Abstract
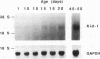
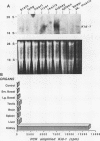
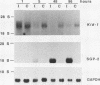
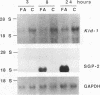
We have identified a new putative transcription factor from the rat kidney, termed Kid-1 (for kidney, ischemia and developmentally regulated gene 1). Kid-1 belongs to the C2H2 class of zinc finger genes. Its mRNA accumulates with age in postnatal renal development and is detected predominantly in the kidney. Kid-1 mRNA levels decline after renal injury secondary to ischemia or folic acid administration, two insults which result in epithelial cell dedifferentiation, followed by regenerative hyperplasia and differentiation. The low expression of Kid-1 early in postnatal development, and when renal tissue is recovering after injury, suggests that the gene product is involved in establishment of a differentiated phenotype and/or regulation of the proliferative response. The deduced protein contains 13 C2H2 zinc fingers at the COOH end in groups of 4 and 9 separated by a 32-amino-acid spacer. There are consensus sites for phosphorylation in the NH2 terminus non-zinc finger region as well as in the spacer region between zinc fingers 4 and 5. A region of the deduced protein shares extensive homology with a catalytic region of Raf kinases, a feature shared only with TFIIE among transcription factors. To determine whether Kid-1 can modulate transcription, a chimeric construct encoding the Kid-1 non-zinc finger region (sense or antisense) and the DNA-binding region of GAL4 was transfected into COS and LLC-PK1 cells together with a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter plasmid containing GAL4 binding sites, driven by either a minimal promoter or a simian virus 40 enhancer. CAT activity was markedly inhibited in cells transfected with the sense construct compared with the activity in cells transfected with the antisense construct. To our knowledge, this pattern of developmental regulation, kidney expression, and regulation of transcription is unique among the C2H2 class of zinc finger-containing DNA-binding proteins.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias J. A., Peterson S. R., Dynan W. S. Promoter-dependent phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by a template-bound kinase. Association with transcriptional initiation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8055–8061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselin C., Marcu K. B. Mode of c-myc gene regulation in folic acid-induced kidney regeneration. Oncogene Res. 1989;5(1):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacallao R., Fine L. G. Molecular events in the organization of renal tubular epithelium: from nephrogenesis to regeneration. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 2):F913–F924. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.6.F913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellefroid E. J., Poncelet D. A., Lecocq P. J., Revelant O., Martial J. A. The evolutionarily conserved Krüppel-associated box domain defines a subfamily of eukaryotic multifingered proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Mechanisms of mRNA decay. Trends Biotechnol. 1990 Jul;8(7):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(90)90167-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M. Determinants of epithelial differentiation during early nephrogenesis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1990 Aug;1(2):127–139. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V12127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. Phosphotransferase sequence homology. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):21–21. doi: 10.1038/329021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call K. M., Glaser T., Ito C. Y., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Rose E. A., Kral A., Yeger H., Lewis W. H. Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at the human chromosome 11 Wilms' tumor locus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90601-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chailler P., Brière N. Integration of proliferation and differentiation phenomena during rodent kidney ontogeny. Growth Dev Aging. 1991 Spring;55(1):11–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe V., Koopman P., McLaren A., Trowsdale J. A mouse zinc finger gene which is transiently expressed during spermatogenesis. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):197–205. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P. Developmentally regulated conversion of mesenchyme to epithelium. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2141–2150. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.10.2666230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M., Henry M., Tange J. D. Experimental folic acid nephropathy. Pathology. 1987 Apr;19(2):143–149. doi: 10.3109/00313028709077125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding M. A., Chadwick L. J., Gattone V. H., 2nd, Calvet J. P. The SGP-2 gene is developmentally regulated in the mouse kidney and abnormally expressed in collecting duct cysts in polycystic kidney disease. Dev Biol. 1991 Aug;146(2):483–490. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hromas R., Collins S. J., Hickstein D., Raskind W., Deaven L. L., O'Hara P., Hagen F. S., Kaushansky K. A retinoic acid-responsive human zinc finger gene, MZF-1, preferentially expressed in myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14183–14187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S. W., Weitzner G., Rozen R., Scriver C. R. A rapid procedure for extracting genomic DNA from leukocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):408–408. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Ptashne M. GAL4 activates gene expression in mammalian cells. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90504-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):414–420. doi: 10.1126/science.1862343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroczek R. A., Siebert E. Optimization of northern analysis by vacuum-blotting, RNA-transfer visualization, and ultraviolet fixation. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jan;184(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in hepatocytes: a window on development. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):427–430. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90169-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitoris B. A., Hoilien C. A., Dahl R., Ahnen D. J., Wilson P. D., Kim J. Characterization of ischemia-induced loss of epithelial polarity. J Membr Biol. 1988 Dec;106(3):233–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01872161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Hage C., Thoenes W. Expression of intermediate filament proteins in fetal and adult human kidney: modulations of intermediate filament patterns during development and in damaged tissue. Lab Invest. 1991 Jul;65(1):74–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugrauer G., Alt F. W., Ekblom P. N-myc proto-oncogene expression during organogenesis in the developing mouse as revealed by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1325–1335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugrauer G., Ekblom P. Contrasting expression patterns of three members of the myc family of protooncogenes in the developing and adult mouse kidney. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):13–25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette A. J., Malt R. A., Sukhatme V. P., Bonventre J. V. Expression of two "immediate early" genes, Egr-1 and c-fos, in response to renal ischemia and during compensatory renal hypertrophy in mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):766–771. doi: 10.1172/JCI114502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Inostroza J., Maxon M. E., Flores O., Admon A., Reinberg D., Tjian R. Structure and functional properties of human general transcription factor IIE. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):369–373. doi: 10.1038/354369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinna L. A. Casein kinase 2: an 'eminence grise' in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 24;1054(3):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard-Jones K., Fleming S., Davidson D., Bickmore W., Porteous D., Gosden C., Bard J., Buckler A., Pelletier J., Housman D. The candidate Wilms' tumour gene is involved in genitourinary development. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):194–197. doi: 10.1038/346194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R. Transcriptional repression in eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):192–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. E., Paller M. S. Differential gene expression in the recovery from ischemic renal injury. Kidney Int. 1991 Jun;39(6):1156–1161. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Nussbaum R., Page D. C. ZFX has a gene structure similar to ZFY, the putative human sex determinant, and escapes X inactivation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1247–1258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh R., Aicher W., Gaul U., Côté S., Preiss A., Maier D., Seifert E., Nauber U., Schröder C., Kemler R. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley C. S., Arnaout M. A. The promoter of the CD11b gene directs myeloid-specific and developmentally regulated expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10525–10529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöcker E., Butter D. Die DNS-Synthese in Leber und Niere junger Ratten. Autoardiographische Untersuchungen mit 3H-Thymidin. Experientia. 1968 Jul 15;24(7):704–705. doi: 10.1007/BF02138326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virca G. D., Northemann W., Shiels B. R., Widera G., Broome S. Simplified northern blot hybridization using 5% sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biotechniques. 1990 Apr;8(4):370–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin A., Zhang G., Jones T. W., Jaken S., Stevens J. L. Mechanism of the nephrogenic repair response. Studies on proliferation and vimentin expression after 35S-1,2-dichlorovinyl-L-cysteine nephrotoxicity in vivo and in cultured proximal tubule epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1992 Apr;66(4):474–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. How the messenger got its tail: addition of poly(A) in the nucleus. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90054-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]