Abstract
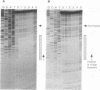
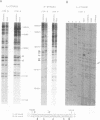
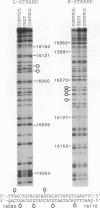
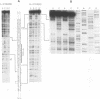
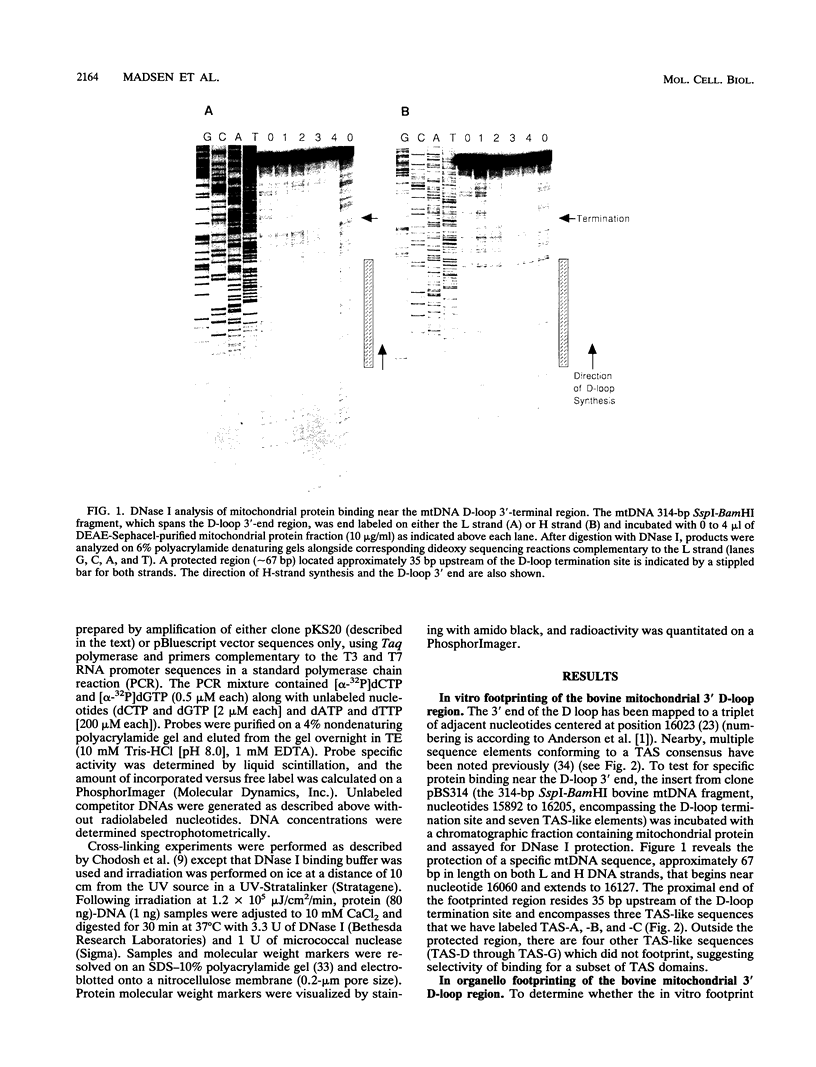
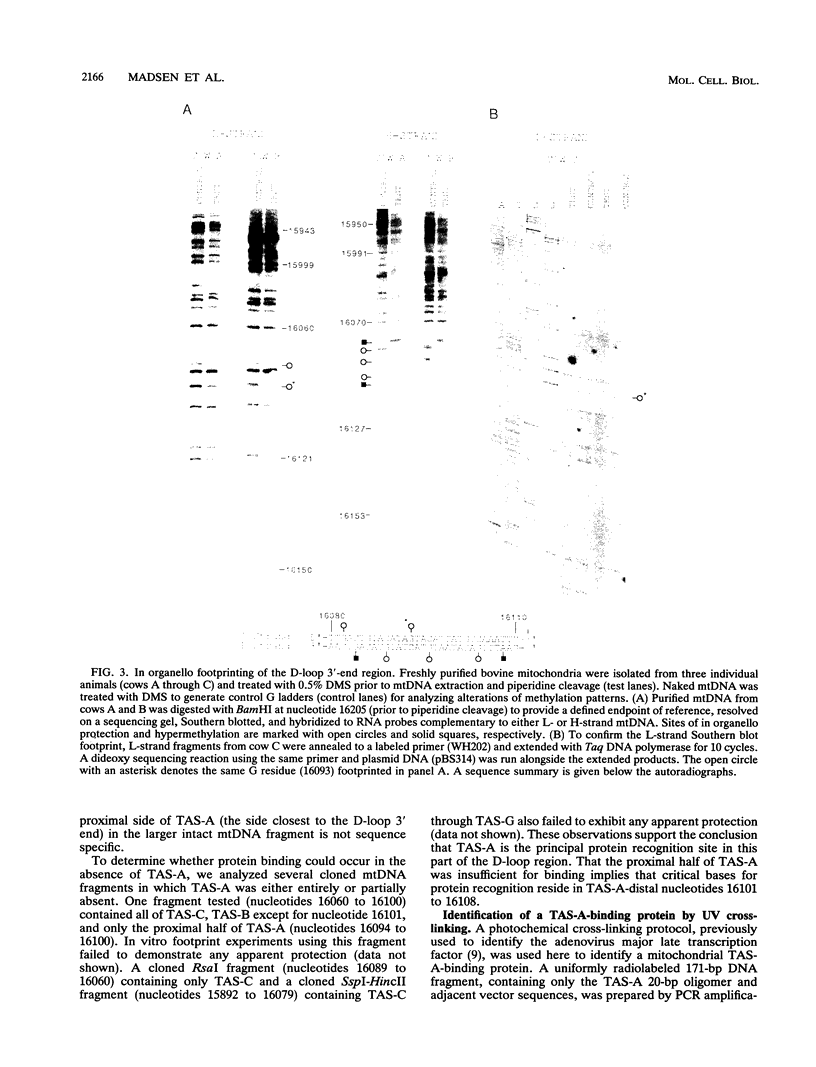
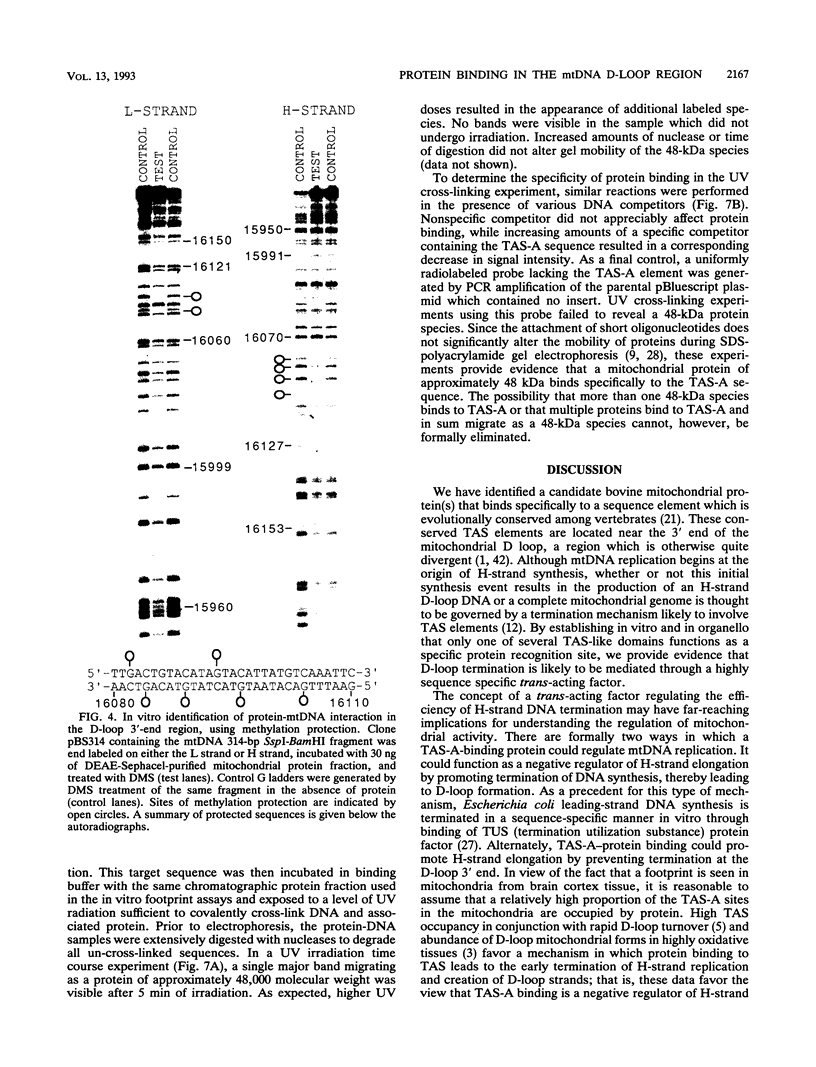
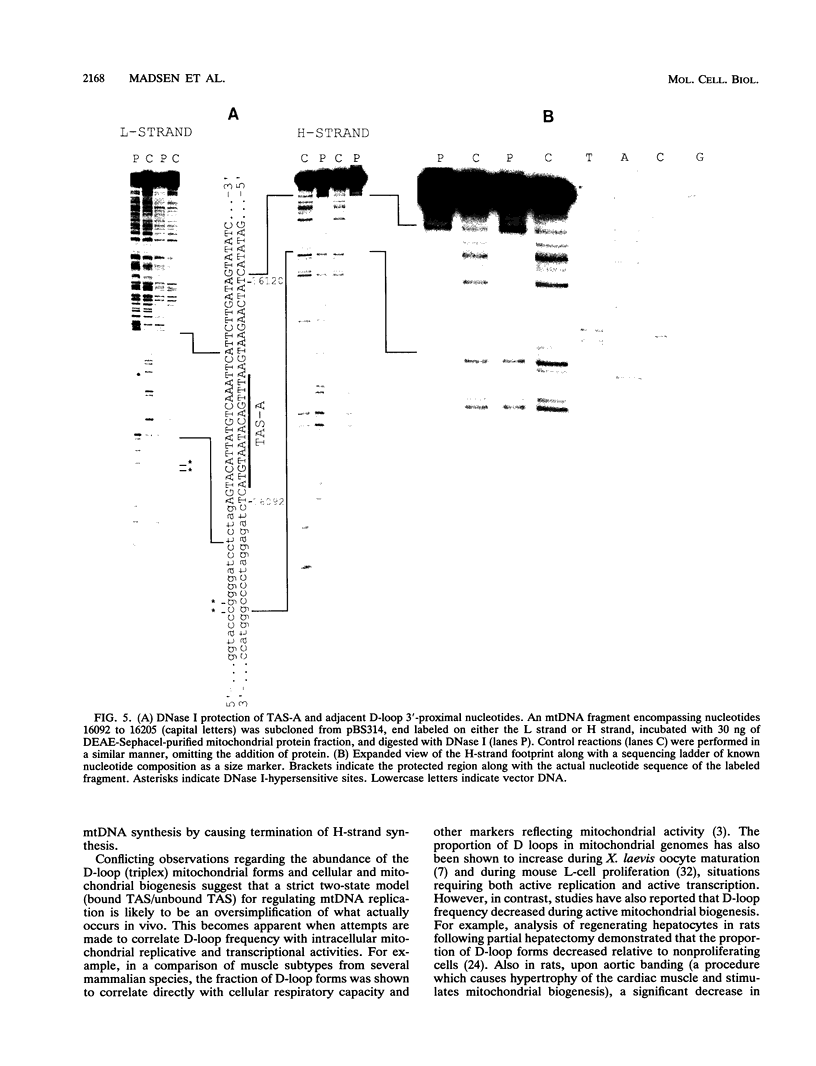
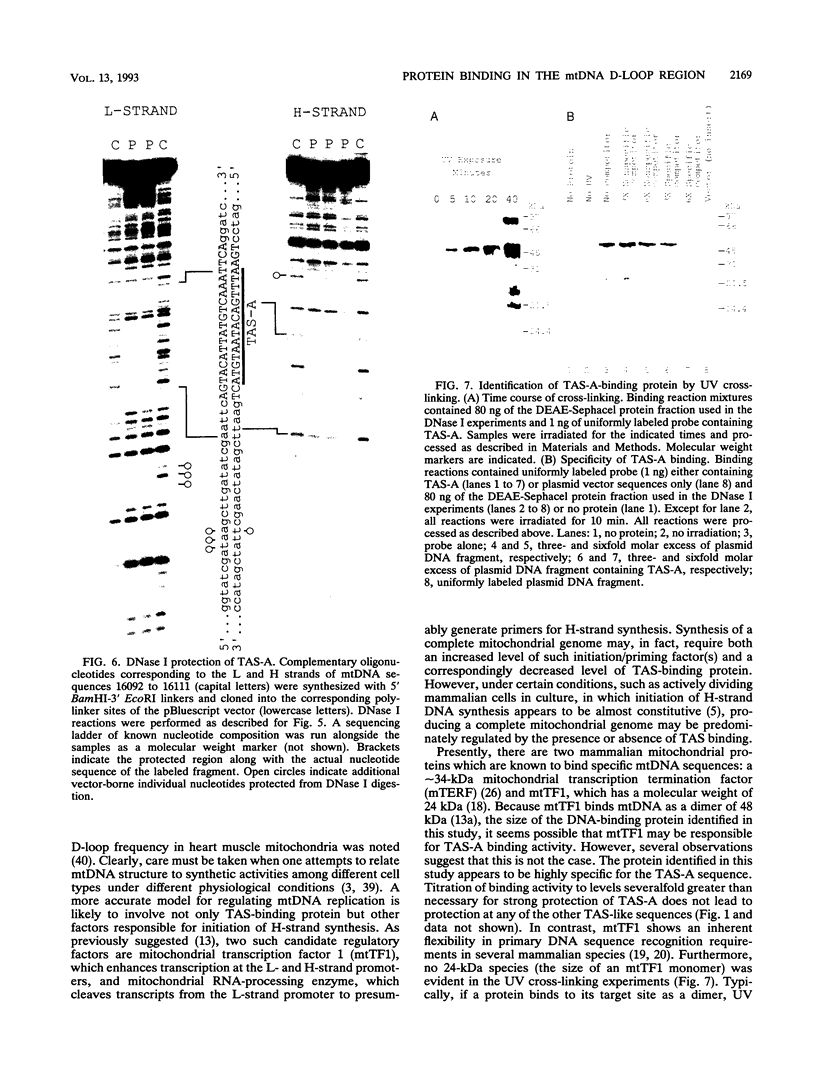
A methylation protection assay was used in a novel manner to demonstrate a specific bovine protein-mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) interaction within the organelle (in organello). The protected domain, located near the D-loop 3' end, encompasses a conserved termination-associated sequence (TAS) element which is thought to be involved in the regulation of mtDNA synthesis. In vitro footprinting studies using a bovine mitochondrial extract and a series of deleted mtDNA templates identified a approximately 48-kDa protein which binds specifically to a single TAS element also protected within the mitochondrion. Because other TAS-like elements located in close proximity to the protected region did not footprint, protein binding appears to be highly sequence specific. The in organello and in vitro data, together, provide evidence that D-loop formation is likely to be mediated, at least in part, through a trans-acting factor binding to a conserved sequence element located 58 bp upstream of the D-loop 3' end.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Eperon I. C., Sanger F., Young I. G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):683–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annex B. H., Kraus W. E., Dohm G. L., Williams R. S. Mitochondrial biogenesis in striated muscles: rapid induction of citrate synthase mRNA by nerve stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):C266–C270. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.2.C266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annex B. H., Williams R. S. Mitochondrial DNA structure and expression in specialized subtypes of mammalian striated muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5671–5678. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of mitochondrial DNA replication in mouse L-cells: kinetics of synthesis and turnover of the initiation sequence. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 15;119(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callen J. C., Tourte M., Dennebouy N., Mounolou J. C. Changes in D-loop frequency and superhelicity among the mitochondrial DNA molecules in relation to organelle biogenesis in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jan;143(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomyn A., Mariottini P., Cleeter M. W., Ragan C. I., Matsuno-Yagi A., Hatefi Y., Doolittle R. F., Attardi G. Six unidentified reading frames of human mitochondrial DNA encode components of the respiratory-chain NADH dehydrogenase. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):592–597. doi: 10.1038/314592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Nuclear gadgets in mitochondrial DNA replication and transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90043-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Replication and transcription of vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:453–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doda J. N., Wright C. T., Clayton D. A. Elongation of displacement-loop strands in human and mouse mitochondrial DNA is arrested near specific template sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6116–6120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunon-Bluteau D. C., Brun G. M. Mapping at the nucleotide level of Xenopus laevis mitochondrial D-loop H strand: structural features of the 3' region. Biochem Int. 1987 Apr;14(4):643–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Lisowsky T., Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. DNA wrapping and bending by a mitochondrial high mobility group-like transcriptional activator protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3358–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. Flexible recognition of rapidly evolving promoter sequences by mitochondrial transcription factor 1. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2202–2217. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foran D. R., Hixson J. E., Brown W. M. Comparisons of ape and human sequences that regulate mitochondrial DNA transcription and D-loop DNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5841–5861. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Dressler D. DNA replication: the rolling circle model. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:473–484. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hehman G. L., Hauswirth W. W. DNA helicase from mammalian mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Parisi M. A., Bennett J. L., Clayton D. A. Impairment of mitochondrial transcription termination by a point mutation associated with the MELAS subgroup of mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):236–239. doi: 10.1038/351236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Marians K. J. Escherichia coli Tus protein acts to arrest the progression of DNA replication forks in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2481–2485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillel Z., Wu C. W. Photochemical cross-linking studies on the interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with T7 DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):2954–2961. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloszy J. O., Coyle E. F. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to endurance exercise and their metabolic consequences. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Apr;56(4):831–838. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.4.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huie M. A., Scott E. W., Drazinic C. M., Lopez M. C., Hornstra I. K., Yang T. P., Baker H. V. Characterization of the DNA-binding activity of GCR1: in vivo evidence for two GCR1-binding sites in the upstream activating sequence of TPI of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2690–2700. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolesz F., Sreter F. A. Development, innervation, and activity-pattern induced changes in skeletal muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:531–552. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Grossman L. I., Robberson D. L., Watson R., Vinograd J. The replication and structure of mitochondrial DNA in animal cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:281–288. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay S. L., Olivo P. D., Laipis P. J., Hauswirth W. W. Template-directed arrest of mammalian mitochondrial DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1261–1267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels G. S., Hauswirth W. W., Laipis P. J. Mitochondrial DNA copy number in bovine oocytes and somatic cells. Dev Biol. 1982 Nov;94(1):246–251. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Decker T., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon induction of gene transcription analyzed by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagley P. Coordination of gene expression in the formation of mammalian mitochondria. Trends Genet. 1991 Jan;7(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajamanickam C., Merten S., Kwiatkowska-Patzer B., Chuang C. H., Zak R., Rabinowitz M. Changes in mitochondrial DNA in cardiac hypertrophy in the rat. Circ Res. 1979 Oct;45(4):505–515. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.4.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin E. D., Wong R. Mitochondrial DNA molecules and virtual number of mitochondria per cell in mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Sep;136(3):507–513. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccone C., Pesole G., Sbisá E. The main regulatory region of mammalian mitochondrial DNA: structure-function model and evolutionary pattern. J Mol Evol. 1991 Jul;33(1):83–91. doi: 10.1007/BF02100199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shay J. W., Pierce D. J., Werbin H. Mitochondrial DNA copy number is proportional to total cell DNA under a variety of growth conditions. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14802–14807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. In vitro transcription of human mitochondrial DNA. Identification of specific light strand transcripts from the displacement loop region. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1268–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. S. Mitochondrial gene expression in mammalian striated muscle. Evidence that variation in gene dosage is the major regulatory event. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12390–12394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. S., Salmons S., Newsholme E. A., Kaufman R. E., Mellor J. Regulation of nuclear and mitochondrial gene expression by contractile activity in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):376–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Meziane A., Callen J. C., Mounolou J. C. Mitochondrial gene expression during Xenopus laevis development: a molecular study. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1649–1655. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]