T200 (Ly-5) glycoprotein-negative mutants. Immunogenetics. 1981 Mar 1;12(5-6):511–523. doi: 10.1007/BF01561692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Kornbluth S., Hanafusa H. Enzymatically inactive p60c-src mutant with altered ATP-binding site is fully phosphorylated in its carboxy-terminal regulatory region. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):937–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90520-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Siegel J. N., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7722–7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnitz L., Sutor S. L., Torigoe T., Reed J. C., Bell M. P., McKean D. J., Leibson P. J., Abraham R. T. Effects of p56lck deficiency on the growth and cytolytic effector function of an interleukin-2-dependent cytotoxic T-cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4521–4530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Picus J., Schultz T., Weiss A. Tyrosine phosphatase CD45 is required for T-cell antigen receptor and CD2-mediated activation of a protein tyrosine kinase and interleukin 2 production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2037–2041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Picus J., Thomas M. L., Weiss A. Tyrosine phosphatase CD45 is essential for coupling T-cell antigen receptor to the phosphatidyl inositol pathway. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):66–68. doi: 10.1038/346066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K. X., Sefton B. M. Analysis of the sites in p56lck whose phosphorylation is induced by tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):803–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K., Sefton B. M. Activated lck tyrosine protein kinase stimulates antigen-independent interleukin-2 production in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4724–4732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Cooper J. A., King C. S., Ziegler S. F., Tinker D. A., Overell R. W., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Neoplastic transformation induced by an activated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (pp56lck). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):540–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miceli M. C., von Hoegen P., Parnes J. R. Adhesion versus coreceptor function of CD4 and CD8: role of the cytoplasmic tail in coreceptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina T. J., Kishihara K., Siderovski D. P., van Ewijk W., Narendran A., Timms E., Wakeham A., Paige C. J., Hartmann K. U., Veillette A. Profound block in thymocyte development in mice lacking p56lck. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):161–164. doi: 10.1038/357161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Pessa-Morikawa T., Autero M., Gassmann M., Andersson L. C., Gahmberg C. G., Burn P. Regulation of the p59fyn protein tyrosine kinase by the CD45 phosphotyrosine phosphatase. Eur J Immunol. 1992 May;22(5):1173–1178. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Shackelford D. A., Hurley T. R., Johnson P., Hyman R., Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S. Expression of CD45 alters phosphorylation of the lck-encoded tyrosine protein kinase in murine lymphoma T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8959–8963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Trowbridge I. S. Coclustering CD45 with CD4 or CD8 alters the phosphorylation and kinase activity of p56lck. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):347–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyron J. F., Verma S., de Waal Malefyt R., Sancho J., Terhorst C., Spits H. The CD45 protein tyrosine phosphatase is required for the completion of the activation program leading to lymphokine production in the Jurkat human T cell line. Int Immunol. 1991 Dec;3(12):1357–1366. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.12.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingel J. T., Thomas M. L. Evidence that the leukocyte-common antigen is required for antigen-induced T lymphocyte proliferation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1055–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90504-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Patel M. D., Weissman A. M., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Antigen activation of murine T cells induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a polypeptide associated with the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1083–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Phillips A. F., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D. Association of the fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K. Temperature-sensitive transformation by Rous sarcoma virus and temperature-sensitive protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):220–229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.220-229.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. L., Lee H. M., Rich S., Soriano P. pp59fyn mutant mice display differential signaling in thymocytes and peripheral T cells. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):741–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90308-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Weiss A. Genetic evidence for the involvement of the lck tyrosine kinase in signal transduction through the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90428-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Bolen J. B. Post-translational alterations of the tyrosine kinase p56lck in response to activators of protein kinase C. Oncogene Res. 1988 May;2(4):385–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. T., Pingel J. T., Nelson J. O., Thomas M. L. CD8+ T-cell clones deficient in the expression of the CD45 protein tyrosine phosphatase have impaired responses to T-cell receptor stimuli. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4415–4422. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamoyska R., Derham P., Gorman S. D., von Hoegen P., Bolen J. B., Veillette A., Parnes J. R. Inability of CD8 alpha' polypeptides to associate with p56lck correlates with impaired function in vitro and lack of expression in vivo. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):278–281. doi: 10.1038/342278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]