Abstract
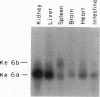
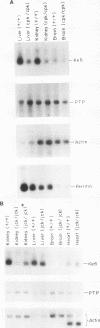
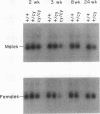
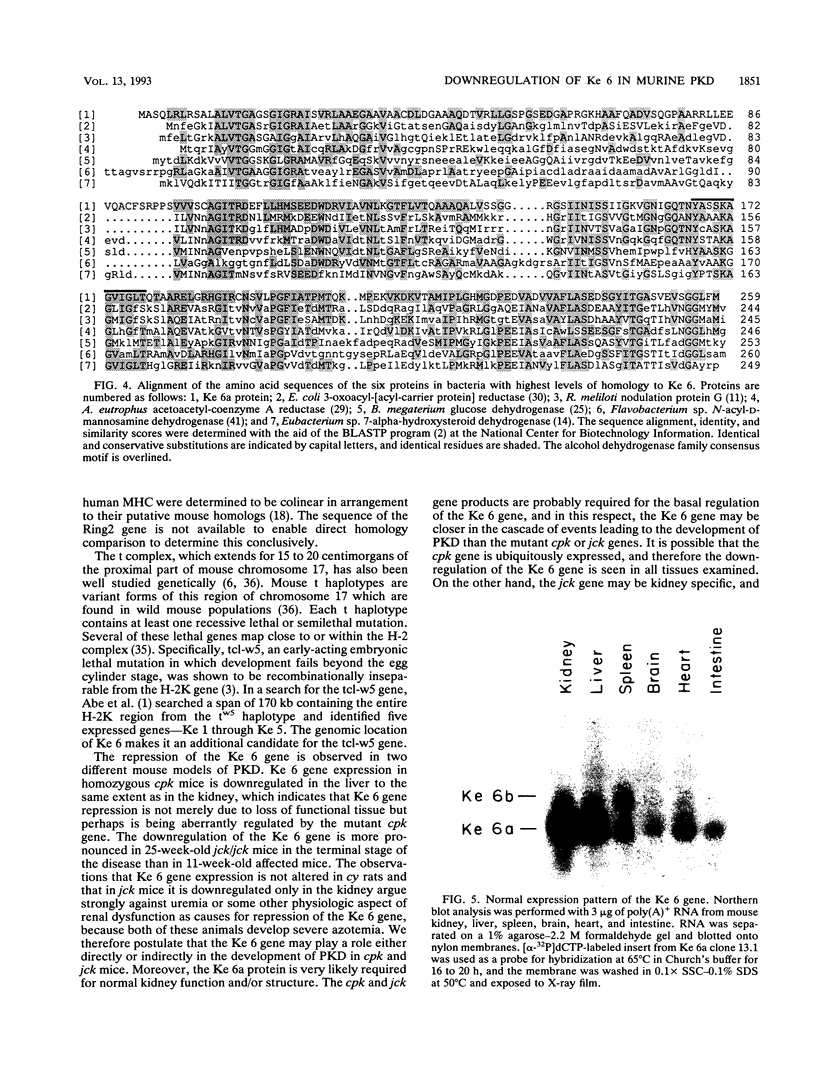
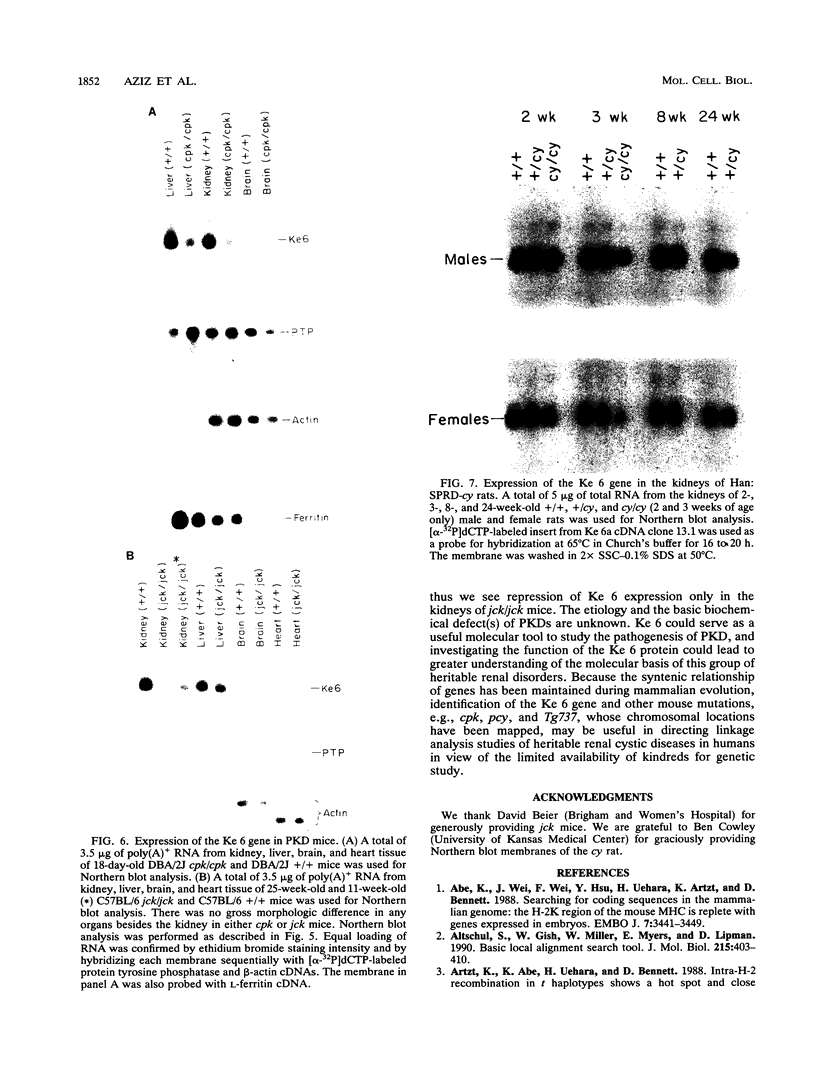
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is characterized by progressive enlargement of the kidneys due to numerous expanding cysts ultimately leading to renal failure. We have identified a gene, Ke 6, located within the H-2K/tw5 region on mouse chromosome 17, which is downregulated in two distinct murine models of heritable PKD. Ke 6 is a member of the short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase family and possess remarkable amino acid sequence conservation with several bacterial proteins with oxidoreductase function. The Ke 6 gene gives rise to two transcripts--a 1-kb Ke 6a mRNA which is abundant in kidney and liver tissue and a 1.4-kb Ke 6b mRNA which is found at a moderate level in spleen tissue. We report here the complete nucleotide sequence of Ke 6a cDNA and the expression of the Ke 6 gene in murine models of PKD. The Ke 6 gene may be intimately involved in the manifestation of these cystic kidney diseases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Wei J. F., Wei F. S., Hsu Y. C., Uehara H., Artzt K., Bennett D. Searching for coding sequences in the mammalian genome: the H-2K region of the mouse MHC is replete with genes expressed in embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3441–3449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. E. Sequence similarity between Pseudomonas dihydrodiol dehydrogenase, part of the gene cluster that metabolizes polychlorinated biphenyls, and dehydrogenases involved in metabolism of ribitol and glucitol and synthesis of antibiotics and 17 beta-oestradiol, testosterone and corticosterone. Biochem J. 1990 May 1;267(3):839–841. doi: 10.1042/bj2670839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davisson M. T., Guay-Woodford L. M., Harris H. W., D'Eustachio P. The mouse polycystic kidney disease mutation (cpk) is located on proximal chromosome 12. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):778–781. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90376-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erba H. P., Eddy R., Shows T., Kedes L., Gunning P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the human gamma-actin gene: differential evolution, location, and expression of the cytoskeletal beta- and gamma-actin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1775–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Swanson J. A., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Extended Region of Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti 1021. II. Nucleotide Sequence, Transcription Start Sites and Protein Products. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):191–201. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry J. L., Jr, Koch W. E., Jennette J. C., McFarland E., Fried F. A., Mandell J. A genetically determined murine model of infantile polycystic kidney disease. J Urol. 1985 Oct;134(4):828–833. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)47448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattone V. H., 2nd, Grantham J. J. Understanding human cystic disease through experimental models. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Nov;11(6):617–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal-Srivastava R., Mallonee D. H., White W. B., Hylemon P. B. Multiple copies of a bile acid-inducible gene in Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4420–4426. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4420-4426.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J. Polycystic kidney disease: neoplasia in disguise. Am J Kidney Dis. 1990 Feb;15(2):110–116. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Haun R. S., Watson S. J., Geahlen R. L., Dixon J. E. Cloning and expression of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson I. M., Poustka A., Trowsdale J. New genes in the class II region of the human major histocompatibility complex. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):417–424. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90327-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson I. M., Trowsdale J. Colinearity of novel genes in the class II regions of the MHC in mouse and human. Immunogenetics. 1991;34(1):5–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00212306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Kakizuka A., Verma I. M. I kappa B gamma, a 70 kd protein identical to the C-terminal half of p110 NF-kappa B: a new member of the I kappa B family. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1109–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90082-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspareit-Rittinghausen J., Rapp K., Deerberg F., Wcislo A., Messow C. Hereditary polycystic kidney disease associated with osteorenal syndrome in rats. Vet Pathol. 1989 May;26(3):195–201. doi: 10.1177/030098588902600302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A., Powis S. H., Glynne R., Radley E., Beck S., Trowsdale J. Second proteasome-related gene in the human MHC class II region. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):667–668. doi: 10.1038/353667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberling W. J., Fain P. R., Kenyon J. B., Goldgar D., Sujansky E., Gabow P. A. Linkage heterogeneity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 1988 Oct 6;319(14):913–918. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810063191405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milutinovic J., Fialkow P. J., Rudd T. G., Agodoa L. Y., Phillips L. A., Bryant J. I. Liver cysts in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Med. 1980 May;68(5):741–744. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90266-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N., Linder M. C. Ferritin: structure, biosynthesis, and role in iron metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1978 Apr;58(2):317–396. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Jongeneel C. V., Nedospasov S. A., Lindahl K. F., Steinmetz M. Tumour necrosis factor and lymphotoxin genes map close to H-2D in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):265–267. doi: 10.1038/325265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peoples O. P., Sinskey A. J. Poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Characterization of the genes encoding beta-ketothiolase and acetoacetyl-CoA reductase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15293–15297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings M., Cronan J. E., Jr The gene encoding Escherichia coli acyl carrier protein lies within a cluster of fatty acid biosynthetic genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5751–5754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeders S. T., Breuning M. H., Davies K. E., Nicholls R. D., Jarman A. P., Higgs D. R., Pearson P. L., Weatherall D. J. A highly polymorphic DNA marker linked to adult polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 16. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):542–544. doi: 10.1038/317542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeders S. T. Multilocus polycystic disease. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):235–237. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Nussbaum R., Page D. C. ZFX has a gene structure similar to ZFY, the putative human sex determinant, and escapes X inactivation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1247–1258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin H. S., Bennett D., Artzt K. Gene mapping within the T/t complex of the mouse. IV: The inverted MHC is intermingled with several t-lethal genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):573–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90464-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M. Mouse t haplotypes. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:179–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Jacques B., Han T. H., MacMurray A., Shin H. S. A putative transmembrane protein with histidine-rich charge clusters encoded in the H-2K/tw5 region of mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):138–145. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Calvet J. P., Dittemore-Hoover D., Yoshida K., Grantham J. J., Gattone V. H., 2nd A hereditary model of slowly progressive polycystic kidney disease in the mouse. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Jan;1(7):980–989. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V17980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Ueyama Y., Hibino T., Kuwahara Y., Suzuki S., Hioki K., Tamaoki N. A new mouse model of genetically transmitted polycystic kidney disease. J Urol. 1986 Jun;135(6):1280–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)46074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto-Otake H., Koyama Y., Horiuchi T., Nakano E. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the N-acyl-D-mannosamine dehydrogenase gene from Flavobacterium sp. strain 141-8 in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1418–1422. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1418-1422.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]