Abstract
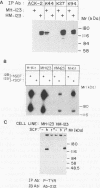
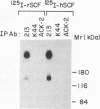
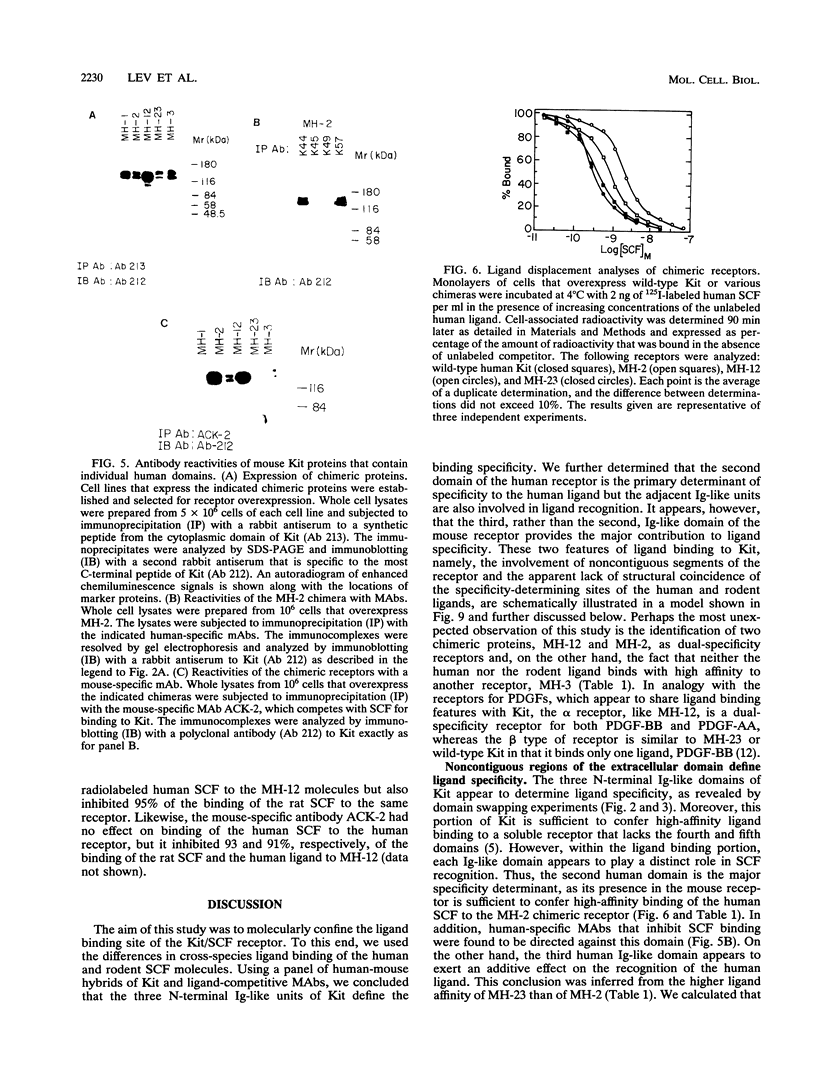
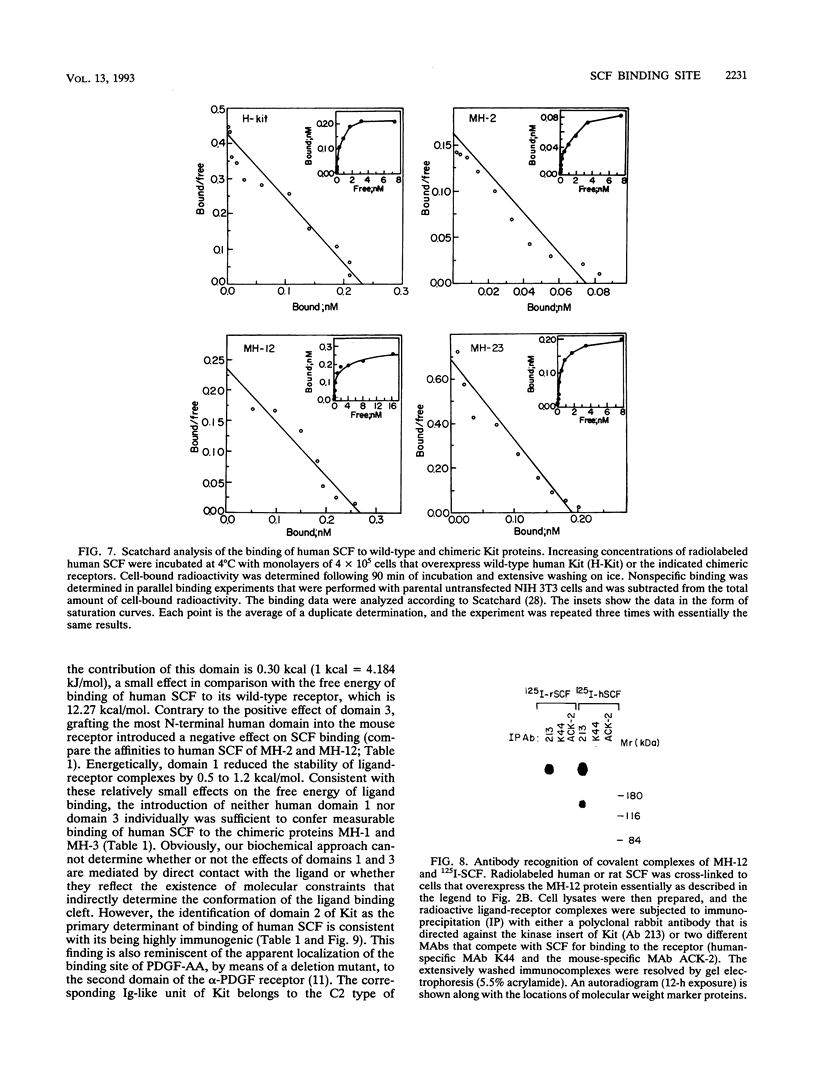
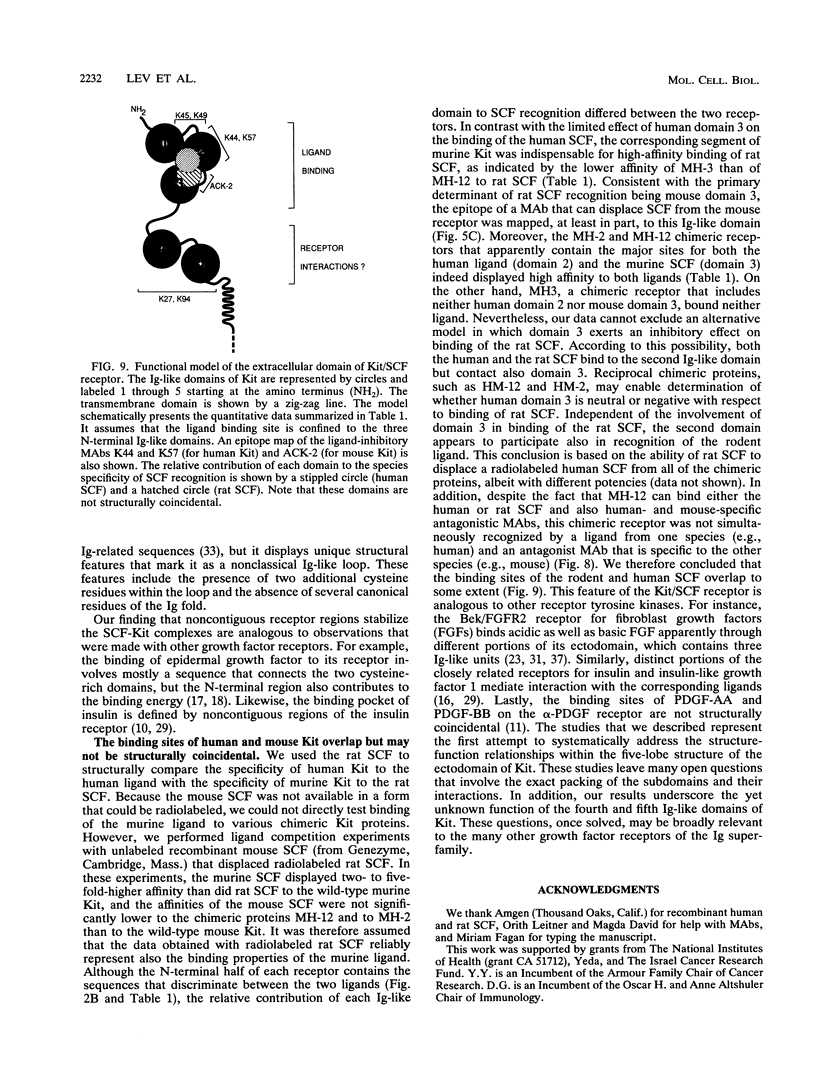
The extracellular portion of the kit-encoded receptor for the stem cell factor (SCF) comprises five immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains. To localize the ligand recognition site, we exploited the lack of binding of human SCF to the murine receptor by using human-mouse hybrids of Kit and species-specific monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) that inhibit ligand binding. Replacement of the three N-terminal Ig-like domains of the murine Kit with the corresponding portion of the human receptor conferred upon the chimeric receptor high-affinity binding of the human ligand as well as of human-specific ligand-inhibitory MAbs. By constructing five chimeric murine Kit proteins which individually contain each of these three human Ig-like units or pairs of them, we found that the second human domain confers upon the mouse Kit high-affinity binding of the human ligand and also binding of species-specific SCF-competitive MAbs. Nevertheless, the flanking Ig-like domains also affect high-affinity recognition of SCF. Moreover, it appears that the determinants that define ligand specificity of the murine and the human receptors do not structurally coincide. This observation allowed us to identify a chimeric receptor that displayed a dual specificity; namely, it bound with high affinity either the human or the murine SCF molecules and reacted with mouse- as well as human-specific ligand-inhibitory MAbs. Conversely, another chimera, which included all of the five Ig-like domains, bound neither ligand. In conclusion, interdomain packing involving the second Ig-like domain of human Kit and noncontiguous structural motifs of the receptor are involved in SCF recognition.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Lyman S. D., Baird A., Wignall J. M., Eisenman J., Rauch C., March C. J., Boswell H. S., Gimpel S. D., Cosman D. Molecular cloning of mast cell growth factor, a hematopoietin that is active in both membrane bound and soluble forms. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90304-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P., Murphy J. E., George P. C., Qiu F. H., Bergold P. J., Lederman L., Snyder H. W., Jr, Brodeur D., Zuckerman E. E., Hardy W. D. A new acute transforming feline retrovirus and relationship of its oncogene v-kit with the protein kinase gene family. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):415–421. doi: 10.1038/320415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P. The kit ligand encoded at the murine Steel locus: a pleiotropic growth and differentiation factor. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90111-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Cho B. C., Donovan P. J., Jenkins N. A., Cosman D., Anderson D., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E. Mast cell growth factor maps near the steel locus on mouse chromosome 10 and is deleted in a number of steel alleles. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90298-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Leder P. The kit ligand: a cell surface molecule altered in steel mutant fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90299-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Rutter W. J. The cysteine-rich domains of the insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors are primary determinants of hormone binding specificity. Evidence from receptor chimeras. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18663–18667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidaran M. A., Yu J. C., Jensen R. A., Pierce J. H., Aaronson S. A. A deletion in the extracellular domain of the alpha platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor differentially impairs PDGF-AA and PDGF-BB binding affinities. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2884–2887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Bäckström G., Ostman A., Hammacher A., Rönnstrand L., Rubin K., Nistér M., Westermark B. Binding of different dimeric forms of PDGF to human fibroblasts: evidence for two separate receptor types. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1387–1393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller T., Hood L. Diversity of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60639-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen T., Andersen A. S., Wiberg F. C., Rasmussen J. S., Schäffer L., Balschmidt P., Møller K. B., Møller N. P. The ligand specificities of the insulin receptor and the insulin-like growth factor I receptor reside in different regions of a common binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4404–4408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Bellot F., Howk R., Ullrich A., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Functional analysis of the ligand binding site of EGF-receptor utilizing chimeric chicken/human receptor molecules. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):421–427. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Fischer R., Ng C., Segre J., Ullrich A., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Noncontiguous regions in the extracellular domain of EGF receptor define ligand-binding specificity. Cell Regul. 1991 May;2(5):337–345. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.5.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Givol D., Yarden Y. Interkinase domain of kit contains the binding site for phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):678–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Yarden Y., Givol D. A recombinant ectodomain of the receptor for the stem cell factor (SCF) retains ligand-induced receptor dimerization and antagonizes SCF-stimulated cellular responses. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10866–10873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Yarden Y., Givol D. Dimerization and activation of the kit receptor by monovalent and bivalent binding of the stem cell factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15970–15977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Suggs S. V., Langley K. E., Lu H. S., Ting J., Okino K. H., Morris C. F., McNiece I. K., Jacobsen F. W., Mendiaz E. A. Primary structure and functional expression of rat and human stem cell factor DNAs. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90301-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Smith C. L., Burgess W. H., Chan A. M., Aaronson S. A. Determination of ligand-binding specificity by alternative splicing: two distinct growth factor receptors encoded by a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):246–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa S., Kusakabe M., Yoshinaga K., Ogawa M., Hayashi S., Kunisada T., Era T., Sakakura T., Nishikawa S. In utero manipulation of coat color formation by a monoclonal anti-c-kit antibody: two distinct waves of c-kit-dependency during melanocyte development. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2111–2118. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peles E., Levy R. B., Or E., Ullrich A., Yarden Y. Oncogenic forms of the neu/HER2 tyrosine kinase are permanently coupled to phospholipase C gamma. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2077–2086. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu F. H., Ray P., Brown K., Barker P. E., Jhanwar S., Ruddle F. H., Besmer P. Primary structure of c-kit: relationship with the CSF-1/PDGF receptor kinase family--oncogenic activation of v-kit involves deletion of extracellular domain and C terminus. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1003–1011. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Hereditary anemias of the mouse: a review for geneticists. Adv Genet. 1979;20:357–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher R., Mosthaf L., Schlessinger J., Brandenburg D., Ullrich A. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 binding specificity is determined by distinct regions of their cognate receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19288–19295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Duan D. S., de Vries C., Peters K. G., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Differential splicing in the extracellular region of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 generates receptor variants with different ligand-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Eisenman J., Baird A., Rauch C., Van Ness K., March C. J., Park L. S., Martin U., Mochizuki D. Y., Boswell H. S. Identification of a ligand for the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90297-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T., Coussens L., Munemitsu S., Dull T. J., Chen E., Schlessinger J., Francke U., Ullrich A. Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3341–3351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Zimmer Y., Shen G. H., Avivi A., Yarden Y., Givol D. A confined variable region confers ligand specificity on fibroblast growth factor receptors: implications for the origin of the immunoglobulin fold. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1885–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Williams D. A., Geissler E. N., Broudy V. C., Martin F. H., Atkins H. L., Hsu R. Y., Birkett N. C., Okino K. H., Murdock D. C. Stem cell factor is encoded at the Sl locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90302-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Wypych J., McNiece I. K., Lu H. S., Smith K. A., Karkare S. B., Sachdev R. K., Yuschenkoff V. N., Birkett N. C., Williams L. R. Identification, purification, and biological characterization of hematopoietic stem cell factor from buffalo rat liver--conditioned medium. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]