Abstract
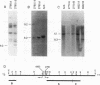
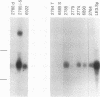
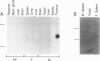
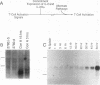
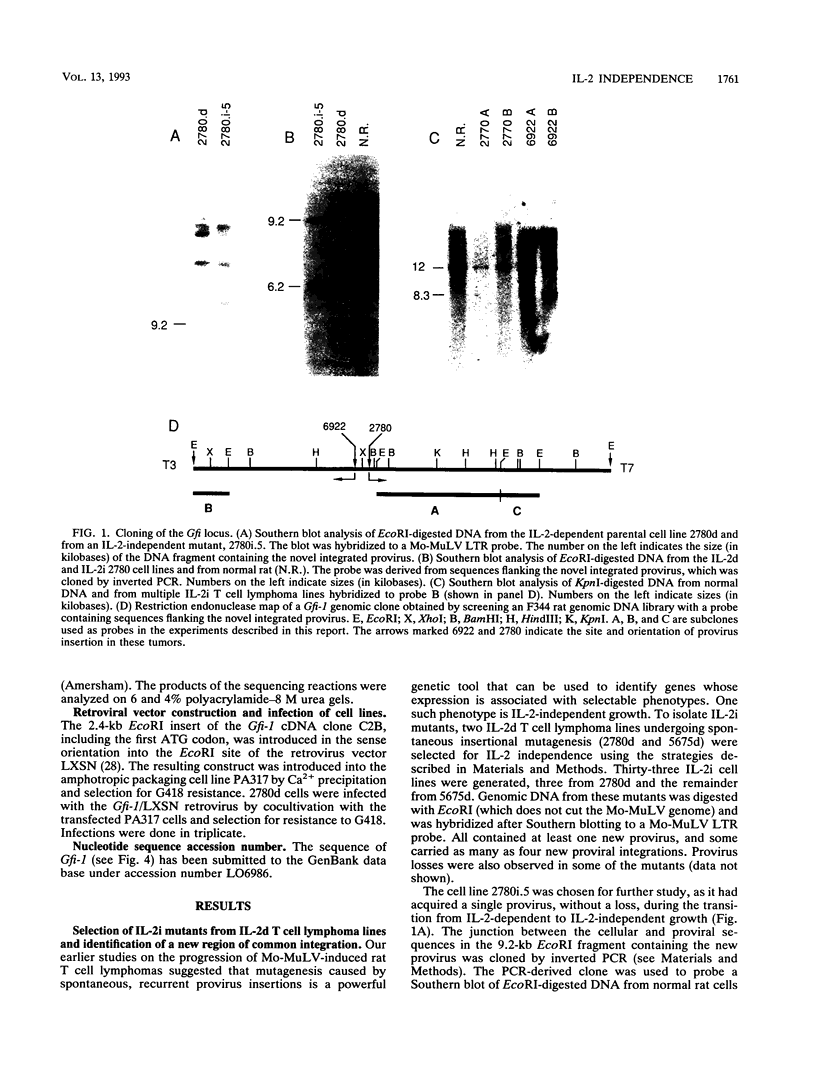
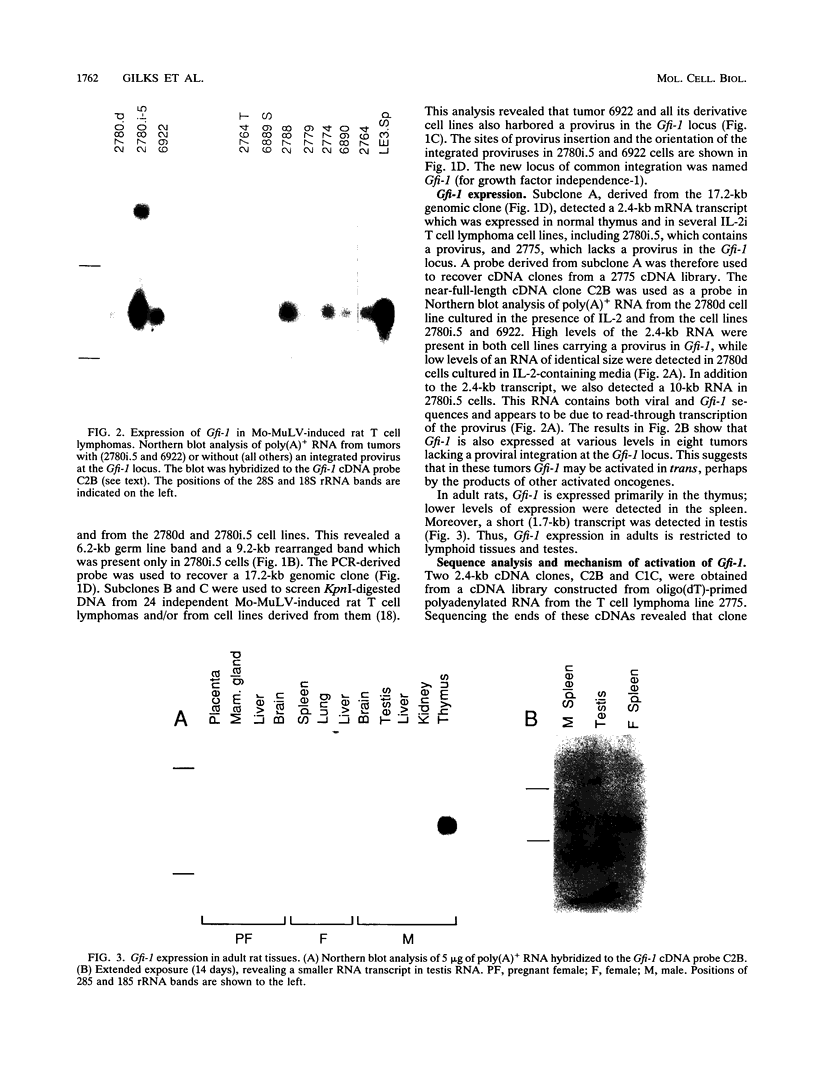
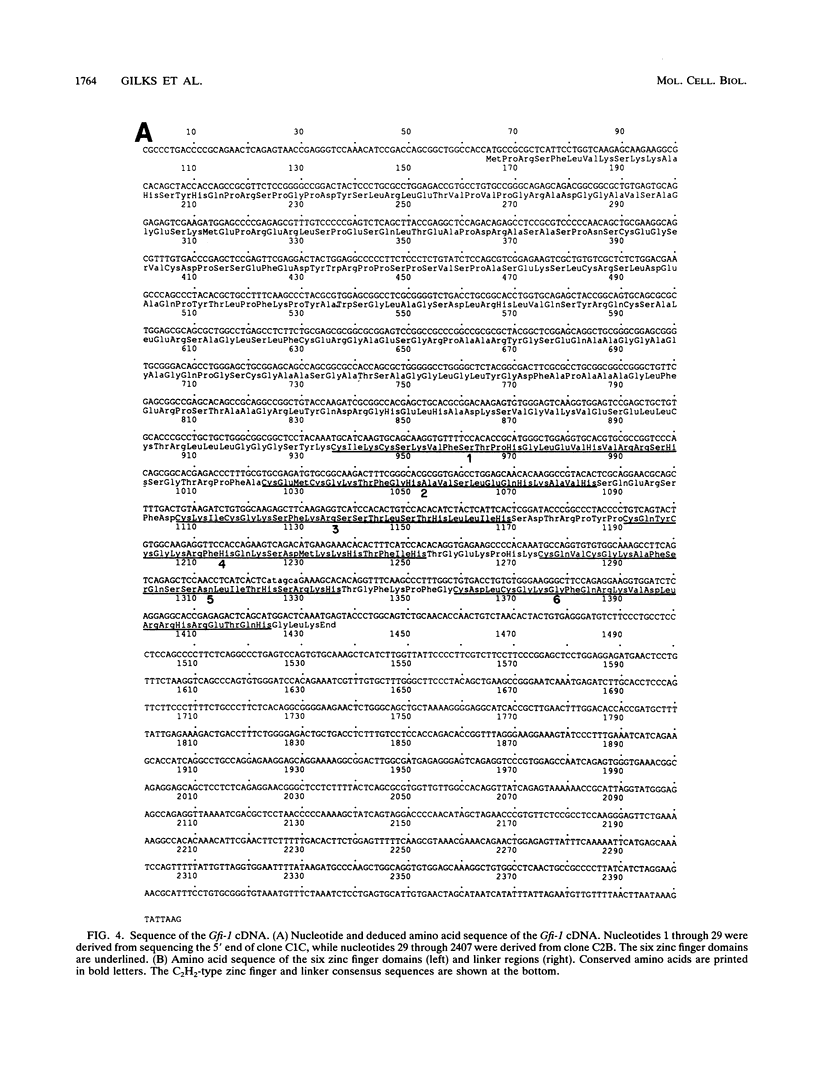
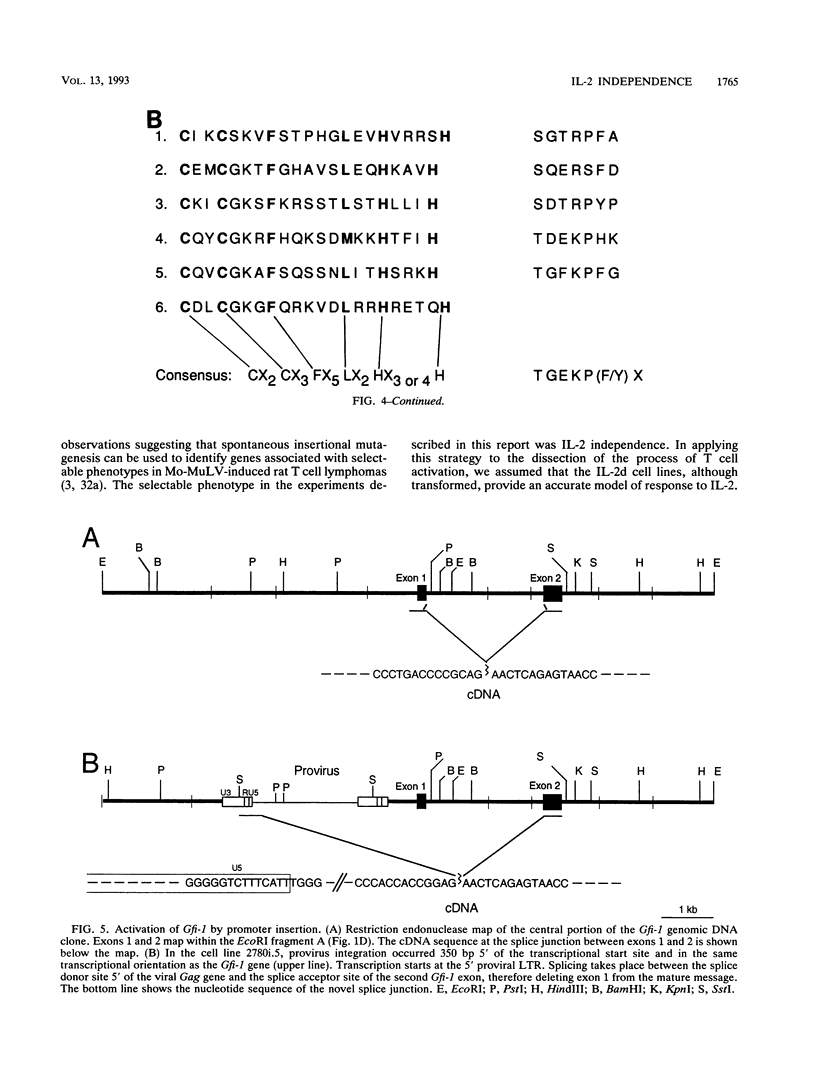
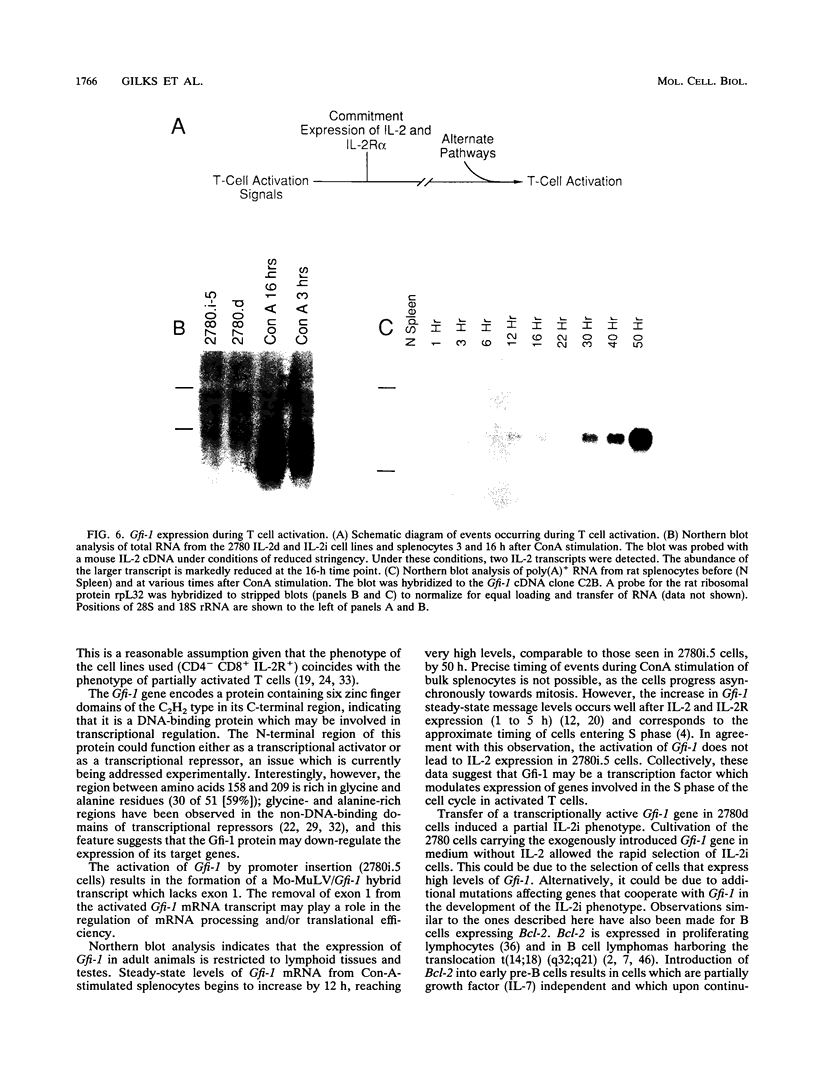
During progression of Moloney murine leukemia virus (Mo-MuLV)-induced rat T cell lymphomas, growth selection results in the expansion of cell clones carrying increasing numbers of integrated proviruses. These new provirus insertions reproducibly contribute to enhanced growth, allowing the emergence of cell clones from the initially heterogeneous population of tumor cells. The Mo-MuLV-induced rat T cell lymphoma lines 2780d and 5675d, which are dependent on interleukin-2 (IL-2) for growth in culture (IL-2d), were placed in IL-2-free medium to select for IL-2-independent (IL-2i) mutants. Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from these mutants, which was hybridized to a Mo-MuLV long terminal repeat probe, revealed that all mutants carried new provirus insertions (from one to four new proviruses per cell line). A locus of integration identified through cloning of the single new provirus detected in one of the IL-2i mutants, 2780i.5, was found to be the target of provirus insertion in 1 additional IL-2i cell line of 24 tested. A full-length cDNA of a gene (growth factor independence-1 [Gfi-1]) activated by promoter insertion in the 2780i.5 cells was cloned and shown to encode a novel zinc finger protein. Gfi-1 is expressed at low levels in IL-2d cell lines cultured in IL-2-containing medium and at high levels in most IL-2i cell lines, including the two harboring a provirus at this locus. Gfi-1 expression in adult animals is restricted to the thymus, spleen, and testis. In mitogen-stimulated splenocytes, Gfi-1 expression begins to rise at 12 h after stimulation and reaches very high levels after 50 h, suggesting that it may be functionally involved in events occurring after the interaction of IL-2 with its receptor, perhaps during the transition from the G1 to the S phase of the cell cycle. In agreement with this, Gfi-1 does not induce the expression of IL-2. Expression of Gfi-1 in 2780d cells following transfer of a Gfi-1/LXSN retrovirus construct contributes to the emergence of the IL-2i phenotype.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman A., Coggeshall K. M., Mustelin T. Molecular events mediating T cell activation. Adv Immunol. 1990;48:227–360. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshi A., Jensen J. P., Goldman P., Wright J. J., McBride O. W., Epstein A. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Cloning the chromosomal breakpoint of t(14;18) human lymphomas: clustering around JH on chromosome 14 and near a transcriptional unit on 18. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):899–906. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear S. E., Bellacosa A., Lazo P. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Hanson C., Levan G., Tsichlis P. N. Provirus insertion in Tpl-1, an Ets-1-related oncogene, is associated with tumor progression in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced rat thymic lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7495–7499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betel I., Martijnse J., van der Westen G. Mitogenic activation and proliferation of mouse thymocytes. Comparison between isotope incorporation and flow-microfluorometry. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Dec;124(2):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borzillo G. V., Endo K., Tsujimoto Y. Bcl-2 confers growth and survival advantage to interleukin 7-dependent early pre-B cells which become factor independent by a multistep process in culture. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):869–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Sklar J. Nucleotide sequence of a t(14;18) chromosomal breakpoint in follicular lymphoma and demonstration of a breakpoint-cluster region near a transcriptionally active locus on chromosome 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7439–7443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R. Contingent genetic regulatory events in T lymphocyte activation. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):355–361. doi: 10.1126/science.2783497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Carney D. N., Bunn P. A., Russell E. K., Jaffe E. S., Schechter G. P., Guccion J. G. Mitogen requirements for the in vitro propagation of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Watson J. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. V. Identification of an interleukin 2-producing human leukemia T cell line. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1709–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Leonard W. J., Wano Y., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. Trans-activator gene of HTLV-II induces IL-2 receptor and IL-2 cellular gene expression. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3010456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. Purification and fractionation of poly(A)+ RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:254–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanellopoulos J. M., De Petris S., Leca G., Crumpton M. J. The mitogenic lectin from Phaseolus vulgaris does not recognize the T3 antigen of human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1985 May;15(5):479–486. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. A., Klein-Szanto A. J., Tsichlis P. N. T-cell lymphoma lines derived from rat thymomas induced by Moloney murine leukemia virus: phenotypic diversity and its implications. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3948–3959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3948-3959.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Truneh A., Smith M. F., Jr, Tsang K. Y. Induction of interleukin 2 receptor (TAC) by tumor necrosis factor in YT cells. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1935–1938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Peffer N. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 receptor gene expression in normal human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6281–6285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Lai C. F., Sigman D. S., Gaynor R. B. Cloning of a cellular factor, interleukin binding factor, that binds to NFAT-like motifs in the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7739–7743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Grossel M. J., Figge J., Hansen U. M. Drosophila Krüppel protein is a transcriptional repressor. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):76–79. doi: 10.1038/346076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipes M. A., Napolitano M., Jeang K. T., Chang N. T., Leonard W. J. Identification, cloning, and characterization of an immune activation gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9704–9708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loughnan M. S., Takatsu K., Harada N., Nossal G. J. T-cell-replacing factor (interleukin 5) induces expression of interleukin 2 receptors on murine splenic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5399–5403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger B., Weiss A., Weyand C., Goronzy J., Stobo J. D. T cell activation: differences in the signals required for IL 2 production by nonactivated and activated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3669–3673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hodgdon J. C., Hussey R. E., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Antigen-like effects of monoclonal antibodies directed at receptors on human T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):988–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Buttimore C. Redesign of retrovirus packaging cell lines to avoid recombination leading to helper virus production. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monuki E. S., Kuhn R., Weinmaster G., Trapp B. D., Lemke G. Expression and activity of the POU transcription factor SCIP. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.1975954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. Mechanisms of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2203–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahwa R., Chatila T., Pahwa S., Paradise C., Day N. K., Geha R., Schwartz S. A., Slade H., Oyaizu N., Good R. A. Recombinant interleukin 2 therapy in severe combined immunodeficiency disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaetinck G., Declercq W., Tavernier J., Nabholz M., Fiers W. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor can induce interleukin 2 receptor expression and cytolytic activity in a rat x mouse T cell hybrid. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1835–1838. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Mier J. W., Woods A. M., Gallo R. C. T-cell lines established from human T-lymphocytic neoplasias by direct response to T-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6815–6819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Alpers J. D., Nowell P. C., Hoover R. G. Sequential expression of protooncogenes during lectin-stimulated mitogenesis of normal human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Tsujimoto Y., Alpers J. D., Croce C. M., Nowell P. C. Regulation of bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression during normal human lymphocyte proliferation. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1295–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.3495884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Mizel S. B. Signal requirements for T lymphocyte activation. I. Replacement of macrophage function with phorbol myristic acetate. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1749–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma P. S., Gruber J. Human T-cell lymphotropic viruses in human diseases. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jul 4;82(13):1100–1106. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.13.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Guimezanes A., Boyer C., Poenie M., Tsien R., Buferne M., Hua C., Leserman L. Pleiotropic loss of activation pathways in a T-cell receptor alpha-chain deletion variant of a cytolytic T-cell clone. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):628–631. doi: 10.1038/325628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorle H., Holtschke T., Hünig T., Schimpl A., Horak I. Development and function of T cells in mice rendered interleukin-2 deficient by gene targeting. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):621–624. doi: 10.1038/352621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1169–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.3131876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukumar S., Carney W. P., Barbacid M. Independent molecular pathways in initiation and loss of hormone responsiveness of breast carcinomas. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):524–526. doi: 10.1126/science.3282307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Lohse M. A. Concerted DNA rearrangements in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymomas: a potential synergistic relationship in oncogenesis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.258-267.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Landgraf B., Bentin J., Valentine M., Lotz M., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Activation of resting T lymphocytes by anti-CD3 (T3) antibodies in the absence of monocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1719–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Cossman J., Jaffe E., Croce C. M. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1440–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.3874430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman K. S., Northrop J. P., Verweij C. L., Crabtree G. R. Transmission of signals from the T lymphocyte antigen receptor to the genes responsible for cell proliferation and immune function: the missing link. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:421–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., De Mey J. R., Goossens J. G. OKT3: a monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibody with potent mitogenic properties. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg K., Parkman R. Severe combined immunodeficiency due to a specific defect in the production of interleukin-2. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 14;322(24):1718–1723. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006143222406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Stobo J. D. Requirement for the coexpression of T3 and the T cell antigen receptor on a malignant human T cell line. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1284–1299. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Wiskocil R. L., Stobo J. D. The role of T3 surface molecules in the activation of human T cells: a two-stimulus requirement for IL 2 production reflects events occurring at a pre-translational level. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. M., Deloria D., Hansen J. A., Dinarello C. A., Loertscher R., Shapiro H. M., Strom T. B. The events of primary T cell activation can be staged by use of Sepharose-bound anti-T3 (64.1) monoclonal antibody and purified interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2249–2255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Weiss A., Imboden J., Kamin-Lewis R., Stobo J. Activation of a human T cell line: a two-stimulus requirement in the pretranslational events involved in the coordinate expression of interleukin 2 and gamma-interferon genes. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1599–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]