Abstract
Human mitochondrial transcription factor A is a 25-kDa protein that binds immediately upstream of the two major mitochondrial promoters, thereby leading to correct and efficient initiation of transcription. Although the nature of yeast mitochondrial promoters is significantly different from that of human promoters, a potential functional homolog of the human transcriptional activator protein has been previously identified in yeast mitochondria. The importance of the yeast protein in yeast mitochondrial DNA function has been shown by inactivation of its nuclear gene (ABF2) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells resulting in loss of mitochondrial DNA. We report here that the nuclear gene for human mitochondrial transcription factor A can be stably expressed in yeast cells devoid of the yeast homolog protein. The human protein is imported efficiently into yeast mitochondria, is processed correctly, and rescues the loss-of-mitochondrial DNA phenotype in a yeast abf2 strain, thus functionally substituting for the yeast protein. Both human and yeast proteins affect yeast mitochondrial transcription initiation in vitro, suggesting that the two proteins may have a common role in this fundamental process.
Full text
PDF
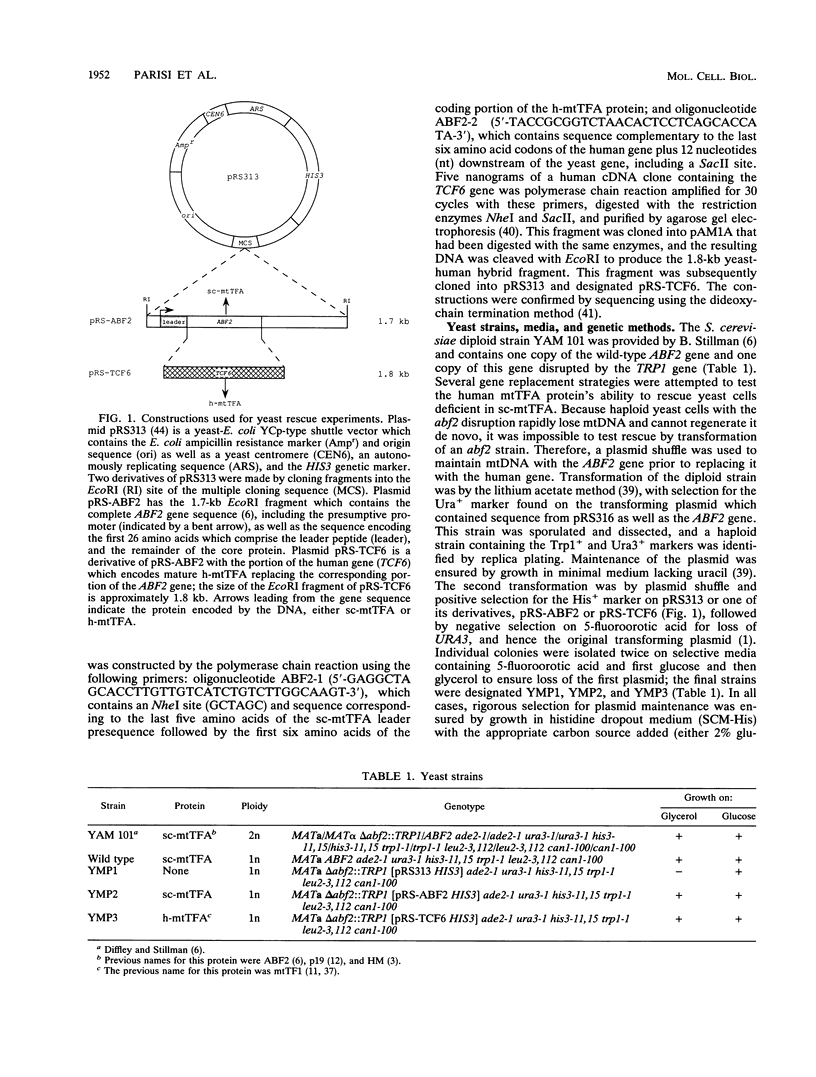









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D., Clayton D. A. The number of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid genomes in mouse L and human HeLa cells. Quantitative isolation of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7991–7995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron F., Jacq C., Rouvière-Yaniv J. Characterization of a histone-like protein extracted from yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4265–4269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Certa U., Colavito-Shepanski M., Grunstein M. Yeast may not contain histone H1: the only known 'histone H1-like' protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a mitochondrial protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):7975–7985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.7975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Replication and transcription of vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:453–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. A close relative of the nuclear, chromosomal high-mobility group protein HMG1 in yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7864–7868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. DNA binding properties of an HMG1-related protein from yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3368–3374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnini C., Artoni N., Marmiroli N. Germination conditions that require mitochondrial function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: utilization of acetate and galactose. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1250–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1250-1253.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangman W. L., Henly J. W., Churchill G., Brewer B. J. Stable maintenance of a 35-base-pair yeast mitochondrial genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1917–1921. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Clayton D. A. A transcription factor required for promoter recognition by human mitochondrial RNA polymerase. Accurate initiation at the heavy- and light-strand promoters dissected and reconstituted in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11330–11338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Clayton D. A. Purification and characterization of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3496–3509. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Lisowsky T., Breen G. A., Clayton D. A. A rapid, efficient method for purifying DNA-binding proteins. Denaturation-renaturation chromatography of human and yeast mitochondrial extracts. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9153–9160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Lisowsky T., Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. DNA wrapping and bending by a mitochondrial high mobility group-like transcriptional activator protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3358–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. Flexible recognition of rapidly evolving promoter sequences by mitochondrial transcription factor 1. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2202–2217. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Topper J. N., Clayton D. A. Promoter selection in human mitochondria involves binding of a transcription factor to orientation-independent upstream regulatory elements. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M. Import of polypeptides into isolated yeast mitochondria. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:329–336. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Amsterdam A., Grosschedl R. DNA-binding properties of the HMG domain of the lymphoid-specific transcriptional regulator LEF-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2567–2578. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley V. R., Jackson D. I., Hextall P. J., Hawkins J. R., Berkovitz G. D., Sockanathan S., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. DNA binding activity of recombinant SRY from normal males and XY females. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):453–456. doi: 10.1126/science.1734522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. H., Jaehning J. A. The yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase specificity factor, MTF1, is similar to bacterial sigma factors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22671–22677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Liu J. F., Wang J. C. Nonhistone proteins HMG1 and HMG2 change the DNA helical structure. Science. 1978 Mar 24;199(4335):1345–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.628842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. V., Walsh M. L., Bockus B. J., Chen L. B. Monitoring of relative mitochondrial membrane potential in living cells by fluorescence microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):526–535. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. V., Walsh M. L., Chen L. B. Localization of mitochondria in living cells with rhodamine 123. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):990–994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. L., Greenleaf A. L., Lehman I. R. Isolation of the nuclear gene encoding a subunit of the yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10348–10351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisowsky T., Michaelis G. A nuclear gene essential for mitochondrial replication suppresses a defect of mitochondrial transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):218–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00337714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmiroli N., Lodi T. Modification of nuclear gene expression by inhibition of mitochondrial translation during sporulation in MAT alpha/MATa diploids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):69–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00328703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters B. S., Stohl L. L., Clayton D. A. Yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase is homologous to those encoded by bacteriophages T3 and T7. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Frazier M. W., Reeder R. H. xUBF contains a novel dimerization domain essential for RNA polymerase I transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1957–1968. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Xie W. Q., Smith S. D., Singer H. A., Rothblum L. I. Differential phosphorylation and localization of the transcription factor UBF in vivo in response to serum deprivation. In vitro dephosphorylation of UBF reduces its transactivation properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. Similarity of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1 to high mobility group proteins. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):965–969. doi: 10.1126/science.2035027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redding K., Holcomb C., Fuller R. S. Immunolocalization of Kex2 protease identifies a putative late Golgi compartment in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):527–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Koerkamp M. J., Touw E. P., Tabak H. F. Specificity factor of yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase. Purification and interaction with core RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12785–12791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Tabak H. F. Mitochondrial RNA polymerase: dual role in transcription and replication. Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. In vitro transcription of human mitochondrial DNA. Identification of specific light strand transcripts from the displacement loop region. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1268–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Fischer W. H., Jones K. A. A thymus-specific member of the HMG protein family regulates the human T cell receptor C alpha enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):656–669. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Fennell D. J. The use of fluorescent DNA-binding agent for detecting and separating yeast mitochondrial DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:335–351. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60963-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Fennell D. J. Visualization of yeast mitochondrial DNA with the fluorescent stain "DAPI". Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:728–733. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu B., Clayton D. A. Assignment of a yeast protein necessary for mitochondrial transcription initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1053–1059. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







