Abstract
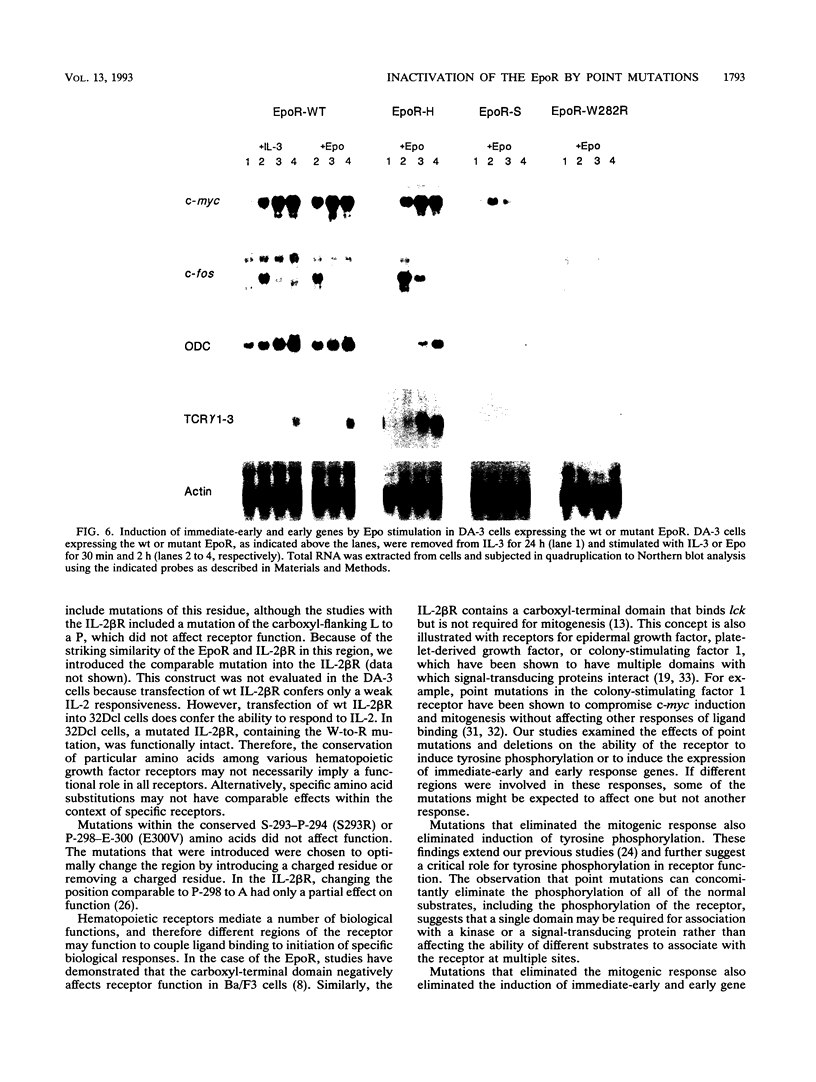
The cytoplasmic domain of the erythropoietin receptor (EpoR) contains a region, proximal to the transmembrane domain, that is essential for function and has homology with other members of the cytokine receptor family. To explore the functional significance of this region and to identify critical residues, we introduced several amino acid substitutions and examined their effects on erythropoietin-induced mitogenesis, tyrosine phosphorylation, and expression of immediate-early (c-fos, c-myc, and egr-1) and early (ornithine decarboxylase and T-cell receptor gamma) genes in interleukin-3-dependent cell lines. Amino acid substitution of W-282, which is strictly conserved at the middle portion of the homology region, completely abolished all the functions of the EpoR. Point mutation at L-306 or E-307, both of which are in a conserved LEVL motif, drastically impaired the function of the receptor in all assays. Other point mutations, introduced into less conserved amino acid residues, did not significantly impair the function of the receptor. These results demonstrate that conserved amino acid residues in this domain of the EpoR are required for mitogenesis, stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation, and induction of immediate-early and early genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askew D. S., Ashmun R. A., Simmons B. C., Cleveland J. L. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. A novel family of growth factor receptors: a common binding domain in the growth hormone, prolactin, erythropoietin and IL-6 receptors, and the p75 IL-2 receptor beta-chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):788–795. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91528-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. C., Kamen R. The human hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1229–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3296190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland J. L., Dean M., Rosenberg N., Wang J. Y., Rapp U. R. Tyrosine kinase oncogenes abrogate interleukin-3 dependence of murine myeloid cells through signaling pathways involving c-myc: conditional regulation of c-myc transcription by temperature-sensitive v-abl. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5685–5695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conscience J. F., Verrier B., Martin G. Interleukin-3-dependent expression of the c-myc and c-fos proto-oncogenes in hemopoietic cell lines. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):317–323. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D., Lyman S. D., Idzerda R. L., Beckmann M. P., Park L. S., Goodwin R. G., March C. J. A new cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90051-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Lodish H. F., Wong G. G. Expression cloning of the murine erythropoietin receptor. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Yoshimura A., Youssoufian H., Zon L. I., Koo J. W., Lodish H. F. The cytoplasmic region of the erythropoietin receptor contains nonoverlapping positive and negative growth-regulatory domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1980–1987. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Cleveland J. L., Rapp U. R., Ihle J. N. Role of myc in the abrogation of IL3 dependence of myeloid FDC-P1 cells. Oncogene Res. 1987 Aug;1(3):279–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Plaetinck G., Van der Heyden J., Cornelis S., Vandekerckhove J., Fiers W., Tavernier J. Molecular basis of a high affinity murine interleukin-5 receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2133–2137. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07747.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga R., Ishizaka-Ikeda E., Pan C. X., Seto Y., Nagata S. Functional domains of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2855–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Kawahara A., Mori H., Shibuya H., Taniguchi T. c-fos gene induction by interleukin 2: identification of the critical cytoplasmic regions within the interleukin 2 receptor beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2022–2026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Kono T., Kobayashi N., Kawahara A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Taniguchi T. Interaction of the IL-2 receptor with the src-family kinase p56lck: identification of novel intermolecular association. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1523–1528. doi: 10.1126/science.2047859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Mori H., Doi T., Taniguchi T. A restricted cytoplasmic region of IL-2 receptor beta chain is essential for growth signal transduction but not for ligand binding and internalization. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90607-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Gress R. E., Lucas P. J., Horak E. M., Waldmann T. A., Bolen J. B. T-lymphocyte interleukin 2-dependent tyrosine protein kinase signal transduction involves the activation of p56lck. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipreos E. T., Wang J. Y. Reversible dependence on growth factor interleukin-3 in myeloid cells expressing temperature sensitive v-abl oncogene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Feb;2(3):277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Doi T., Yamada G., Hatakeyama M., Minamoto S., Tsudo M., Miyasaka M., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Murine interleukin 2 receptor beta chain: dysregulated gene expression in lymphoma line EL-4 caused by a promoter insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1806–1810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey-Prevot B., Nabel G., Palacios R., Baltimore D. Abelson virus abrogation of interleukin-3 dependence in a lymphoid cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4133–4135. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The molecular control of cell division, differentiation commitment and maturation in haemopoietic cells. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):27–30. doi: 10.1038/339027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliaccio G., Migliaccio A. R., Kreider B. L., Rovera G., Adamson J. W. Selection of lineage-restricted cell lines immortalized at different stages of hematopoietic differentiation from the murine cell line 32D. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):833–841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura O., D'Andrea A., Kabat D., Ihle J. N. Induction of tyrosine phosphorylation by the erythropoietin receptor correlates with mitogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4895–4902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T., Maruyama M., Yamada G., Hatakeyama M., Taniguchi T. The integrity of the conserved 'WS motif' common to IL-2 and other cytokine receptors is essential for ligand binding and signal transduction. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3191–3197. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Barsoumian E. L., Hatakeyama M., Taniguchi T. Signal transduction by interleukin 2 receptor beta chain: importance of the structural integrity as revealed by site-directed mutagenesis and generation of chimeric receptors. Int Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(2):149–156. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Narazaki M., Hibi M., Yawata H., Yasukawa K., Hamaguchi M., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Critical cytoplasmic region of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130 is conserved in the cytokine receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11349–11353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. H., Di Fiore P. P., Aaronson S. A., Potter M., Pumphrey J., Scott A., Ihle J. N. Neoplastic transformation of mast cells by Abelson-MuLV: abrogation of IL-3 dependence by a nonautocrine mechanism. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):685–693. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle D. E., Wojchowski D. M. Localized cytosolic domains of the erythropoietin receptor regulate growth signaling and down-modulate responsiveness to granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle F. W., Wojchowski D. M. Proliferative action of erythropoietin is associated with rapid protein tyrosine phosphorylation in responsive B6SUt.EP cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):609–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Cleveland J. L., Shurtleff S. A., Sherr C. J. Myc rescue of a mutant CSF-1 receptor impaired in mitogenic signalling. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):361–363. doi: 10.1038/353361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Shurtleff S. A., Downing J. R., Sherr C. J. A point mutation at tyrosine-809 in the human colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor impairs mitogenesis without abrogating tyrosine kinase activity, association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, or induction of c-fos and junB genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6738–6742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein Y., Morishita K., Cleveland J. L., Ihle J. N. Interleukin 3 (IL-3) induces transcription from nonrearranged T cell receptor gamma loci in IL-3-dependent cell lines. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2059–2071. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura A., D'Andrea A. D., Lodish H. F. Friend spleen focus-forming virus glycoprotein gp55 interacts with the erythropoietin receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum and affects receptor metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4139–4143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura A., Lodish H. F. In vitro phosphorylation of the erythropoietin receptor and an associated protein, pp130. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):706–715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon L. I., Moreau J. F., Koo J. W., Mathey-Prevot B., D'Andrea A. D. The erythropoietin receptor transmembrane region is necessary for activation by the Friend spleen focus-forming virus gp55 glycoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2949–2957. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]