Abstract
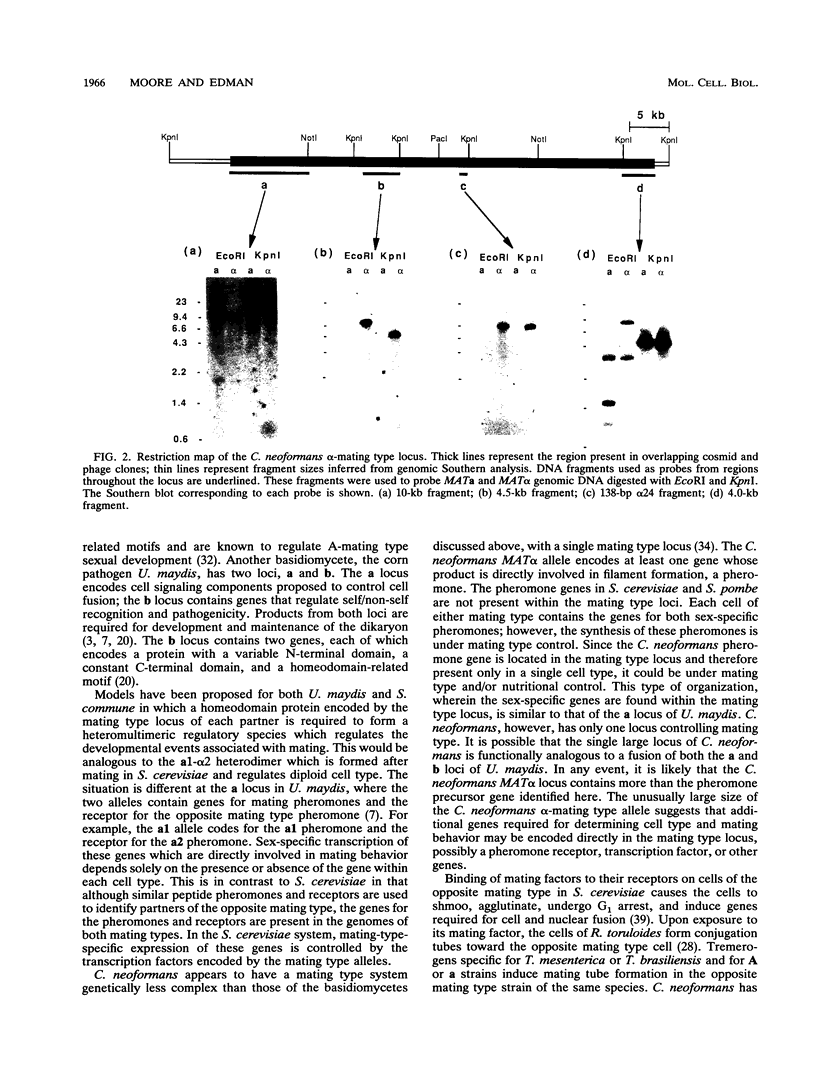
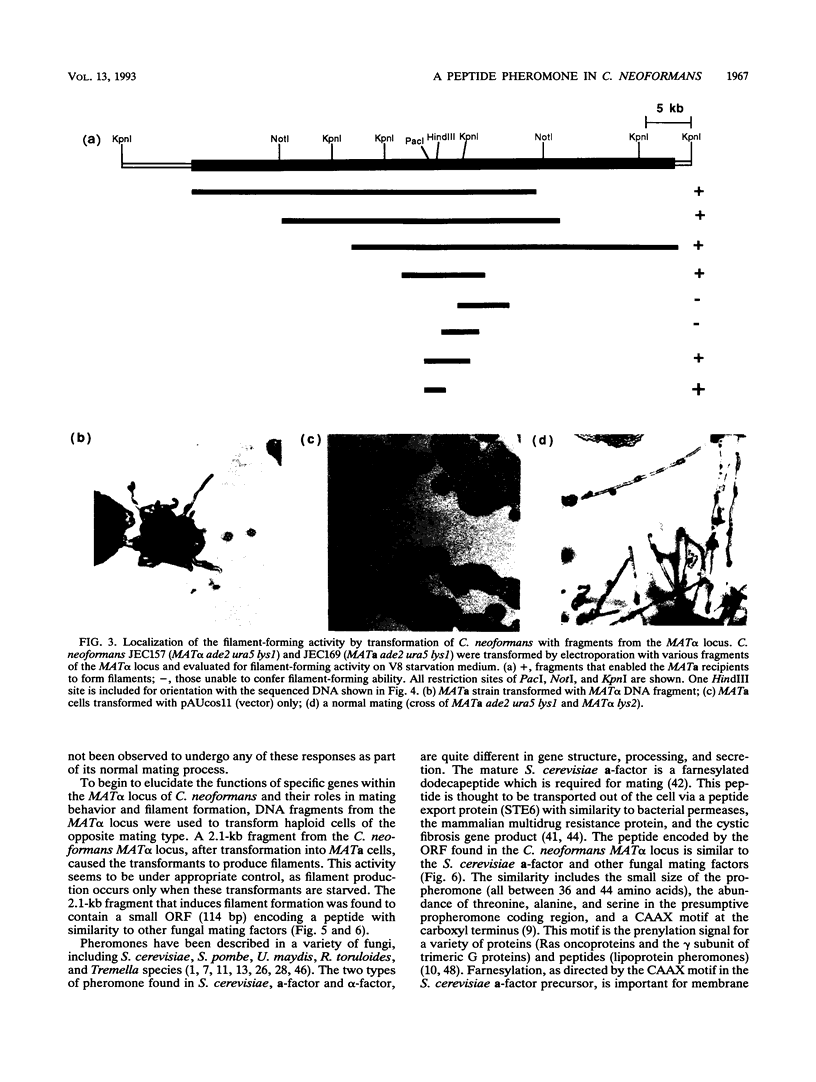
The opportunistic fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans has two mating types, MATa and MAT alpha. The MAT alpha strains are more virulent. Mating of opposite mating type haploid yeast cells results in the production of a filamentous hyphal phase. The MAT alpha locus has been isolated in this study in order to identify the genetic differences between mating types and their contribution to virulence. A 138-bp fragment of MAT alpha-specific DNA which cosegregates with alpha-mating type was isolated by using a difference cloning method. Overlapping phage and cosmid clones spanning the entire MAT alpha locus were isolated by using this MAT alpha-specific fragment as a probe. Mapping of these clones physically defined the MAT alpha locus to a 35- to 45-kb region which is present only in MAT alpha strains. Transformation studies with fragments of the MAT alpha locus identified a 2.1-kb XbaI-HindIII fragment that directs starvation-induced filament formation in MATa cells but not in MAT alpha cells. This 2.1-kb fragment contains a gene, MF alpha, with a small open reading frame encoding a pheromone precursor similar to the lipoprotein mating factors found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Ustilago maydis, and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. The ability of the MATa cells to express, process, and secrete the MAT alpha pheromone in response to starvation suggests similar mechanisms for these processes in both cell types. These results also suggest that the production of pheromone is under a type of nutritional control shared by the two cell types.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Kusaka I., Fukui S. Morphological change in the early stages of the mating process of Rhodosporidium toruloides. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):710–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.710-718.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akada R., Minomi K., Kai J., Yamashita I., Miyakawa T., Fukui S. Multiple genes coding for precursors of rhodotorucine A, a farnesyl peptide mating pheromone of the basidiomycetous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3491–3498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderegg R. J., Betz R., Carr S. A., Crabb J. W., Duntze W. Structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating hormone a-factor. Identification of S-farnesyl cysteine as a structural component. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18236–18240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banuett F. Identification of genes governing filamentous growth and tumor induction by the plant pathogen Ustilago maydis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3922–3926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banuett F. Ustilago maydis, the delightful blight. Trends Genet. 1992 May;8(5):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölker M., Urban M., Kahmann R. The a mating type locus of U. maydis specifies cell signaling components. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90182-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Solski P. A., Der C. J., Buss J. E. p21ras is modified by a farnesyl isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8323–8327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. Protein isoprenylation and methylation at carboxyl-terminal cysteine residues. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:355–386. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J. Mating pheromones of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: purification and structural characterization of M-factor and isolation and analysis of two genes encoding the pheromone. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):951–960. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duntze W., MacKay V., Manney T. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a diffusible sex factor. Science. 1970 Jun 19;168(3938):1472–1473. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3938.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C. Isolation of telomerelike sequences from Cryptococcus neoformans and their use in high-efficiency transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2777–2783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kwon-Chung K. J. Isolation of the URA5 gene from Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformans and its use as a selective marker for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4538–4544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegel T. W. The pheromonal control of mating in yeast and its phylogenetic implication: a review. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Apr;27(4):373–389. doi: 10.1139/m81-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A., Shadomy H. J., Jacobson E. S. Decreased virulence in stable, acapsular mutants of cryptococcus neoformans. Mycopathologia. 1982 Jul 23;79(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00636177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giasson L., Specht C. A., Milgrim C., Novotny C. P., Ullrich R. C. Cloning and comparison of A alpha mating-type alleles of the Basidiomycete Schizophyllum commune. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jul;218(1):72–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00330567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillissen B., Bergemann J., Sandmann C., Schroeer B., Bölker M., Kahmann R. A two-component regulatory system for self/non-self recognition in Ustilago maydis. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):647–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass N. L., Grotelueschen J., Metzenberg R. L. Neurospora crassa A mating-type region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4912–4916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass N. L., Vollmer S. J., Staben C., Grotelueschen J., Metzenberg R. L., Yanofsky C. DNAs of the two mating-type alleles of Neurospora crassa are highly dissimilar. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):570–573. doi: 10.1126/science.2840740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. A regulatory hierarchy for cell specialization in yeast. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):749–757. doi: 10.1038/342749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Fungal physiology. Yeast branches out. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):190–191. doi: 10.1038/357190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Life cycle of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):536–553. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.536-553.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. S., Emery H. S. Catecholamine uptake, melanization, and oxygen toxicity in Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):401–403. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.401-403.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya Y., Sakurai A., Tamura S., Takahashi N. Structure of rhodotorucine A, a novel lipopeptide, inducing mating tube formation in Rhodosporidium toruloides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91505-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Burke J., Smith M., Klar A., Beach D. Four mating-type genes control sexual differentiation in the fission yeast. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1537–1547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Ochs H. D., Latt S. A. Specific cloning of DNA fragments absent from the DNA of a male patient with an X chromosome deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4778–4782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Edman J. C., Wickes B. L. Genetic association of mating types and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):602–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.602-605.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. Morphogenesis of Filobasidiella neoformans, the sexual state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1976 Jul-Aug;68(4):821–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Rhodes J. C. Encapsulation and melanin formation as indicators of virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):218–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.218-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kües U., Casselton L. A. Homeodomains and regulation of sexual development in basidiomycetes. Trends Genet. 1992 May;8(5):154–155. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90207-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kües U., Richardson W. V., Tymon A. M., Mutasa E. S., Göttgens B., Gaubatz S., Gregoriades A., Casselton L. A. The combination of dissimilar alleles of the A alpha and A beta gene complexes, whose proteins contain homeo domain motifs, determines sexual development in the mushroom Coprinus cinereus. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):568–577. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S., Caldwell G. A., Miller D., Xue C. B., Naider F., Becker J. M. Significance of C-terminal cysteine modifications to the biological activity of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae a-factor mating pheromone. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3603–3612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Neiman A. M., Herskowitz I. Signal transduction during pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:699–728. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L. The role of similarity and difference in fungal mating. Genetics. 1990 Jul;125(3):457–462. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Chen P., Berkower C., Sapperstein S., Kistler A. Biogenesis of yeast a-factor involves prenylation, methylation and a novel export mechanism. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1992 Feb;61(2):115–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00580617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Herskowitz I. The a-factor pheromone of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is essential for mating. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1309–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K. The structure of transposable yeast mating type loci. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):753–764. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond M., Gros P., Whiteway M., Thomas D. Y. Functional complementation of yeast ste6 by a mammalian multidrug resistance mdr gene. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):232–234. doi: 10.1126/science.1348873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakagami Y., Yoshida M., Isogai A., Suzuki A. Peptidal Sex Hormones Inducing Conjugation Tube Formation in Compatible Mating-Type Cells of Tremella mesenterica. Science. 1981 Jun 26;212(4502):1525–1527. doi: 10.1126/science.212.4502.1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Kim R., Sterne R., Thorner J., Kim S. H., Rine J. Genetic and pharmacological suppression of oncogenic mutations in ras genes of yeast and humans. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):379–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2569235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Trueblood C. E., Yang C. C., Mayer M. P., Rosenberg S., Poulter C. D., Kim S. H., Rine J. Enzymatic coupling of cholesterol intermediates to a mating pheromone precursor and to the ras protein. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1133–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2204115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Specht C. A., Stankis M. M., Giasson L., Novotny C. P., Ullrich R. C. Functional analysis of the homeodomain-related proteins of the A alpha locus of Schizophyllum commune. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7174–7178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staben C., Yanofsky C. Neurospora crassa a mating-type region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stankis M. M., Specht C. A., Yang H., Giasson L., Ullrich R. C., Novotny C. P. The A alpha mating locus of Schizophyllum commune encodes two dissimilar multiallelic homeodomain proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7169–7173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]