Abstract
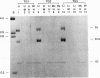
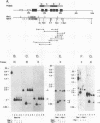
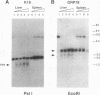
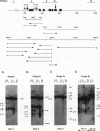
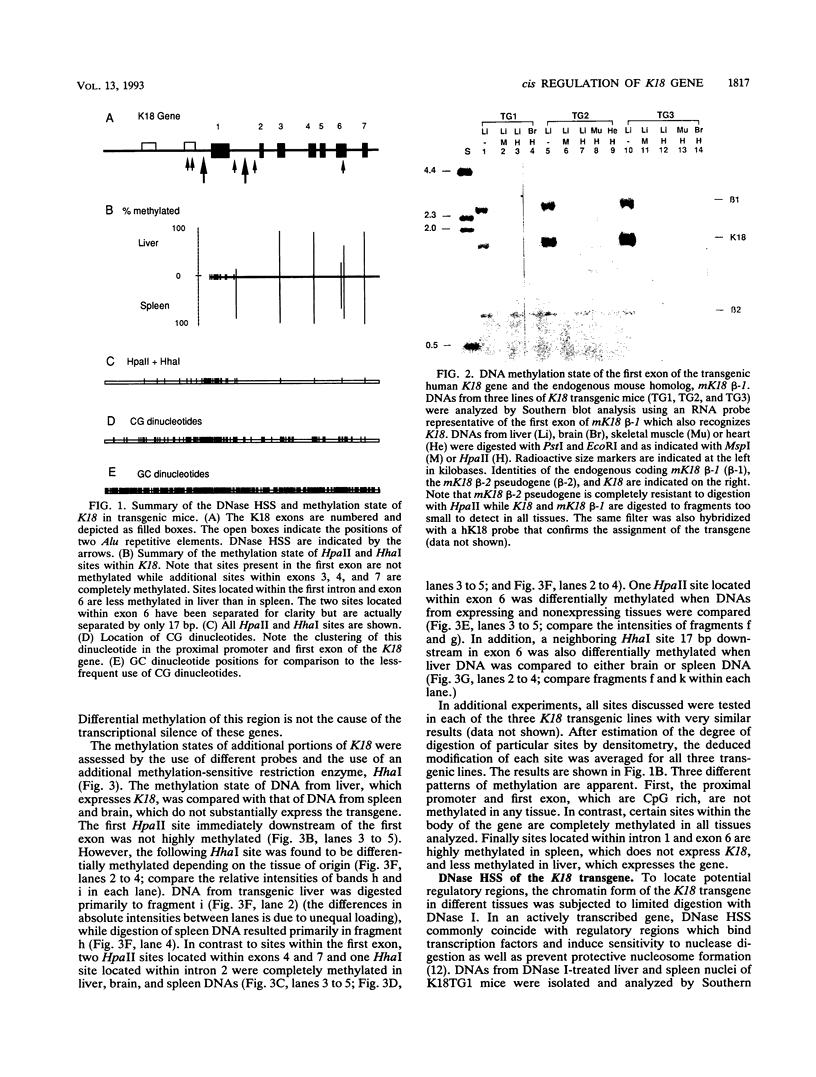
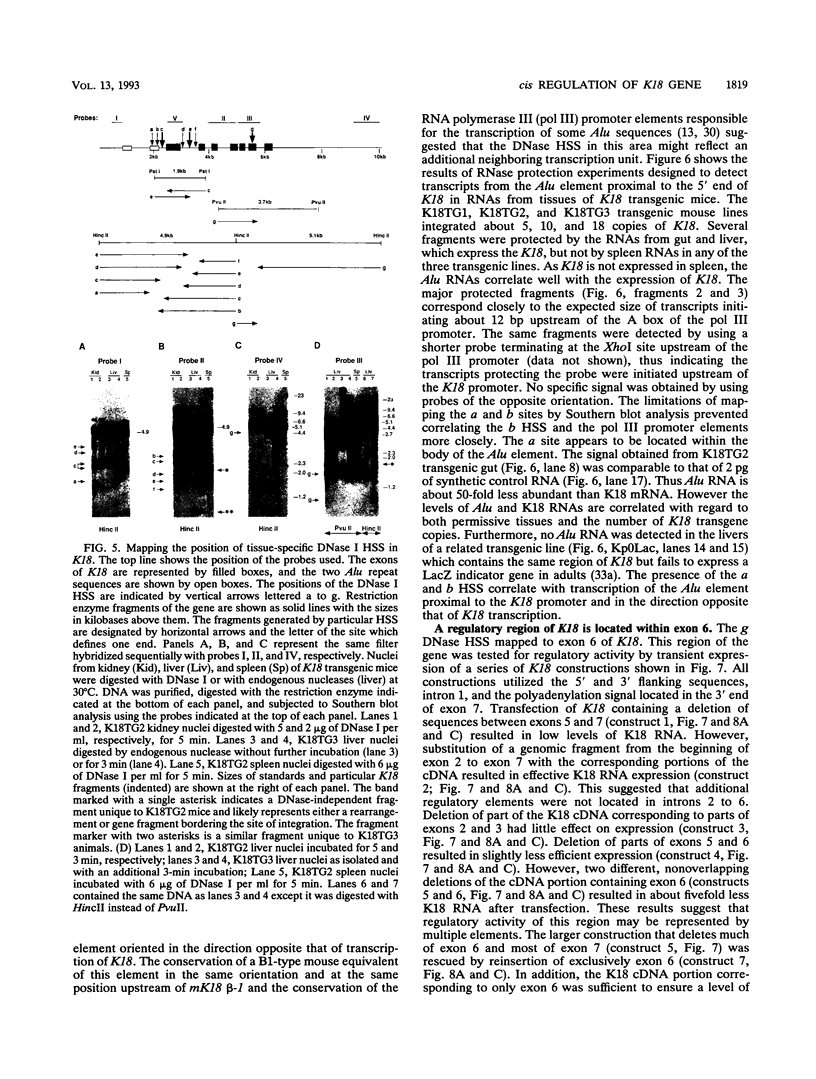
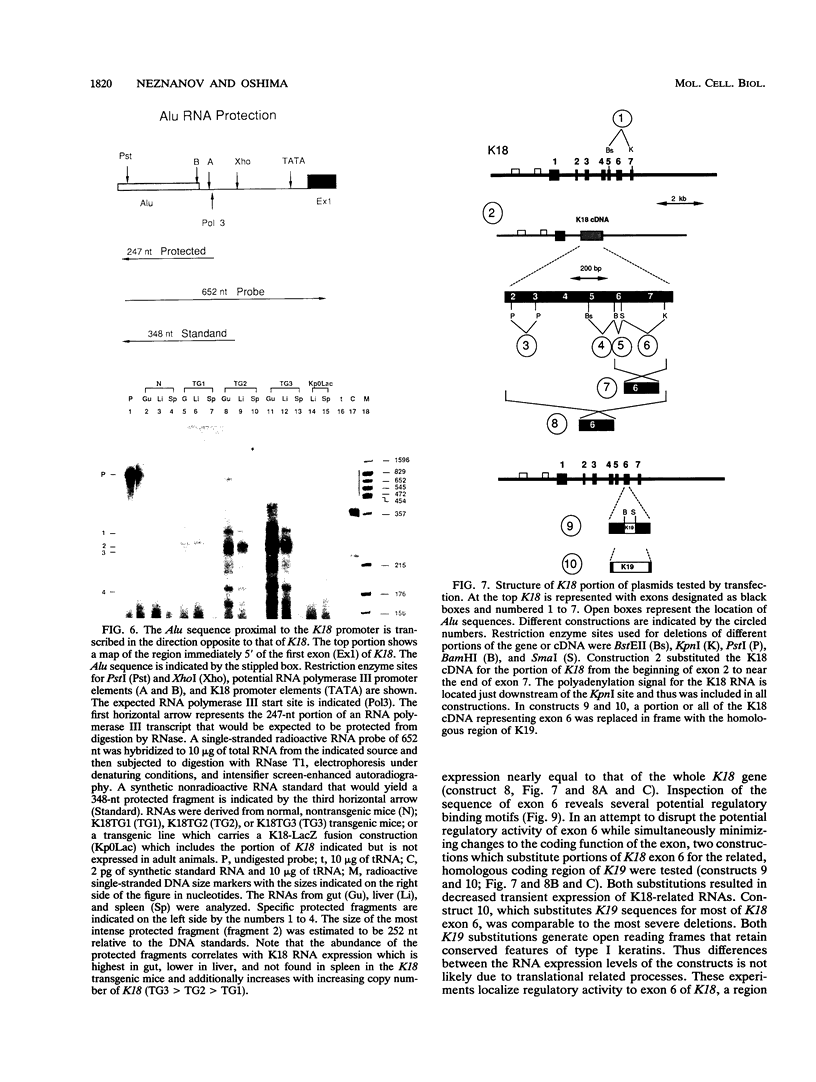
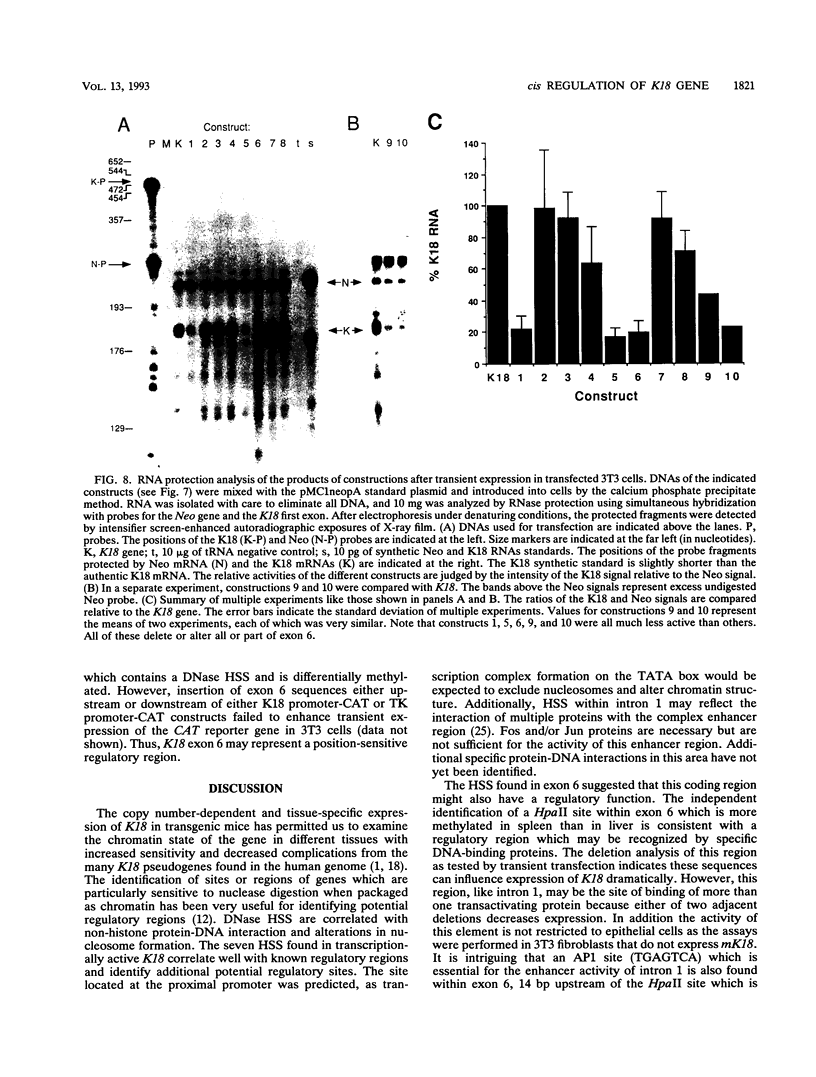
The gene coding for human keratin 18 (K18), a type I intermediate filament protein found in a variety of simple epithelia, is regulated correctly in transgenic mice but is promiscuously expressed after direct transfection into cell culture lines. We have begun an investigation of the mechanisms responsible for the correct regulation of K18 with a comparison of the chromatin state of K18 in permissive and nonpermissive transgenic mouse tissues to identify seven expression-specific, DNase-hypersensitive sites that correlate with known or potential regulatory regions of the gene. Four of these sites are associated with the proximal promoter region and the first intron that has been implicated previously in the transcriptional control of K18. Two hypersensitive sites are associated with a conserved Alu repetitive sequence located immediately upstream of the proximal promoter elements. Transcription of this Alu element in a direction opposite that of K18 was correlated with K18 expression in transgenic tissues. The final hypersensitive site was mapped to exon 6. The potential importance of this region for the expression of K18 was supported by the results of transient expression of the gene and various deleted constructions. In addition, exon 6 and the intron 1 regulatory region were distinguished from the remainder of K18 by differential DNA methylation in expressing and nonexpressing tissues. The CpG-rich proximal promoter and first exon regions remain unmethylated in both permissive and nonpermissive tissues. These results suggest that DNA methylation is not the primary mechanism of control of the gene. An Alu RNA polymerase III transcription unit and exon 6 are implicated in regulation of K18.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe M., Oshima R. G. A single human keratin 18 gene is expressed in diverse epithelial cells of transgenic mice. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1197–1206. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antequera F., Boyes J., Bird A. High levels of de novo methylation and altered chromatin structure at CpG islands in cell lines. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A., Taggart M., Frommer M., Miller O. J., Macleod D. A fraction of the mouse genome that is derived from islands of nonmethylated, CpG-rich DNA. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenberg M. Concerted gene duplications in the two keratin gene families. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(3):203–211. doi: 10.1007/BF02100075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brûlet P., Babinet C., Kemler R., Jacob F. Monoclonal antibodies against trophectoderm-specific markers during mouse blastocyst formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4113–4117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmon M. Co-expression of specific acid and basic cytokeratins in teratocarcinoma-derived fibroblasts treated with 5-azacytidine. Dev Biol. 1985 Jul;110(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Rüther U., Tripodi M., Wagner E. F., Cortese R. Expression of human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein genes in cultured cells and in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):259–266. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Denk H., Kalt R., Schmid E. Biochemical and immunological identification of cytokeratin proteins present in hepatocytes of mammalian liver tissue. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Feb;131(2):299–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko M. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Rhoades D. A., Gajdusek D. C. Monoclonal antibody analysis of keratin expression in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3482–3485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. H., Sakamoto K. Alu interspersed repeats: selfish DNA or a functional gene family? New Biol. 1990 Sep;2(9):759–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson B. W., Grund C., Schmid E., Bürki K., Franke W. W., Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. Intermediate filaments of the cytokeratin type and desmosomes in preimplantation embryos. Differentiation. 1980;17(3):161–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1980.tb01093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Tretjakoff I., Beaudet L., Peterson A. Expression and assembly of a human neurofilament protein in transgenic mice provide a novel neuronal marking system. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1085–1095. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp A. C., Bosch F. X., Hergt M., Kuhn C., Winter-Simanowski S., Schmid E., Regauer S., Bartek J., Franke W. W. Cytokeratins and cytokeratin filaments in subpopulations of cultured human and rodent cells of nonepithelial origin: modes and patterns of formation. Differentiation. 1989 Dec;42(2):81–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesh D. A., Ceceña G., Darmon Y. M., Vasseur M., Oshima R. G. Posttranslational regulation of keratins: degradation of mouse and human keratins 18 and 8. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1553–1565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesh D. A., Oshima R. G. Cloning of the human keratin 18 gene and its expression in nonepithelial mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1540–1550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesh D. A., Oshima R. G. Complete structure of the gene for human keratin 18. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):339–347. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G., Abrams L., Kulesh D. Activation of an intron enhancer within the keratin 18 gene by expression of c-fos and c-jun in undifferentiated F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):835–848. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G. Developmental expression of murine extra-embryonic endodermal cytoskeletal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3414–3421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G., Howe W. E., Klier F. G., Adamson E. D., Shevinsky L. H. Intermediate filament protein synthesis in preimplantation murine embryos. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):447–455. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90294-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G. Identification and immunoprecipitation of cytoskeletal proteins from murine extra-embryonic endodermal cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8124–8133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G. Intermediate filament molecular biology. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90067-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G., Millán J. L., Ceceña G. Comparison of mouse and human keratin 18: a component of intermediate filaments expressed prior to implantation. Differentiation. 1986;33(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G., Trevor K., Shevinsky L. H., Ryder O. A., Ceceña G. Identification of the gene coding for the Endo B murine cytokeratin and its methylated, stable inactive state in mouse nonepithelial cells. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):505–516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfett C. L., Hofbauer R., Brudzynski K., Edwards D. R., Denhardt D. T. Differential screening of a cDNA library with cDNA probes amplified in a heterologous host: isolation of murine GRP78 (BiP) and other serum-regulated low-abundance mRNAs. Gene. 1989 Oct 30;82(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Stable C., Shen C. K. Competitive and cooperative functioning of the anterior and posterior promoter elements of an Alu family repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2041–2052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai Y., Takemoto Y., Matsumoto M., Morita T., Matsushiro A., Nozaki M. Sequence of EndoA gene encoding mouse cytokeratin and its methylation state in the CpG-rich region. Gene. 1991 Aug 15;104(2):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Rosenberg M., Ross S., Tyner A., Fuchs E. Tissue-specific and differentiation-specific expression of a human K14 keratin gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1563–1567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Grindlay G. J., Bushel P., Mendelsohn L., Allan M. Negative regulation of the human epsilon-globin gene by transcriptional interference: role of an Alu repetitive element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1209–1216. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K., Legouy E., Stewart V., Depinho R., Alt F. W. Differential regulation of the N-myc gene in transfected cells and transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2096–2103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]